
Does plaque build up on the outside of the arteries?
I don't think plaque builds up on the outside of the arteries. It is just that sometimes the walls of the arteries bulge outward when plaque builds up rather than narrowing the Lumen.
What is atherosclerosis thickening of arteries?
Atherosclerosis thickening or hardening of the arteries. It is caused by a buildup of plaque in the inner lining of an artery. Plaque is made up of deposits of fatty substances, cholesterol, cellular waste products, calcium, and fibrin. As it builds up in the arteries, the artery walls become thickened and stiff.
How does cholesterol build up in the arteries?
Low-density lipoproteins (LDL, the “bad” cholesterol) are responsible for creating the buildup of plaque in the arteries. 2 When plaque builds up in the arteries, the body responds by sending white blood cells that attempt to digest LDL, which then turns into toxins.
What causes a bulging artery to bulge out?
The Dr. said there was plaque buildup on the outside of the artery, which causes it to bulge out, rather than the typical plaque buildup narrowing the artery.
What is the plaque on the walls of your arteries made up of?
Plaque (fatty deposits) build up in your arteries is called atherosclerosis. These deposits are made up of cholesterol, fatty substances, cellular waste products, calcium and fibrin (a clotting material in the blood).
What is the deposit of plaque on the walls of a coronary artery called?
Plaque buildup causes the inside of the arteries to narrow over time. This process is called atherosclerosis. Coronary artery disease is caused by plaque buildup in the wall of the arteries that supply blood to the heart (called coronary arteries). Plaque is made up of cholesterol deposits.
What is inside an artery?
Your arteries carry blood that has oxygen and nutrients in it. Your heart pumps oxygen-rich blood into the biggest artery in your body — your aorta. This branches off into parts that feed smaller and smaller arteries, eventually reaching your entire body.
What is the stuff that clogs your arteries?
Plaque is a mixture of fat, calcium, cholesterol, and waste from the cells in the body. This mix can stick to the walls of the arteries, making these blood vessels narrower. When this happens, it is called atherosclerosis.
Can you reverse plaque buildup in your arteries?
The key is lowering LDL and making lifestyle changes. "Making plaque disappear is not possible, but we can shrink and stabilize it," says cardiologist Dr. Christopher Cannon, a Harvard Medical School professor. Plaque forms when cholesterol (above, in yellow) lodges in the wall of the artery.
What can remove plaque from arteries?
To remove plaque from arteries, the following procedures are performed:Angioplasty. ... Coronary Artery Bypass Graft. ... Coronary Stent. ... Rotational Atherectomy.
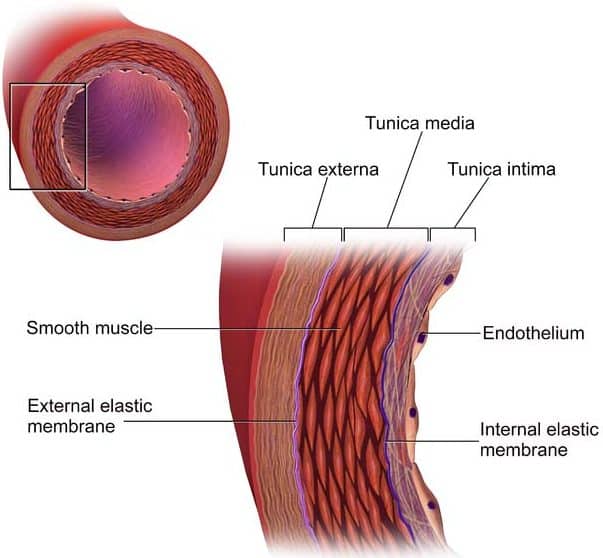
What are the three layers that make up the wall of an artery?
Each artery is a muscular tube lined by smooth tissue and has three layers: The intima, the inner layer lined by a smooth tissue called endothelium. The media, a layer of muscle that lets arteries handle the high pressures from the heart. The adventitia, connective tissue anchoring arteries to nearby tissues.
What are the three layer tissues of arterial walls?
The normal artery wall comprises three layers: the tunica intima, the tunica media, and the tunica adventitia.
Which layer of an artery wall contains endothelium?
The tunica intima consists of a layer of endothelial cells lining the lumen of the vessel, as well as a subendothelial layer made up of mostly loose connective tissue.
What foods reduce calcification?
Fruits And Vegetables With Higher Potassium Levels May Help Reduce Arterial Sclerosis And Calcification. Scientists publishing a new study in the journal JCI Insight have concluded that high-potassium foods such as avocados and bananas protect the arteries against hardening or calcification.
Is there a drug that dissolves plaque in arteries?
A drug made from a highly purified form of EPA (an omega-3 fatty acid found in fish) appears to help reduce plaque in the heart's arteries, according to a study published online Aug.
What foods cause plaque build up?
The study, published Aug. 13 in Science, suggests that consuming food rich in saturated fat and choline - a nutrient found in red meat, eggs and dairy products - increases the number of metabolites that build plaques in the arteries.
What is called atherosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis is a specific type of arteriosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is the buildup of fats, cholesterol and other substances in and on the artery walls. This buildup is called plaque. The plaque can cause arteries to narrow, blocking blood flow. The plaque can also burst, leading to a blood clot.
What is arterial plaque quizlet?
A deposit of fatty material on the inner lining of an arterial wall.
What is ischemia?
What is ischemia? Ischemia is a condition in which the blood flow (and thus oxygen) is restricted or reduced in a part of the body. Cardiac ischemia is the name for decreased blood flow and oxygen to the heart muscle.
What causes atherosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis is a hardening of your arteries caused by gradual plaque buildup. Risk factors include high cholesterol, high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking, obesity, lack of exercise and a diet high in saturated fat.
What is the cause of plaque buildup in the arteries?
Low-density lipoproteins (LDL, the “bad” cholesterol) are responsible for creating the buildup of plaque in the arteries. 2. When plaque builds up in the arteries, the body responds by sending white blood cells that attempt to digest LDL, which then turns into toxins. More and more white blood cells are attracted to the area where ...
What causes plaque in the body?
Causes of Plaque. Plaque consists of cholesterol, fat, calcium, fibrin, and cellular waste products. 1 Its formation involves a complex process in which waxy cholesterol adheres to the arterial walls, causing them to thicken, harden, and narrow. This eventually leads to atherosclerosis.
What is the role of cholesterol in the body?
It plays an important part in the production of vitamin D, hormones, and substances that aid in food digestion. 2 There are two types of cholesterol: high-density lipoproteins (HDL, known as the “good” cholesterol) take cholesterol from other parts of the body back to the liver, which then eliminates it from the body.
How to reduce plaque atherosclerosis?
To reduce atherosclerosis risk caused by plaque, experts recommend lifestyle changes that include eating a healthy diet without any processed foods or animal products. Primarily plant-based diets (fruit, vegetable, legumes, whole grains) have been shown to improve blood flow and reverse coronary artery disease to some degree. 6
When does the risk of atherosclerosis increase?
In men, the risk increases after age 45. In women, the risk increases after age 55. Family history of early heart disease: Atherosclerosis risk increases if your father or brother was diagnosed with heart disease before 55 years or if your mother or sister was diagnosed with heart disease before 65 years.
Does atorvastatin remove plaque?
Even with the lifestyle changes noted above, plaque won’t entirely disappear. With treatment, healthcare providers are able to target smaller blockages of soft plaque by reducing the cholesterol that will shrivel the plaque. 6 To remove the cholesterol within the plaque, prescribed statins target LDL cholesterol. These include atorvastatin (Lipitor) and rosuvastatin (Crestor), which work by hindering the liver enzyme responsible for cholesterol production. Ezetimibe (Zetia) may also be included in a patient’s protocol to impede cholesterol absorption in the digestive tract. 6
Can plaque build up in the arteries be prevented?
Plaque build-up in the arteries is inevitable, but many risk factors may lead to atherosclerosis. Several of these risk factors can be controlled and help delay or prevent atherosclerosis, while others can’t be controlled.
Why does plaque build up on the inside of the artery?
However, a gradual buildup of plaque or thickening due to inflammation occurs on the inside of the walls of the artery. This reduces blood flow and oxygen supply to the vital body organs and extremities.
What is atherosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis thickening or hardening of the arteries. It is caused by a buildup of plaque in the inner lining of an artery.
How is atherosclerosis treated?
Treatment for atherosclerosis may include lifestyle changes, medicine, and surgery.
What are the complications of atherosclerosis?
Plaque buildup inside the arteries reduces the blood flow. A heart attack may occur if the blood supply is reduced to the heart. A damaged heart muscle may not pump as well and can lead to heart failure. A stroke may occur if the blood supply is cut off to the brain. Severe pain and tissue death may occur if the blood supply is reduced to the arms and legs.
What are some medications that can be used to treat atherosclerosis?
Medicines that may be used to treat atherosclerosis include: Antiplatelet medicines. These are medicines used to decrease the ability of platelets in the blood to stick together and cause clots. Aspirin, clopidogrel, ticlopidine, and dipyridamole are examples of antiplatelet medicines. Anticoagulants.
How to prevent atherosclerosis?
You can prevent or delay atherosclerosis by reducing risk factors. This includes adopting a healthy lifestyle. A healthy diet, losing weight, being physically active, and not smoking can help reduce your risk of atherosclerosis. A healthy diet includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean meats, skinless chicken, seafood, and fat-free or low-fat dairy products. A healthy diet also limits sodium, refined sugars and grains, and solid fats.
How is a bypass created?
During the surgery, a bypass is created by grafting a piece of a healthy vein from elsewhere in the body and attaching it above and below the blocked area of a coronary artery. This lets blood flow around the blockage. Veins are usually taken from the leg or from the chest wall.
What fatty acids increase adiponectin?from en.wikipedia.org
Mice fed the omega-3 fatty acids eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) have shown increased plasma adiponectin. Curcumin, capsaicin, gingerol, and catechins have also been found to increase adiponectin expression. Phylogenetic distribution includes expression in birds and fish.
What is the structure of adiponectin?from en.wikipedia.org
Structure. Adiponectin is a 244-amino-acid-long polypeptide (protein). There are four distinct regions of adiponectin. The first is a short signal sequence that targets the hormone for secretion outside the cell; next is a short region that varies between species; the third is a 65-amino acid region with similarity to collagenous proteins;
Where is adiponectin secreted?from en.wikipedia.org
Adiponectin is secreted from adipose tissue (and also from the placenta in pregnancy) into the bloodstream and is very abundant in plasma relative to many hormones. Many studies have found adiponectin to be inversely correlated with body mass index in patient populations.
Why does calcium build up in the arteries?from india.com
Why does calcium build up in arteries? Calcium accumulates in the arteries of the heart after plaque builds up and calcifies over time. This happens as a result of decline in estrogen, lack of exercise, stress, smoking, but mostly due to poor dietary habits.
How to reduce calcium in arteries?from india.com
So, you can prevent calcium buildup in your arteries by choosing a diet rich in vitamin K2 and exercising regularly. Both these things will help circulation and prevent plaque that leads to calcification. The key is to avoid saturated fat (to be kept under 7 percent) and dietary cholesterol. Saturated fat is found in abundance in foods like whole milk, high-cut meats, high-fat cheese and packaged cookies and doughnuts. Dietary cholesterol in high amounts too is a problem so you should try to restrict your consumption of egg yolks and liver meat. Having healthy foods like green leafy vegetables, oats and berries are good for your cardiovascular health and they can help prevent the calcification in your arteries. Also Read - A New Diabetes Medication Brings Hope to Resolve The Dual Problem of Sugar And the Heart
What is plaque buildup?from verywellhealth.com
With plaque buildup, the artery walls harden and their passageway narrows, limiting blood flow to other organs and body parts that need oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to function. This results in a condition known as atherosclerosis and can lead to a number of other serious cardiovascular conditions.
How to reduce plaque atherosclerosis?from verywellhealth.com
To reduce atherosclerosis risk caused by plaque, experts recommend lifestyle changes that include eating a healthy diet without any processed foods or animal products. Primarily plant-based diets (fruit, vegetable, legumes, whole grains) have been shown to improve blood flow and reverse coronary artery disease to some degree. 6
What are the symptoms of a blocked carotid artery?from verywellhealth.com
These may range from sudden weakness, confusion, paralysis, speech problems (speaking and understanding), and vision issues to severe headache, dizziness, and loss of consciousness. 5.
Where does plaque form?from health.harvard.edu
Plaque forms when cholesterol (above, in yellow) lodges in the wall of the artery.
Does atorvastatin remove plaque?from verywellhealth.com
Even with the lifestyle changes noted above, plaque won’t entirely disappear. With treatment, healthcare providers are able to target smaller blockages of soft plaque by reducing the cholesterol that will shrivel the plaque. 6 To remove the cholesterol within the plaque, prescribed statins target LDL cholesterol. These include atorvastatin (Lipitor) and rosuvastatin (Crestor), which work by hindering the liver enzyme responsible for cholesterol production. Ezetimibe (Zetia) may also be included in a patient’s protocol to impede cholesterol absorption in the digestive tract. 6
