What causes a stroke in the pons of the brain?
A stroke involving the pons can be caused by either a blood clot (ischemic stroke) or a bleed (hemorrhagic stroke). 1 An ischemic stroke occurs when a blood clot forms, blocking the blood flow through an artery to a certain region in the brain.
What is a Pons stroke?
The pons contains nerves and nerve tracts, also called pathways. These nerves and pathways send messages between different parts of the brain. A pons stroke is also called a pontine stroke.
What causes the pons to become inflamed?
Causes. This can happen because the blood vessels that supply blood to the pons and the rest of the brainstem are located in the back of the neck, and may become injured as result of neck trauma or sudden pressure or movements of the head or neck.
What are the risk factors for a pontine stroke?
The risk factors for a pontine stroke are the same as those for strokes in other areas of the brain. They include: 4 Pontine strokes are diagnosed with a neurologic exam. Some imaging tests can help confirm the diagnosis. These include: Pontine strokes are diagnosed after a neurologic exam. Imaging tests can help confirm the diagnosis.
What does stroke in the pons mean?
A pontine cerebrovascular accident (also known as a pontine CVA or pontine stroke) is a type of ischemic stroke that affects the pons region of the brain stem. A pontine stroke can be particularly devastating and may lead to paralysis and the rare condition known as Locked-in Syndrome (LiS).
What happens when pons is damaged?
When the injury to the pons is complete, the patient may pass away. If a patient with a complete injury survives, he or she could develop locked in syndrome. In this syndrome, the person has no sensory or motor function, except for the ability to move their eyes up and down. Some people can also blink.
Can you survive a pontine stroke?
Massive pontine hemorrhage with comatose condition has a poor prognosis and bad outcome despite adequate surgical treatment. However, this case report gives a different result. Providing adequate prophylactic treatment to prevent secondary brain injury resulted in a very good recovery at the 6-month follow-up.
What causes pontine strokes?
Ventro-caudal pontine infarction is caused due to decreased blood flow in the paramedian perforating arteries arising from the basilar artery. Affected individuals have contralateral motor hemiparesis or hemiplegia due to the large infarcts of the unilateral corticospinal tract.
How do you recover from a pons stroke?
Treatment for Pontine Stroke A common treatment for ischemic pons stroke (i.e. pontine infarct) is tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), where an injection helps dissolve the clot. Another treatment option involves an embolectomy, where a stent is surgically inserted into the artery to remove the clot.
Can pons damage be reversed?
The disorder can't be cured, but its symptoms can be treated. CPM is one of the two types of osmotic demyelination syndrome (ODS). The other type, known as extrapontine myelinosis (EPM), occurs when myelin is destroyed in areas of the brain that aren't in the brain stem.
What is the average lifespan after a stroke?
The median survival time after a first stroke are: at 60-69 years of age–6.8 years for men and 7.4 years for women; at 70-79 years of age–5.4 years for men and 6.4 years for women; and at 80 years and older–1.8 years for men and 3.1 years for women.
What does the pons control?
Your pons is a part of your brainstem, a structure that links your brain to your spinal cord. It handles unconscious processes and jobs, such as your sleep-wake cycle and breathing. It also contains several junction points for nerves that control muscles and carry information from senses in your head and face.
Is pontine hemorrhage curable?
Treatment and prognosis Pontine hemorrhages have a poor prognosis, with large bleeds being almost universally fatal. Open surgical evacuation of the clot is usually not performed, although stereotactic clot aspiration has been advocated by some 5.
Can you live without a pons?
Life without a pons would not be possible. Without it, information from the lower brainstem and spinal cord would not be received by the brain. Life may be possible with a damaged pons, but functions may be impaired.
What is the survival rate of brain stem stroke?
After 3 months, 10% of the patients with isolated brainstem infarction had died and 55.6% were functionally independent. Mortality was 43.5% in patients with combined brainstem infarction.
Can someone recover from a brain stem stroke?
There are also rare causes, like injury to an artery due to sudden head or neck movements. Recovery is possible. Because brain stem strokes do not usually affect language ability, the patient is often able to participate more fully in rehabilitation.
What is a stroke involving the pons called?
The extent of damage depends on the location and size of the stroke. 4 . In rare instances, a stroke involving the pons, typically called a pontine stroke, may be the result of an injury to an artery caused by sudden head or neck trauma.
What are the symptoms of a stroke in the pons?
1 . Some of the symptoms of a pontine stroke include a combination of the following: 2 . Balance difficulty. Vertigo (spinning sensation) Dizziness.
What is the difference between a stroke and a hemorrhagic stroke?
An ischemic stroke occurs when a blood clot blocks the blood flow through an artery to a certain region in the brain. A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel ruptures, reducing or halting the flow of blood to a region in the brain. Whether a stroke is ischemic or hemorrhagic, once the blood supply to a region of the brain is interrupted, ...
What tests are used to diagnose pontine stroke?
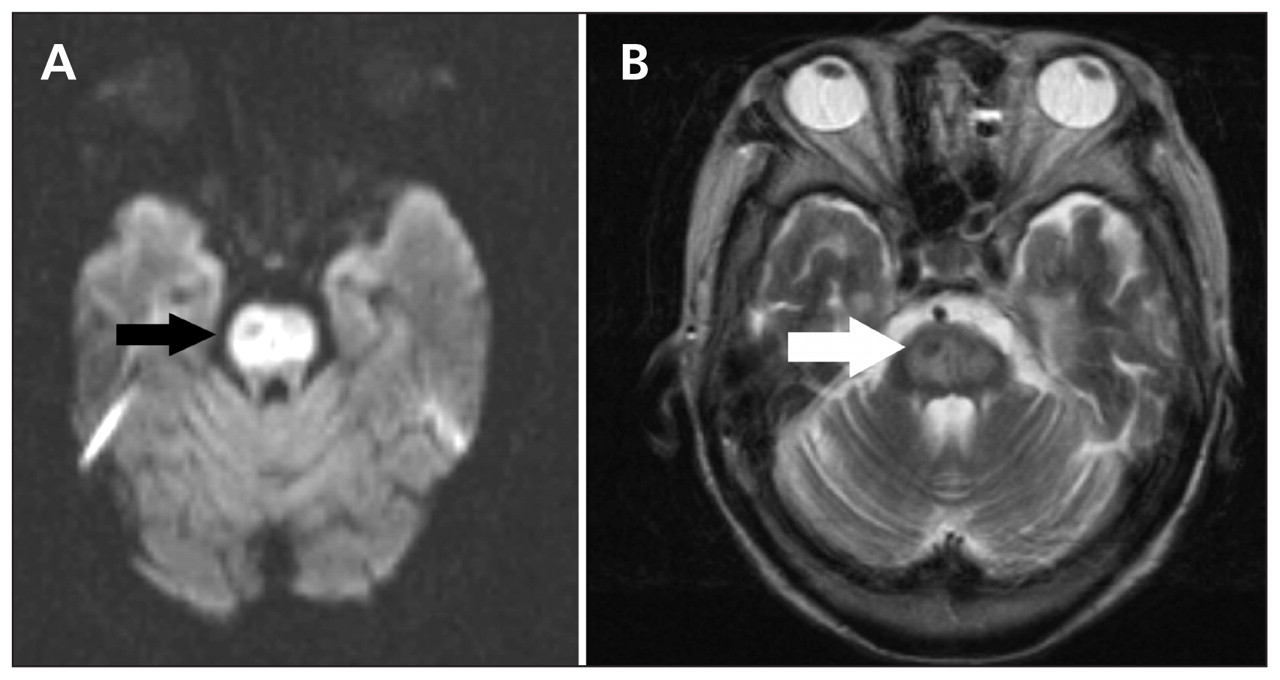
Diagnosis of a pontine stroke requires a thorough neurologic examination. Some diagnostic imaging tests, such as brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and brain magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) or computerized tomography (CT) angiogram, can help confirm the diagnosis of a pontine stroke. 5
What is the name of the hindbrain?
In scientific terms, the pons is sometimes known as the hindbrain, a name that is based on the location of the pons in relation to the rest of the brain during the development of the brain in the embryo (developing baby). Verywell / Hilary Allison.
How long after stroke can you use tPA?
In certain patients, tPA can be used up to 4.5 hours after onset of stroke symptoms. 6 . During recovery after a stroke, there are several stroke treatments that can help maximize improvement, including blood thinners, fluid management, treatment of heart problems, and maintaining adequate nutrition. 7 .
What happens when you have a stroke?
Whether a stroke is ischemic or hemorrhagic, once the blood supply to a region of the brain is interrupted, brain cells begin to die, resulting in brain damage. The bleeding of hemorrhage can also cause damage due to pressure and irritation to nearby brain structures.
What are the symptoms of a stroke on the back of the pons?
Other common pontine stroke symptoms include double vision, vertigo, and dizziness. After a pontine stroke, some patients also experience difficulty swallowing, speech deficits, numbness, ...
How often does a pontine stroke occur?
Pontine Stroke Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments. Every 40 seconds, someone in the United States suffers a stroke, according to the latest data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. While some individuals may experience long-term motor deficits as a result of a stroke, it’s possible for stroke survivors to make a full recovery ...
What is a pontine CVA?
A pontine cerebrovascular accident (also known as a pontine CVA or pontine stroke) is a type of ischemic stroke that affects the pons region of the brain stem. A pontine stroke can be particularly devastating and may lead to paralysis and the rare condition known as Locked-in Syndrome (LiS). Fortunately, it has been estimated ...
What happens if you have a stroke in the brain?
A stroke affecting the brainstem can result in extensive loss of motor function and other deficits. A patient’s exact symptoms will vary depending on the severity of the pontine stroke, as well as its specific location. This is because cranial nerves serve different functions in different areas of the brain stem and within the pons itself. ...
How many strokes are preventable?
Fortunately, it has been estimated that up to 80 percent of strokes are preventable. In this post, we will discuss the underlying anatomy of the brain stem, pontine stroke risk factors, and how to prevent a stroke naturally.
What is the most common type of stroke?
An ischemic stroke occurs when a blood clot within a blood vessel disrupts or blocks blood flow to the brain. Ischemic strokes are by far the most common category, representing nearly 90 percent of all strokes, and about 10 percent of all ischemic stroke s take place in the brain stem, according to the National Stroke Association.
What is the brain stem?
The brain stem controls the central nervous system (CNS) and is situated along the base of the brain between the spinal cord and the two cerebral hemispheres. The brain stem is made up of three sections: the midbrain (mesencephalon), the medulla oblongata (myelencephalon), and the pons (metencephalon). Each of these controls a specific set of ...
How to diagnose a stroke in a pons?
It may be possible to diagnose a pons stroke by observation and medical imaging such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and magnetic resonance angiography. These tests allow doctors to visualize what is happening inside the pons and locate a blood clot or another blockage.
What causes damage to the pons?
Damage to the pons can occur in several ways. Most commonly, this includes: A stroke caused by a blood clot. A stroke caused by another blockage of blood flow. A stroke caused by hemorrhage. A stroke related to trauma to the brain. Diagnosing a Locked-in Stroke and Locked-In Syndrome.
Why does the PONs prevent movement?
Because of this, damage to the pons can prevent the brain from sending signals to the rest of the body to produce intentional movement. The pons also plays a role in controlling breathing and the nerve communication necessary to speak, swallow, and make most facial movements.
Why do doctors call it pontine strokes?
Doctors often call them pontine strokes because they specifically affect an area of the brain stem known as the pons. When a stroke disrupts blood flow to the pons, it prevents the brain from communicating with the spinal cord and nervous system. This causes symptoms of locked-in syndrome. Understanding the Causes of Locked-In Syndrome.
What causes locked in syndrome?
Understanding the Causes of Locked-In Syndrome. In most cases, locked-in syndrome occurs following some injury or damage to the pons. The pons is a key structure in the brain stem that provides a pathway for communication between the cerebrum, cerebellum, and spinal cord. Most of the body’s motor fibers run through this area.
How to survive a stroke?
A crucial factor in survival is getting immediate medical care including medications to break up the blood clot or otherwise stop the stroke from doing more damage. Restoring blood flow to the brain stem as soon as possible could limit the damage done and save their life.
What happens if a doctor doesn't treat a stroke?
If your doctor failed to diagnose or treat your locked-in stroke quickly, you could pursue a payout that would cover your medical care, ongoing care costs, medical and communication devices, pain and suffering, and more.