How long does it take to recover from a pneumothorax?
The time that it will take for an individual to completely recover from a Pneumothorax depends on the type of injury that caused it. In cases where a car accident or a penetrating injury such as a gunshot or a stab wound caused the Pneumothorax, then it may take anywhere from four to Eight weeks after treatment of the underlying cause for an individual to completely recover from a Pneumothorax.
Does a pneumothorax heal on its own?
Treatment for a pneumothorax usually involves inserting a needle or chest tube between the ribs to remove the excess air. However, a small pneumothorax may heal on its own. The main symptoms of a pneumothorax are sudden chest pain and shortness of breath. Severity of symptoms may depend on how much of the lung is collapsed.
What are the signs and symptoms of pneumothorax?
The symptoms of pneumothorax can vary from mild to life-threatening and may include:
- shortness of breath
- chest pain, which may be more severe on one side of the chest
- sharp pain when inhaling
- pressure in the chest that gets worse over time
- blue discoloration of the skin or lips
- increased heart rate
- rapid breathing
- confusion or dizziness
- loss of consciousness or coma
What is the recovery time for pneumothorax?
WebMD adds: “It usually takes one or two weeks to recover from pneumothorax.” However, the website states the recovery period can be longer depending on the severity of the condition. What we know about CJ McCollum’s condition

How does a person get pneumothorax?
A collapsed lung occurs when air escapes from the lung. The air then fills the space outside of the lung between the lung and chest wall. This buildup of air puts pressure on the lung, so it cannot expand as much as it normally does when you take a breath. The medical name of this condition is pneumothorax.
What are the symptoms of a spontaneous pneumothorax?
Spontaneous pneumothorax most commonly presents without severe symptoms....Signs and symptomsChest tightness.Easy fatigue.Rapid heart rate.Bluish color of the skin caused by lack of oxygen.Nasal flaring.Chest wall retractions.
What is the most common cause of pneumothorax?
CausesChest injury. Any blunt or penetrating injury to your chest can cause lung collapse. ... Lung disease. Damaged lung tissue is more likely to collapse. ... Ruptured air blisters. Small air blisters (blebs) can develop on the top of the lungs. ... Mechanical ventilation.
Is spontaneous pneumothorax fatal?
In around 10% of cases, secondary spontaneous pneumothorax is fatal. The risk is higher if you have HIV or COPD.
What are 3 signs and symptoms of a pneumothorax?
What are the Symptoms of Pneumothorax?Sharp, stabbing chest pain that worsens when trying to breath in.Shortness of breath.Bluish skin caused by a lack of oxygen.Fatigue.Rapid breathing and heartbeat.A dry, hacking cough.
Can you have a pneumothorax and not know?
This is the space between the outside of your lung and your ribcage. A small pneumothorax may cause few or no symptoms. A large pneumothorax can squash the lung and cause it to collapse. A bilateral pneumothorax is when air leaks out of both lungs and causes them to collapse – but this is rare.
How do you tell if your lung has collapsed?
Signs of a collapsed lung include:Chest pain on one side especially when taking breaths.Cough.Fast breathing.Fast heart rate.Fatigue.Shortness of breath.Skin that appears blue.
How long can you live with one collapsed lung?
Doctors call the surgery to remove a lung a pneumonectomy. Once you've recovered from the operation, you can live a pretty normal life with one lung. You'll still be able to do normal, everyday tasks without a problem.
What Is A Spontaneous Pneumothorax?
A spontaneous pneumothorax is when part of your lung collapses. It happens if air collects in the pleural space (the space between your lungs and c...
What Causes A Spontaneous Pneumothorax?
There is no clear cause for a spontaneous pneumothorax. It may occur when an air pocket in the lung breaks open. This allows air to leak out and be...
What Increases My Risk For A Primary Spontaneous Pneumothorax?
1. Being a tall, thin male 2. Having had a spontaneous pneumothorax before 3. Scuba diving, flying, or climbing to high altitudes 4. Smoking
What Increases My Risk For A Secondary Spontaneous Pneumothorax?
Ask your healthcare provider for more information about these and other risk factors for a secondary spontaneous pneumothorax: 1. Lung diseases and...
What Are The Signs and Symptoms of A Spontaneous Pneumothorax?
You may have any of the following: 1. Shortness of breath 2. Chest pain 3. Uneven chest movement when you breathe 4. Rapid heartbeat
How Is A Spontaneous Pneumothorax Diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will ask about your signs and symptoms and examine you. He will listen to your lungs. You may need any of the following te...
How Is A Spontaneous Pneumothorax Treated?
Treatment will depend on the size of your pneumothorax. If your pneumothorax is small, it may resolve on its own. The goal of treatment is to remov...
What Are The Risks of A Spontaneous Pneumothorax?
1. Air may continue to enter the pleural space and you may get a tension pneumothorax. With a tension pneumothorax, the injured lung and trapped ai...
When Should I Contact My Healthcare Provider?
1. You have a fever. 2. You hear a crackling noise or feel popping when you touch your skin. 3. You have questions about your condition or care.
When Should I Seek Immediate Care Or Call 911?
1. You have new or increased shortness of breath. 2. Your throat or the front of your neck is pushed to one side. 3. You are sweating and feel like...
How old is too old to have pneumothorax?
The type of pneumothorax caused by ruptured air blisters is most likely to occur in people between 20 and 40 years old, especially if the person is very tall and underweight.
What causes a small air blister on the top of the lungs?
Cystic lung diseases, such as lymphangioleiomyomatosis and Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome, cause round, thin-walled air sacs in the lung tissue that can rupture, resulting in pneumothorax. Ruptured air blisters. Small air blisters (blebs) can develop on the top of the lungs.
What happens when a lung collapses?
In a collapsed lung, air from the lung leaks into the chest cavity. The example shown is a complete left pneumothorax.
How to tell if you have a collapsed lung?
On some occasions, a collapsed lung can be a life-threatening event. Treatment for a pneumothorax usually involves inserting a needle or chest tube between the ribs to remove the excess air. However, a small pneumothorax may heal on its own.
Do pneumothorax run in families?
Genetics. Certain types of pneumothorax appear to run in families.
Can pneumothorax be mechanical?
Mechanical ventilation. A severe type of pneumothorax can occur in people who need mechanical assistance to breathe. The ventilator can create an imbalance of air pressure within the chest. The lung may collapse completely.
What is spontaneous pneumothorax?
A spontaneous pneumothorax is the sudden onset of a collapsed lung without any apparent cause, such as a traumatic injury to the chest or a known lung disease. A collapsed lung is caused by the collection of air in the space around the lungs. This buildup of air puts pressure on the lung, so it cannot expand as much as it normally does when you take a breath. In most cases of spontaneous pneumothorax, a small area in the lung that is filled with air, called a bleb, ruptures, causing the air to leak into the space around the lung.
What causes pneumothorax in young people?
Other risk factors include connective tissue disorders, smoking, and activities such as scuba diving, high altitudes and flying.
What is the purpose of a chest tube for pneumothorax?
In most cases, the placement of the chest tube allows the lung to re-expand fully and quickly.
How long can a child stay in the hospital after a pneumothorax surgery?
The chest tube can be left in place for several days. During that time, your child must stay in the hospital for continued evaluation. She will undergo a series of chest X-rays to monitor the pneumothorax and determine if it is improving or worsening.
What is the name of the area in the lung that is filled with air?
In most cases of spontaneous pneumothorax, a small area in the lung that is filled with air, called a bleb , ruptures, causing the air to leak into the space around the lung. Spontaneous pneumothorax can be either small or large. A small spontaneous pneumothorax may resolve without treatment, while larger pneumothorax may need surgical intervention.
How long after discharge do you need to see a surgeon for pneumothorax?
If your child has an operation or receives inpatient treatment with a chest tube or oxygen therapy to treat spontaneous pneumothorax, you will need to make an appointment to see the surgeon for follow-up three to four weeks after discharge.
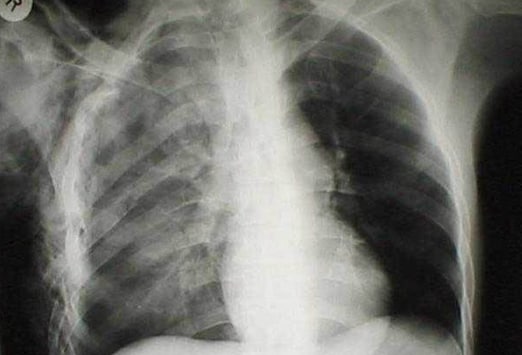
What is the image of a collapsed lung?
This is a chest x-ray of a patient with a collapsed lung. The image shows a large right-sided pneumothorax, caused by a collection of air in the space around the lung.
What is Spontaneous Pneumothorax?
A spontaneous pneumothorax is the sudden onset of a collapsed lung without any apparent cause, such as a traumatic injury to the chest or a known lung disease . A collapsed lung is caused by the collection of air in the space around the lungs.
What age group is most likely to develop spontaneous pneumothorax?
Risk Factors of Spontaneous Pneumothorax. Sex : Young men 20-30 years old may develop a collapsed lung that is usually associated with a bleb (like a blister) on the surface of the lung. Women age 30-40 may develop catamenial PTX associated with Endometriosis and their menstrual cycle,
What is the first step in a pneumothorax?
As long as the patient is stable, not hypoxic, and the pneumothorax is small, the first step is observation. If the patient is unstable, hypoxic, or the pneumothorax is large, then the pleura is drained with a catheter or a chest tube. Usually, the pneumothorax and the air leak will resolve.
How common is pneumothorax in men?
Primary spontaneous pneumothorax is more common in men than in women. This condition occurs in 7.4 to 18 per 100,000 men each year and 1.2 to 6 per 100,000 women each year.
How many blebs are there in a person with a pneumothorax?
Affected individuals may have one bleb to more than thirty blebs. Once a bleb ruptures and causes a pneumothorax, there is an estimated 13 to 60 percent chance that the condition will recur.
What causes a bleb to rupture?
Many things can cause a bleb to rupture, such as changes in air pressure or a very sudden deep breath. Often, people who experience a primary spontaneous pneumothorax have no prior sign of illness; the blebs themselves typically do not cause any symptoms and are visible only on medical imaging.
What is the term for the accumulation of air in the space between the lungs and the chest cavity?
Collapse Section. Primary spontaneous pneumothorax is an abnormal accumulation of air in the space between the lungs and the chest cavity (called the pleural space) that can result in the partial or complete collapse of a lung. This type of pneumothorax is described as primary because it occurs in the absence of lung disease such as emphysema.
Is pneumothorax a spontaneous or spontaneous injury?
This type of pneumothorax is described as primary because it occurs in the absence of lung disease such as emphysema. Spontaneous means the pneumothorax was not caused by an injury such as a rib fracture. Primary spontaneous pneumothorax is likely due to the formation of small sacs of air (blebs) in lung tissue that rupture, ...
Can you develop spontaneous pneumothorax without a mutation?
Primary spontaneous pneumothorax most often occurs in people without an identified gene mutation. The cause of the condition in these individuals is often unknown. Tall young men are at increased risk of developing primary spontaneous pneumothorax; researchers suggest that rapid growth of the chest during growth spurts may increase the likelihood of forming blebs. Long-term smoking also greatly increases the risk of developing primary spontaneous pneumothorax in both men and women.
What causes spontaneous pneumothorax?
[2] . In rare cases, the condition can be caused by mutations in the FLCN gene . In these cases, the condition follows an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance. [1] . In addition, several genetic disorders have been linked ...
Why is pneumothorax called primary?
It is called primary because it occurs in the absence of lung disease such as emphysema and spontaneous because the pneumothhorax was not caused by an injury such as a rib fracture. Primary spontaneous pneumothorax is likely caused by the formation of small sacs of air (blebs) in lung tissue that rupture, causing air to leak into the pleural space. ...
What is the term for the accumulation of air in the pleural space?
Primary spontaneous pneumothorax is an abnormal accumulation of air in the pleural space (the space between the lungs and the chest cavity) that can result in the partial or complete collapse of a lung. It is called primary because it occurs in the absence of lung disease such as emphysema and spontaneous because the pneumothhorax was not caused by ...
Can a bleb cause a pneumothorax?
The blebs that lead to primary spontaneous pneumothorax may be present in an individual's lung (or lungs) for a long time before they rupture. A change in air pressure or a very sudden deep breath may cause a rupture to occur. In most cases, there are no prior signs of illness. Once a bleb ruptures and causes a pneumothorax, ...
What is a spontaneous pneumothorax?
Spontaneous pneumothorax can be termed as: Primary (PSP) in the absence of any obvious precipitating factor, or. Secondary (SSP) when associated with underlying pulmonary diseases or conditions, such as cystic fibrosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, malignancy, etc.
Where are pneumothoraces confined?
Some pneumothoraces are small and confined to the top of the lung; these can often be observed with close follow up. The majority of these patients have complete resolution of the problem and approximately 80 percent will have no further problems with collapse of the lung.
How long does it take for a pneumothorax to heal?
Complete resolution of an uncomplicated pneumothorax can take up to 10 days. The five-year recurrence rate for PSP ranges from 28 to 32 percent, most of them taking place within 1 to 2 years after the first episode.
What is the term for the abnormal presence of air in the space between the lungs and the chest cavity?
Pneumothorax is the abnormal presence of air in the space between the lungs and the chest cavity (known as the pleural space ), which can lead to a partial or complete collapse of the respective lung. Pneumothorax can be classified as: Traumatic (result of an accident or other medical treatment), or. Spontaneous.
What causes a pleural space to leak?
Most cases of primary spontaneous pneumothorax are due to the formation of small sacs of air ( blebs) in the lungs that rupture, causing air to leak into the pleural space. This creates pressure on the lung that leads to its collapse.
What are the genetic disorders that are linked to PSP?
Genetic disorders that have been linked to PSP include Marfan syndrome, homocystinuria and Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome (BHD).
What happens if you rupture your chest?
Typically, the result of a rupture is the acute onset of chest pain and shortness of breath. However, up to 10 percent of patients may be asymptomatic while others have such mild symptoms that they may not even seek out medical care.
What is spontaneous pneumothorax?
Spontaneous pneumothorax is a lung disease that may lead to partial or complete lung collapse. To know about the causes, symptoms and treatment for this, read on. Spontaneous pneumothorax is also called lung collapse. It is said to be spontaneous, as there is no prolonged painful injury to the lungs or chest.
What is the first stage of pneumothorax?
At the first stage of diagnosis, a stethoscope is used by the physician to check the breathing pattern . This reveals whether the breathing pattern is normal or not, and helps in further diagnosis. Chest X-ray can be performed, to confirm the diagnosis of spontaneous pneumothorax. The chest X-ray displays the amount of air that is trapped between the chest and the lung. Arterial blood gases may also be done, wherein the level of oxygen and carbon-dioxide in the blood is measured.
Why does my lung collapse?
As discussed earlier, lung collapse results from an undesirable collection of air or gas between the chest and lung. The lung does not inflate normally, due to the presence of this unwanted air/gas. It is of two types, i.e., primary spontaneous pneumothorax and secondary spontaneous pneumothorax.
What is the most common lung disease?
COPD is found to be the most common lung disease, which leads to secondary spontaneous pneumothorax. People above 60 years of age are mostly affected by this disease. Given below, is the list of lung disorders that may cause this disease. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Lung cancer. Tuberculosis.
What causes a person's lung to collapse?
Smoking is found to be the chief cause, in almost 80% of the cases. Change in atmospheric pressure and proximity to loud sound are also some of the causes. People below 40 years are mostly affected by this type of lung collapse.
Can pneumothorax be cured without treatment?
The form of treatment depends on the amount of air/gas gathered. Primary spontaneous pneumothorax gets cured without any treatment, if it is not severe. If the air has gathered in more amount, then the physician inserts a chest tube which removes the extra air/gas. For the implantation of chest tube, the patient needs to be hospitalized.
Is COPD a type of lung disease?
Person having any type of lung disease is prone to be affected by this type of collapse of the lungs. COPD is found to be the most common lung disease, which leads to secondary spontaneous pneumothorax.
What is spontaneous pneumothorax?
Pneumothorax is defined as the presence of air in the pleural space. Although intrapleural pressures are negative ...
What is pneumothorax in respiratory?
pathogenesis. pneumothorax. Pneumothorax is defined as the presence of air in the pleural space. Although intrapleural pressures are negative throughout most of the respiratory cycle [ 1 ], air does not enter into the pleural space because the sum of all the partial pressures of gases in the capillary blood averages only 93.9 kPa (706 mmHg).
What causes a PSP?
Most authors believe that spontaneous rupture of a subpleural bleb, or of a bulla, is always the cause of PSP [ 11 ], but alternative explanations are available [ 12, 13 ]. Although the majority of PSP patients, including children [ 14 ], present blebs or bullae 15 – 18 ], it is unclear how often these lesions actually are the site of air leakage [ 19 – 21 ]. Only a minority of blebs are actually ruptured at the time of thoracoscopy or surgery, whereas often other lesions are present (“pleural porosity” [ 19 – 21 ]: areas of disrupted mesothelial cells at the visceral pleura, replaced by an inflammatory elastofibrotic layer with increased porosity, allowing air leakage into the pleural space). The latter phenomenon may explain the high recurrence rates of up to 20% of bullectomy alone (without associated pleurodesis) as therapy [ 22 – 25 ]. The development of blebs, bullae and areas of pleural porosity may be linked to a variety of factors, including distal airway inflammation [ 21 – 26 ], hereditary predisposition [ 27 ], anatomical abnormalities of the bronchial tree [ 28 ], ectomorphic physiognomy with more negative intrapleural pressures [ 29] and apical ischaemia [ 30] at the apices [ 31 ], low body mass index and caloric restriction [ 15, 32 ], and abnormal connective tissue [ 33, 34 ]. The role of increased plasma aluminium concentrations in the pathogenesis of PSP remains unresolved [ 35, 36 ].
How does air enter the pleural space?
As in PSP, air may enter the pleural space through various mechanisms: direct alveolar rupture (as in emphysema or necrotic pneumonia), via the lung interstitium, or backwards via the bronchovascular bundle and mediastinal pleura (pneumomediastinum). Recurrence rates usually are higher when compared to those for PSP, ranging up to 80% of cases, ...
What are the three events that must have occurred if air is present in the pleural space?
Hence, if air is present in the pleural space, one of three events must have occurred: 1) communication between alveolar spaces and pleura; 2) direct or indirect communication between the atmosphere and the pleural space; or 3) presence of gas-producing organisms in the pleural space.
Is secondary spontaneous pneumothorax life threatening?
Because lung function in these patients is already compromised, secondary spontaneous pneumothorax (SSP) often presents as a potentially life-threatening disease, requiring immediate action, in contrast with PSP, which is more of a nuisance than a dangerous condition.
Can a PA chest radiograph show pleural air?
In cases with a small PSP, computed tomography (CT) may be necessary to diagnose the presence of pleural air. Routine expiratory chest radiographs are useless [ 10 ]. It is important to realise that a contralateral shift of the trachea and mediastinum is a completely normal phenomenon in spontaneous pneumothorax, and not at all suggestive for tension pneumothorax; this observation should therefore in no way influence treatment strategies [ 1 ].
What are the factors that contribute to a collapsed lung?
Stab wound. Lifestyle factors associated with collapsed lung are: Drug use, especially inhaled drugs. Flying that involves drastic changes in air pressure. Scuba or deep-sea diving. Smoking. People with certain other risk factors may be more likely to have a collapsed lung. These are: Family history of pneumothorax.
Why does my lungs collapse?
It can occur due to abnormal air sacs in the lungs that break apart and release air. Secondary spontaneous pneumothorax: Several lung diseases may cause a collapsed lung. These include chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cystic fibrosis and emphysema.
How to prevent lung from collapsing again?
Your provider makes an incision and inserts a tube. Then your provider uses chemicals (such as doxycycline or talc) to attach the lung to the chest cavity, eliminating extra space in the chest cavity.
What is a collapsed lung?
A collapsed lung occurs when air enters the pleural space, the area between the chest wall and the lung. Air in the pleural space can build up and press against the lung, causing it to collapse partially or fully. Also called a deflated lung or pneumothorax, a collapsed lung needs immediate medical care.
What is the condition where the lung collapses?
Endometrial tissue lines the uterus. With endometriosis, it grows outside the uterus and attaches to an area inside the chest. The endometrial tissue forms cysts that bleed into the pleural space, causing the lung to collapse.
What is the condition where the chest is hard to breathe?
A collapsed lung occurs when air gets inside the chest cavity (outside the lung) and creates pressure against the lung. Also known as pneumothorax, collapsed lung is a rare condition that may cause chest pain and make it hard to breathe. A collapsed lung requires immediate medical care.
Why do you put a tube in your chest?
Chest tube drainage: If you have a larger pneumothorax, your provider may put a hollow tube in your chest to reduce the air in the pleural space. As the air pressure decreases, the lung re-expands and heals. You may have this tube in place for a couple of days or longer.