
What is holoprosencephaly and what causes it?
Holoprosencephaly is a disorder caused by the failure of the prosencephalon (the embryonic forebrain) to sufficiently divide into the double lobes of the cerebral hemispheres. The result is a single-lobed brain structure and severe skull and facial defects.
What increases the risk of holoprosencephaly in pregnant women?
Diabetes in the mother during the pregnancy can increase the risk of holoprosencephaly in the fetus. However, for most children, no known intrauterine exposure is identified that is causally related to holoprosencephaly in that child.
Which facial deformities are associated with holoprosencephaly and cyclopia?
Alobar holoprosencephaly, in which the brain has not divided at all, is usually associated with severe facial deformities. Cyclopia: single eye or partially divided eye in single orbit with a proboscis above the eye
What genes are involved in holoprosencephaly?
These changes cause the genes and their proteins to function abnormally, and this affects the development of the brain, resulting in holoprosencephaly. Some of these genes are SHH, SIX3, TGIF1, ZIC2, PTCH1, FOXH1, NODAL, CDON, FGF8, and GLI2.
What causes holoprosencephaly in pregnancy?
The most common known cause of HPE in humans is maternal type 2 diabetes mellitus. In pregnancies of diabetic mothers, the chance for HPE to occur is about 1%. Approximately 25%-50% of individuals with HPE have a chromosome error as the underlying cause of their HPE.
What is holoprosencephaly and why does it occur?
Holoprosencephaly occurs when the brain fails to divide properly into the right and left hemispheres. This condition is called nonsyndromic to distinguish it from other types of holoprosencephaly caused by genetic syndromes, chromosome abnormalities, or substances that cause birth defects (teratogens).
Is there a cure for holoprosencephaly?
While there is no cure for HPE, treatment is symptomatic and supportive. Some symptoms and conditions caused by HPE are as follows: cyclopia, median cleft lip and palate, seizures, missing front teeth, closley set eyes, small head, multiple hormone deficiencies, feeding difficulties, developmental delays and more.
How early can holoprosencephaly be detected?
Ultrasound done at 18-20 weeks gestation is the ideal modality for screening for holoprosencephaly [6, 7], though the earliest detection of the alobar variety of holoprosencephaly has been reported at 10-12 weeks using the transvaginal ultrasonography (TVS).
Can holoprosencephaly be diagnosed before birth?
Holoprosencephaly can sometimes be detected prenatally through ultrasound or MRI, though mild forms may not be reliably detected prenatally. Treatment and care for the issues associated with holoprosencephaly are supportive and based on the specific medical issues present for an individual child.
Do babies with HPE survive?
HPE affects about one in 5,000 live births. Most children with HPE have the severe form of the disorder. Therefore, the majority do not survive past the first six months of life.
Is holoprosencephaly fatal?
Half of children with severe HPE (alobar HPE) die between four to five months of age, and only 20% survive beyond the first year of life. Holoprosencephaly (HPE) is a birth defect in which the forebrain (prosencephalon) fails to develop normally.
What are some interesting facts about holoprosencephaly?
In most cases of holoprosencephaly, the malformations are so severe that babies die before birth. In less severe cases, babies are born with normal or near-normal brain development and facial deformities that may affect the eyes, nose, and upper lip.
Is holoprosencephaly fatal?
Half of children with severe HPE (alobar HPE) die between four to five months of age, and only 20% survive beyond the first year of life. Holoprosencephaly (HPE) is a birth defect in which the forebrain (prosencephalon) fails to develop normally.
Do babies with HPE survive?
HPE affects about one in 5,000 live births. Most children with HPE have the severe form of the disorder. Therefore, the majority do not survive past the first six months of life.
What are some interesting facts about holoprosencephaly?
In most cases of holoprosencephaly, the malformations are so severe that babies die before birth. In less severe cases, babies are born with normal or near-normal brain development and facial deformities that may affect the eyes, nose, and upper lip.
What causes HPE disease?
HPE is a disorder in which the fetal brain does not grow forward and divide as it is supposed to during early pregnancy (incomplete cleavage of the embryonic forebrain/failure of the prosencephalon to cleave into the cerebral and lateral hemispheres).
What is the cause of holoprosencephaly?
Holoprosencephaly is a complex brain malformation caused by the failure of the prosencephalon (the embryonic forebrain) to sufficiently divide into the double lobes of the cerebral hemispheres, occurring between the 18th and the 28th day of gestation and affecting both the forebrain and the face 1). The result is a single-lobed brain structure and ...
Which facial anomalies are observed in holoprosencephaly?
In most of the cases, facial anomalies are observed in holoprosencephaly, like 3): Cyclopia, in which a single, midline, fused eye exists in a single orbit below a proboscis. Ethmocephaly, in which ocular hypotelorism is present with an interorbital proboscis.
What is a holoprosencephaly MRI?
MRI in axial plane depicting middle interhemispheric variant of holoprosencephaly in which the anterior portions of the frontal lobes and the occipital lobes are well separated. The sylvian fissures are oriented nearly vertically and are abnormally connected across the midline over the vertex of the brain (red/thin arrows). The genu and splenium of the corpus callosum appear normally formed, but the callosal body is typically absent. The hypothalamus and lentiform nuclei are normally separated; however, the caudate nuclei and the thalami remain incompletely separated.#N#B. The facial appearance is usually normal.
How many children with semilobar holoprosencephaly are alive?
More than 50% of children with semilobar or lobar holoprosencephaly were alive at 1 year of age 26). Of those with lobar holoprosencephaly, about 50% are able to walk (some require assistance), have normal to mildly impaired hand function, and can speak single words (some speak in multiword sentences) 27).
How many live births are there in holoprosencephaly?
The incidence of holoprosencephaly has been estimated at 1 in 250 during early embryonic development, and approximately 1 in 10,000–20,000 live births 5).
What is the common origin of the embryonic forebrain and mid-face?
A series of facial anomalies are frequently associated, owing to the common origin of the embryonic forebrain and mid-face from the prechordal mesoderm, along with some other anomalies. Alobar holoprosencephaly, in which the brain has not divided at all, is usually associated with severe facial deformities.
Is holoprosencephaly a risk factor?
A careful family history by a clinic al geneticist familiar with holoprosencephaly is critical, as genetic changes associated with holoprosencephaly, even in a mildly affected individual, would be considered a risk factor for manifestations such as developmental delay.
What causes holoprosencephaly in the fetus?
Causes. Holoprosencephaly is a birth defect that arises during the first few weeks of the pregnancy. Diabetes in the mother during the pregnancy can increase the risk of holoprosencephaly in the fetus. However, for most children, no known intrauterine exposure is identified that is causally related to holoprosencephaly in that child.
Who should assess holoprosencephaly?
Relatives of a child with holoprosencephaly may have an increased risk of having a child with holoprosencephaly, and this should be assessed and discussed by the child’s physicians, especially the neurologist and/or clinical geneticist.
What is the failure of the prosencephalon?
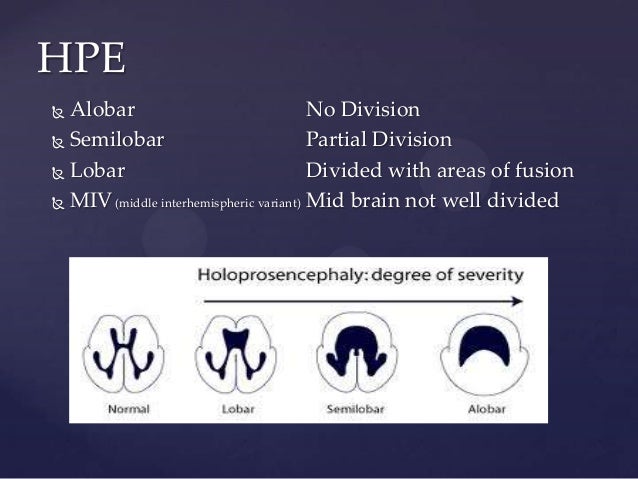
Holoprosencephaly (HPE) is the failure of the prosencephalon, or forebrain, to develop normally. The forebrain is a region of the brain in the fetus that develops into parts of the adult brain, including the cerebral cortex. Instead of the normal complete separation of the left and right halves of the forebrain, there is an abnormal continuity between the two sides. There are several different types of holoprosencephaly. In the alobar form, there is no separation between the right and left halves at all. In semilobar HPE, at least some separation of the two halves is present. In the lobar form, most of the brain has separated into right and left sides, though there is incomplete division into the two halves.
What is the most common chromosomal abnormality associated with HPE?
The most common chromosomal abnormality associated with HPE is when there are 3 copies of chromosome 13 (trisomy 13), although a number of other chromosomal changes can also cause holoprosencephaly. In other children, holoprosencephaly is due to a change in a specific gene.
How many live births are there in holoprosencephaly?
The incidence of holoprosencephaly has been estimated at 1 in 250 during early embryonic development, and approximately 1 in 16,000 live births.
Can holoprosencephaly affect the brain?
Holoprosencephaly can also occur in certain genetic syndromes in which there are other medical issues besides those mentioned in this report that affect organs in addition to the brain and face (e.g., Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome).
What is holoprosencephaly?
Listen. Holoprosencephaly is an abnormality of brain development in which the brain doesn't properly divide into the right and left hemispheres. The condition can also affect development of the head and face. There are 4 types of holoprosencephaly, distinguished by severity. From most to least severe, the 4 types are alobar, semi-lobar, lobar, ...
How many types of holoprosencephaly are there?
There are 4 types of holoprosencephaly, distinguished by severity. From most to least severe, the 4 types are alobar, semi-lobar, lobar, and middle interhemispheric variant (MIHV). [1] . In general, the severity of any facial defects corresponds to the severity of the brain defect.
What is the term for a complete failure of the brain to divide into the right and left hemispheres
Alobar holoprosencephaly is when there is a complete failure of the brain to divide into right and left hemispheres which results in the loss of midline structures of the brain and face as well as fusion of the cavities of the brain, known as lateral ventricles and the third ventricle (which are normally separated).
How long do people with semilobar holoprosencephaly live?
More than 50 percent of children with semi-lobar or lobar holoprosencephaly without significant malformations of other organs are alive at age 12 months. [1] . The life expectancy for individuals with semi-lobar holoprosencephaly depends on the underlying cause of the condition and the presence of associated anomalies.
How long can a child live with holoprosencephaly?
However, a significant proportion of more mildly affected children (as well as some severely affected children) survive past age 12 months. More than 50 percent of children with semi-lobar or lobar holoprosencephaly without significant malformations of other organs are alive at age 12 months. [1] The life expectancy for individuals with semi-lobar holoprosencephaly depends on the underlying cause of the condition and the presence of associated anomalies. [2] [4]
What is the name of the condition where the brain is fused in the middle?
Lobar holoprosencephaly, is when there are two ventricles (right and left) but the cerebral hemispheres are fused in the frontal cortex. Features may include bilateral cleft lip , closely spaced eyes, depressed nose or an almost normal looking face. Middle interhemispheric variant results when the brain is fused in the middle.
What are the features of semilobar holoprosencephaly?
Other features may include a flattened bridge and tip of the nose, one nostril, a median cleft lip or bilateral cleft lip, and a cleft palate . Lobar holoprosencephaly, is when there are two ventricles ...
How is holoprosencephaly classified?
Lobar (mild) – The least frequent form of HPE. The brain is divided but there is some fusion of structures and mild abnormalities.
What causes HPE?
Although the cause of holoprosencephaly is not known, it has been linked to both genetic alterations and environmental exposures.
How common is HPE?
Between 1 in 5,000-10,000 babies are born with HPE each year. Since only about 3% of fetuses with HPE survive till birth, the actual frequency may be as high as 1 in 200-250.
What are the risks of reoccurrence?
The risk of reoccurrence is small in most families, but genetic counseling is recommended.
What is the prognosis for a child with HPE?
Babies with the most severe forms of holoprosencephaly often die before they are born or shortly after birth. However some children even with the most severe forms of HPE may live several months or years after birth. Children with the mildest forms of HPE may have a normal life span.
What is the name of the brain disorder that occurs in less than 12% of children with HPE?
Lobar (mild) Occurs in less than 12% of children with HPE. The brain is almost completely divided. Problems (or abnormalities) of the brain are mild/less severe. Some children have a version called Septopreoptic HPE. This type is very mild/less severe. Only a small area of the brain is not divided.
What is the term for a birth defect that occurs when the brain divides into two halves?
Holoprosencephaly (HPE) is a birth defect that occurs very early in pregnancy, when the developing brain grows and divides into two halves, or hemispheres. In HPE, a part of the brain called the prosencephalon does not grow forward and divide as it should. Holo = whole or entire (not separated into two halves)
What is the most common type of HPE?
Alobar (severe) This is the most common type of HPE. The brain is not divided at all. Severe problems are present because: some parts of the brain may not completely develop or may be missing entirely. some parts of the brain may be “stuck” together.
How many births are affected by HPE?
HPE affects between 1 in 5,000 to 10,000 live births. Since many of these pregnancies end in miscarriage, the true rate of HPE may be higher: one in 200-250. Current studies show that only 3% of fetuses with HPE survive to delivery. The majority do not survive past the first six months of life.
What type of scan is used to diagnose hydrocephalus?
Brain scans (MRI or CAT scans) to diagnose the condition. Scans may be repeated annually if your child has hydrocephalus. Genetic testing for chromosome abnormalities or gene mutations during the initial work-up for HPE and may be repeated as genetic testing advances.
4 subtypes of holoprosencephaly
One of the most severe forms where the brain is not divided into right and left hemispheres and remains as one.
Top Life Expectancy of Someone With Holoprosencephaly Related Articles
Brain and spinal tumor are diseases in which cancer (malignant) cells begin to grow in the tissues of the brain. Tumors that start in the brain are called primary brain tumors. Tumors that start in the brain and spread to other organs are called primary brain tumors.
