
Some common causes are:
- A degenerative disease (such as arthritis)
- An inner ear disorder
- Stroke
- Foot conditions
- A neurologic condition
- Something as simple as ill-fitting shoes
What is a myopathic gait?
Myopathic gait. Sometimes called a waddling gait, a myopathic gait is characterized by a side-to-side movement when walking. It is often due to a weakness in the pelvic area. Myopathic gait can be due to hip problems present since birth. It may be a symptom of muscular dystroph y, another muscle disease, or spinal muscle weakness.
What causes walking/gait disorders?
Causes of walking/gait disorders can range from arthritis to a neurological condition to something as simple as ill-fitting footwear. The variety of gait disorders call for different treatments. What is a gait disorder? Gait is a person’s pattern of walking.
What causes gluteus medius gait?
A myopathic gait is caused by weakness of the hip girdle muscles, most often due to myopathy and most characteristically due to muscular dystrophy. (1,2) The hip abductor muscles, especially the gluteus medius, are vital in stabilizing the pelvis while walking. This gait pattern is sometimes referred to as a gluteus medius gait.
What causes waddling gait in DMD?
Waddling Gait in Muscular Dystrophy Duchenne m uscular d ystrophy (DMD) is a genetic condition that causes muscle weakness that becomes more severe over time. It's one of four conditions caused by a change in a protein called dystrophin, which helps keep muscle cells together.
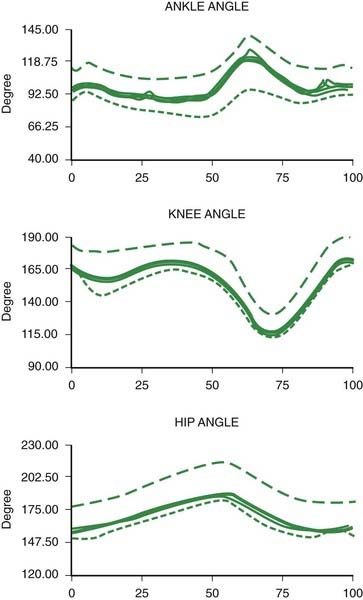
What are the main causes for a waddling gait?
Waddling gait in children is commonly caused by hip disorders such as developmental hip dysplasia, septic sequelae in the hip, bilateral Perthes disease and slipped capital femoral epiphysis.
How do I fix myopathic gait?
How Is Waddling Gait Treated?Canes and walkers for balance.Physical therapy to help with strength, balance, and flexibility.Fall prevention measures.Leg braces or splints to help with foot alignment.Medicine.Surgery or prostheses.
Which nerve is damaged in waddling gait?
superior gluteal nerve lesionsBilateral superior gluteal nerve lesions often result in a waddling gait. The gluteus medius is a thick, fan-shaped muscle originating from the outer aspect of the ilium superiorly from the iliac crest, the middle gluteal nerve inferiorly and the gluteal line posteriorly.
What is the most common gait abnormality?
Epidemiology and classification of gait disorders Among the neurological causes, sensory ataxia (18 %) and parkinsonian (16 %) gait disorders were the most common, followed by frontal (8 %), cerebellar ataxic gait disorders, cautious gait and hypotonic paretic, spastic, vestibular and dyskinetic gait disorders.
Can you fix waddling gait?
0:354:32Do You Waddle When You Walk? Weak Hips? How to Stop ... - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipBy going to the direction. If you don't think about this your body does it automatically. So youMoreBy going to the direction. If you don't think about this your body does it automatically. So you keep your balance.
Can gait disorders be cured?
Physical therapy and other treatments can help alleviate or cure an abnormal gait. People should seek medical advice and treatment if needed to help deal with their condition.
What is the Parkinson's gait?
'Parkinsonian gait' is a distinctive, less steady walk that arises from changes in posture, slowness of movement (bradykinesia) and a shortened stride.
How is gait affected by gluteus medius weakness?
In waddling gait weakness in the gluteus medius muscles leads the hip on the swinging side to drop during gait, in an attempt to counteract, the patient bends the trunk towards the other side, resulting in the gait to appear waddling.
How do I stop walking like a duck?
Are there home remedies for duck-footedness?Retrain your stance. Become more conscious of the way you position your feet when you walk or stand. ... Use orthotic inserts. Look for orthotic inserts that support and lift the arch of the foot. ... Stretching and exercising.
What part of the brain controls gait instability?
Four studies found that lower GM volume in temporal lobe regions [37,38,42,43], cerebellum [37,40,43,44] and basal ganglia, insula, and limbic systems [33,37,38,40] was associated with disrupted gait.
What diseases affect your ability to walk?
“Your brain is responsible for both your movements and your balance. As a result, diseases that affect the brain, like vascular disease, normal pressure hydrocephalus, multiple sclerosis and Parkinson's disease, can all make it difficult to walk.” The way you walk can give early warning signs of these diseases.
What your gait says about you?
These studies also say that the way you walk, including speed, tells a lot about your personality traits. “A faster pace is linked to higher levels of conscientiousness, and openness, and lower levels of neuroticism,” revealed the researchers. So, what your gait tells about your personality, let's find out.
How do I reset my gait?
1:141:50QUICK GAIT FIX - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIt's rotated in your hips joint. And then when you turn around and begin to walk normal your legsMoreIt's rotated in your hips joint. And then when you turn around and begin to walk normal your legs just turn around. So try it one minute in exaggerated.
How long does it take to correct gait?
A more minor correction to increase your athletic performance, say, or to remedy a step torqued by high heels or an aging body can often be accomplished in as little as six weeks with regular practice (and maybe some in-shoe orthotics).
How can I improve my gait pattern?
Gait Training ExercisesWalking on a treadmill.Lifting your legs.Sitting down.Standing up.Stepping over objects.
How do you normalize gait?
2:053:29Normalizing Gait Asymmetries and Function with the WOODWAY CURVEYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo what we can do. We can use this band. And put the band around his waist over his hips low. AndMoreSo what we can do. We can use this band. And put the band around his waist over his hips low. And while you can do this on the motorized treadmill or on from walking.
What is neuropathic gait?
A neuropathic gait is sometimes known as a foot drop. One foot flops down when your leg lifts up, so you need to pull your knee up high enough to prevent your toes from dragging on the ground when you walk. Neuropathic gait may be a symptom of multiple sclerosis (MS), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), or peripheral neuropathy.
How to tell if you have gait disorder?
Doctors can look at how you are moving and figure out what type of gait disorder you are showing. The way your body moves will give them clues about the underlying cause of your gait problems. This can help them diagnose the issue and plan for treatments.
What is the name of the movement that you can't walk straight?
It may be a symptom of muscular dystroph y, another muscle disease, or spinal muscle weakness. Ataxic gait. Ataxic gait is known for a staggering movement when walking. You may weave from side to side and be unable to walk a straight line.
What is hemiplegic gait?
Hemiplegic gait. Hemiplegic gait is a disorder that affects one side of the body. One of your arms will stay at your side and not move while you walk. You will drag the leg on the same side in a semi-circle to bring it forward. A hemiplegic gait is often the result of a stroke.
What doctor should I see if I have difficulty walking?
If you are having difficulty walking, you should speak to a doctor. You may need to see a specialist such as a neurologist, orthopedist, or podiatrist to determine the cause of your gait disorder. Diagnosis could include physical exams, blood tests, and imaging such as x-rays or MRI.
What is the meaning of gait?
Common Types of Gait Disorders. Other Causes of Gait Disorders. Treatment for Gait Disorders. The word gait refers to the movement you use to walk or run. Walking is a complex series of movements that requires your brain, bones, and muscles to work together, with help from your heart and lungs.
Why do my feet feel weak?
Pain or weakness in your feet may be a consideration, as well. You may have balance issues from a problem with your inner ear that affects movement. Medical conditions such as heart disease, respiratory difficulties, and obesity can also affect your mobility and how you move. Treatment for Gait Disorders.
Overview
Myopathy refers to diseases that affect skeletal muscles (muscles that connect to your bones). These diseases attack muscle fibers, making your muscles weak.
Diagnosis and Tests
You should first contact your primary care doctor to alert them to the symptoms you’re concerned about. Depending on the nature of your symptoms, you might be referred to a specialist such as a neurologist or a rheumatologist.
Management and Treatment
After determining your specific type of myopathy, your healthcare provider will develop a treatment plan specific to your symptoms.
Living With
Although myopathy is a long-term (chronic) disease whether inherited or acquired, you can take steps to improve your health to help control your illness. These might include:
Why does walking make you gait?
Walking involves balance and coordination of muscles so that the body is propelled forward in a rhythm, called the stride. There are numerous possibilities that may cause an abnormal gait. Some common causes are: A degenerative disease (such as arthritis) An inner ear disorder. Stroke.
What are the different types of gait disorders?
The following gait disorders are so distinctive as to earn names: 1 Propulsive gait. This type of gait is seen in patients with parkinsonism. It is characterized by a stooping, rigid posture, and the head and neck are bent forward. Steps tend to become faster and shorter. 2 Scissors gait. This type of gait gets its name because the knees and thighs hit or cross in a scissors-like pattern when walking. The legs, hips, and pelvis become flexed, making the person appear as though he or she is crouching. The steps are slow and small. This type of gait occurs often in patients with spastic cerebral palsy. 3 Spastic gait. Common to patients with cerebral palsy or multiple sclerosis, spastic gait is a way of walking in which one leg is stiff and drags in a semicircular motion on the side most affected by long-term muscle contraction. 4 Steppage gait. A “high stepping” type of gait in which the leg is lifted high, the foot drops (appearing floppy), and the toes points downward, scraping the ground, when walking. Peroneal muscle atrophy or peroneal nerve injury, as with a spinal problem (such as spinal stenosis or herniated disc), can cause this type of gait. 5 Waddling gait. Movement of the trunk is exaggerated to produce a waddling, duck-like walk. Progressive muscular dystrophy or hip dislocation present from birth can produce a waddling gait.
What is spastic gait?
Common to patients with cerebral palsy or multiple sclerosis, spastic gait is a way of walking in which one leg is stiff and drags in a semicircular motion on the side most affected by long-term muscle contraction. Steppage gait.
What is a high stepping gait?
A “high stepping” type of gait in which the leg is lifted high, the foot drops (appearing floppy), and the toes points downward, scraping the ground, when walking.
What is the name of the disorder where the head and neck are bent forward?
The following gait disorders are so distinctive as to earn names: Propulsive gait. This type of gait is seen in patients with parkinsonism. It is characterized by a stooping, rigid posture, and the head and neck are bent forward. Steps tend to become faster and shorter. Scissors gait.
How to improve balance and flexibility?
Physical therapy and strengthening exercises may be appropriate in other cases to improve balance, strength and flexibility. You should also receive instruction in fall prevention. Maintaining proper foot alignment may require in-shoe splints or leg braces. A shoe lift may help in cases of an unequal leg length.
Which gait is faster?
Steps tend to become faster and shorter. Scissors gait. This type of gait gets its name because the knees and thighs hit or cross in a scissors-like pattern when walking. The legs, hips, and pelvis become flexed, making the person appear as though he or she is crouching. The steps are slow and small.
What is a waddling gait?
A waddling gait is a symptom of several types of MD, including: Duchenne MD. This disorder occurs almost exclusively in boys and affects the arms, legs, and pelvis. One of the first signs is having difficulty crawling or getting up from the floor. Duchenne MD is diagnosed in early childhood. Becker MD.
What is the name of the condition that causes muscle weakness and loss of muscle tissue in the thighs?
One form of SMA, called autosomal dominant spinal muscular atrophy with lower extremity predominance, causes muscle weakness and loss of muscle tissue in your thighs. This form of SMA is rare and typically begins in early childhood.
How to treat hip dysplasia in infants?
If caught early, it can usually be treated with assistive devices, such as a harness or brace. Older infants may need a body cast or surgery for proper treatment.
How to tell if a baby has hip dysplasia?
Additional symptoms of infant hip dysplasia include: legs of different lengths. limping or tiptoe walking. reduced mobility or flexibility in one leg or on one side of the body . uneven skin folds on the thighs. Pediatricians usually screen for infant hip dysplasia at birth and during regular checkups for the first year.
What is spinal muscular atrophy?
Spinal muscular atrophy. Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a hereditary neurological disorder. It causes deterioration of your spinal cord’s motor neurons, resulting in muscle weakness and other symptoms.
Can you have a waddling gait while pregnant?
Both of these factors can also cause a waddling gait. Having a waddling gait while pregnant is normal and nothing to be concerned about. In fact, it can even reduce your risk of falling. Waddling gaits tend to go away after you give birth, but you may continue to have one for several months. Trusted Source.
What causes myopathy?
Other causes of myopathy include immune disorders that cause inflammation and pain. Numerous inherited myopathies exist and may be associated with progressive weakness, atrophy (wasting), inflammation, muscle fiber metabolism dysfunction, muscle spasm, or rigidity. The signs and symptoms of myopathy will vary depending on the type ...
What are the risk factors for myopathy?
A number of factors increase the risk of developing myopathy. Not all people with risk factors will get myopathy. Risk factors for myopathy include:
What are the potential complications of myopathy?
Complications of untreated myopathy can be serious . You can help minimize your risk of serious complications by following the treatment plan you and your health care professional design specifically for you. Complications of myopathy include:
What is myopathy in a muscle?
What is myopathy? Myopathy refers to any disease that affects muscle tissue. Diseases of the muscle result in weakness, inflammation, tetany (spasms), or paralysis. Myopathy can be the result of either inherited or acquired causes. Acute "acquired" myopathies, such as acute stiffness, spasm, or cramp, are common.
What causes muscle dysfunction?
Myopathy causes dysfunction of the muscles due to inflammation or disease and can cause a number of symptoms. The symptoms can vary in intensity among individuals.
What causes muscle cramps and muscle fatigue?
Myopathy develops as the result of either inherited (congenital or genetic) disorders or acquired conditions of the muscles. Most commonly, people develop acquired myopathy from muscle fatigue, electrolyte imbalance, or dehydration, resulting in stiffness or cramping.
What are congenital myopathies?
Congenital myopathies, that are present at birth. Familial periodic paralysis. Glycogen storage disease of muscle (including Pompe’s disease) Mitochondrial myopathies (abnormalities of the cellular components known as mitochondria) Muscular dystrophy.
Why does my horse have a neuropathic gait?
(Steppage Gait, Equine Gait) Seen in patients with foot drop (weakness of foot dorsiflexion), the cause of this gait is due to an attempt to lift the leg high enough during walking so that the foot does not drag on the floor. If unilateral, causes include peroneal nerve palsy and L5 radiculopathy.
What are the eight gait abnormalities?
Gait Abnormalities. There are eight basic pathological gaits that can be attributed to neurological conditions: hemiplegic, spastic diplegic, neuropathic, myopathic, Parkinsonian, choreiform, ataxic (cerebellar) and sensory. Observation of these gait are an important aspect of diagnosis that may provide information about several musculoskeletal ...
What is the gait of cerebral palsy?
I get that we should mention in the context of the hemiplegic gait. This is the gait that is commonly seen in cerebral palsy. It's a diplegia gait, if you will, with hemiplegia on both sides. It’s a gait that I'm sure you’ve seen often in children and in adults affected by this from childhood. Typically the patients have extensor spasm and almost seem to be walking on tiptoe and although they have some circumduction they have a lot of adductor spasm that keeps their feet close together so they tend to be walking on tiptoe the arm is flexed like this. The adduction is a prominent feature in fact in some parts of the world where children do not get adductor releases you might actually see a scissors gait where the leg swings all the way over to the other side and again. That is another manifestation of the diplegia gait.
What is the gait of walking in the dark?
Talking about proprioception leads me to the other gait related to proprioception. Once again if you have trouble with your proprioception and cannot feel when your foot has arrived on the floor you are relying on a lot of visual cues and especially in the dark. You might develop what's called a stomping or stamping gait where you tend to walk like this needing to slam your foot down to get the vibration in your trunk to let you know that your foot has landed. So this gait may be much more prominent in the dark and not as evident in the daytime because they can see where they're going.
What is hemiplegic gait?
If the condition is mild the hand may not be flexed up like that and the only manifestation might just be a little circumduction and the hand may not be swinging normally the way the other hand swing. That is called the hemiplegic gait. It's important to understand why they do what they do when you cut the pyramidal tract. On the left side you have abnormalities of tone that manifests on the right side. So you develop flexion hypertonia in the upper limb and extensor hypertonia in the lower limb and that accounts for the leg being like that and the hand being like this. In addition, they develop much more distal weakness than proximity weakness. Their shoulder is strong and the fingers are very weak.
What is the most common gait you see in hemiplegia?
The most common gauge you will see is the hemiplegic gait and this is one that you see in hemiplegia where the arm is typically in this posture and the leg on the affected side is typically somewhat stiff.
What is the gait of Parkinson's?
Another case that we would commonly identify is the gait of Parkinson’s disease. It's a posture that's characterized by universal flexion. Every joint is flexed and the patient typically will take very small steps. This is called a festination gait. The French call it the marche. A petit power walk of little steps and there might also be an associated tremor with the gait. The patient may have a myriad other abnormalities related to the Parkinson's that we are not going to cover in this session.
