Causes
To prevent Raynaud's episodes or ease symptoms
- Run warm water over your hands or feet to increase blood flow. ...
- Swing your arms in a circle at the sides of your body ("windmilling") to increase blood flow.
- If your doctor prescribes medicine to help Raynaud's, take it exactly as prescribed. ...
- If another condition causes your Raynaud's, make sure to follow your treatment for that condition.
Symptoms
Primary Raynaud syndrome is commonly treated with a calcium channel blocker. It often does not cause symptoms; however, high blood pressure can increase the risk of stroke, heart attacks, and heart failure.
Prevention
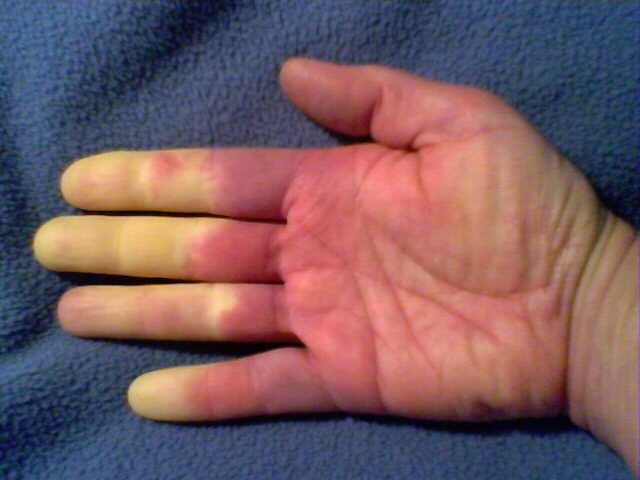
Raynaud’s Disease symptoms. When you’re cold, anxious or stressed, your fingers and toes may change colour. This can be accompanied by: pain. numbness. pins and needles. difficulty moving the affected area. prickly feeling or stinging pain upon warming or stress relief. A Raynauld’s attack normally turns skin white as a result of blood ...
Complications
Primary Raynaud's is more common and tends to be less severe than secondary Raynaud's. Secondary Raynaud's is caused by an underlying disease, condition, or other factor. This type of Raynaud's is often called Raynaud's phenomenon.
How can we prevent Raynaud's phenomenon?
Does Raynaud's cause high blood pressure?
What are the symptoms of Raynauds disease?
What is more severe Raynaud's primary or secondary?
See more

How Serious Is Raynaud's Phenomenon?
Raynaud's phenomenon is common and does not usually cause severe problems. You can often treat the symptoms yourself by keeping warm. Sometimes it can be a sign of a more serious condition.
What is Raynaud's phenomenon associated with?
Raynaud's phenomenon is caused by overly-sensitive blood vessels within the fingers and toes. They are more affected by cold and stress. The blood vessels narrow substantially, causing a decrease in blood flow and associated color change. The lack of blood flow often results in a pale, or white, discoloration.
Is Raynaud's Phenomenon an autoimmune disease?
Raynaud's phenomenon may be a sign of an underlying autoimmune disorder such as scleroderma or lupus, so it's important to see your doctor for diagnosis. Management options include avoiding cold weather and sudden temperature changes.
What is the difference between Raynaud's disease and Raynaud's phenomenon?
Raynaud's disease: Occurs on its own and isn't connected with another disease or condition. This is also called primary Raynaud's syndrome. Raynaud's phenomenon: Occurs due to an underlying condition, medication or lifestyle factor. This is also called secondary Raynaud's syndrome.
What organs does Raynaud's affect?
Raynaud phenomenon is a condition in which the body's normal response to cold or emotional stress is exaggerated, resulting in abnormal spasms (vasospasms) in small blood vessels called arterioles. The disorder mainly affects the fingers but can also involve the ears, nose, nipples, knees, or toes.
What is the best treatment for Raynaud's?
To widen blood vessels and increase blood flow, your doctor might prescribe: Calcium channel blockers. These drugs relax and open small blood vessels in your hands and feet, reducing the severity and number of attacks in most people with Raynaud's. These drugs can also help heal skin ulcers on your fingers or toes.
What is the life expectancy of someone with Raynaud's disease?
Under the broad definition, the median survival time was 11.0 years (95% CI: 10.0–12.1 years) for white subjects without RP, compared to 8.1 years (95% CI: 6.0–11.8 years) for white subjects with RP.
Can Raynaud's affect the heart?
There's no known link between Raynaud's and heart disease.
Does Raynaud's get worse with age?
Raynaud's disease (also referred to as Raynaud's syndrome or Raynaud's phenomenon) is estimated to affect up to 10% of New Zealanders. It is a progressive condition, meaning it tends to worsen as a person gets older.
What can be mistaken for Raynaud's?
Acrocyanosis and Raynaud's are similar conditions and may be confused in the clinical setting. Both conditions are cold-sensitive and may result in a cyanotic discoloration of the affected areas, with most prominent manifestations occurring in the hands and feet.
Can Raynaud's be cured?
There is no cure for Raynaud's that occurs on its own (primary Raynaud's). But you may be able to control it by avoiding the things that trigger it. Keep your body warm.
How do I get tested for Raynaud's?
A cold stimulation test involves placing your fingers in an ice water bath to find out if you have Raynaud's syndrome.
Is Raynaud's caused by poor circulation?
Technically, Raynaud's phenomenon is a circulation problem, but it's very different than what doctors mean by poor circulation, says Dr. Shmerling.
How does Raynaud disease affect the heart?
Patients with both primary and secondary Raynaud's phenomenon have an abnormally low blood penetration in the heart tissue, which likely explains the increased death rates from heart disease in these patients.
What is scleroderma caused by?
Scleroderma results from an overproduction and accumulation of collagen in body tissues. Collagen is a fibrous type of protein that makes up your body's connective tissues, including your skin. Doctors don't know exactly what causes this process to begin, but the body's immune system appears to play a role.
Is Raynaud's disease curable?
There is no cure for Raynaud's that occurs on its own (primary Raynaud's). But you may be able to control it by avoiding the things that trigger it. Keep your body warm.
What is secondary Raynaud's?
Secondary Raynaud's. Also called Raynaud's phenomenon, this form is caused by an underlying problem. Although secondary Raynaud's is less common than the primary form, it tends to be more serious.
What are the symptoms of Raynaud's disease?
Signs and symptoms of Raynaud's disease include: Cold fingers or toes. Color changes in your skin in response to cold or stress. Numb, prickly feeling or stinging pain ...
What causes a person's arteries to narrow?
Symptoms. Raynaud's disease causes smaller arteries that supply blood flow to the skin to narrow in response to cold or stress. The affected body parts, usually fingers and toes, might turn white or blue and feel cold and numb until circulation improves, usually when you get warm. Signs and symptoms of Raynaud's disease include: ...
How to prevent Raynaud's attacks?
Prevention. To help prevent Raynaud's attacks: Bundle up outdoors. When it's cold, don a hat, scarf, socks and boots, and two layers of mittens or gloves before you go outside. Wear a coat with snug cuffs to go around your mittens or gloves, to prevent cold air from reaching your hands. Also use chemical hand warmers.
What is the disease that causes blood vessels to narrow?
In Raynaud's disease , smaller arteries that supply blood to your skin become narrow, limiting blood flow to affected areas (vasospasm). Women are more likely than men to have Raynaud's disease , also known as Raynaud's or Raynaud's phenomenon or syndrome. It appears to be more common in people who live in colder climates.
Why do my hands and feet get cold?
Doctors don't completely understand the cause of Raynaud's attacks , but blood vessels in the hands and feet appear to overreact to cold temperatures or stress.
How long does it take for Raynaud's to heal?
After you warm up, the return of normal blood flow to the area can take 15 minutes.
What is Raynaud’s phenomenon?
Raynaud’s phenomenon is a condition that causes the blood vessels in the hands and feet to narrow, decreasing blood flow. When this happens, parts of the body—usually the fingers and toes—become cold and numb, and change color (usually, to white or blue). An attack usually happens from exposure to cold or stress.
Why do Raynaud's attacks happen?
They do understand that attacks usually happen when people with Raynaud’s phenomenon are exposed to cold or stress.
How to keep Raynaud's symptoms under control?
Most people with Raynaud’s phenomenon can keep symptoms under control by avoiding getting cold. In some cases, medications and surgery can help.
What causes blood vessels to narrow?
Raynaud’s phenomenon causes blood vessels to narrow, leading to decreased blood flow, usually in the fingers and toes.
What does it mean when your fingers are cold?
During an attack, your fingers and toes may feel very cold or numb. Raynaud’s phenomenon is also called Raynaud’s disease or Raynaud’s syndrome.
How does Raynaud's phenomenon affect blood vessels?
In people with Raynaud’s phenomenon, blood vessels in the hands and feet appear to overreact to cold temperatures or stress. They narrow and limit blood supply.
How many types of Raynaud's phenomenon are there?
There are two types of Raynaud’s phenomenon.
What causes Raynaud's syndrome?
Other possible causes of secondary Raynaud’s phenomenon include: Traumatic vasospasm from vibrating tools or repeated pounding with the palm of the hand (hyothenar hammer syndrome) Carpal tunnel syndrome.
What is Raynaud's phenomenon?
What is Raynaud’s phenomenon? Raynaud’s phenomenon (also called Raynaud’s disease or Raynaud’s syndrome) is a disorder that affects the blood vessels in the fingers and toes. Blood vessels in the nose, lips or ear lobes may also be affected.
Why do my fingers and toes go white?
This disorder is characterized by episodic spasms, called vasospastic attacks, which cause the small blood vessels in the fingers and toes to constrict (tighten or close) in response to temperature extremes, certain occupational exposures, or excitement. With Raynaud’s, the skin on the affected areas becomes white or bluish and cold or numb.
How does Raynaud's disease affect the fingers?
Some of these diseases reduce blood flow to the fingers and toes by causing the blood vessel walls to thicken and the vessels to constrict too easily . Raynaud’s phenomenon occurs in about 85 to 95 percent of patients with scleroderma and is present in about one-third of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (lupus).
How do you know if you have cyanosis?
Other symptoms that occur during cyanosis are feeling cold and numbness. Rubor (redness) occurs as the blood returns to the affected areas. After an attack is over, throbbing and tingling may occur in the fingers and toes. Attacks of Raynaud's Phenomenon can last from less than a minute to several hours.
What to do if a doctor suspects Raynaud's phenomenon?
If a doctor suspects Raynaud’s phenomenon, he or she will thoroughly evaluate the patient’s medical history and perform a complete physical exam to rule out other medical problems. Often, it is fairly easy to diagnose Raynaud’s, but more difficult to identify the form of the disorder.
What is secondary Raynaud's?
Secondary Raynaud’s Phenomenon. Less common than the primary form, however, secondary Raynaud’s phenomenon is often a more serious disorder. Secondary Raynaud’s is caused by an underlying disease or condition. It is especially common in people with connective tissue diseases. Some of these diseases reduce blood flow to the fingers ...
What is Raynaud's phenomenon?
Raynaud’s Phenomenon: Causes, Symptoms and Solutions. Raynaud’s phenomenon, also called Raynaud’s disease or syndrome, is a relatively common but often unrecognized condition. It is a vascular disorder that occurs when blood vessels temporarily overreact to low temperatures, emotional stress, or other exposures.
Who first described the Raynaud phenomenon?
This phenomenon was first described in 1862 by the French physician Maurice Raynaud, who at the time was a medical student ( 1 ). It was first called “Raynaud’s disease” but later referred to as “Raynaud’s phenomenon.”.
What is secondary Raynaud's?
Secondary Raynaud’s is associated with another condition or disease. The most common conditions associated with Raynaud’s are autoimmune connective tissue or rheumatic diseases such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, or scleroderma. Raynaud’s is often the earliest indication of an underlying connective tissue disease.
Why is it important to avoid cold with Raynaud's?
With secondary Raynaud’s, it is important to address the underlying condition to improve Raynaud’s symptoms. Avoiding cold is the most important strategy for anyone with Raynaud’s phenomenon.
How to treat Raynaud's disease?
You should keep your whole body warm by wearing layered clothing, avoiding rapidly shifting temperatures, and avoiding cold and breezy conditions. For example, wear a hat, scarf, earmuffs, warm gloves, boots, and thick socks when you go outside in cold temperatures. It may also be helpful to wear gloves and socks to bed during winter.
Why is it important to manage stress if you have Raynaud's disease?
Stress and anxiety cause blood vessels to constrict and reduce circulation. The sympathetic nervous system is activated, and your body has a fight or flight response during times of extreme stress or anxiety. This affects blood flow. It is important to reduce anxiety and manage stress if you have Raynaud’s.
How many people have Raynaud's?
Raynaud’s affects up to 10% of the general population ( 2 ). Women are more likely than men to get Raynaud’s. It is estimated that 5-20% of women and 4-14% of men have Raynaud’s ( 3 ). Primary Raynaud’s usually manifests between the ages of 15 to 25, while secondary Raynaud’s occurs more often in people over the age of 35.

Overview
Symptoms
Causes
Risk Factors
Complications
- Raynaud's (ray-NOSE) disease causes some areas of your body — such as your fingers and toes — to feel numb and cold in response to cold temperatures or stress. In Raynaud's disease, smaller arteries that supply blood to your skin become narrow, limiting blood flow to affected areas (vasospasm). Women are more likely than men to have Raynaud's disease, also known as Rayna…
Prevention
- Signs and symptoms of Raynaud's disease include: 1. Cold fingers or toes 2. Color changes in your skin in response to cold or stress 3. Numb, prickly feeling or stinging pain upon warming or stress relief During an attack of Raynaud's, affected areas of your skin usually first turn white. Then, they often turn blue and feel cold and numb. As you warm and your circulation improves, t…