Sialadenitis causes include:
- Bacterial or viral infection.
- Dehydration.
- Recent illness.
- Certain medications, such as diuretics, antihistamines and beta-blockers.
- Sjögren’s syndrome, an autoimmune disease.
- Poor oral hygiene.
What is the pathophysiology of sialadenosis/sialosis?
Sialosis (sialadenosis) is a chronic, bilateral, diffuse, non-inflammatory, non-neoplastic swelling of the major salivary glands that primarily affects the parotid glands, but occasionally involves the submandibular glands and rarely the minor salivary glands (Scully 2008). This can be painless or in some instances tender.
What is sialadenitis?
Sialadenitis is an infection of the salivary glands. It is usually caused by a virus or bacteria. ... Sialadenitis is most commonly due to bacterial infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus.
What causes sialadenitis in dogs?
Summary Summary. Sialadenitis is an infection of the salivary glands. It is usually caused by a virus or bacteria. The parotid (in front of the ear) and submandibular (under the chin) glands are most commonly affected.
What is sialosis of the salivary glands?
Sialosis or Sialadenosis of the Salivary Glands. Sialosis (sialadenosis) is a chronic, bilateral, diffuse, non-inflammatory, non-neoplastic swelling of the major salivary glands that primarily affects the parotid glands, but occasionally involves the submandibular glands and rarely the minor salivary glands (Scully 2008).
What is the name of the swelling of the salivary glands?
Is sialosis idiopathic or idiopathic?
Is pilocarpine good for sialadenosis?
Is salivary gland swelling a symptom of sialosis?
See 1 more
About this website

What is the most common cause of sialadenitis?
The most common causes of acute salivary gland infections are bacteria, especially Staphylococcus aureus, or staph. Viruses and fungi can also cause infection in the glands. (Mumps is an example of a viral infection of the parotid glands.)
How is Sialadenosis treated?
Acute sialadenitis: Most cases receive treatment with conservative medical management; this includes hydration, warm compresses, and massage, pain relief with analgesics (e.g., NSAIDs), sialogogues. Empiric antibiotic therapy starts with amoxicillin/clavulanate or clindamycin.
Is sialadenitis cancerous?
Chronic sclerosing sialadenitis is a rare disease that is often clinically diagnosed as a malignant lesion.
Does sialadenitis go away?
Sialadenitis refers to a swollen salivary gland. It's caused by infections, autoimmune diseases and salivary gland stones. When a salivary gland becomes inflamed, it can stop functioning. Sialadenitis usually goes away in about a week.
Is sialadenitis contagious?
Is Sialadenitis contagious? If sialadenitis is due to mumps or other infectious diseases then it can be transferred to others via coughing, sneezing or contact with infected saliva.
Do you need antibiotics for sialadenitis?
Initial treatment for sialadenitis is with antibiotics active against S. aureus (eg, dicloxacillin, 250 mg orally 4 times a day, a 1st-generation cephalosporin, or clindamycin), modified according to culture results.
What are the symptoms of sialadenitis?
Symptoms of sialadenitis include enlargement, tenderness, and redness of one or more salivary glands. These are the glands in the mouth, located near the ear (parotid), under the tongue (sublingual), and under the jaw bone (submaxillary), plus numerous small glands in the tongue, lips, cheeks and palate.
How do you prevent sialadenitis?
How to Prevent Sialadenitis? The risk of sialadenitis can be reduced by maintaining good oral hygiene. It is advisable to brush and floss teeth twice daily. Eating a well balanced diet and drinking one and half to two liters of water daily is also helpful.
How do you get an infected salivary gland?
Viral infections, such as mumps, often affect the salivary glands....Bacterial infections are most often the result of a:Blockage from salivary duct stones.Poor cleanliness in the mouth (oral hygiene)Low amounts of water in the body, most often while in the hospital.Smoking.Chronic illness.Autoimmune diseases.
How do you treat sialadenitis naturally?
massaging the affected gland. applying warm compresses to the affected gland. rinsing your mouth with warm salt water. sucking on sour lemons or sugar-free lemon candy to encourage saliva flow and reduce swelling.
How can I unclog my salivary glands?
Your healthcare provider may start with treatments such as:Increasing fluids.Putting moist heat on the area.Massaging the gland and duct.Sucking on candies to promote saliva secretion.Using pain medicines.Stopping use of any medicines that decrease saliva production, if medically possible.
What doctor treats sialadenitis?
An ENT (ear, nose, and throat) specialist, or otolaryngologist, may diagnose Sjogren's syndrome based on persistent symptoms of dry eyes and/or mouth, parotid gland enlargement, and abnormal blood test results. A lip biopsy can confirm the diagnosis. Sjogren's syndrome is treated conservatively with symptomatic relief.
How do you get rid of sialolithiasis?
Home remediesSucking on citrus fruits or hard candies. Sucking on a wedge of lemon or orange increases the flow of saliva, which can help dislodge the stone. ... Drinking plenty of fluids. Regular fluid intake helps keep the mouth hydrated and can increase saliva flow.Gentle massage. ... Medications. ... Sucking on ice cubes.
How long does it take to heal a salivary gland infection?
A salivary gland infection may last around a 1 week, though some minor swelling may linger for a few weeks.
How do you get rid of a salivary gland infection?
TreatmentAntibiotics if you have a fever or pus drainage, or if the infection is caused by bacteria. ... Surgery or aspiration to drain an abscess if you have one.A new technique, called sialendoscopy, uses a very small camera and instruments to diagnose and treat infections and other problems in the salivary glands.
Is salivary Mucocele an emergency?
This is a potentially very serious problem, and treatment must be instituted rapidly because these pets may die from acute respiratory distress. Difficulty swallowing may be another sign that a pharyngeal mucocele is present.
Submandibular Sialadenitis/Sialadenosis Treatment & Management - Medscape
Acute sialadenitis. Medical management - Hydration, antibiotics (oral versus parenteral), warm compresses and massage, sialogogues [] . Surgical management - Consideration of incision and drainage versus excision of the gland in cases refractory to antibiotics, incision and drainage with abscess formation, gland excision in cases of recurrent acute sialadenitis
Phenobarbital-responsive sialadenosis in dogs: case series
Phenobarbital-responsive sialadenosis (PRS) is a rare idiopathic disease in dogs. Vomiting, retching, and gulping with bilateral enlargement of the submandibular salivary glands are the more frequent clinical signs. A thorough diagnostic examination must be performed to rule out the most important s …
Submandibular Sialadenitis And Sialadenosis - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf
Submandibular glands are major paired salivary glands. It is located in the submandibular triangle covered by the investing layer of deep cervical fascia. Mylohyoid muscle separates the superficial and deep lobe of the glands. Submandibular glands drain into the mouth via Wharton’s duct, which courses between the sublingual gland and hyoglossus muscle; it opens through a small opening ...
Sialosis - British & Irish Society for Oral Medicine
3 Sialosis April 2016 www.bsom.org.uk the salivary glands. In rare cases of very severe salivary gland swelling, in which no underlying cause has been identified, surgery may be considered.
What are the risk factors for sialadenitis?
Major risk factors for sialadenitis include reduced salivary secretion and duct obstruction. Hyposecretion of saliva can occur in dehydrated people, postoperative patients, immunocompromised, and undernourished. Medications that decrease salivary flow like antihistaminics, diuretics,beta-blockers can predispose to sialadenitis. Decreased salivary production can occur in patients with a history of radiation to the head and neck region, long-standing xerostomia (e.g., Sjogren syndrome), and those with chronic illness. Salivary duct obstruction is usually due to sialolithiasis, ductal stricture, ductal foreign body, and external compression of the duct.
How to manage sialadenitis?
Chronic sialadenitis: Medical management is with hydration, oral hygiene, pain relief, sialogogues. In cases of infection, broad-spectrum antibiotics are added. In the case of sialolithiasis, salivary gland stone removal should take place, using interventional sialendoscopy or direct surgical removal. [10][11] EWSL under ultrasonic guidance is used for intraglandular duct stone removal.Recurrent sialadenitis (>3 episodes/year) or in chronic sclerosing sialadenitis: excision of the salivary gland is the recommendation.
What is the name of the inflammation of the salivary gland?
Sialadenitis is inflammation of the salivary gland. Sialadenitis of the submandibular gland is less common than that of the parotid gland. Acute sialadenitis is usually due to bacterial or viral infections and usually presents with rapid onset pain and swelling.
What causes submandibular gland swelling?
Sialadenosis is a benign,non-inflammatory swelling of salivary glands usually associated with metabolic conditions. This activity reviews the epidemiology, pathophysiology, histopathology, clinical features, treatment, and management of submandibular sialadenitis and sialadenosis. This activity also discusses complications, the prognosis of submandibular sialadenosis, and sialadenitis and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in evaluating and treating patients with this condition.
What is chronic sialadenitis?
Chronic sialadenitis is characterized by recurrent or persistent of the salivary gland. Chronic sialadenitis is usually due to obstruction, e.g., calculi, stricture, and usually presents with swelling without erythema.
How long does it take for sialadenitis to resolve?
Complete resolution is usually the expectation following conservative outpatient management. Most of the acute symptoms resolve in a week; however, edema takes a longer time to disappear. Chronic sialadenitis can have multiple relapses and remissions.
Is salivary gland swelling neoplastic?
Sialdenosis is nonneoplastic,non -inflammatory swelling of the salivary gland in association with acinar hypertrophy and ductal atrophy. Sialdenosis presents as non-tender swelling that is often bilateral and symmetric. Sialadenosis is often associated with systemic metabolic conditions.
What causes sialadenitis?
Sialadenitis is usually caused by a virus or bacteria. Poor oral hygiene can contribute to getting sialadenitis.
What is the most common form of sialadenitis?
Who gets sialadenitis? Sialadenitis is most common among elderly adults with salivary gland stones, calcified structures that can form inside a salivary gland and block the flow of saliva into the mouth. Sialadenitis can also occur in other age groups, including infants during the first few weeks of life.
What is the condition called when the salivary gland is inflamed?
Sialadenitis refers to the inflammation of a salivary gland, which produces saliva to aid in digestion. The condition is most common among elderly adults and mostly affects the parotid and submandibular glands.
How to diagnose Sialadenitis?
Sialadenitis is usually diagnosed though a physical examination and a history of your symptoms . Sometimes, the glands may need to be examined with a scope.
What is the disease that affects men and women of all races equally?
Sialadenitis affects men and women of all races equally.
Can sialadenitis be treated without treatment?
Without proper treatment, sialadenitis can develop into a severe infection, especially in elderly or sick people. It is important to see a doctor right away if you have any of the symptoms.
Is salivary gland a chronic condition?
It can be an acute (sudden), chronic (long term), or recurrent condition. It is a rare condition.
What is it?
Sialadenosis; is a non-specific term used to describe an uncommon, benign, non-inflammatory, non-neoplastic enlargement of a salivary gland, usually the Parotid Gland but occasionally affects the Submandibular Glands and rarely, the Minor Salivary Glands.
Causes
Several causes have been recorded, most of which are associated with (mal-) nutrition, metabolism or drugs and have a unifying feature in autonomic neuropathy.
Drugs
Among the wide range of drugs that may induce sialosis, anti-hypertensive agents are prominent.
Nutritional Disorders
Any disorder that affects the digestion of food or its absorption over a prolonged period, can result in sialosis, and malnutrition may contribute to sialosis in alcoholics.
What is the cause of sialadenitis?
Sialadenitis is most commonly due to bacterial infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Other bacteria which can cause the infections include include streptococci, coliforms, and various anaerobic bacteria. Although less common than bacteria, several viruses have also been implicated in sialadenitis. These include the mumps virus, HIV, ...
How to tell if you have sialadenitis?
Signs and symptoms of sialadenitis may include fever, chills, and unilateral pain and swelling in the affected area. The affected gland may be firm and tender, with redness of the overlying skin. Pus may drain through the gland into the mouth. [1] [2] [3]
What is the name of the infection of the salivary glands?
Sialadenitis is an infection of the salivary glands. It is usually caused by a virus or bacteria. The parotid (in front of the ear) and submandibular (under the chin) glands are most commonly affected. Sialadenitis may be associated with pain, tenderness, redness, and gradual, localized swelling of the affected area. Sialadenitis most commonly affects the elderly and chronically ill especially those with dry mouth or who are dehydrated, but can also affected people of any age including newborn babies. Diagnosis is usually made by clinical exam but a CT scan, MRI scan or ultrasound may be done if the doctor suspects an abscess or to look for stones. Treatment may include an antibiotic (if bacterial), warm compresses, increasing fluid intake and good oral hygiene. Most salivary gland infections go away on their own or are cured with treatment. Complications are not common. [1] [2] [3] [4]
How long does it take for sialadenitis to go away?
Acute symptoms usually resolve within 1 week; however, edema in the area may last several weeks. Complications are not common, but may occur and can include abscess of the salivary gland or localized spreading of bacterial infection (such as cellulitis or Ludwig's angina ). [1] [2] [3] [4]
What are the complications of sialadenitis?
Complications are not common, but may occur and can include abscess of the salivary gland or localized spreading of bacterial infection (such as cellulitis or Ludwig's angina ). [1] [2] [3] [4] In chronic or relapsing sialadenitis, the prognosis depends on the underlying cause of the infection. [1]
Is sialadenitis a bacterial infection?
If the infection is bacterial, an antibiotic effective against whichever bacteria is present will be the treatment of choice. If the infection is due to a virus, such as herpes, treatment is usually symptomatic but may include antiviral medications. [1] [2] [3] [4] In addition, since sialadenitis usually occurs after decreased flow of saliva ...
Can a kink in the salivary duct cause a kink in the salivary duct?
A stone or a kink in the salivary duct can also diminish saliva flow, as can certain medications (such as antihistamines, diuretics, psychiatric medications, beta-blockers, or barbiturates).
What is the infection of the salivary gland?
A salivary gland infection is also called sialadenitis and is caused by bacteria or viruses. A salivary stone or other blockage of the salivary gland duct can contribute to an acute infection. Chronic inflammation of a salivary gland can cause it to stop functioning.
Who is most at risk for salivary gland infection?
Although the condition can affect anyone, including infants, those most at risk for salivary gland infection are elderly and chronically ill people.
What are the symptoms of a salivary infection?
Salivary infection symptoms can include: Pain, tenderness and redness. Hard swelling of the salivary gland and the tissues around it. Fever and chills. Drainage of infectious fluid from the gland.
What is sialoadenitis?
Sialoadenitis is an inflammation or infection of one or more of your salivary glands. A small stone can block the salivary gland and cause inflammation. Infection may be caused by a virus or bacteria. You can develop sialoadenitis on one or both sides of your face.
What are the signs and symptoms of sialoadenitis?
Pain and swelling of a salivary gland, especially during or right after eating
How can I manage or prevent sialoadenitis?
Drink liquids as directed. You may need to drink more liquids than usual. Ask how much liquid to drink each day and which liquids are best for you. Good choices of liquids for most people include water, tea, soup, juice, or milk.
Why does saliva decrease?
Decreased saliva caused by dehydration, radiation, or other medicines
How to get rid of swollen glands?
Apply a warm, wet cloth and massage the swollen area as directed. This may help relieve swelling and pain by pushing the pus out of the gland.
What is the name of the swelling of the salivary glands?
Sialosis or Sialadenosis of the Salivary Glands. Sialosis (sialadenosis) is a chronic, bilateral, diffuse, non-inflammatory, non-neoplastic swelling of the major salivary glands that primarily affects the parotid glands, but occasionally involves the submandibular glands and rarely the minor salivary glands (Scully 2008).
Is sialosis idiopathic or idiopathic?
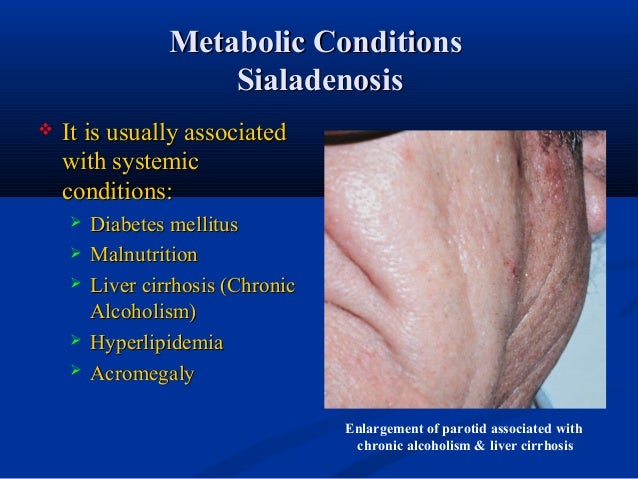
Sialosis may be idiopathic or may be associated with the following: chronic malnutrition. obesity. diabetes mellitus. alcoholism. liver disease. eating disorders. drugs (ie antihypertensives) (Duggan 1957 from Chen 2013)
Is pilocarpine good for sialadenosis?
Mahler (1993) and Park (2009) identified that "Pilocarpine has proved to be beneficial in the treatment of sialadenosis in bulimic patients" and "This article presents a case of painful sialoadenomegaly associated with hyperamylasemia in a bulimic patient successfully managed with pilocarpine".
Is salivary gland swelling a symptom of sialosis?
Sialosis (sialadenosis) is a chronic, bilateral, diffuse, non-inflammatory, non-neoplastic swelling of the major salivary glands that primarily affects the parotid glands, but occasionally involves the submandibular glands and rarely the minor salivary glands (Scully 2008). This can be painless or in some instances tender.