
Legacy pesticides: Chlordanes, DDTs, Dieldrin, and Toxaphene
- These pesticides were banned years ago but are still found in some fish in certain California water bodies.
- Learn more about legacy pesticides.
What do pond chemicals do for fish?
Your family of fish needs a clean and safe swimming area for them to survive and thrive. Pond chemicals are used in killing algae and eliminating other dangerous particles living or may live in the pond. What are the best and safest pond chemicals?
Are there any harmful chemicals in fish?
Chemicals in Fish. Certain chemicals can be of potential health concern because of their toxicity and their ability to accumulate in fish tissue. Harmful chemicals enter the environment through natural processes, industrial and agricultural use, mining, spills, and improper disposal. Fish can take in these chemicals from the food they eat or...
What is fish waste in the ocean?
in the Ocean. Fish waste may include, but is not limited to, particles of flesh, skin, bones, entrails, shells or liquid stick water. Fish wastes degrade rapidly in warm temperatures. If not appropriately stored or managed, fish wastes create aesthetic problems and strong odors as a result of bacterial decomposition.
How can I reduce my exposure to harmful chemicals while fishing?
You can reduce your exposure to harmful chemicals by following our advisories and tips for catching, preparing, and cooking fish. Mercury is a metal found in coal, rocks, and soil, and has been detected in fish all over the world. Learn more about mercury.

What is the waste produced by fish?
These operations generate discards which mainly include muscle-trimmings (15–20%), skin and fins (1–3%), bones (9–15%), heads (9–12%), viscera (12–18%), and scales (5%) [22].
How is fish waste converted to fertilizer?
Here's how it works: Fish are typically raised in indoor tanks, troughs or outdoor ponds, where they produce excrement. The water with the waste from the tank flows to a hydroponics tray where plants grow in the water without soil. The waste is toxic to the fish but is a rich fertilizer for the plants.
What can you do with fish waste?
Landfill Disposal: Commercial fish waste may be disposed in a permitted landfill willing to accept it. Land Application: Fish waste may be ground and tilled into agricultural or silvicultural land as fertilizer, provided the waste is processed and treated as prescribed in the solid waste regulations.
Which two important products of our use are made from fish wastes?
Fish waste can also be used for production of various value added products such as proteins, oil, amino acids, minerals, enzymes, bioactive peptides, collagen and gelatin.
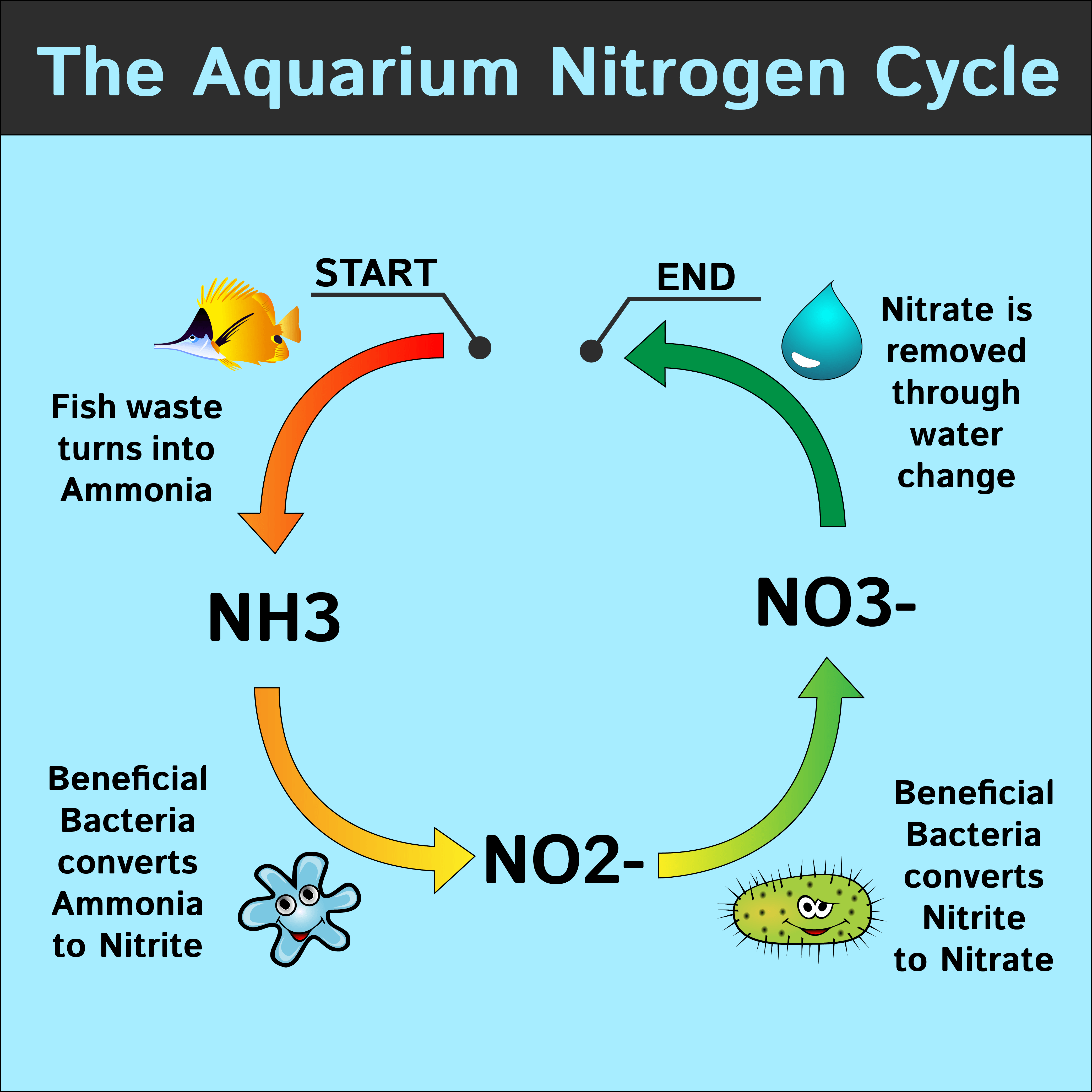
Is fish poop high in nitrogen?
Fish poop into the water they live in. That poopy water is high in nitrogen, which is an essential nutrient for plants. Plant roots take up nitrogen from the water, purifying it and leaving it clean enough for fish to live in.
Do plants break down fish waste?
Do aquatic plants eat fish poop? Aquatic plants do eat fish poop, but to a much lesser extent than soil. The main reason is that aquatic plants do not have a soil microbiome, which is beneficial to the digestion of fish poop. Additionally, aquatic plants do not have the digestive enzymes to break down fish poop.
Is fish waste harmful to the environment?
Food, including fish that have gone to waste, when left to rot or disposed of in a landfill, is a major source of greenhouse gases (GHG). In fact, this waste contributes to an estimated 8 percent of all man-made GHG emissions and comes mostly in the form of methane.
Is it OK to throw fish guts in the ocean?
Remember that depositing any sort of fish entrails into the water is illegal! All waste should be thrown into the trash, not the water.
Should you throw fish guts back in the water?
Clean fish offshore and toss fish waste in open, unrestricted water or at sea. Clean fish at home and compost the waste. Freeze and then reuse fish parts as bait. When no other option exists, bag the fish waste and dispose of it in the garbage.
What are the 3 kinds of waste in the fish industry?
The fish processing schemes in terms of raw material, source of utility and unit processes vary between plants. Most of the processing industries, fish processing operations produce waste such as solid waste and liquid waste. This waste contains organic contaminants in soluble, colloidal and particulate form.
Can fish waste be recycled?
Many fish processing plants have jumped into recycling technology, making good use of nearly all their “waste”. That's a lot of happy kitties (although the dogfish might not appreciate the loss in food)! Recycling fish products instead of creating a permitted outfall is better for ecosystems.
What value-added products can be made out of fish waste and by products from fish processing?
To minimize food loss and waste in the fish value chains and, at the same time, improve fish waste management strategies, several methods can be used to convert by-products into value added products: animal feed ingredients (fishmeal and fish oil), biofuel and biogas, dietetic products (chitosan), pharmaceuticals ( ...
Can fish poop be used as fertilizer?
This farming method uses fish poop to fertilize crops, feed urban communities, and protect the planet. At Oko Farms, produce is grown through a process called aquaponics, where freshwater fish are raised in one tank and their waste is transported to another that contains crops, fertilizing them.
How do you make fermented fish fertilizer?
Let's Get StartedChop up the fish, or fish parts, as small as you can to help the blender/ processor.Place bits into a blender. ... Add your 3-parts of water, and ⅓-part of brown sugar.Blend until smooth! ... Pour into your fermentation vessel (plastic jug, bottle – anything with a cap.)More items...•
How does fish fertilizer help plants?
As fish fertilizer improves soil health, it also increases soil fertility by providing the primary nutrients necessary for plants to thrive. Fish fertilizers offer a source of burn-free nitrogen, along with the other primary nutrients of phosphorus and potassium.
How do you compost fish guts?
Like composting other fish craps like fish skins, the guts need to be cleaned and then tossed together with enough carbon materials like sawdust, wood chips and leaves. They decompose quite easily and quickly, unlike the skins.
What are the compounds extracted from fish?
For this reason, this paragraph provides an overview of the extraordinary potential of fish byproducts, listing the possible applications found so far for the most interesting compounds extracted from fish byproducts (e.g., collagen, peptides, chitin, oil, enzymes ).
Why is fish waste important?
For this reason, a better fish-waste management is needed to overcome environmental issues and for the fully use of biomass for purposes of high-commercial value , at the same time. In this context, the growing recent attention to alternative uses of fish byproducts plays an important role in the economic growth and sustainable development. Several studies have been reported to analyze their possible uses, as they represent a rich source of value-added compounds, including enzymes, bioactive peptides, and bio-polymers, with many possible uses in several fields [10,11].
How to extract collagen from fish waste?
Different procedures have been proposed to extract collagen from fish waste. Acid extraction procedure is the most common method to extract collagen from fish waste, and the obtained product is referred to as acid-soluble collagen (ASC). Collagen extraction is obtained using acids, such as acetic acid or HCl, which solubilized the collagen chains, improving the extraction yield. Pepsin extraction procedure consists in the treatment of the collagen fibres with the pepsin to cleave the specific regions in order to promote solubilisation and increase collagen extraction yield; in this case, the extracted collagen is named pepsin-soluble collagen (PSC) [49].
What is the market for marine collagen?
The Marine Collagen Market has been estimated to reach USD 983.84 million by 2025, growing at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 7.4%. The growth of the marine collagen market is due to the use of collagen in the cosmetic, food and beverage industry [48], and fish waste represents a huge and cheap source of collagen for the industry [49].
How much of fish is processed?
More than 70% of the total fish caught is subjected to further processing before being placed on the market [19], resulting in the production of large amounts (approximately 20–80%) of fish waste, depending on the level of processing (e.g., gutting, scaling, filleting) and species, because each species has a specific composition, size, shape and intrinsic chemistry [20,21]. These operations generate discards which mainly include muscle-trimmings (15–20%), skin and fins (1–3%), bones (9–15%), heads (9–12%), viscera (12–18%), and scales (5%) [22]. Fish processing is an important need for large fish companies both to reduce the costs related to transport of inedible parts of the fish and to increase stability and quality of products, removing parts, such as the viscera, that might contain bacteria and enzymes, which represent a risk for processing and storage of the fish [23]. Preserving the nutritional quality of products represents one of the main challenges for the industry. The degradation of proteins by enzymes is a key aspect that should be minimized, as a high degree of hydrolysis could produce bitter-tasting peptides [23,24], and together with the lipid peroxidation, lead variability in raw materials [24,25]. Acceptable levels of lipid and protein hydrolysis are enormously dependent on the product, based on its end use [26,27]. Hydrolysis determines structural and conformational changes, with possible negative effects on the physicochemical and functional properties of proteins [23]. For this reason, the control of the autolysis and auto-oxidation of these products is fundamental for their use [20]. This represents a real challenge for fishing vessels, which require more advanced equipment and technologies for capture and better handling, necessary to maintain the quality of the byproducts [28,29]. Moreover, to ensure food safety and consumer protection, increasingly stringent hygiene measures have been implemented at the National and International level.
What are fish byproducts?
Fish byproducts are a nutritionally important source of proteins, fatty acids, and minerals, as their composition is similar to that of fish fillet and other food products used for consumption. Studies conducted on meagre and gilthead sea bream fish species have shown that skin is the most significant protein source, trimmings and bones are rich in calcium, and the head, intestines, and bones are a good source of lipids [34]. Specifically, the mean value of all fish byproducts, calculated on a dry weight basis, is 49.22–57.92% for protein content, 21.79–30.16% for ash content, and 7.16–19.10% for fat content [35,36,37]. The latter value is slightly higher than those found by [34].
How has fish consumption increased?
In the last years, fish products consumption has seen a huge increase following its recognition as a key component of a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle. Based on the Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO), United States, the total fisheries and aquaculture production has shown a considerable increase of more than eightfold between 1954 and 2014, driven by advances in fishing technologies and rapid developments in aquaculture; in 2014, the global fishery production was 93.4 million tons [2]. In the period 1961–2016, the growth in the global fish supply had a notable increase, with an average annual growth rate of 3.2%, higher than the growth rate of world’s population (1.6%), even surpassing that of meat from land animals (2.8%). World fish consumption per capita increased from 9.0 kg in 1961 to 20.2 kg in 2015, and preliminary estimates indicate further growth for 2016 and 2017 to approximately 20.3 kg and 20.5 kg, respectively [3]. Consequently, also the amount of fish waste has undergone a dramatic increase across the world. Currently, the post-catch fish losses represent a huge economic and environmental concern occurring in most fish distribution chains, with large amounts of landed fish lost or discarded between landing and consumption [2]. It is important to underline that today the expansion of consumption is driven not only by the increase in production, but also by different factors, including the reduction of wastage. In fact, although the continuous increase in fish consumption in 2016 a small decrease in global capture fisheries production (90.9 million tons) was observed, compared to the previous two years [3]. In order to promote environmentally, economically, and socially sustainable EU fishing practices, the main recent objectives pursued by the EU Common Fisheries Policy (CFP) are the drastic reduction/prohibition of discards and the use of the captured biomass as best as possible [4].
Background
Monitoring fish for chemical contamination in lakes and reservoirs is a critical activity for protecting human health because these areas are important for sport fishing and other recreational activities. The 2008 Biennial National Listing of Fish Advisories reports that 43% of the nation’s lake acres are under fish consumption advisories.
What are the Basic Elements of the Study Design?
EPA worked with partner agencies over a four-year period (2000-2003) to collect fish from 500 lakes and reservoirs selected randomly from the estimated 147,000 target lakes and reservoirs in the lower 48 states.
Who Participated in the Study?
EPA formed a national network of study partners to pursue a broad range of activities, from development of the study design to collection of fish for the study. Important contributors include:
Why do fish wastes stink?
If not appropriately stored or managed, fish wastes create aesthetic problems and strong odors as a result of bacterial decomposition. The organic components of the waste have a high biological oxygen demand and, if not managed properly, high oxygen demand poses environmental and health problems. Some fish wastes are transported for disposal at sea.
What are the environmental concerns associated with the disposal of fish wastes into ocean waters?
Environmental concerns associated with disposal of fish wastes into ocean waters include: reduced oxygen levels in the seawaters at the ocean bottom; burial or smothering of living organisms; and. introduction of disease or non-native and invasive species to the ecosystem of the sea floor.
Do you need a permit to dispose of fish waste?
Ocean Disposal of Fish Wastes. Under the Marine Protection, Research and Sanctuaries Act (MPRSA), a permit is not required for the ocean disposal of fish wastes unless such disposal occurs in: any other location where EPA finds that such disposal may reasonably be anticipated to endanger health, the environment or ecological systems.
How long does it take for a fish to decompose?
Feed the fish the right amount of food they can devour. Feeding them more than what they can eat in 60 seconds to 3 minutes is left to decompose in the pond. Always purchase fish foods that don’t sink to the bottom of the pond. Natural food, supplementary food, and complete foods are the three types of food for the fish.
What is the best chemical to use to clean a pond?
API Pond ECOFIX Sludge Destroyer pond chemical is excellent in keeping the pond water clean while decreasing the overall maintenance of your fish pond.
How to improve oxygen distribution in pond?
To improve oxygen distribution and movement to the fish and the plants in the pond, you can install pond aerators – this also adds an aesthetic view to your pond.
How long does blue lake pond dye last?
Safety is well guaranteed to humans, fish, plants, and other pets. Keep your pond clean for approximately 30 days. This pond chemical can work effectively as other expensive products sold in the market.
Why do fish need a pond?
Your family of fish needs a clean and safe swimming area for them to survive and thrive. Pond chemicals are used in killing algae and eliminating other dangerous particles living or may live in the pond.
What are some good plants to clean a pond?
But do not place too many plants. It may result in oxygen deficiency during the nighttime. Some of the most effective and beneficiary cleaning plants for a pond are water lilies, watercress, water theme hornwort, and taro.
What is the ratio of fish population to water?
Otherwise, this can cause genetic drift when population size is too small for the pond or imbalance water pond when overpopulation occurs. A suggested ratio for the fish population is 1:10, meaning one fish for every ten gallons of water.
What is the waste from a hydroponics tank?
This waste is a rich fertilizer for plants despite being toxic to fish. As nutrients are absorbed by the plants, the water is purified by the water for the fish.
Why is Glenn's fish system monitored?
Glenn says the system needs to be monitored to ensure everything is running smoothly and stays in balance. You must pay close attention to if your fish are eating or not, whether or not the water is circulating correctly and how your plants are growing.
What type of fish should I use for aquaponics?
What Type of Fish to Use for your Aquaponic System. The fish that is the most commonly raised in aquaponics systems is tilapia but you can still use koi fish waste if you have a koi pond or water garden. Glenn also recommends crayfish, Murray cod, barramundi, goldfish, sunfish, koi, common carp, trout, and catfish.
Where did aquaponics originate?
Aquaponics, which started in ancient Mexico and China, is becoming increasingly popular all over the world as a local food production method, Glenn reports. He fields questions regularly from people who are interested in starting a small-scale aquaponics operation in their backyard koi ponds, and sometimes commercial-scale aquaponics farms as well ...
What is the crop produced by aquaponics?
In addition to plants and fish, one other crop is naturally produced by an aquaponics system – “good” bacteria where the toxic components contained in fish waste are converted into nutrients that are consumed by the plants .
What fish does Glenn recommend?
Glenn also recommends crayfish, Murray cod, barramundi, goldfish, sunfish, koi, common carp, trout, and catfish. He advises choosing freshwater species. Each species can be fed a standard diet made just for them that can be found at pet stores or feed suppliers.
How big is a fish tank?
Containers can range greatly in size from 20-40 gallon plastic totes up to big plastic aquariums that are 6-10 feet wide and 4-5 feet deep.
Background
Why Is This Study Important?
- The National Lake Fish Tissue Study is important because it: 1. Generated data to develop the first statistically-based national estimates of the median concentrations of persistent, bioaccumulative and toxic chemicals in lake fish. 2. Provided a national baseline for tracking reductions of persistent, bioaccumulative, and toxic chemicals in freshwater fish as a result of p…
What Are The Basic Elements of The Study Design?
- EPA worked with partner agencies over a four-year period (2000-2003) to collect fish from 500 lakes and reservoirs selected randomly from the estimated 147,000 target lakes and reservoirs in the lower 48 states. The lakes were divided into 6 size categories, ranging in size from 2.5 to over 900,000 surface acres, with a similar number of lakes in each category. Before sampling, field te…
What Chemicals Did EPA Select For The Study?
- The study involved analyzing the fish tissue for: 1. 2 metals (mercury and 5 forms of arsenic) 2. 17 dioxins and furans 3. 159 PCB congener measurements (representing results for 209 congeners) 4. 46 pesticides 5. 40 other semivolatile organics (e.g., phenols)
Who Participated in The Study?
- EPA formed a national network of study partners to pursue a broad range of activities, from development of the study design to collection of fish for the study. Important contributors include: 1. EPA Office of Water (Agency lead for the study) 2. EPA Office of Research and Development 3. EPA Office of Prevention, Pesticides, and Toxic Substances 4. EPA Regional Offices 5. State an…
What Information Is available?