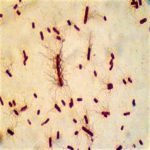
CULTURE CHARACTERISTICS OF PROTEUS VULGARIS (PR. VULGARIS)
| Cultural Characteristics | Nutrient Agar Medium (NAM) | MacConkey Agar medium | Blood Agar Medium | EMB Agar medium |
| Surface | Glistening | Smooth | Glistening | Glistening |
| Color | Greyish white | Colorless or Pale colored | Greyish white | Colorless |
| Structure | Translucent | Transparent | Translucent –Opaque | Transparent |
| Hemolysis | ----- | ----- | γ-Hemolysis (Non-hemolytic) | ----- |
| Susceptibility Testing Text: | Potassium cyanide : - |
|---|---|
| Aerobic Growth Tests Text: | Urea hydrolysis : + |
| Temperature For Growth Text: | at 37°C : Yes |
| Colony Appearance Text: | smooth : Yes,shiny : Yes |
| Colony Color Text: | cream : Yes |
What is the shape of Proteus vulgaris?
Proteus vulgaris is a rod-shaped, nitrate-reducing, indole + and catalase -positive, hydrogen sulfide -producing, Gram-negative bacterium that inhabits the intestinal tracts of humans and animals. It can be found in soil, water, and fecal matter.
What are the diagnostic tests for Proteus vulgaris?
Proteus vulgaris. P. vulgaris also tests positive for the methyl red (mixed acid fermentation) test and is also an extremely motile organism. When P. vulgaris is tested using the API 20E identification system it produces positive results for sulfur reduction, urease production, tryptophan deaminase production, indole production,...
Is Proteus vulgaris motile or nonmotile?
Motility – Proteus Vulgaris is an actively motile bacterium and well known for the swarming growth on an ordinary medium like NAM. Flagella – Pr. Vulgaris is a flagellated bacterium with a Peritrichous flagella arrangement i.e. flagella are present all over the surface of the bacterium.
What is the morphology of P vulgaris?
P. vulgaris is a rod-shaped, Gram negative bacterium between 1-3 microns in size, and is extremely motile, utilizing peritrichous flagella as its source of motility (2).

What does Proteus vulgaris look like?
Proteus vulgaris is a rod-shaped, nitrate-reducing, indole-positive and catalase-positive, hydrogen sulfide-producing, Gram-negative bacterium that inhabits the intestinal tracts of humans and animals. It can be found in soil, water, and fecal matter.
What color is Proteus vulgaris on EMB?
CULTURE CHARACTERISTICS OF PROTEUS VULGARIS (PR. VULGARIS)Cultural CharacteristicsNutrient Agar Medium (NAM)EMB Agar mediumElevationEffuseEffuseSurfaceGlisteningGlisteningColorGreyish whiteColorlessStructureTranslucentTransparent3 more rows•May 21, 2018
How is Proteus vulgaris identified?
vulgaris is tested using the API 20E identification system it produces positive results for sulfur reduction, urease production, tryptophan deaminase production, indole production, sometimes positive gelatinase activity, and saccharose fermentation, and negative results for the remainder of the tests on the testing ...
What are the characteristics of Proteus vulgaris?
P. vulgaris is a rod-shaped, chemoorganotrophic, Gram-negative bacteria between 1 and 3 microns in size (2). It is motile by peritrichous flagella, and does not have capsules or spores (2). A key characteristic of genus Proteus is swarming ability, and a simple Dienes test is used to differentiate between strains (17).
How do you differentiate Proteus mirabilis and Proteus vulgaris?
Proteus mirabilis (indole negative) is the most frequent Proteus species associated with urinary tract infections, but indole-positive Proteus species like Pr. vulgaris, which are more often resistant to ampicillin, may also cause urinary tract infections. These species are often associated with an alkaline urine.
What is the arrangement of Proteus vulgaris?
Proteus Vulgaris is a rod shaped Gram-Negative chemoheterotrophic bacterium. The size of the individual cells varies from 0.4 to 0.6 micrometers by 1.2 to 2.5 micrometers. P. vulgaris possesses peritrichous flagella, making it actively motile.
Where is Proteus vulgaris commonly found?
human intestinal tractProteus species are most commonly found in the human intestinal tract as part of normal human intestinal flora, along with Escherichia coli and Klebsiella species, of which E coli is the predominant resident. Proteus is also found in multiple environmental habitats, including long-term care facilities and hospitals.
Does Proteus grow on EMB?
EMB agar was originally devised by Holt-Harris and Teague and further modified by Levine....Result Interpretation on EMB Agar.OrganismsGrowthProteus mirabilisLuxuriant growth; colorless coloniesSalmonella TyphimuriumLuxuriant growth; colorless colonies4 more rows•Jan 4, 2022
Is Proteus vulgaris indole positive?
The indole-positive members of the Proteeae, including Proteus vulgaris, Providencia spp., and M. morganii, typically are resistant to ampicillin and cefazolin, as is the indole-negative species Proteus penneri.
How does Proteus vulgaris look on MSA?
Proteus grow on the Blood agar plate in successive waves to form a thin filmy layer of concentric circles ( swarming). Proteus do not swarm in the MacConkey agar medium and form smooth, pale or colourless (NLF) colonies. increasing the concentration of agar in the medium, raising it to 6% instead of 1-2%.
What shape is P. vulgaris?
rod-shapedA species of gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria that occurs in soil, fecal matter, and sewage.
What is the shape of Proteus vulgaris?
Shape – Proteus Vulgaris is a short, straight rod shape (bacillus) bacterium. Size – The size of Proteus Vulgaris is about 1–3 µm × 0.5 µm (micrometer). Arrangement Of Cells – Pr. vulgaris is arranged singly, in pairs, or in short chains and sometimes in clusters. Motility – Proteus Vulgaris is an actively motile bacterium and well known for ...
What media is used to grow Proteus vulgaris?
Commonly the NAM & MacConkey Agar medium is used for the cultivation of Proteus Vulgaris in Laboratory.
Is Proteus Vulgaris a bacterial?
MORPHOLOGY OF PROTEUS VULGARIS (MICROSCOPIC VIEW) Motility – Proteus Vulgaris is an actively motile bacterium and well known for the swarming growth on an ordinary medium like NAM. Flagella – Pr. Vulgaris is a flagellated bacterium with a Peritrichous flagella arrangement i.e. flagella are present all over the surface of the bacterium.
Does Proteus Vulgaris grow on blood agar?
In Blood Agar medium, the Proteus Vulgaris exhibits the swarming and the growth occurs in the whole media plate. Usually, it produces non-hemolytic growth on Blood agar plate but some of the strains are β-Hemolytic. PROTEUS VULGARIS CULTURE ON BLOOD AGAR MEDIUM.
Characteristics and morphology
Like all gram-negative bacteria, bacteria of the genus Proteus they are characterized by the presence of a covering composed of two lipid membranes, between which is a thin peptidoglycan network.
How is it spread?
They are opportunistic pathogenic bacteria, especially associated with upper urinary tract infections such as urolithiasis, which is the formation of stones in the kidney or bladder, urethritis, prostatitis, cystitis and acute pyelonephritis.
Symptoms
When the body comes into contact with pathogenic bacteria, specifically when the bacteria adhere to uroepithelial cells, numerous response events are initiated in the endothelial mucous cells, including the secretion of interleukins and activation of programmed cell death, among others. .
Treatments
Depending on the degree of complication of the infections, the treatments may vary. For women with uncomplicated infections, empirical treatments suggest the use of oral quinolone or sulfamethoxazole for no more than a couple of days.
Where can Proteus mirabilis be found?
Proteus mirabilis and Proteus vulgaris are commensals of the normal flora of the human gastrointestinal tract, but they also can be found in water and soil. There are opportunistic pathogens that can infect the lungs, or wounds, and frequently cause urinary tract infections.
Does Ps aeruginosa have imipenem?
Imipenem resistance in Ps. aeruginosa can occur following selection of mutants that hyperproduce the group 1 cephalosporinase and which are also deficient in an outer membrane protein (OprD or D2) which specifically transports imipenem, but not cephalosporins or monobactams. View chapter Purchase book.
Is Citrobacter resistant to imipenem?
Some strains of Citrobacter, Enterobacter, Proteus vulgaris, Providencia, Ps. aeruginosa and Serratia spp. may be resistant to imipenem and other β-lactam agents, often because of the selection of stably derepressed mutants expressing high levels of group 1 β-lactamases coupled with decreased intracellular drug levels due to porin mutations or increased efflux.
What is the genus of Proteus vulgaris?
2. Description and significance. Proteus vulgaris is one of five bacterial species within the genus Proteus, and one of three species within the genus that are opportunistic pathogens (1). P. vulgaris is a rod-shaped, Gram negative bacterium between 1-3 microns in size, and is extremely motile, utilizing peritrichous flagella as its source ...
How many genes are in the Proteus vulgaris genome?
The genome of P. vulgaris has 3.97 million base pairs and 3,660 genes. It is circular in structure, and contains 3,513 proteins, 14 rRNa proteins, 77 tRNA proteins, and 53 pseudogenes (15). Bacteria from the genus Proteus can be differentiated on the basis of O-antigen variability, the serospecificity of the lipopolysaccharide can decipher between strains of Proteus rods divided into the groups: P. mirabilis, P. vulgaris, P. penneri, P. hauseri, and P. myxofaciens (16). The chemical structure of the sugar part of the lipopolysaccharide may play a role in enhancing pathogenicity (16).
What are the applications of P. vulgaris?
P. vulgaris may also have positive applications, such as biofuel production (12) , aromatic contribution to cheese ripening (13), and plant growth promotion (14), but further research is needed to prove the effectiveness and validity of these applications. 3. Genome structure.
What is P. vulgaris?
P. vulgaris is also known to cause numerous types of nosocomial infections, including those of the urinary tract, burns, and other exposed wounds, and can be associated with various types of brain abscesses (9, 10, 11).
Is P. vulgaris resistant to antibiotics?
In the last decade, P. vulgaris has become less sensitive and more resistant to antibiotics, such as levofloxacin, meropenem, and ciprofloxacin, increasing the risk of a sepsis postoperative infection in Gujarat, India (13). P. vulgaris has also been identified as the main microbial pollutant in drinking water of Rajasthan, India (23).
Is P. vulgaris a fecal disease?
P. vulgaris present in water or soil conditions usually indicates fecal pollution, which poses a dangerous health risk when consumed in the form of food or water, such as the occurrence of P. vulgaris in raw shellfish (21). For example, several antibiotic-resistant strains of P. vulgaris were identified in the intestines of shrimp in Turkey.
Is P. vulgaris anaerobic or anaerobic?
P. vulgaris is facultatively anaerobic and has both a respiratory and fermentative type metabolism (3). It is capable of phenylalanine deaminase and urease production, and glucose, maltose, and sucrose fermentation (18, 19).
Where is Proteus found?
Proteus is also found in multiple environmental habitats, including long-term care facilities and hospitals. In hospital settings, it is not unusual for gram-negative bacilli to colonize both the skin and oral mucosa of both patients and hospital personnel. Infection primarily occurs from these reservoirs.
What is the bacterium #122?
Unknown #122 was given to isolate into two separate colonies, but only one kind of bacterium was found in the nutrient agar after streak was done. Gram stain showed this bacterium to be a gram-positive bacteria, it showed the blue colored rods.
What is the oxidase test?
The oxidase test was used to show if the organism produced cytochrome oxidase, with the addition of the oxidase reagent. The result, which presented the color blue after 15 minutes. After the data was collected, this test showed that this could only be Bacillius cereus, as it came out to be a positive reaction.
Is Alt 5 a negative bacterium?
Alt 5 was given as a substitute for a gram-negative bacterium, due to no growth in original test tube (#122). The gram stain showed red colored rods. The oxidase test was performed on unknown #122 gram positive, showed to be positive.
Is Proteus vulgaris gram negative?
For this test, I was able to finalize the result of my unknown to be Proteus vulgaris. Proteus species are part of the Enterobacteriaceae family of gram-negative bacilli. Proteus organisms are implicated as serious causes of infections in humans, along with Escherichia, Klebsiella, Enterobacter, and Serratia species.
Cultural Characteristics of Citrobacter freundii
Smooth, convex, translucent, or opaque grey colored with a shiny surface and entire margin; mucoid or rough colonies occasionally.
Cultural Characteristics of E. coli
Greyish to white-colored large, circular and convex colonies; smooth and rough colonies.
Cultural Characteristics of Klebsiella oxytoca
Circular, dome-shaped, mucoid, translucent or opaque, yellow to cream-colored colonies; 2-3 mm diameter.
Cultural Characteristics of Klebsiella pneumoniae
Circular, dome-shaped, mucoid, translucent, or opaque greyish white colonies; 2-3 mm diameter.
Cultural Characteristics of Proteus mirabilis
Pale white colonies as swarming growth with successive waves to form a thin filmy layer of concentric circles.
Cultural Characteristics of Proteus vulgaris
3-4 mm. in diameter, colorless, lenticular with either an entire or a finely, radially striated edge and a ‘beaten copper ’ surface.
Cultural Characteristics of Serratia marcescens
Red, smooth, convex, entire, and round colonies; red color due to production of pigment.

Morphology of Proteus Vulgaris
Culture Requirements of Proteus Vulgaris
- ⇒ Special requirements – Proteus Vulgaris have no complex nutritional requirements and readily grow in an ordinary media like Nutrient Agar medium (NAM). Commonly the NAM & MacConkey Agar medium is used for the cultivation of Proteus Vulgaris in Laboratory. ⇒Optimum temperature – Proteus Vulgarisranges from 10–43°C but the optimum temperature for most of t…
Culture Characteristics of Proteus Vulgaris
- Check out the Morphology & Culture Characteristics of Klebsiella pneumoniae In Liquid culture media like Trypticase soy broth or Nutrient broth & Peptone Water, the growth of the bacterium occurs as a uniform turbidity in the broth medium with a powdery deposit and Ammoniacal smell which is further analyzed for the morphology (under the microscope), gram reaction, biochemica…
Content
Characteristics and Morphology
- Like all gram-negative bacteria, bacteria of the genus Proteusthey are characterized by the presence of a covering composed of two lipid membranes, between which is a thin peptidoglycan network. The outer membrane of these bacteria contains a lipid bilayer rich in characteristic lipoproteins, polysaccharides, and lipopolysaccharides. In addition, they are covered by fimbriae …
How Is It Spread?
- They are opportunistic pathogenic bacteria, especially associated with upper urinary tract infections such as urolithiasis, which is the formation of stones in the kidney or bladder, urethritis, prostatitis, cystitis and acute pyelonephritis. Brain abscesses have also been described as forms of bacterial infection caused by P. vulgarisin humans. P....
Symptoms
- When the body comes into contact with pathogenic bacteria, specifically when the bacteria adhere to uroepithelial cells, numerous response events are initiated in the endothelial mucous cells, including the secretion of interleukins and activation of programmed cell death, among others. . Endotoxins present in the cell membrane also trigger cascades of inflammatory respon…
Treatments
- Depending on the degree of complication of the infections, the treatments may vary. For women with uncomplicated infections, empirical treatments suggest the use of oral quinolone or sulfamethoxazole for no more than a couple of days. When it comes to symptoms of cases of acute infection, quinolones are also used, but for longer periods, or some third-generation antibi…
References
- Alberts, B., Johnson, A., Lewis, J., Morgan, D., Raff, M., Roberts, K., & Walter, P. (2015). Molecular Biology of the Cell(6th ed.). New York: Garland Science.
- González, G. (2018). Proteus Infections Clinical Presentation. Retrieved from www.emedicine.medscape.com/article/226434-clinical
- Hickman, F. W., Steigerwalt, A. G., Farmer, J. J., Brenner, D. O. N. J., Control, D., & Carolina, N. …
- Alberts, B., Johnson, A., Lewis, J., Morgan, D., Raff, M., Roberts, K., & Walter, P. (2015). Molecular Biology of the Cell(6th ed.). New York: Garland Science.
- González, G. (2018). Proteus Infections Clinical Presentation. Retrieved from www.emedicine.medscape.com/article/226434-clinical
- Hickman, F. W., Steigerwalt, A. G., Farmer, J. J., Brenner, D. O. N. J., Control, D., & Carolina, N. (1982). Identification of Proteus penneri sp. nov., Formerly Known As Proteus vulgaris Indole Ne...
- Koronakis, V., Cross, M., Senior, B., Koronakis, E. V. A., & Hughes, C. (1987). The Secreted Hemolysins of Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris, and Morganella morganii Are Genetically Related to Ea...