What is the Suez Canal?
The Suez Canal ( Arabic: قَنَاةُ ٱلسُّوَيْسِ , Qanātu as-Suways) is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia. The canal is part of the Silk Road that connects Europe with Asia.
Why did Egypt close the Suez Canal?
Because of tensions with Israel, Egypt closed the canal during the Suez Crisis of 1956–57 and the Arab-Israeli War of 1967. The Isthmus of Suez, the sole land bridge between the continents of Africa and Asia, is of relatively recent geologic origin.
What is the most important canal in the world?
Suez CanalShips in the Suez Canal in Egypt. One of the world's most important shipping lanes, the Suez Canal connects the Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea.© Oleksandr Kalinichenko/Shutterstock.com. The Suez Canal.Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.
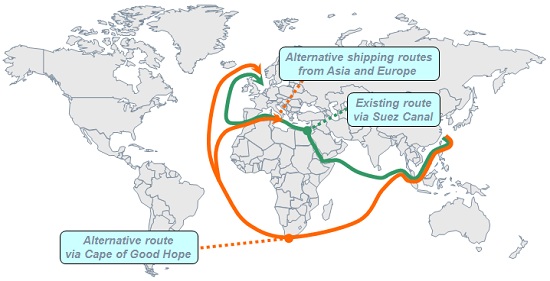
What were the alternatives to the Suez Canal?
Before the canal's opening in 1869, goods were sometimes offloaded from ships and carried overland between the Mediterranean and the Red Sea. The main alternative is around Cape Agulhas, the southernmost point of Africa, commonly referred to as the Cape of Good Hope route.
What country is the ship stuck in the Suez Canal from?
Registered in Panama, she is owned by Shoei Kisen Kaisha, a Japanese firm. Leased to the Taiwan-based container shipping company Evergreen Marine for operation, she was managed by Bernhard Schulte Shipmanagement at the time of the incident.
Who controls Suez Canal now?
Suez Canal Authority (SCA) is an Egyptian state-owned authority which owns, operates and maintains the Suez Canal. It was set up by the Egyptian government to replace the Suez Canal Company in the 1950s which resulted in the Suez Crisis.
What is the purpose of Suez Canal?
The Suez canal is a significant route for energy, commodities, consumer goods and componentry from Asia and the Middle East to Europe. The canal's location also makes it a key regional hub for shipping oil and other hydrocarbons.
How much does it cost for a ship to go through the Suez Canal?
Suez Canal Transit and Pilotage Fees: The fee is approx. US$7 per ton. Total fee may vary from US$300-700. From 1 May, 2022, there is no Suez Canal measurement for yachts up to 300 tons, on the basis that the yacht's tonnage is recorded in the yacht's registration certificate.
Who controls the Panama Canal?
The treaty led to full Panamanian control effective at noon on December 31, 1999, and the Panama Canal Authority (ACP) assumed command of the waterway. The Panama Canal remains one of the chief revenue sources for Panama.
How many miles does the Suez Canal save?
Intro. In 1869, the Suez Canal was opened, greatly reducing the distance between Britain and India by some 4,500 miles as ships no longer needed to travel round southern Africa.
How long does it take a ship to go through the Suez Canal?
12 to 16 hoursHow long does it take to a vessel to transit the canal ? It takes 12 to 16 hours. How many days per year the canal is available for navigation ? The canal is available for navigation all over the year.
Is Panama and Suez Canal same?
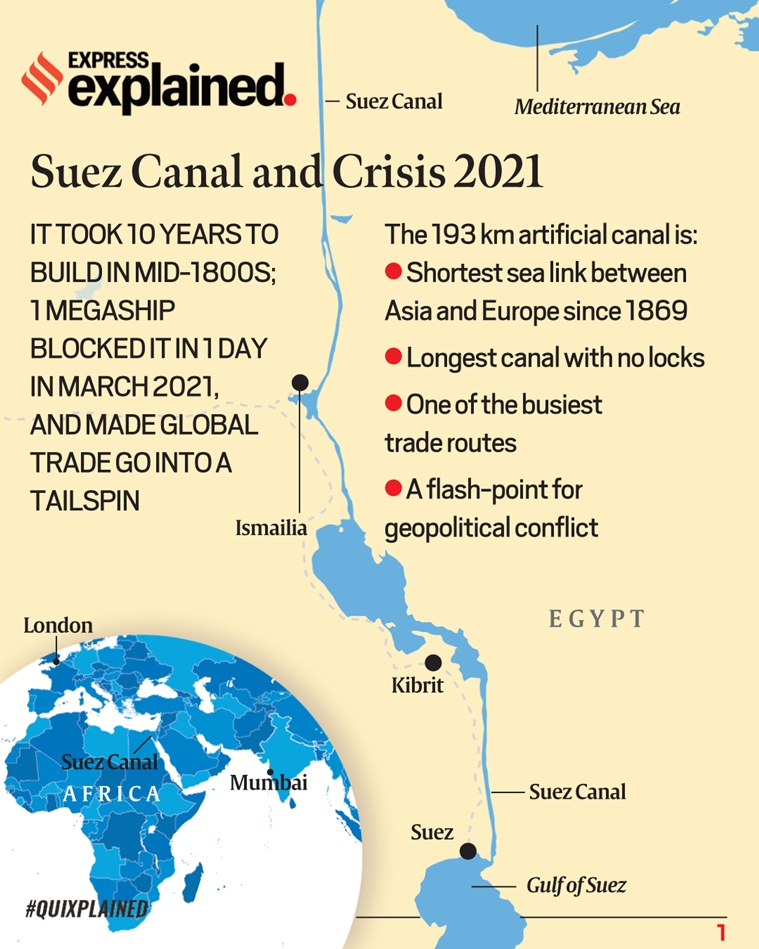
The Suez Canal has an extension of 193 kilometers, and connects the Mediterranean Sea with the Red Sea. The Panama Canal is 80 kilometers long, and connects the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans.
Is Panama and Suez Canal same?
The Suez Canal has an extension of 193 kilometers, and connects the Mediterranean Sea with the Red Sea. The Panama Canal is 80 kilometers long, and connects the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans.
Why did the US intervene in the Suez Crisis?
The Suez Crisis was the result of the American and British decision not to finance Egypt's construction of the Aswan High Dam, in response to Egypt's growing ties with communist Czechoslovakia and the Soviet Union.
When did Britain lose the Suez Canal?
Historians conclude the crisis "signified the end of Great Britain's role as one of the world's major powers". The Suez Canal was closed from October 1956 until March 1957.
Is the Suez Canal one way?
Egypt's President Abdel Fattah el-Sisi has formally opened the new Suez Canal expansion, allowing two-way traffic for the first time via a 75 km parallel channel that will reduce transit times by up to seven hours.
What is the Suez Canal?
The Suez Canal is a human-made waterway that cuts north-south across the Isthmus of Suez in Egypt. The Suez Canal connects the Mediterranean Sea to...
Why is the Suez Canal important?
The Suez Canal is important because it is the shortest maritime route from Europe to Asia. Prior to its construction, ships headed toward Asia had...
How has the Suez Canal changed throughout history?
Various forms of what is today the Suez Canal existed in Egypt between 1850 BCE and 775 CE, although primarily to facilitate trade between the Nile...
How was the Suez Canal’s construction paid for?
The Suez Canal was financed by the Suez Canal Company, a joint-stock company headquartered in Paris. At the time of its founding, France had 52 per...
What is the international status of the Suez Canal?
The Suez Canal’s international status has a murky history. Per the 1888 Convention of Constantinople, the canal is open to ships of all nations in...
How many ships use the Suez Canal?
In 2018 there were 18,174 transits of the Suez Canal, according to the Suez Canal Authority. That number rose to 18,880 in 2019, or about 51.5 per...
What is the Suez Canal?
The Suez Canal is a human-made waterway that cuts north-south across the Isthmus of Suez in Egypt. The Suez Canal connects the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea, making it the shortest maritime route to Asia from Europe. Since its completion in 1869, it has become one of the world’s most heavily used shipping lanes.
When was the Suez Canal completed?
Prior to construction of the canal (completed in 1869), the only important settlement was Suez, which in 1859 had 3,000 to 4,000 inhabitants. The rest of the towns along its banks have grown up since, with the possible exception of Al-Qanṭarah. Ships in the Suez Canal in Egypt.
What is the name of the waterway that runs north-south across the Isthmus of Suez?
Editor of Oxford Regional Economic Atlas: The Middle East and North Africa. See Article History. Alternative Title: Qanāt al-Suways. Suez Canal, Arabic Qanāt al-Suways, sea-level waterway running north-south across the Isthmus of Suez in Egypt to connect the Mediterranean and the Red seas. The canal separates the African continent from Asia, ...
How many lakes does the canal run through?
The canal does not take the shortest route across the isthmus, which is only 121 km (75 miles). Instead, it utilizes several lakes: from north to south, Lake Manzala (Buḥayrat al-Manzilah), Lake Timsah (Buḥayrat al-Timsāḥ), and the Bitter Lakes—Great Bitter Lake (Al-Buḥayrah al-Murrah al-Kubrā) and Little Bitter Lake ...
What is the only land bridge between Africa and Asia?
The Isthmus of Suez, the sole land bridge between the continents of Africa and Asia, is of relatively recent geologic origin. Both continents once formed a single large continental mass, but during the Paleogene and Neogene periods (about 66 to 2.6 million years ago) the great fault structures of the Red Sea and Gulf of Aqaba developed, with the opening and subsequent drowning of the Red Sea trough as far as the Gulf of Suez and the Gulf of Aqaba. In the succeeding Quaternary Period (about the past 2.6 million years), there was considerable oscillation of sea level, leading finally to the emergence of a low-lying isthmus that broadened northward to a low-lying open coastal plain. There the Nile delta once extended farther east—as a result of periods of abundant rainfall coincident with the Pleistocene Epoch (2,588,000 to 11,700 years ago)—and two river arms, or distributaries, formerly crossed the northern isthmus, one branch reaching the Mediterranean Sea at the narrowest point of the isthmus and the other entering the sea some 14.5 km (9 miles) east of present Port Said.
How many bends are there in the Suez Canal?
The Suez Canal is an open cut, without locks, and, though extensive straight lengths occur, there are eight major bends. To the west of the canal is the low-lying delta of the Nile River, and to the east is the higher, rugged, and arid Sinai Peninsula.
Why is the Suez Canal important?
The Suez Canal is important because it is the shortest maritime route from Europe to Asia. Prior to its construction, ships headed toward Asia had to embark on an arduous journey around the Cape of Good Hope at the southern tip of Africa.
How long is the Suez Canal?
The Suez Canal extends from Port Tewfik in Suez City to Port Said in northeast Egypt. At the time of its opening in 1869, the canal was 164 km long. But several enlargements and developments have increased the canal’s total length by about 30 km to 193.3 km. It is 205 m wide and 24 m deep.
When was the Suez Canal opened?
The Suez Canal was officially opened on November 17, 1869. Egypt, France, and Britain jointly owned the canal until 1956, when it was nationalized by the Egyptian government, leading to Suez Crisis.
What is the name of the artificial waterway that connects the Red Sea to the Mediterranean Sea?
The Suez Canal is an artificial waterway between southern Asia and northern Africa that connects the Red Sea to the Mediterranean Sea via the Isthmus of Suez.
How much draft can a ship carry in the Suez Canal?
Although the Suez Canal can handle larger ships and more traffic than most canals, including the Panama Canal, it can only allow passage of water vessels of up 240,000 tons deadweight or 20 meters draft. The ships or vessels must also not exceed 68 m in height above the water surface and a beam of 77.5 meters (width at the widest point). Supertankers and larger ships can reduce their drafts by offloading their cargo onto smaller cargo-ship owned by the Suez Canal Authority and reload once they have transited the canal.
How long did it take to sail through the Suez Canal?
Ships passed through the canal in convoys and used by-passes, including Port Said, Ballah, Tinsah, and Deversoir. It took a ship 12-16 hours to sail through the canal.
Which two seas did the Ottomans dig?
In the 16th century, the Ottomans contemplated digging a canal connecting the Mediterranean and the Red Sea and link Constantinople to the Indian Ocean trade routes. However, the project was too costly to be completed.
How long did it take to build the canal?
The canal’s construction began on April 25, 1859, and was completed after ten years. According to multiple sources, at least 30,000 people worked on-site at any given time, and more than 1.5 million people of different nationalities were involved in the construction.
Which countries have agreed to draw the Suez Canal?from suezcanal.gov.eg
An agreement was made between France, Austria, Hungary, Spain, Britain, Italy, the Netherlands, Russia and Turkey to draw a final system that ensures freedom of navigation through the Suez Canal ([6]).
When did the Suez Canal begin?from britannica.com
Various forms of what is today the Suez Canal existed in Egypt between 1850 BCE and 775 CE, although primarily to facilitate trade between the Nile River Delta and the Red Sea. Between 1859 and 1869, Egyptian khedive Saʿīd Pasha partnered with France’s Suez Canal Company to build the present canal connecting the Mediterranean and Red seas.
How important is the Suez Canal?from mywaterearth.com
The tumultuous history of the Suez Canal showed how important it was and still is. Shipping analysts estimated that this traffic jam caused by the Japanese ship Ever Given had held up nearly $10 billion in trade every day. A few accidental groundings of vessels have closed the canal since then. The most notable, until this week, was a three-day shutdown in 2004 when a Russian oil tanker ran aground. But the real story of the Suez Canal is its history.
What is the name of the waterway that runs north-south across the Isthmus of Suez?from britannica.com
Editor of Oxford Regional Economic Atlas: The Middle East and North Africa. See Article History. Alternative Title: Qanāt al-Suways. Suez Canal, Arabic Qanāt al-Suways, sea-level waterway running north-south across the Isthmus of Suez in Egypt to connect the Mediterranean and the Red seas. The canal separates the African continent from Asia, ...
How long would it take to travel through the Suez Canal?from mywaterearth.com
Today, a ship traveling from a port in Italy to India, for instance, would cover around 4,400 nautical miles if it passed through the Suez Canal a journey that, at a speed of 20 knots, would take about nine days.
What was the largest ship to transit the Suez Canal?from suezcanal.gov.eg
On October 31st, 1976, the giant Liberian oil tanker “Asoscandia” transited the Suez Canal. Its maximum capacity was 254 thousand tons, its length was 348.5 m., its width was 51.9 m., and its draft was 65.6 feet. It transited in ballast at a draft of 28 feet, and it was the largest ship to transit at the time since its inauguration in 1869.
How many people helped build the Suez Canal?from mywaterearth.com
An estimated 1.4 million workers help construct it. In 1854, Ferdinand de Lesseps, who was the former French consulate to Cairo, secured an agreement with the Ottoman governor of Egypt to build a canal 100 miles across the Isthmus of Suez.
When did the Suez Canal shut down?
The most notable, until this week, was a three-day shutdown in 2004 when a Russian oil tanker ran aground. But the real story of the Suez Canal is its history.
How important is the Suez Canal?
The tumultuous history of the Suez Canal showed how important it was and still is. Shipping analysts estimated that this traffic jam caused by the Japanese ship Ever Given had held up nearly $10 billion in trade every day. A few accidental groundings of vessels have closed the canal since then. The most notable, until this week, was a three-day shutdown in 2004 when a Russian oil tanker ran aground. But the real story of the Suez Canal is its history.
How long would it take to travel through the Suez Canal?
Today, a ship traveling from a port in Italy to India, for instance, would cover around 4,400 nautical miles if it passed through the Suez Canal a journey that, at a speed of 20 knots, would take about nine days.
What would happen if there was no Suez Canal?
Without the Suez Canal, shipping ships traveling between those parts of the world would have to go around the entire continent of Africa, adding hefty costs and substantially extending their journey times.
When was the Suez Canal built?
Construction of the Suez Canal began in April 1859, early on digging was done by hand using picks and shovels wielded by forced laborers. Later, European workers with dredgers and steam shovels arrived at the construction site. Labor disputes and a cholera epidemic slowed construction, and the Suez Canal was not completed ...
What treaty did Britain sign with Egypt?
After years of occupation, Great Britain created the Anglo-Egyptian treaty of 1936 made Egypt virtually independent, but Britain kept the rights for the protection of the canal. After WWll and under pressure from the United Nations, Britain and France withdrew in December, and Israeli forces departed in March 1957.
Who owns the Suez Canal?
In 1962, Egypt made its final payments for the canal to the Suez Canal Company who were the previous owner-operators, taking full control, and now is 100% maintained by the state-owned Suez Canal Authority (SCA) of Egypt.
What happened to the canal in Egypt?
Several ships were trapped within the canal during that blockade and were unable to leave until the north end was reopened in January 1957. The second closing was a consequence of the Arab-Israeli war of June 1967, during and after which the canal was the scene of much fighting between Egypt and Israel and for several years formed the front line between the two armies. Egypt physically barricaded both ends of the canal, and 15 ships, known as the “Yellow Fleet” for the desert sand they slowly accumulated, were trapped in the canal’s Great Bitter Lake for the entire duration of the war. The international crews of the anchored ships provided each other with mutual support and camaraderie, though by 1969 most of the crew members had been allowed to leave. With the reopening of the canal in June 1975 and the signing of a peace treaty between Egypt and Israel in 1979, all ships (including those of Israeli registration) again had access to the waterway, though only 2 of the 15 trapped vessels were able to leave under their own power.
When was the canal used in the Spanish American War?
The history of international use of the canal during wartime includes denial of passage to Spanish warships during the Spanish-American War of 1898 and permission of passage for a squadron of the Russian navy during the Russo-Japanese War in 1905 and for Italian vessels during Italy’s invasion of Ethiopia in 1935–36.
When was the canal reopened?
With the reopening of the canal in June 1975 and the signing of a peace treaty between Egypt and Israel in 1979, all ships (including those of Israeli registration) again had access to the waterway, though only 2 of the 15 trapped vessels were able to leave under their own power. William B. Fisher Charles Gordon Smith.
1. Significance Of The Suez Canal
The importance of the Suez Canal is majorly due to its location. It is the only place that connects the sea of Europe (Mediterranean Sea) with the Arabian Sea (Indian Ocean) and the countries of Asia to the Pacific.
2. The Idea Of The Suez Canal
The idea behind the ‘Suez Canal’ was to link the Mediterranean Sea to the Erythraean Sea, now known as the Red Sea, which excited Egypt’s rulers and colonisers.
3. Suez Canal Company
The construction plan of the Suez Canal was started by the French diplomat De Lesseps in 1854. In 1858 a company was established to build the Suez Canal, named Universal Suez Ship Canal Company. The Universal Suez Ship Canal Company was entrusted with the construction and operation of the canal for the next 99 years.
4. Transfer of Powers to Egyptian Government
Egypt gained independence in 1936, but the rights to the Suez Canal remained with Britain. In 1947, an agreement was reached between the Suez Canal Company and the Egyptian government. It was decided that the Egyptian government would get its ownership over the canal if the 99-year lease with the company were cancelled.
6. The Outbreak Of The Suez Canal Crisis
The Israeli forces attacked first on 29 October 1956, with the British and French troops joining them later. The original plan was to attack at once, but transportation issues of the French and British forces had caused a delay in their plan.
7. Casualties That Happened During The Suez Canal crisis
If we talk about the casualties that took place in the Suez Canal crisis, then it is worth noting that there was a huge loss of army men in this war of the Suez crisis. While the British casualties stood at 16 dead and 96 people were wounded, the French casualties stood as 10 killed and 33 wounded.
8. When Has The Suez Canal Been Closed?
For the first time on 26 July 1956, this canal was closed due to the controversy arising after the announcement of the nationalisation of the canal. Britain and France were furious at this announcement of nationalisation and hence attacked Egypt. Later a settlement was reached, and the waterway was reopened again.
When did the Suez Canal start?
The Suez Crisis began on October 29, 1956, when Israeli armed forces pushed into Egypt toward the Suez Canal after Egyptian president Gamal Abdel Nasser (1918-70) nationalized the canal, a valuable waterway that controlled two-thirds of the oil used by Europe. The Israelis were soon joined by French and British forces, ...
When did Egypt shut down the Suez Canal?
Ten years later, Egypt shut down the canal following the Six-Day War (June 1967). For almost a decade, the Suez Canal became the front line between the Israeli and Egyptian armies. In 1975 as a gesture of peace, Egyptian President Anwar el-Sadat reopened the Suez Canal.
Why Did the U.S. Intervene in the Suez Crisis?
The response of President Dwight Eisenhower’s administration was measured. It warned the Soviets that reckless talk of nuclear conflict would only make matters worse, and cautioned Khrushchev to refrain from direct intervention in the conflict. However, Eisenhower (1890-1969) also issued stern warnings to the French, British and Israelis to give up their campaign and withdraw from Egyptian soil. Eisenhower was upset with the British, in particular, for not keeping the United States informed about their intentions. The United States threatened all three nations with economic sanctions if they persisted in their attack. The threats did their work. The British and French forces withdrew by December; Israel finally bowed to U.S. pressure in March 1957, relinquishing control over the canal to Egypt.
What was the catalyst for the Israeli-British-French attack on Egypt?
The catalyst for the joint Israeli-British-French attack on Egypt was the nationalization of the Suez Canal by Egyptian leader Gamal Abdel Nasser in July 1956. The situation had been brewing for some time. Two years earlier, in the wake of World War II, the Egyptian military had begun pressuring the British to end their military presence (which had been granted in the 1936 Anglo-Egyptian Treaty) in the canal zone. Nasser’s armed forces also engaged in sporadic battles with Israeli soldiers along the border between the two countries, and the Egyptian leader did nothing to conceal his antipathy toward the Zionist nation.
What did the Soviets do to help Egypt?
The Soviets, eager to exploit Arab nationalism and gain a foothold in the Middle East, supplied arms from Czechoslovakia to the Egyptian government beginning in 1955, and eventually helped Egypt construct the Aswan Dam on the Nile River after the United States refused to support the project. Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev (1894-1971) railed against the invasion and threatened to rain down nuclear missiles on Western Europe if the Israeli-French-British force did not withdraw.
What happened after the Suez Crisis?
Aftermath of The Suez Crisis. In the aftermath of the Suez Crisis, Britain and France, once the seat of empires , found their influence as world powers weakened as the United States and Soviet Union took a more powerful role in world affairs. British Prime Minister Anthony Eden resigned two months after withdrawing British troops.
How long is the Red Sea?
At 120 miles long, it connects the Mediterranean Sea to the Indian Ocean by way of the Red Sea, allowing goods to be shipped from Europe to Asia and back more directly. Its value to international trade made it a nearly instant source of conflict among Egypt’s neighbors—and Cold War superpowers vying for dominance.