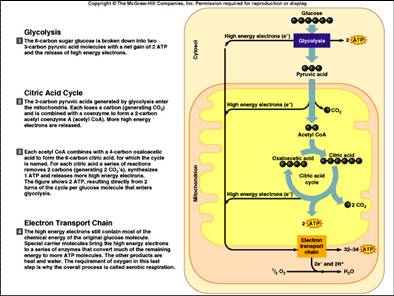
What are the 3 steps in order of cellular respiration?
- Glycolysis. In glycolysis, glucose—a six-carbon sugar—undergoes a series of chemical transformations. ...
- Pyruvate oxidation. Each pyruvate from glycolysis goes into the mitochondrial matrix—the innermost compartment of mitochondria. ...
- Citric acid cycle. ...
- Oxidative phosphorylation. ...
What is cellular respiration and where does it occur?
Cellular respiration occurs inside cells; specifically, cellular respiration happens inside the mitochondria, the powerhouse of the cell. Cellular respiration is a critical function by which cells release energy for various cellular activities like locomotion, biosynthesis, and even the transportation of molecules between membranes.
What are the three pathways of cellular respiration?
What are the 3 pathways of cellular respiration?
- st- Glycolosis. Splitting sugars in cytoplasm, energy investment phase -> 2 ATP molecules combine with glucose molecule.
- nd- Oxidation. Pyruvates moving into mitochondria, through oxidation pyruvates broken into water.
- rd- Krebs Cycle/Citric Acid Cycle.
- th- Electron Transport Chain.
What are the 3 phases of the cellular respiration process?
- stage 1. glycolysis.
- stage 2. citric acid cycle/krebs cycle.
- stage 3. oxidative phosphorylation.
- oxidative phosphorylation consists of.. ETC and chemiosmosis to produce ATP.
- occurs in cytoplasm. glycolysis.
- anaerobic portion.
- breaks down glucose to 2 molecules pyruvate.
- occurs in mitochondrial matrix.

Which of the following best define cellular respiration?
Which of the following is the best definition of cell respiration? A controlled release of energy, in the form of ATP, from organic compounds in cells.
What are 4 characteristics of cellular respiration?
The overall mechanism of cellular respiration involves four subdivisions: glycolysis, in which glucose molecules are broken down to form pyruvic acid molecules; the Krebs cycle, in which pyruvic acid is further broken down and the energy in its molecule is used to form high-energy compounds such as NADH; the electron ...
What is the main function of cellular respiration?
What is the purpose of cellular respiration? Cellular respiration is used to generate usable ATP energy in order to support many other reactions in the body. ATP is particularly important for energetically unfavorable reactions that would otherwise not occur without an energy input.
What does cellular respiration require?
Cellular respiration can occur both aerobically (using oxygen), or anaerobically (without oxygen). During aerobic cellular respiration, glucose reacts with oxygen, forming ATP that can be used by the cell. Carbon dioxide and water are created as byproducts.
What are the 4 stages of cellular respiration and where do they occur?
In eukaryotes, the 4 stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, transition reaction (pyruvate oxidation), the Krebs cycle (also known as the citric acid cycle), and oxidative phosphorylation through the electron transport chain.
What are the types of cellular respiration?
There are two main types of cellular respiration—aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration. Aerobic respiration is a specific type of cellular respiration, in which oxygen (O2) is required to create ATP.
What are the three stages of cellular respiration?
The three stages of cellular respiration are glycolysis, Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation by the electron transport system (ETS).
What is cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that uses glucose to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), an organic compound the body can use for ene...
What is the purpose of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is used to generate usable ATP energy in order to support many other reactions in the body. ATP is particularly important for...
What are the main steps of cellular respiration?
There are three main steps of cellular respiration: glycolysis; the citric acid (TCA) or the Krebs cycle; and the electron transport chain, where o...
Where does cellular respiration take place?
Cellular respiration takes place in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of each cell of the body. Glycolysis occurs inside the cytoplasm, while the TCA...
What are the reactants of cellular respiration?
The reactants of cellular respiration vary at each stage, but initially, it requires an input of glucose, ATP, and NAD+. NAD+, a nicotinamide deriv...
What are the products of cellular respiration?
The final end products of cellular respiration are ATP and H2O. Glycolysis produces two pyruvate molecules, four ATPs (a net of two ATP), two NADH,...
What are the rate-determining enzymes in cellular respiration?
There are three primary rate-determining enzymes in cellular respiration. These enzymes catalyze the rate-limiting steps, which are the slowest rea...
What diseases can affect cellular respiration?
Several diseases can affect cellular respiration. Since cellular respiration is so vital to bodily functions, many of these diseases severely affec...
What are the most important facts to know about cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a series of chemical reactions that break down glucose to produce ATP, which may be used as energy to power many reactions...
What is the process of cellular respiration?
cellular respiration, the process by which organisms combine oxygen with foodstuff molecules, diverting the chemical energy in these substances into life-sustaining activities and discarding, as waste products, carbon dioxide and water. Organisms that do not depend on oxygen degrade foodstuffs in a process called fermentation. (For longer treatments of various aspects of cellular respiration, see tricarboxylic acid cycle and metabolism .)
How does cellular respiration work?
Discover how cellular respiration transforms your food into energy usable by your cells. Cellular respiration releases stored energy in glucose molecules and converts it into a form of energy that can be used by cells. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. See all videos for this article. Cellular respiration, the process by which organisms combine oxygen ...
What is the process of cellular respiration in which glucose is oxidized to carbon dioxide and water?
(For longer treatments of various aspects of cellular respiration, see tricarboxylic acid cycle and metabolism .) During the process of glycolysis in cellular respiration, glucose is oxidized to carbon dioxide and water.
What is the process of glycolysis?
Glycolysis (which is also known as the glycolytic pathway or the Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas pathway) is a sequence of 10 chemical reactions taking place in most cells that breaks down a glucose molecule into two pyruvate (pyruvic acid) molecules. Energy released during the breakdown of glucose and other organic fuel molecules from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins during glycolysis is captured and stored in ATP. In addition, the compound nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD +) is converted to NADH during this step ( see below ). Pyruvate molecules produced during glycolysis then enter the mitochondria, where they are each converted into a compound known as acetyl coenzyme A, which then enters the TCA cycle. (Some sources consider the conversion of pyruvate into acetyl coenzyme A as a distinct step, called pyruvate oxidation or the transition reaction, in the process of cellular respiration.)
What is the process by which food molecules are metabolized to obtain chemical?
algae: Cellular respiration. Cellular respiration in algae, as in all organisms, is the process by which food molecules are metabolized to obtain chemical...
What is the energy released during the breakdown of glucose and other organic fuel molecules from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins during?
Energy released during the breakdown of glucose and other organic fuel molecules from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins during glycolysis is captured and stored in ATP. In addition, the compound nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD +) is converted to NADH during this step ( see below ).
What is the electron transport chain?
electron transport chain. The series of steps by which electrons flow to oxygen permits a gradual lowering of the energy of the electrons. This part of the oxidative phosphorylation stage is sometimes called the electron transport chain. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc./Catherine Bixler.
What happens to cellular respiration without oxygen?
Without the presence of oxygen, also known as an anaerobic environment, regular cellular respirationcannot take place and a process known as fermentation takes over.
Who was the first person to win the Nobel Prize for cellular respiration?
Otto Warburg won the Nobel Prize in 1931 for his research into cellular respiration, showing that cancer thrives in anaerobic (without oxygen ) or acidic conditions.
What is the process of breaking down molecules to release energy for other cellular processes?
a catabolic process (see CATABOLISM) occurring in cells where complex organic molecules are broken down to release energy for other cellular processes. Cell respiration usually occurs in the presence of oxygen (see AEROBIC RESPIRATION) but some organisms can respire without oxygen (see ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION ).
What virus affects mitochondrial respiration?
Effect of measles virus (M V) on mitochondrial respiration.
What is the function of mitochondria?
Well-functioning cell mitochondria promote good health. Without the presence of oxygen, also known as an anaerobic environment, regular cellular respiration cannot take place and a process known as fermentation takes over. Alternate energy resources.
How does solar energy convert into chemical energy?
Here solar energy is converted into chemical energy and encapsulated in organic substances, while oxygen is released in air to be taken up again by other plants and by animals in the process of cellular respiration. By the blend of water and minerals with sunlight and C [O.sub.2], green plants form link between earth and sky.
What is the process of respiration?
In simple terms, respiration is the process through which the nutrients we eat are converted into useful energy. As we know, the cell is the structural and functional unit of life and each cell requires energy to perform their functions.
Which level of respiration takes place at the smallest level of the body?
Therefore, respiration that takes place at the smallest level of our body i.e cellular level is called cellular respiration. The process ensures that each cell performs its function perfectly. Let us have a detailed look at the cellular respiration that takes place in humans.
What are the two types of metabolic reactions?
Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions occurring inside the cells to convert biochemical energy obtained from the food into a chemical compound called adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Metabolism refers to a set of chemical reactions carried out for maintaining the living state of the cells in an organism. These can be divided into two categories: 1 Catabolism – the process of breaking molecules to obtain energy. 2 Anabolism – the process of synthesizing all compounds required by the cells.
What is the chemical compound that converts biochemical energy from food into ATP?
Cellular Respiration. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions occurring inside the cells to convert biochemical energy obtained from the food into a chemical compound called adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
What is the process of breaking molecules to obtain energy?
These can be divided into two categories: Catabolism – the process of breaking molecules to obtain energy. Anabolism – the process of synthesizing all compounds required by the cells. Therefore, respiration is ...
Why does breathing make you run faster?
It is because your body requires extra energy for running, which was provided by respiration. This resulted in rapid breathing. Breathing is an integral part of respiration but as a whole, it is a phenomenon that keeps our body going.
What is the process of breaking down glucose into carbon dioxide and water?
The process of breakdown of glucose to release energy , which can be utilized by our body to perform daily chores like walking, sitting or even thinking, is known as respiration.
What is cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a metabolic process consisting of a series of steps to convert chemical energy (sugar) into a usable form of energy (ATP) in the cell. The reactions involved in cellular respiration are catabolic reactions that involve the breakdown of larger organic molecules into smaller forms.
How is cellular respiration determined?
The efficiency of cellular respiration is determined by the number of ATP molecules produced at the end of the process.
What is Fermentation?
Lactic acid fermentation is a type of fermentation (anaerobic respiration) in which complex organic compounds like glucose are converted into lactic acid while releasing some amount of cellular energy.
Why is aerobic respiration more efficient than anaerobic respiration?
The efficiency of aerobic respiration is higher than the anaerobic one because the double bond in oxygen molecule assists the process of ATP production.
Which type of respiration is the most efficient?
Aerobic respiration is the most efficient type of cellular respiration which occurs in most eukaryotes and some prokaryotes.
Which pathway of cellular respiration produces the largest number of ATPs?
Aerobic respiration equation. In aerobic respiration, one glucose molecule combines with an oxygen molecule and ADP to form carbon dioxide, water, and energy. Aerobic respiration is the most efficient pathway of cellular respiration that produces the largest number of ATPs.
What is the process of converting sugar into ATP?
Cellular respiration is a metabolic process consisting of a series of steps to convert chemical energy (sugar) into a usable form of energy (ATP) in the cell.
What is the process of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
Where does cellular respiration happen?
Cellular Respiration happens in your cells and you entire body is made up of cells, it goes on all throughout your body including your lungs and brain. Comment on DonaShae's post “Cellular Respiration happ...”. Button opens signup modal.
How many carbons are in a pyruvate?
Glycolysis. Six-carbon glucose is converted into two pyruvates (three carbons each). ATP and NADH are made. These reactions take place in the cytosol.
What is the name of the molecule that is converted to a two carbon molecule?
Pyruvate travels into the mitochondrial matrix and is converted to a two-carbon molecule bound to coenzyme A, called acetyl CoA. Carbon dioxide is released and NADH is made. Citric acid cycle. The acetyl CoA combines with a four-carbon molecule and goes through a cycle of reactions, ultimately regenerating the four-carbon starting molecule.
What is the cycle of carbon dioxide and NADH?
Carbon dioxide is released and NADH is made. Citric acid cycle. The acetyl CoA combines with a four-carbon molecule and goes through a cycle of reactions, ultimately regenerating the four-carbon starting molecule. ATP (or, in some cases, GTP), NADH, and FADH_2 are made, and carbon dioxide is released.
How is ATP produced?
Oxidative phosphorylation is powered by the movement of electrons through the electron transport chain , a series of proteins embedded in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.
What is the process of converting glucose into pyruvate?
Glycolysis. In glycolysis, glucose—a six-carbon sugar—undergoes a series of chemical transformations. In the end, it gets converted into two molecules of pyruvate, a three-carbon organic molecule. In these reactions, ATP is made, and is converted to . Pyruvate oxidation.
