Watson and Crick Experiment As the details on structure of DNA was discovered in the early 1950's, James D. Watson and Francis Crick
Francis Crick
Francis Harry Compton Crick OM FRS was a British molecular biologist, biophysicist, and neuroscientist. In 1953, he co-authored with James Watson the academic paper proposing the double helix structure of the DNA molecule. Together with Watson and Maurice Wilkins, he w…
Full Answer
Did Watson and Crick really discover DNA?
They did not discover DNA – it was first identified in 1869 – but until 1953 no one had known what it did. Watson and Crick demonstrated how DNA carries the genetic code that determines the characteristics of a living thing. It is, they say, a large and complicated molecule – in the shape of a double helix.
What method did Watson and Crick use?
What method did Watson and Crick use to determine the structure of DNA? X-ray crystallographyTaken in 1952, this image is the first X-ray picture of DNA, which led to the discovery of its molecular structure by Watson and Crick.
What did Watson and Crick use to find DNA?
The DNA double helix structure proposed by Watson and Crick was based upon "Watson-Crick" bonds between the four bases most frequently found in DNA (A, C, T, G) and RNA (A, C, U, G). However, later research showed that triple-stranded, quadruple-stranded and other more complex DNA molecular structures required Hoogsteen base pairing .
What are Watson and Crick famous for discovering?
- When Watson was a kid, he appeared as a contestant on the radio show Quiz Kids.
- Watson became the second person to make his genetic sequence available online.
- Both Crick and Watson had strong personalities. ...
- Crick and Watson used Rosalind Franklin's images of the DNA molecule without her permission.
See more

How did Watson and Crick determine the structure of DNA?
The Watson and Crick DNA structure is a collaboration of the work of many scientists dating back several decades before their model became a realit...
What are Watson-Crick base pairs?
Watson and Crick base pairs are based on the findings of Erwin Chargaff. When studying the chemical composition of DNA, he found that no matter how...
What two things did Watson and Crick discover?
Watson and Crick determined that DNA was double-stranded and took the shape of a twisted ladder or double helix. They also proved that complementar...
What is Watson and Crick model of DNA?
The Watson and Crick model of DNA is a double stranded helix. Phosphate molecules make up the back bone of each strand and the complementary bases...
Table of Contents
James Watson and Francis Crick were scientists during the middle part of the twentieth century. The work of Watson and Crick extends back several decades prior to their actual scientific discoveries as they utilized information and research of several other scientists to ultimately complete their own experiments.
Watson and Crick Experiment
Science is often collaborative, whether intentional or not. This collaborative nature is demonstrated through Watson and Crick's experiments, which were based on the ideas and research of several other scientists including:
What was the main goal of Watson and Crick?
Their main goal remained that they wanted to project the structure and functionality of the DNA strand as well as how the connection of it and the physical structure was affecting DNA.
When was DNA discovered?
As the details on structure of DNA was discovered in the early 1950's , James D. Watson and Francis Crick believed that DNA would be better understood and represented in a three dimensional structure.
What did Crick and Watson discover?
They seized on this problem during their very first encounter, in the summer of 1951, and pursued it with single-minded focus over the course of the next eighteen months. This meant taking on the arduous intellectual task of immersing themselves in all the fields of science involved: genetics, biochemistry, chemistry, physical chemistry, and X-ray crystallography. Drawing on the experimental results of others (they conducted no DNA experiments of their own), taking advantage of their complementary scientific backgrounds in physics and X-ray crystallography (Crick) and viral and bacterial genetics (Watson), and relying on their brilliant intuition, persistence, and luck, the two showed that DNA had a structure sufficiently complex and yet elegantly simple enough to be the master molecule of life.
What evidence did Watson and Crick use?
A more enduring controversy has been generated by Watson and Crick's use of Rosalind Franklin's crystallographic evidence of the structure of DNA , which was shown to them, without her knowledge, by her estranged colleague, Maurice Wilkins, and by Max Perutz. Her evidence demonstrated that the two sugar-phosphate backbones lay on the outside of the molecule, confirmed Watson and Crick's conjecture that the backbones formed a double helix, and revealed to Crick that they were antiparallel. Franklin's superb experimental work thus proved crucial in Watson and Crick's discovery. Yet, they gave her scant acknowledgment. Even so, Franklin bore no resentment towards them. She had presented her findings at a public seminar to which she had invited the two. She soon left DNA research to study tobacco mosaic virus. She became friends with both Watson and Crick, and spent her last period of remission from ovarian cancer in Crick's house (Franklin died in 1958). Crick believed that he and Watson used her evidence appropriately, while admitting that their patronizing attitude towards her, so apparent in The Double Helix, reflected contemporary conventions of gender in science.
What did Franklin prove about the backbones of sugar phosphate?
Her evidence demonstrated that the two sugar-phosphate backbones lay on the outside of the molecule, confirmed Watson and Crick's conjecture that the backbones formed a double helix, and revealed to Crick that they were antiparallel. Franklin's superb experimental work thus proved crucial in Watson and Crick's discovery.
When did Watson and Crick publish their findings?
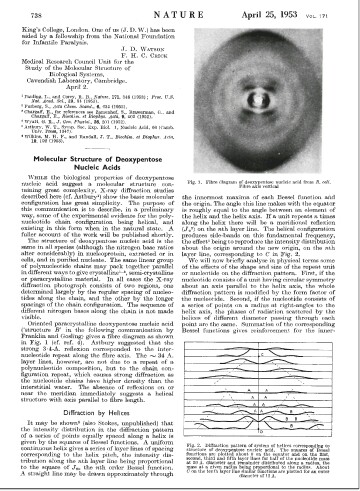
Watson and Crick published their findings in a one-page paper, with the understated title "A Structure for Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid," in the British scientific weekly Nature on April 25, 1953, illustrated with a schematic drawing of the double helix by Crick's wife, Odile. A coin toss decided the order in which they were named as authors.
What was the significance of Watson and Crick's original article in Nature?
Its true significance became apparent, and its circulation widened, only towards the end of the 1950s, when the structure of DNA they had proposed was shown to provide a mechanism for controlling protein synthesis , and when their conclusions were confirmed in the laboratory by Matthew Meselson, Arthur Kornberg, and others.
What was Franklin's contribution to Watson and Crick's discovery?
Franklin's superb experimental work thus proved crucial in Watson and Crick's discovery. Yet, they gave her scant acknowledgment. Even so, Franklin bore no resentment towards them. She had presented her findings at a public seminar to which she had invited the two.
Who discovered the structure of DNA?
Moreover, he had pioneered the method of model building in chemistry by which Watson and Crick were to uncover the structure of DNA.
What is the Watson and Crick model of DNA?
Watson and Crick model of DNA provides one of the best ways to demonstrate the structure of double-helix DNA. A DNA is a polymer composed by the combination of several monomer units ( deoxyribonucleotides) linked by the phosphodiester bond. In the discovery of DNA, many scientists have contextualized the structure of DNA, ...
Who invented the X-ray diffraction method?
Maurice Wilkins, Rosalind Franklin and co-workers introduced the photographs of the DNA by the method of “X-ray Diffraction”. R. Franklin has introduced the super X-ray diffraction photograph of DNA.
Which way is DNA twisted?
The DNA is twisted in “Right-handed direction” or we can say in a “ Clockwise direction ”.
Who discovered the double helical structure of DNA?
Two scientists, James Watson (an American molecular biologist, geneticist and zoologist) along with Francis Crick (a British molecular biologist, biophysicist and neurologist) have demonstrated the double-helical structure of DNA. James Watson and Francis Crick collaborated with the Maurice Wilkins and Rosalind Franklin to introduce the DNA model.
Who created the three dimensional model of DNA?
An English physicist and Molecular biologist, William Thomas Astbury gave the three dimensional model of DNA through X-ray crystallography.
Who discovered DNA?
Before Watson and Crick, Friedrick Miescher, P. A. Levene, W.T. Astbury, Maurice Wilkins and Rosalind Franklin were ...
Which model of DNA was the most successful?
Watson and Crick’s model is the most successful model of DNA for which they have won the Noble Price in Physiology and Medicine in 1962 which they shared with Maurice Wilkins, but not with the Rosalind Franklin due to her unfortunate death in 1958.
What was Watson and Crick's solution?
Watson and Crick’s solution was formally announced on April 25, 1953, following its publication in that month’s issue of Nature magazine. The article revolutionized the study of biology and medicine. Among the developments that followed directly from it were pre-natal screening for disease genes; genetically engineered foods; the ability to identify human remains; the rational design of treatments for diseases such as AIDS; and the accurate testing of physical evidence in order to convict or exonerate criminals.
What happened between Watson and Crick?
Crick and Watson later had a falling-out over Watson’s book, which Crick felt misrepresented their collaboration and betrayed their friendship. A larger controversy arose over the use Watson and Crick made of work done by another DNA researcher, Rosalind Franklin.
What were the developments that followed directly from the AIDS epidemic?
Among the developments that followed directly from it were pre-natal screening for disease genes; genetically engineered foods; the ability to identify human remains; the rational design of treatments for diseases such as AIDS; and the accurate testing of physical evidence in order to convict or exonerate criminals.
Who suggested that DNA was a double helix?
California chemist Linus Pauling suggested an incorrect model at the beginning of 1953, prompting Watson and Crick to try and beat Pauling at his own game. On the morning of February 28, they determined that the structure of DNA was a double-helix polymer, or a spiral of two DNA strands, each containing a long chain of monomer nucleotides, ...
Who discovered the double helix structure of DNA?
On February 28, 1953, Cambridge University scientists James D. Watson and Francis H.C. Crick announce that they have determined the double-helix structure of DNA, the molecule containing human genes. The molecular biologists were aided significantly by the work of another DNA researcher, Rosalind Franklin, although she is not included in ...
Who said we had found the secret of life?
In his best-selling book, The Double Helix (1968), Watson later claimed that Crick announced the discovery by walking into the nearby Eagle Pub and blurting out that “we had found the secret of life.”.
When was DNA discovered?
Though DNA—short for deoxyribonucleic acid—was discovered in 1869, its crucial role in determining genetic inheritance wasn’t demonstrated until 1943. In the early 1950s, Watson and Crick were only two of many scientists working on figuring out the structure of DNA.
Where did Watson hear Wilkins talk about DNA?
At a conference in the spring of 1951 at the Zoological Station at Naples, Watson heard Wilkins talk on the molecular structure of DNA and saw his recent X-ray crystallographic photographs of DNA. He was hooked.
What was James Watson's award for?
In 2005 James Watson was honored with the Othmer Gold Medal from the Chemical Heritage Foundation, now the Science History Institute, for his scientific talent, which has given the world a new intellectual understanding of the nature of life, making possible modern biotechnology and a better life for all mankind.
What was Wilkins' idea for DNA?
It was Wilkins’s idea to study DNA by X-ray crystallographic techniques, which he had already begun to implement when Franklin was appointed by Randall. The relationship between Wilkins and Franklin was unfortunately a poor one and probably slowed their progress.
When did Maurice Wilkins start using X-ray equipment?
Maurice Wilkins with X-ray crystallographic equipment about 1954.
Who created the DNA model?
James Watson and Francis Crick with their DNA model at the Cavendish Laboratories in 1953. To request permission to use this photo, please visit the Science Photo Library website at www.photoresearchers.com.
Who were the scientists who created the DNA model?
James Watson, Francis C rick, Maurice Wilkins, and Rosalind Franklin. At King’s College London, Rosalind Franklin obtained images of DNA using X-ray crystallography, an idea first broached by Maurice Wilkins. Franklin’s images allowed James Watson and Francis Crick to create their famous two-strand, or double-helix, model.
Who was James Watson?
James Watson and Francis Crick. Meanwhile, in 1951, 23-year-old James Watson, a Chicago-born American, arrived at the Cavendish Laboratory in Cambridge. Watson had two degrees in zoology: a bachelor’s degree from the University of Chicago and a doctorate from Indiana University, where he became interested in genetics.
Who were the two scientists who spent their time piecing together information that other scientists had published?
James Watson and Francis Crick were two researchers who spent their time piecing together information that other scientists had published. They also spent time talking with scientists who were busy in their labs running experiments. One of these scientists was Rosalind Franklin (25 July 1920 – 16 April 1958).
Who discovered the shape of DNA?
In 1962, James Watson, Francis Crick and Maurice Wilkins got the Nobel Prize for the discovery of the shape of DNA. Photo 51 was an X-ray diffraction image that gave them some crucial pieces of information. It was only after seeing this photo that Watson and Crick realized that DNA must have a double helical structure.
How did Rosalind Franklin decide to become a scientist?
At the age of 15, Rosalind Franklin decided she wanted to become a scientist. Her father did not like this at all, because it was not considered to be appropriate. Yet she was determined and stuck to her plan. It was not always easy though. From 1951 to 1953, Franklin worked at King’s College in London. Her gender and her upper-class background made life difficult. It seems that some of her colleagues sneered at the way she spoke. On top of this women were not even allowed to enter the senior common room. This made her very angry, because many male colleagues had lunch there. However, none of this stopped Rosalind Franklin from making crucial contributions to science.
What did Rosalind Franklin do to help scientists?
Contributions to Science. Rosalind Franklin used a technique called X-ray crystallography to find out the 3D shape of molecules. She applied this technique to different samples. Early in her career she worked on carbon and coal.
What did Rosalind Franklin discover?
Rosalind Franklin used a technique called X-ray crystallography to find out the 3D shape of molecules. She applied this technique to different samples. Early in her career she worked on carbon and coal. Later she started working on biological subjects. She made major contributions to the discovery of the shape of DNA. After her work on this molecule, she also gave new insights into the first virus that was ever discovered: the Tobacco Mosaic Virus. She thought the virus might be hollow and only consist of one strand of RNA. Although no proof existed at that time, she turned out to be right. Unfortunately, this was not confirmed until after her death.
What technique did Rosalind Franklin use to make her famous photo?
While a lot of Rosalind Franklin's work used X-ray crystallography she also used other X-ray diffraction techniques. Her famous image of DNA called Photo 51 was made using a X-ray technique that did not require the sample to be in crystal form.
Who was the first scientist to discover the structure of DNA?
One of these scientists was Rosalind Franklin (25 July 1920 – 16 April 1958). She was an expert in a technique called X-ray crystallography. Her work would hold the key to discovering the structure of DNA, the blueprint of life.
What was Watson's research project?
Watson's research project involved using X-rays to inactivate bacterial viruses. Watson then went to Copenhagen University in September 1950 for a year of postdoctoral research, first heading to the laboratory of biochemist Herman Kalckar.
Why did Watson want to learn X-ray diffraction?
After obtaining some results from his phage and other experimental research conducted at Indiana University, Statens Serum Institut (Denmark), CSHL, and the California Institute of Technology, Watson now had the desire to learn to perform X-ray diffraction experiments so he could work to determine the structure of DNA.
What did Watson do in 1968?
From 1968 Watson served as director of Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL), greatly expanding its level of funding and research. At CSHL, he shifted his research emphasis to the study of cancer, along with making it a world-leading research center in molecular biology. In 1994, he started as president and served for 10 years. He was then appointed chancellor, serving until he resigned in 2007 after making comments claiming that there is a genetic link between intelligence and race. In 2019, following the broadcast of a documentary in which Watson reiterated these views on race and genetics, CSHL revoked his honorary titles and severed all ties with him.
Why are the names of the Nobel Prize winners omitted?
Because the monument memorializes only American laureates, Francis Crick and Maurice Wilkins (who shared the 1962 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine) are omitted . Watson, Crick, and Wilkins were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1962 for their research on the structure of nucleic acids.
Why did Watson say I turned against the left wing?
In 2007, Watson said, "I turned against the left wing because they don't like genetics, because genetics implies that sometimes in life we fail because we have bad genes. They want all failure in life to be due to the evil system."
What is the name of the book that Watson wrote?
Watson has written many science books, including the textbook Molecular Biology of the Gene (1965) and his bestselling book The Double Helix (1968). Between 1988 and 1992, Watson was associated with the National Institutes of Health, helping to establish the Human Genome Project, which completed the task of mapping the human genome in 2003.
How many children does Watson have?
Watson married Elizabeth Lewis in 1968. They have two sons, Rufus Robert Watson (b. 1970) and Duncan James Watson (b. 1972). Watson sometimes talks about his son Rufus, who suffers from schizophrenia, seeking to encourage progress in the understanding and treatment of mental illness by determining how genetics contributes to it.
