
The Zygomycetes are fungi that thrive in soil and dead plant material. They also have an exquisite taste for dung. They are often seen as rapid growers that quickly devour simple carbon sources and therefore in ecological perspective are seen as typical r-strategists.
Where do Zygomycete hyphae live?
They are mostly terrestrial in habitat, living in soil or on decaying plant or animal material. Some are parasites of plants, insects, and small animals, while others form symbiotic relationships with plants. Zygomycete hyphae may be coenocytic, forming septa only where gametes are formed or to wall off dead hyphae.
What is the function of zygomycetes in food?
Some of them are used in the fermentation of food items while a few others are employed to produce enzymes, acids, etc. Saprophytic species spoil our food stuffs. Some zygomycetes are important mycorrhizal fungi and a few others are human pathogens.
How many genera are in the zygomycetes?
The Zygomycetes are a diverse group of fungi consisting of 10 orders, 18 families, and 122 genera (Benny et al. 2001), almost half of the genera being in the Mucorales. Thomas N. Taylor, ... Edith L. Taylor, in Fossil Fungi, 2015
Where are zygomycetous fungi found?
Zygomycetous fungi are typically endocommensals, particularly being found in the digestive tract of aquatic larvae of a wide range of insect and other arthropod groups, including crustaceans and diplopods playing a role as animal hosts.
How do zygomycetes feed?
The Zygomycetes are fungi that thrive in soil and dead plant material. They also have an exquisite taste for dung. They are often seen as rapid growers that quickly devour simple carbon sources and therefore in ecological perspective are seen as typical r-strategists.
How do Zygomycota mostly live?
They are mostly terrestrial in habitat, living in soil or on decaying plant or animal material. Some are parasites of plants, insects, and small animals, while others form symbiotic relationships with plants.
How do zygomycetes grow?
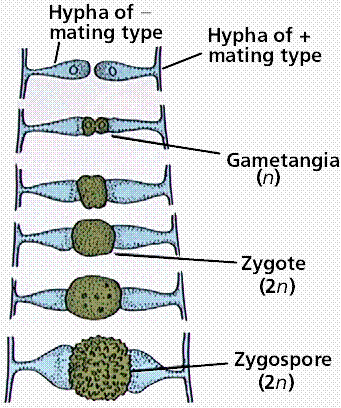
Zygomycota usually reproduce asexually by producing sporangiospores. Zygomycota reproduce sexually when environmental conditions become unfavorable. To reproduce sexually, two opposing mating strains must fuse or conjugate, thereby, sharing genetic content and creating zygospores.
What is unique about zygomycetes?
Zygomycetes are a unique form of fungi because they possess the ability to reproduce both sexually, by creating zygospores, and asexually. Most fungi cannot sexually reproduce. Zygospores are created through the fusion of two other spores.
What type of fungi is Zygomycota?
Zygomycota, or zygote fungi, is a former division or phylum of the kingdom Fungi. The members are now part of two phyla the Mucoromycota and Zoopagomycota. Approximately 1060 species are known. They are mostly terrestrial in habitat, living in soil or on decaying plant or animal material.
Do zygomycetes move?
Basidiomycota and Ascomycota are more closely related to one another than either is to Zygomycota or Chytridiomycota....ZygomycetesMotile (move with flagella/undulipodia)nohabitatmostly terrestrialcell organizationfilamentousReproductive structureszygospores3 more columns
How is zygospore produced?
Zygospores are created by the nuclear fusion of haploid cells. In fungi, zygospores are formed in zygosporangia after the fusion of specialized budding structures, from mycelia of the same (in homothallic fungi) or different mating types (in heterothallic fungi), and may be chlamydospores.
What is the life cycle of zygomycetes?
Zygomycete life cycle. Zygomycetes have asexual and sexual phases in their life cycles. In the asexual phase, spores are produced from haploid sporangia by mitosis (not shown). In the sexual phase, plus and minus haploid mating types conjugate to form a heterokaryotic zygosporangium.
What do you mean by zygomycetes?
[ zī′gō-mī-sē′tēz ] n. A subclass of fungi characterized by sexual reproduction resulting in the formation of a large multinucleate spore formed by union of similar gametes.
Which of the following are characteristics of Zygomycota?
The identifying characteristics of the Zygomycota are the formation of a zygospore during sexual reproduction and the lack of hyphal cell walls except in reproductive structures.
Are zygomycetes true fungi?
The zygomycetes are a relatively small group of fungi belonging to the Phylum Zygomycota.
What is the life cycle of Zygomycota?
Zygomycete life cycle. Zygomycetes have asexual and sexual phases in their life cycles. In the asexual phase, spores are produced from haploid sporangia by mitosis (not shown). In the sexual phase, plus and minus haploid mating types conjugate to form a heterokaryotic zygosporangium.
Where can Zygomycota be found?
soilThe phylum Zygomycota represents a heterogenous group of mainly saprobes, usually found in the soil or in association with plants, fungi, animals, or humans as opportunistic pathogens. In addition, some are facultative or obligate parasites, the latter especially of arthropod and fungal hosts.
How do zygomycetes reproduce asexually?
The Zygomycota typically reproduce asexually by means of non-motile sporangiospores. Sexual reproduction is by gametangial copulation and results in the formation of zygospores. Some species are heterothallic and have a bipolar mating type system which is biallelic but there are some which are homothallic.
Which of the following are characteristics of Zygomycota?
The identifying characteristics of the Zygomycota are the formation of a zygospore during sexual reproduction and the lack of hyphal cell walls except in reproductive structures.
What are zygomycetes found in?
Zygomycetes, especially members of the genus Mucor (Mucorales), are encountered on all, or nearly all, collections of dung from wild animals (see Murie 1974 for information on North American animals; accompanying a mammalogist or herpetologist into the field to find places to collect is also useful). However, only a few, or sometimes one or no species of Zygomycetes, are present on dung of laboratory-reared animals. These fungi are not cellulosic, as far as is known, and therefore grow only on the water-soluble nutrients contained in dung. Suitable dung is dark, shiny, and as fresh as possible. Because the nutrients have been leeched from dung that appears rough or is whitish, such droppings are not a good source of Zygomycetes; spores may have been washed away or may be too old to germinate.
What is a zygomycota?
The Zygomycota are terrestrial fungi with a well-developed, coenocytic, haploid my celium. The thallus is haploid, and chitin and chitosan are significant constituents of the hyphal cell wall. Asexual reproduction in the zygomycetes results in nonmotile spores called sporangiospores. Sexual spores, or zygospores, are produced when two morphologically similar gametangia of opposite mating types fuse. These fungi are saprophytes or weak pathogens, causing postharvest molds and soft rots. For example, some species of Mucor are soil inhabitants that penetrate fruit (through wounds or at the calyx) that have fallen to the orchard floor. Within two months of cold storage, the fruit are completely decayed and fungal mycelium emerges in tufts through the cuticle.
What is zygomycetes on a radiograph?
Zygomycetes are angioinvasive, leading to thrombosis, pulmonary infarction, and hemorrhage, with radiographs showing cavitation and halo sign. From: Clinical Respiratory Medicine (Fourth Edition), 2012. Download as PDF. About this page.
How to collect dung from animals?
Dung should be collected using forceps and rubber gloves to decrease the possibility of contracting diseases. Most dung from small animals will be dry if the environment is also dry. Wet dung should be placed in paper bags; it should not be stored in airtight containers, including plastic bags, because fungal growth will commence before the dung can be plated out in the laboratory. When completely dry, dung pellets can be stored in airtight containers in a refrigerator for long periods.
Where are zygomycetous fungi found?
Zygomycetous fungi are typically endocommensals, particularly being found in the digestive tract of aquatic larvae of a wide range of insect and other arthropod groups, including crustaceans and diplopods playing a role as animal hosts.
Do zygomycetes grow in dung?
However, only a few, or sometimes one or no species of Zygomycetes, are present on dung of laboratory-reared animals. These fungi are not cellulosic, as far as is known, and therefore grow only on the water-soluble nutrients contained in dung. Suitable dung is dark, shiny, and as fresh as possible.
Does voriconazole increase zygomycosis?
Because zygomycetes are resistant to voriconazole, an association between increasing voriconazole use and the relatively higher prevalence of zygomycosis was suggested. However, increasing zygomycosis has been reported before the availability of voriconazole 20 at the same institution where a strong association between prior voriconazole use and breakthrough zygomycosis was subsequently made. 19 Additional data from the same center suggest that the prevalence of zygomycosis increased from 0.9% (1989–93) to 4% (1994–98), only to decrease to 3% for the 1999–2003 period (which includes the period after which voriconazole became widely used at the same institution). 21
Where do zygomycetes come from?
Zygomycetes have been isolated mainly from the soil, where they rapidly colonize any source of easily degradable carbohydrates or proteins.
What is a zygomycota?
Zygomycota It i a paraphyletic group that group more than 1,300 pecie of fungi with different evolutionary origin. Thee have the common characteritic of producing zygopore, which are thick-walled, har
How many species of Kickxellomycotina are there?
Kickxellomycotina and Zoopagomycotina include about 180 species in each subphylum. Many of these fungi are invertebrate parasites, arthropod commensals, or saprotrophs. Some of them are important as insect pest pathogens.
How many species of zygomycosis are there?
More than 30 species of Zygomycota are involved in human infections. Among them Mucorales is the most abundant. Among fungal infections, zygomycoses are exceptionally serious, with a mortality rate greater than 50%.
What is the name of the group of fungi that produces zygospores?
Zygomycota It is a paraphyletic group that groups more than 1,300 species of fungi with different evolutionary origins. These have the common characteristic of producing zygospores, which are thick-walled, hard-walled zygotes, through which sexual reproduction occurs.
How many taxa are there in Mortierellomycotina?
Mortierellomycotina is home to over 100 taxa of saprotrophic soil organisms. All species in this subphylum are ubiquitous soil dwellers and saprotrophs, some of them are also plant symbionts.
What is Rhizopus oryzae used for?
Rhizopus oryzae It is used in the production of alcoholic beverages, in Asia and Africa. Actinomucor elegans It is used in the preparation of tofu, a common soy-based food in oriental cuisine. They are also used as meat tenderizers, yellow coloring for margarine, among others.
Why are zygomycetes important?
Economically the zygomycetes are of significant importance. Some of them are used in the fermentation of food items while a few others are employed to produce enzymes, acids, etc. Saprophytic species spoil our food stuffs. Some zygomycetes are important mycorrhizal fungi and a few others are human pathogens.
What are some examples of zygomycetes?
Some of the zygomycetes are of great interest for having developed peculiar methods of spore dispersed. “Fungus shotgun” of spore dispersal of Pilobolus and forceful propulsion of the asexual spores of the Entomophthorales are the common examples. Animal trapp-mechanism of the zoopagales is of common interest.
What is the term for a weak parasite on plants?
Chiefly Saprophytes, some weak parasites on plants, a few endoparasites of vertebrates; mycelium extensive, asexual reproduction by sporangiospores or rarely by conidia Zygospore wall may be formed by modification of gametangial walls.
How many species are in the zygomycetes?
It comprises 450 species which are grouped under 70 genera.
Is mycelium well developed?
The mycelium is well developed. When young it lacks cross walls but the old hype may be septate. Septa also appear in connection with development of reproductive bodies or to seal off injuries.
How do zygomycota recognize compatible sexual partners?
Recognition of compatible sexual partners in zygomycota is based on a cooperative biosynthesis pathway of trisporic acid. Early trisporoid derivatives and trisporic acid induce swelling of two potential hyphae, hence called zygophores, and a chemical gradient of these inducer molecules results in a growth towards each other. These progametangia come in contact with each other and build a strong connection. In the next stage, septae are established to limit the developing zygospore from the vegetative mycelium and in this way the zygophores become suspensor hyphae and gametangia are formed. After dissolving of the fusion wall, cytoplasm and a high number of nuclei from both gametangia are mixed. A selectional process (unstudied) results in a reduction of nuclei and meiosis takes place (also unstudied until today). Several cell wall modifications, as well as incorporation of sporopollenin (responsible for the dark colour of spores) take place resulting in a mature zygospore.
What is the role of blue light in a zygomycota?
When light, particularly blue light, is involved in the regulation of fungal development, it directs the growth of fungal structures and activates metabolic pathways. For instance, the zygomycota use light as signal to promote vegetative reproduction and growth of aerial hyphae to facilitate spore dispersal.
What is the suspensor of a zygophore?
At this point the zygophore is then called the suspensor. Vesicles accumulate at the fusion septum at which time it begins to dissolve. A little before the fusion septum completely dissolves, the primary outer wall begins to thicken. This can be seen as dark patches on the primary wall as the fusion septum dissolves.
What is the function of chlamydospores?
Chlamydospores are asexual spores different from sporangiospores. The primary function of chlamydospores is the persistence of the mycelium and they are released when the mycelium degrades. Chlamydospores have no mechanism for dispersal. In zygomycetes the formation of chlamydospores is usually intercalar.
How are mitospores formed?
Mitospores. In zygomycetes, mitospores (sporangiospores) are formed asexually. They are formed in specialized structures, the mitosporangia (sporangia) that contain few to several thousand of spores, depending on the species. Mitosporangia are carried by specialized hyphae, the mitosporangiophores (sporangiophores).
What is a zoopagomycotina?
Zoopagomycotina : Zoopagales. Zygomycota, or zygote fungi, is a former division or phylum of the kingdom Fungi. The members are now part of two phyla the Mucoromycota and Zoopagomycota. Approximately 1060 species are known. They are mostly terrestrial in habitat, living in soil or on decaying plant or animal material.
Do zygomycetes grow in salt water?
Furthermore, while the majority of the zygomycetes only grow at high water activities, some of them are able to grow in salt concentrations of at least 15%.
What is a zygomycetes?
Zygomycetes is not the name of particular fungus, but rather the name of a Class of fungi. This Class includes three Orders (Mucorales, Mortierellales, and Entomophthorales). These Orders in turn contain a number of specific fungi (see table below).
Is mucormycosis a zygomycosis?
First, Mucor spp. are only rarely the cause of zygomycosis ( Rhizopus spp. are the most common cause).
What are some examples of zygomycetes?
Two examples illustrate the important role of zygomycetes in human lives: Rhizopus stolonifer and Glomus versiforme. Rhizopus stolonifer. This is one of the best-known and most familiar members of phylum Zygomycota.
Where do zygomycetes live?
They usually reside in the guts of these animals and are thought to provide vitamins to their hosts. Members of zygomycetes in the order of Entomophthorales have great ecological significance based on their parasitic relation with insects and other small pest animals.
What is the name of the filaments that a zygomycetes form?
They are rapidly growing, nonphotosynthetic organisms that characteristically form filaments called hyphae. Hyphae are highly branched to form an interwoven network mass called mycelium. All zygomycetes are terrestrial and reproduce by means of spores. No motile cells are formed at any stage of their life cycle.
Why are endomycorrhizae important?
Since the impoverished farmers there are often unable to afford fertilizers, endomycorrhizae play a critical role in making phosphates available to crops in these regions. The commercial applications of endomycorrhizae to crops in other regions to reduce fertilizer use and increase yields appear to be an increasingly attractive possibility as well.
What are fungi that eat bread called?
Others, such as Glomus versiforme, may form intimate and mutually beneficial symbiotic associations with plant roots called mycorrhizae (literally, “fungus roots”).
How does G. versiforme obtain carbohydrates?
In return, G. versiforme obtains carbohydrates from the host plants.
What is the name of the phylum of zygospores?
In the process, the walls between the two touching gametangia dissolve, fusing their haploid nuclei to form diploid zygospores (hence the name Zycomycota for this phylum). Zygospores have very thick walls and thus are very hardy, able to tolerate extreme environment conditions. Zygospores are dispersed through the air and can remain dormant until conditions are favorable for growth.
