
What does the kidney do in the excretory system?
The kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra make up the excretory system. This technique is chargeable for eradicating waste through urine and sustaining correct chemical balances within the physique. Waste will get filtered out from the blood by way of the kidneys, which convert it to urine and excrete it through the urethra. 1.
How are the kidneys related to the excretory system?
Role of Various Excretory Systems
- Kidneys are responsible for filtering waste products and excess water from the blood.
- The liver breaks down spare amino acids and other toxins within the blood.
- Additionally, the large intestine has the responsibility of eliminating solid wastes left after the digestion of food.
What do kidneys help to remove from body?
The kidneys:
- Release hormones, such as renin, that help to regulate blood pressure
- Make erythropoietin, a hormone that aids formation of red blood cells
- Convert vitamin D into a form that can be used by the body's tissues
What are the kidneys excretory functions?
What are the 5 main functions of the excretory system?
- Remove waste products and medicines from the body.
- Balance the body’s fluids.
- Balance a variety of electrolytes.
- Release hormones to control blood pressure.
- Release a hormone to control red blood cell production.
- Help with bone health by controlling calcium and phosphorus.
How is your kidney health?
Use our online curriculum to get individualized information for your stage of kidney disease .
Why Are the Kidneys So Important?
Most people know that a major function of the kidneys is to remove waste products and excess fluid from the body. These waste products and excess fluid are removed through the urine. The production of urine involves highly complex steps of excretion and re-absorption. This process is necessary to maintain a stable balance of body chemicals.
What Are Some of the Causes of Chronic Kidney Disease?
Chronic kidney disease is defined as having some type of kidney abnormality, or "marker", such as protein in the urine and having decreased kidney function for three months or longer.
How is Chronic Kidney Disease Detected?
Early detection and treatment of chronic kidney disease are the keys to keeping kidney disease from progressing to kidney failure. Some simple tests can be done to detect early kidney disease. They are:
How is Kidney Failure Treated?
Kidney failure may be treated with hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis or kidney transplantation. Treatment with hemodialysis (the artificial kidney) may be performed at a dialysis unit or at home. Hemodialysis treatments are usually performed three times a week. Peritoneal dialysis is generally done daily at home. Continuous Cycling Peritoneal Dialysis requires the use of a machine while Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis does not. A kidney specialist can explain the different approaches and help individual patients make the best treatment choices for themselves and their families.
How to detect kidney disease?
They are: A test for protein in the urine. Albumin to Creatinine Ratio (ACR), estimates the amount of a albumin that is in your urine . An excess amount of protein in your urine may mean your kidney's filtering units have been damaged by disease.
What is the most common inherited kidney disease?
Polycystic kidney disease is the most common inherited kidney disease. It is characterized by the formation of kidney cysts that enlarge over time and may cause serious kidney damage and even kidney failure. Other inherited diseases that affect the kidneys include Alport's Syndrome,primary hyperoxaluria and cystinuria.
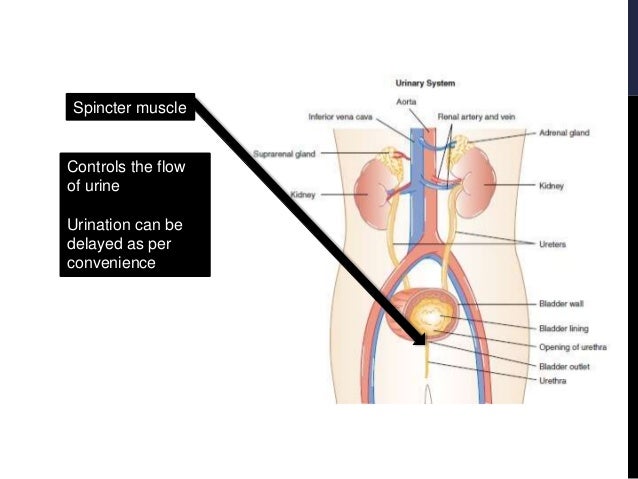
How does the kidney work?
Under the drive of arterial pressure , water and salts are filtered from the blood through the capillaries of the glomerulus into the lumen, or passageway, of the nephron, and then most of the water and the substances that are essential to the body are reabsorbed into the blood. The remaining filtrate is drained off as urine. The kidneys, thus, help maintain a constant internal environment despite a wide range of changes in the external environment.
How does blood flow into the kidney?
Blood flows into your kidney through the renal artery. This large blood vessel branches into smaller and smaller blood vessels until the blood reaches the nephrons. In the nephron, your blood is filtered by the tiny blood vessels of the glomeruli and then flows out of your kidney through the renal vein.
How does ADH affect kidney function?
Certain hormones and hormonelike substances are intimately related to renal function. Some of these, such as ADH , are produced outside the kidney and travel to the kidney via the blood as chemical messengers. Others are produced within the kidney and appear to exert only a local effect. The role of ADH in controlling diuresis has already been discussed. ADH regulates water excretion by increasing the permeability of the collecting ducts to water and salt and by accelerating water and ion transfer in a direction determined by the osmotic gradient. The receptors at the base of the brain form part of the feedback mechanism that stimulates ADH output if the osmotic concentration of extracellular fluid is high, so as to concentrate the urine, and reduces ADH output and so dilutes the urine if osmotic concentration of ECF and of plasma falls.
What hormone is released into the blood when sodium levels fall?
Aldosterone ,a hormone secreted by the kidneys, regulates the transfer of sodiumfrom the nephron to the blood. When sodium levels in the blood fall,aldosterone is released into the blood, causing more sodium to passfrom the nephron to the blood. This causes water to flow into theblood by osmosis. Renin is released into the blood to control aldosterone.
What hormone is responsible for red blood cell production?
Erythropoietin is an essential hormone for red blood cell production. Without it, definitive erythropoiesis does not take place. Under hypoxic conditions, the kidney will produce and secrete erythropoietin to increase the production of red blood cells by targeting CFU-E, pro erythroblast and basophilic erythroblast subsets in the differentiation. Erythropoietin has its primary effect on red blood cell progenitors and precursors by promoting their survival through protecting these cells from apoptosis, or cell death.
Where does the filtrate go in the kidney?
This process is called secretion. The secreted ions combine with the remaining filtrate and become urine. The urine flows out of the nephron tubule into a collecting duct. It passes out of the kidney through the renal pelvis, into the ureter, and down to the bladder.
How does the body use waste?
As blood flows through the body it picks up waste and carries this to the kidneys using the kidney arteries. The waste in your blood comes from the normal breakdown of active tissues and from the food you eat. Your body uses food for energy and selfrepair. After the body has taken what it needs, from the food, the waste is sent to the blood. The kidneys filter out the waste products and excess fluids from the body and dispose of them in the form of urine, via the bladder. The clean blood flows back to the other parts of the body. If your kidneys did not remove this waste, it would build up in the blood and cause damage to your body.
