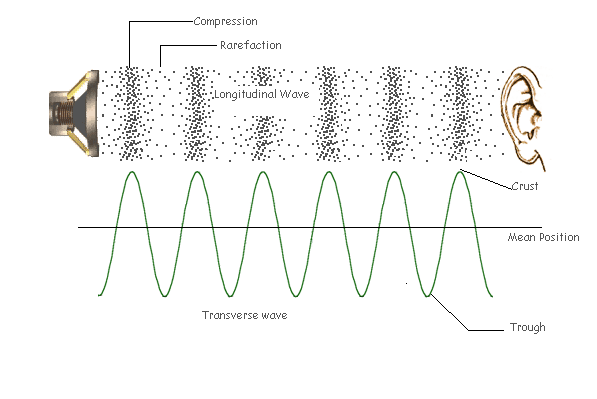
In a transverse wave, the particles move perpendicular to the direction of the wave motion. Click play to see the motion of a transverse wave. In a longitudinal wave, the particles move parallel to the direction of the wave.
Full Answer
What is the highest part of a transverse wave called?
The highest point on a wave is called the crest and the lowest point is called the trough. The highest point of a transverse wave is called the CREST, while the lowest point of a traverse wave is called the TROUGH. Like the other helpful person said, the highest point of a transverse wave is called a crest.
What does a transverse wave look like?
When you picture a wave in your mind, you probably envision a squiggly line with peaks and valleys. This is exactly what a transverse wave looks like. It’s a moving wave that oscillates perpendicular to the direction of its propagation. Transverse waves can be electromagnetic or mechanical in nature.
Which waves have the shortest wavelength?
Order is as follows (shortest to longest wavelength): Gamma, X-Rays, UV, Visible, Infrared, Microwaves, Radio Waves. Gamma has the shortest wavelength because it has a higher frequency, meaning more waves in a second than any other radiation, which results in the short wavelength. Click to see full answer. Also, what is the shortest wavelength?
What are examples of transverse waves found in nature?
transverse wave, motion in which all points on a wave oscillate along paths at right angles to the direction of the wave’s advance. Surface ripples on water, seismic S (secondary) waves, and electromagnetic ( e.g., radio and light) waves are examples of transverse waves.

1. What is the Formula for Wave Velocity?
The wave velocity is the speed at which a wave moves with particles making oscillations about their mean position.The formula of the wave’s velocit...
2. Why is the Wave Speed Constant?
The speed of the wave is an attribute of the medium.Changing wave speed requires a change in the medium itself. So, if the medium in which the wave...
3. Does Tension Affect Wave Speed?
Yes, it does!On increasing the tension in a string, the speed of the wave increases, which in turn, increases the wave frequency, i.e., the number...
4. What is a Transverse wave?
This is a wave in which the medium's particles move in a direction that is opposite to that of the wave. Consider the following situation: if a rop...
5. How are Transverse waves formed?
As a result of particles moving up and down (i.e vibrations).Here the particle always moves in the opposite direction.When a motion perpendicular t...
6. What are Some Properties of a Transverse Wave?
The properties of transverse waves are as follows:The crests and troughs of transverse waves are like peaks of a mountain.Particles move in a direc...
7. How do we calculate the speed of the wave on a string?
A wave's velocity is determined by multiplying the distance traveled by the time it took to travel that distance. This is computed by dividing the...
8. What are the examples of Transverse waves?
Light waves, radio waves, and other electromagnetic waves are all transverse waves. Transverse waves are the waves that form on the water's surface...
9. Where can I get revision notes for Physics?
Vedantu provides revision notes for the subjects, including Physics. You can visit the website of Vedantu and get access to the revision notes. The...
What is a Transverse Wave?
In Physics, a transverse wave is a moving wave whose oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of the wave. A simple demonstration of the wave can be created on a horizontal length of the string by securing one end of the string and moving the other up and down. Light is another example of a transverse wave, where the oscillations are electric and magnetic fields that are at right angles to the ideal light rays that describe the direction of propagation.
How does a transverse wave reflect?
The way in which a transverse wave reflects depends on whether it is fixed at both ends. First, let us discuss a case where the waves are fixed at both ends. The image below shows a transverse wave that is reflected from a fixed end. When a transverse wave meets a fixed end, the wave is reflected but inverted.
What are the two ways to categorize waves?
Categorizing waves on this basis leads to two notable categories: transverse waves and longitudinal waves. A transverse wa ve is a wave in which particles move perpendicular to ...
What is longitudinal wave?
A longitudinal wave is a wave in which the particles move in a direction parallel to the wave propagation. In this article, our focus will be on transverse waves and their characteristics. You can check out our article on longitudinal waves to understand their characteristics.
What happens when a transverse wave meets a fixed end?
The image below shows a transverse wave that is reflected from a fixed end. When a transverse wave meets a fixed end, the wave is reflected but inverted. This swaps the peak with troughs and the troughs with peaks.
What are some examples of transverse waves?
Some examples of transverse waves are listed below: The ripples on the surface of the water. Electromagnetic waves. Stadium or a human wave. Ocean Waves. The secondary waves of an earthquake.
What is the peak of a wave?
The peak is the top point of the wave and trough is the bottom point of the wave. Refer to the diagram below for the visual representation of these terms. Following are a few important terminologies to know: Amplitude – The maximum displacement of a particle from its equilibrium position.
What Are Transverse Waves?
Transverse waves are the waves in which the vibrations move in a direction perpendicular to that of the direction of propagation of the wave.
What are the properties of transverse waves?
The properties of transverse waves are as follows: 1 The crests and troughs of transverse waves are like peaks of a mountain. 2 Particles move in a direction perpendicular to the direction of propagation of a wave.
What is the wave in which there is a flow of energy?
We conclude that the transverse waves are the waves in which there is a flow of energy, while the mass remains at its position.
What happens to the wave frequency when tension increases?
On increasing the tension in a string, the speed of the wave increases, which in turn, increases the wave frequency, i.e., the number of waves in a given length.
What is the energy flow of a ripple?
The energy flow is in the form of vibrations. So this ascending and descending nature of ripples is like that of waves.
When do particles invert?
As we took an example of a string. Here, when the wave of particles reaches the end, they invert while coming back. This means when a crest reaches the end while coming back, it turns to a trough as shown in the image below:
What does symmetrical mean in waves?
By symmetrical, I mean, this wave is regular. If we cut a section of a particular crest, then and observe that this section repeats end-to-end to make up the whole wave.
Why do transverse waves occur?
Transverse waves commonly occur in elastic solids due to the shear stress generated; the oscillations in this case are the displacement of the solid particles away from their relaxed position, in directions perpendicular to the propagation of the wave. These displacements correspond to a local shear deformation of the material.
What are some examples of transverse waves?
Another example is the waves that are created on the membrane of a drum. The waves propagate in directions that are parallel to the membrane plane, but the membrane itself gets displaced up and down, perpendicular to that plane. Light is another example of a transverse wave, where the oscillations are the electric and magnetic fields, ...
How to describe a circularly polarized wave?
By combining two waves with same frequency, velocity, and direction of travel, but with different phases and independent displacement directions , one obtains a circularly or elliptically polarized wave. In such a wave the particles describe circular or elliptical trajectories, instead of moving back and forth.
What is the superposition of sinusoidal waves?
In a homogeneous elastic medium, complex oscillations (vibrations in a material or light flows) can be described as the superposition of many simple sinusoidal waves, either transverse (linearly polarized) or longitudinal.
What is a longitudinal wave?
The standard example of a longitudinal wave is a sound wave or "pressure wave" in gases, liquids, or solids, whose oscillations cause compression and expansion ...
What is the illustration of the electric and magnetic fields along a ray in a simple light wave?
For any plane perpendicular to the ray, each field has always the same value at all points of the plane. Propag ation of a transverse spherical wave in a 2d grid (empirical model) In physics, a transverse wave is a wave whose oscillations are perpendicular to ...
How many directions can a wave move?
There are two independent (orthogonal) directions that the waves can move. (This is true for any two directions at right angles, up and down and right and left are chosen for clarity.) Any waves launched by moving your hand in a straight line are linearly polarized waves. But now imagine moving your hand in a circle.
What are the parts of a transverse wave?
Parts of a transverse wave include the crest, trough, amplitude and wavelength. The crest is the top of the wave, and the trough is the bottom. The amplitude refers to the height of the wave from the midpoint, or rest point, of the wave. The wavelength is the length it takes for the wave to complete one cycle.
What is the middle of a transverse wave called?
The middle of a transverse wave is called the equilibrium or rest position. This is the point at which the particles experience no disturbance. The crest is the highest point of upward displacement of the wave moving through a medium. The trough is the point of lowest displacement. Amplitude refers to the maximum displacement from the rest position.
What is the difference between trough and wavelength?
Amplitude is the measurement of the height of the wave, either from the rest point to the crest or from the rest point to the trough. The wavelength is the measure of one complete cycle from one crest to the next crest ...
What are ocean waves used for?
Ocean waves are also transverse, and these are used for many recreational activities such as surfing and swimming. They can also be used to generate renewable electricity from the wave motion.
Is visible light a transverse wave?
Visible light, radio waves, microwaves and the rest of the electromagnetic spectrum are transverse waves, as well as ocean waves.
Can electromagnetic waves cause cancer?
Electromagnetic waves can also have some undesirable effects: gamma rays and x-rays can damage DNA and cause cancer after prolonged exposure (although the amounts used in medical imaging are low enough to be safe); UV light can cause sunburn and sometimes even skin cancer; and lasers can blind or burn if used incorrectly.
