What function does a bursa serve?
Their function is to reduce friction caused by muscles and tendons moving against skin and bones, as well as to facilitate movement. A knee bursa, also known as a subcutaneous prepatellar bursa, aids with movement when we walk, run, stretch, or even cross our legs.
Does Bursa heal on its own?
Bursitis generally gets better on its own. Conservative measures, such as rest, ice and taking a pain reliever, can relieve discomfort. If conservative measures don't work, you might require: Medication. If the inflammation in your bursa is caused by an infection, your doctor might prescribe an antibiotic.
What happens if you pop a bursa?
- red or swollen
- hot and sore
- painful - usually with a dull, aching pain
- sensitive and painful if you try to press on or move it.
What is the importance of Bursa?
- Congenital anomalies include duplication cysts and cystic lymphangiomas.
- A hematoma or a biloma are classed as traumatic injuries.
- Inflammatory states could be due to an abscess, a pseudocyst or even acute pancreatitis.

What happens when bursa is removed?
If the bursa is severely damaged, the surgeon may remove the entire inflamed sac. The incision is closed with stitches. Removal of a bursa does not affect the way the muscles or joints work and can permanently relieve the pain and swelling caused by bursitis.
What is a bursa and what is it's function in a joint?
A bursa is a small, fluid-filled sac within your body that lies near bony prominences and joints. The bursa acts as a cushion between muscles, ligaments, and bones and allows structures to glide and slide past one another with ease and with minimal friction.
Why is bursa important?
Tendons, ligaments, muscles, and skin must glide over bones during joint movement. Tiny, slippery sacs of fluid called bursae facilitate this gliding motion by providing a thin cushion and reducing friction between the surfaces.
What does the bursa do?
A bursa is a closed, fluid-filled sac that works as a cushion and gliding surface to reduce friction between tissues of the body. The major bursae (this is the plural of bursa) are located next to the tendons near the large joints, such as in the shoulders, elbows, hips, and knees.
What is the fluid in bursitis?
Synovial fluid is produced by the synovial membrane. This viscous, lubricating fluid is contained in the bursa sac.
What causes inflamed bursa?
The most common causes of bursitis are repetitive motions or positions that put pressure on the bursae around a joint. Examples include: Throwing a baseball or lifting something over your head repeatedly. Leaning on your elbows for long periods.
What is the largest bursa in the body?
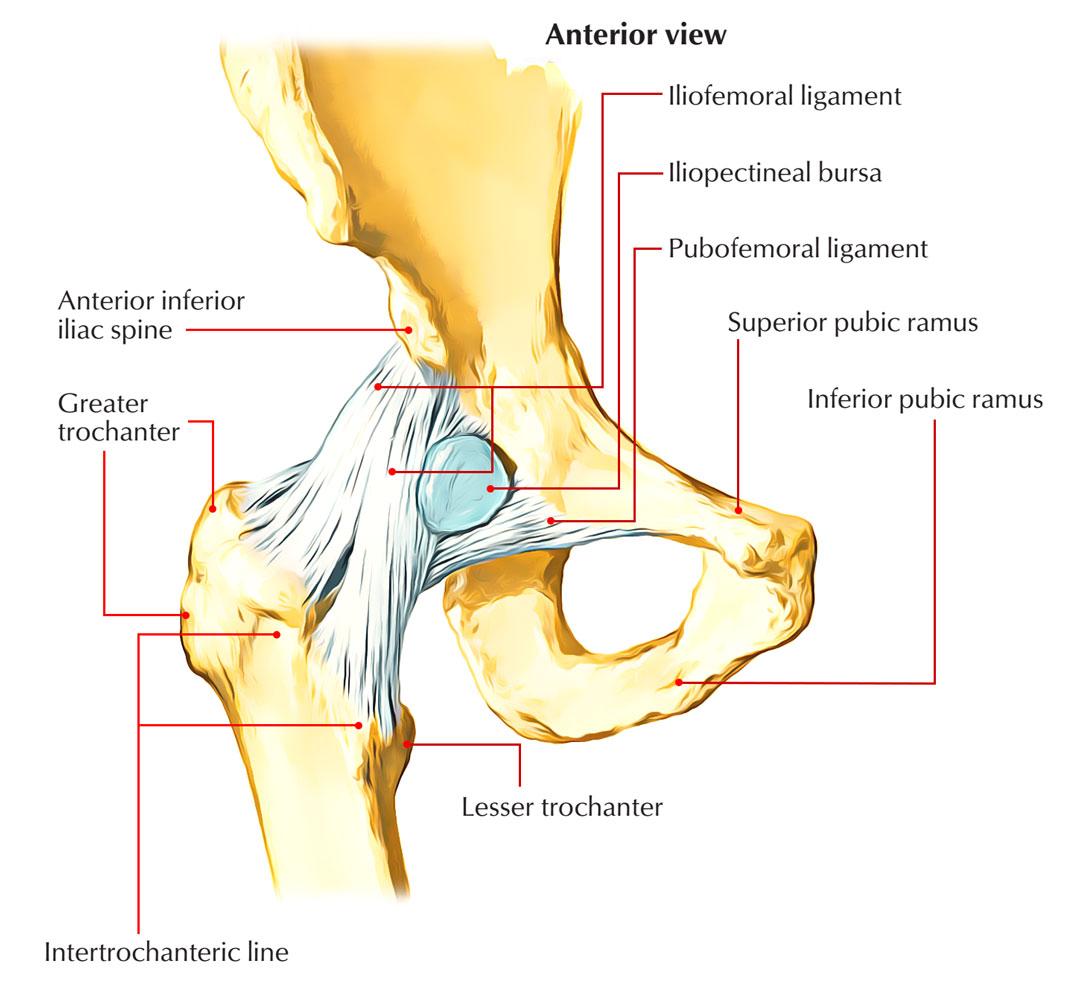
The iliopsoas bursa is known for being the largest bursa in the human body, which extends into the iliac fossa and lies between the lesser trochanter and the iliopsoas tendon.
Can bursitis cause other problems?
For example, shoulder bursitis can lead to “frozen shoulder,” a slowly-developing condition where the shoulder becomes stiff and painful and its range of motion becomes severely curtailed. Of course, immobility could have other causes, like fracture, impingement, dislocation, or a tendon or cartilage tear.
Why is bursitis so painful?
Bursitis is the painful swelling of bursae. Bursae are fluid-filled sacs that cushion your tendons, ligaments, and muscles. When they work normally, bursae help the tendons, ligaments, and muscles glide smoothly over bone. But when the bursae are swollen, the area around them becomes very tender and painful.
Can a bursitis burst?
If the bursitis is left untreated, the fluid filled sack has the potential to rupture.
Why does bursitis hurt more at night?
Bursitis in the shoulder is a common culprit of nighttime shoulder pain because laying on your side can compress the bursa, increasing the level of pain you'd normally feel with the bursitis.
How do you stop bursa inflammation?
Apply ice to reduce swelling for the first 48 hours after symptoms occur. Apply dry or moist heat, such as a heating pad or taking a warm bath. Take an over-the-counter medication, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) or naproxen sodium (Aleve, others), to relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
What is the function of a bursa?
Bursae function to facilitate musculoskeletal movement. They do this by providing a cushion, reducing friction, and dissipating force to and within...
Does bursitis go away?
Depending on the cause, bursitis can be acute (lasting for a short period of time) or chronic (requiring prolonged care). Treatment options include...
Where is the bursa located?
Bursae are located all over the body. Most commonly, they can be found in the joints of the shoulders, elbows, hips, and knees.
What is the bursa in the human body?
A bursa in the human body is a fluid-filled sac. It is usually found within the major joints of the body.
What is a Bursa?
A bursa is defined as a fluid-filled sac located within the joints of the body. The plural word for bursa is bursae. A bursa is designed to provide a cushion, reduce friction, and dissipate force in relatively tight spaces with multiple moving parts.
Bursa Function
Generally speaking, bursae function to reduce friction and dissipate force within joints. They work as a cushion to absorb shock and facilitate musculoskeletal movement. There are different types of bursae with specific functions that will be discussed in more detail throughout this lesson.
Bursa Anatomy
Concerning bursa anatomy, the thin outer lining of a bursa is called a synovial membrane. It is a layer of connective tissue that lines bursae, joint cavities, and tendon sheaths. This membrane is made up of cells that produce synovial fluid, which is a slippery, viscous, and lubricating.
Bursa Locations in the Body
Bursae have many locations in the body. Most of them are found within large joints, including:
Types of Bursae
As mentioned, there are different types of bursae with specific functions in the body. Bursae are typically named based on their location.
What is the bursa in anatomy?
Bursa, plural bursas or bursae, within the mammalian body, any small pouch or sac between tendons, muscles, ...
Why do bursas form?
Adventitious, or accidental, bursas arise in soft tissues as a result of repeated subjections to unusual shearing stresses, particularly over bony prominences. Adventitious bursas are not permanent, though they typically form in areas affected by chronic friction, such as the foot.
What is the synovial bursa?
The synovial bursas are closed, thin-walled sacs, lined with synovial membrane. Bursa s are found between structures that glide upon each other, and all motion at diarthroses entails some gliding, the amount varying from one joint to another. The bursal fluid, exuded by the synovial membrane, is called…. ligament.
Why do bursas cause gout?
The cause of most cases of bursitis appears to be local mechanical irritation, although bursas may also be involved along with the joints and tendon sheaths in rheumatoid arthritis and gout. Diseases of the bursa also occur in domestic animals.
What is the bursa on the inner side of the big toe?
A bunion is an adventitious bursa that develops on the inner side of the base of the big toe in association with hallux valgus (deviation of the first toe such that it lies on top of or below the other toes). Wearing narrow, pointed shoes is a major contributory factor.
Where are the synovial bursas located?
In humans a majority of synovial bursas are located near the large joints of the arms and legs. Submuscular bursas are located between muscles and bony prominences and, in some instances, between neighbouring muscles.
What is the name of the pouch between the tendons, muscles, and skin?
See Article History. Alternative Titles: bursae, bursas. Bursa, plural bursas or bursae, within the mammalian body, any small pouch or sac between tendons, muscles, or skin and bony prominences at points of friction or stress. The bursas are classified by type as adventitious, subcutaneous, synovial, or submuscular.
Why are bursae important?
They are very important in movement of the bones because they help reduce friction. Without them, movement would be difficult and even painful.
What is the pathology of the bursa?
Pathology of the bursa is called bursitis. The most common causes of bursitis are overuse and extreme pressure. Other causes include blunt trauma to the bursa, inflammatory processes such as rheumatoid arthritis and gout, and infection. Infection requires the use of antibiotics with treatment.
How to treat bursitis?
Treatment for infectious bursitis requires antibiotics. Treatment for all other types of bursitis is rest of the inflamed joint, application of ice, and the use of anti-inflammatory medicines. Lesson Summary. Bursae are fluid-filled sacs that reduce friction for movement of the bone.
What are the four types of bursae?
The four types of bursae include adventitious, subcutaneous, synovial, and sub-muscular. Adventitious types can form after birth. This takes place wherever there is constant friction. A bunion is an adventitious type of bursa that develops when shoes rub on the outside of someone's big toe.
What happens when the bursae become inflamed?
Bursitis happens when the bursae are irritated and become inflamed. They lose their functional ability and become a problem instead of a help to the joint. The bursae become larger, and the fluid is thicker. This causes increased friction, basically the opposite of the bursae's primary function.
How many types of bursa are there?
There are four different types of bursa in the body. Three are present at birth. One, known as the adventitious type, develops in any area where there is constant use and friction. An example of the adventitious type you may have seen is on the feet of older women. It is called a bunion. Bunions form usually on the side of the great toe and are caused from wearing high heel shoes. The shoe rubs on the foot and creates the adventitious bursa, sometimes called the accidental bursa.
What is the bursae filled with?
Bursae are filled with a thin layer of thick fluid, like the consistency of a raw egg white, and a lining of synovial fluid, which also works as a shock absorber for the joint and supplies molecules to the cartilage. This is known as dissipating force.
Where are the bursas located?
The other bursa knee locations are: 1 Anteriorly - front of the knee: pretibial and deep infrapatellar bursa 2 Medially - inner side: medial gastrocnemius bursa, the bursa between semitendinosus tendon and the head of the tibia and occasionally there is a bursa between the tendons of semimembranosus and semitendinosus 3 Laterally - outer side: lateral gastrocnemius, fibular, fibulopopliteal and the subpopliteal bursae
Why do bursas sit on the knee?
They sit between two surfaces, usually muscle and bone, to reduce friction, a bit like ball bearings. This allows everything to move smoothly preventing inflammation. Sometimes the knee bursa get damaged, known as bursitis, which can cause pain.
What is the deep and superficial infrapatellar bursa?
2. Infrapatellar Bursa. There are actually two infrapatellar bursa both found underneath the kneecap protecting the patellar tendon. They are known as the deep and superficial infrapatellar bursa. Inflammation here is known as infrapatellar bursitis, or Clergyman's Knee, and is usually caused by more erect kneeling than with prepatellar bursitis - ...
What causes a bursa knee to hurt?
1. Inflamed: i.e. swollen known as bursitis or. 2. Dried out: i.e. they lose the fluid inside them. This results in more friction on the bone and muscles/tendons leading to bursa knee pain. Usually a combination of strengthening and stretching exercises, medication and injections helps them to recover.
Where is the suprapatellar bursa located?
5. Suprapatellar bursa. This is found above the kneecap underneath the quadriceps tendon at the bottom of the thigh preventing friction from the femur.
Which side of the tibia is the bursa?
Medially - inner side: medial gastrocnemius bursa, the bursa between semitendinosus tendon and the head of the tibia and occasionally there is a bursa between the tendons of semimembranosus and semitendinosus. Laterally - outer side: lateral gastrocnemius, fibular, fibulopopliteal and the subpopliteal bursae.
Where is the Pes Anserine Bursa located?
This is found on the inner side of the knee approximately two inches below the joint between the tendons of the sartorius, gracilis and semitendinosis muscles and the medial collateral ligament.
What is a Bursa Sac?
A bursa sac is a thin, fluid-filled sac that sits between joints in the body. Bursae function as a smooth, gliding cushion between bones and opposing surfaces such as muscles, tendons, ligaments, and skin. The major bursae in the body are located adjacent to the tendons near our largest joints, including the hips, knees, shoulders and elbows.
What Size is a Bursa?
Bursae vary in size depending on where they are located in the body. The healthiest bursae are usually very thin while larger joints have larger bursae. On average, the bursa between the kneecap and skin is just a few millimeters thick and about four inches in diameter.
How Many Bursae are in My Body?
An adult body typically contains about 160 bursae. They can be just underneath your skin, or wedged deep below muscles and tissues. While some bursae are present at birth, others develop later in parts of the body where frequent friction occurs. For example, you have probably only had the bursae in your elbows since you were about 7 years old.
What Health Issues are Related to Bursae?
A condition called bursitis occurs when the synovial membrane of a bursa becomes inflamed, usually due to excessive friction or an injury. Sometimes, however, the inflammation can be a symptom of an underlying condition like rheumatoid arthritis. Bursitis is most commonly experienced in the hip, shoulder, knee and elbow.
