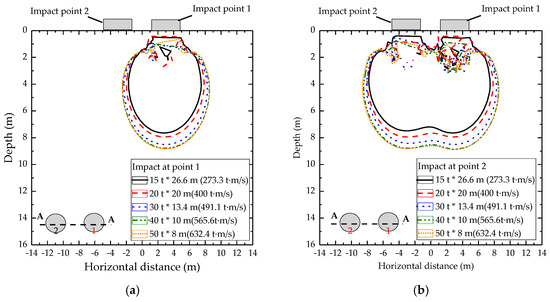
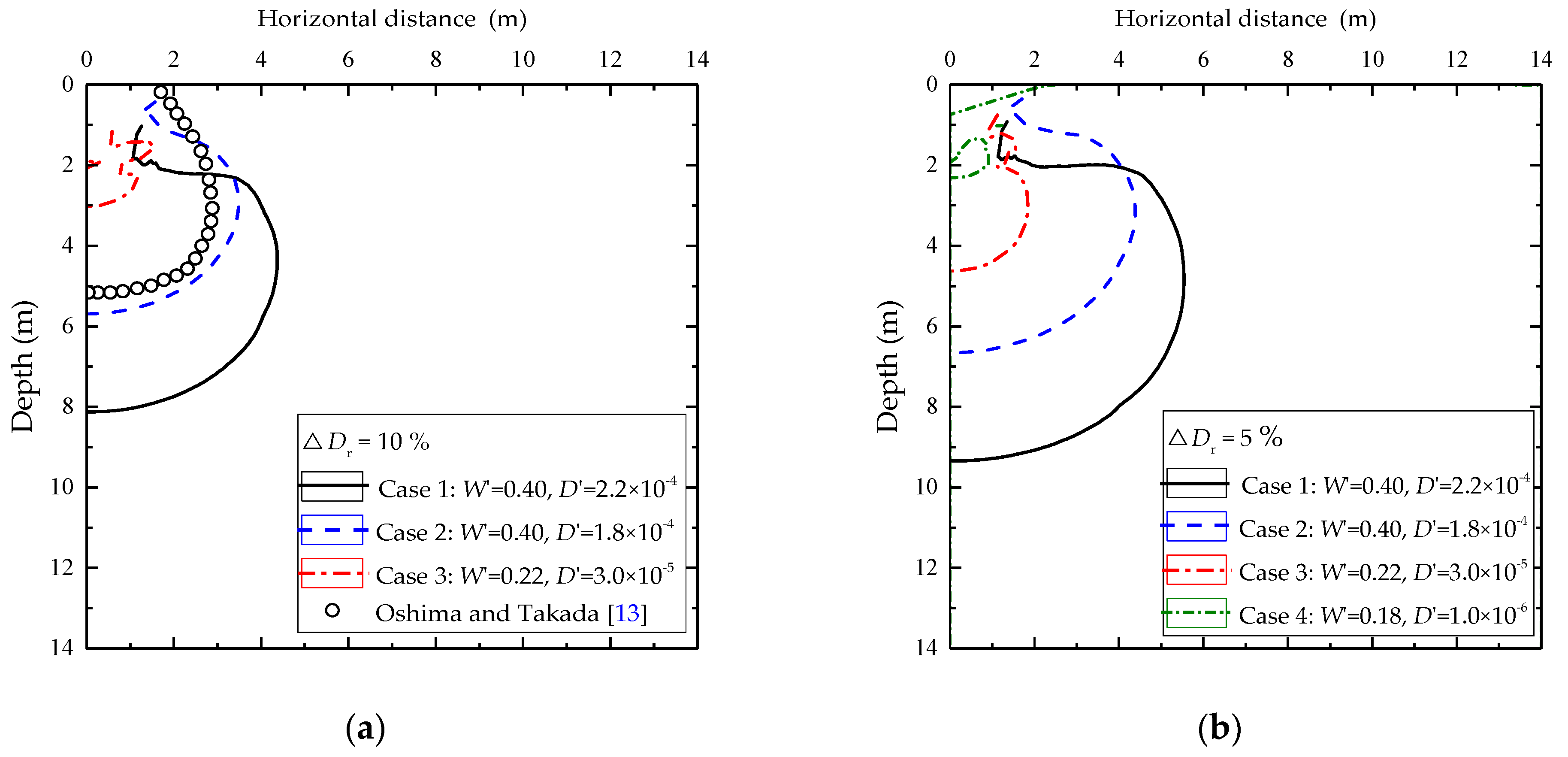
Dynamic compaction is an efficient and cost-effective soil improvement technique that uses the dynamic effect of high energy impacts to densify weak soil. The dynamic effect is generated by dropping a static weight (15-40 tones) from a defined height (10-30 m).
What is dynamic compaction of soil?
Dynamic compaction of Soil. Dynamic compaction is a ground improvement technique in which a drop weight is used to densify the soils and fill materials.
What are the limitations of dynamic compaction?
Dynamic compaction is not appropriate if water depth is less than 1.5m. It cannot be applied if soft cohesive soils are located in the upper part of the compaction. Dynamic compaction is not effective when soils have fines content in excess of 20%. Requires an intensive in situ testing programme to examine the result of compaction.
What is the difference between compaction and consolidation?
Compaction is the compression of soil by the expulsion of air from the voids of the soil. Consolidation is the compression of soil by the expulsion of water from voids of the soil. 2. It is a quick process. It is a slow process. 3. Short term loading is required. Long term loading is required.
What is the difference between dynamic compaction and grid pattern?
These drop locations are generally located on a grid pattern. The subsurface conditions and foundation loading and geometry determines the spacing of the grid pattern. Dynamic compaction utilizes the dynamic effect of high energy impacts which are caused by the drop weight of steel.
What is static and dynamic compaction?
Static compaction gives higher value in density of soil and CBR values. The static compaction onto Soil A specimen has given the value of MDD= 1.86 Mg/m3, and the CBR value was 22.62%. Whereas, the dynamic compaction applied onto Soil A specimen has given the value of MDD= 1.74 Mg/m3, and the CBR value was 20.14%.
Where the dynamic compaction is used?
Dynamic compaction is suitable for densification of loose sand deposits such as those typically occurring in coastal, glacial, and alluvial deposits, as well as for dredged or hydraulically placed fills.
What are different types of dynamic compaction methods?
Common dynamic compaction techniques include: the Dynamic Compaction (or Heavy Tamping) method, the Rapid Impact Compaction (RIC), and. the High Energy Impact Compaction (HEIC) techniques.
Which soil is suitable for dynamic compaction?
coarse grained sandThe dynamic compaction is used to improve weak soil such as loose medium to coarse grained sand with salt or clay content.
What are the method of compaction?
The method of compaction is primarily of four types such as kneading, static, dynamic or impact and vibratory compaction.
What is mean by dynamic consolidation?
Dynamic consolidation is a method of compacting soil deposits using a falling weight. It is used to speed up expected soil-settlement at an thus increase the load-bearing capacity of the soil without the use of extra back filing and settlement time.
What is static compaction?
A static compaction method is described to determine equivalent static pressure equivalent to the standard, reduced standard and the reduced modified Proctor test. The relationship between water content and dry unit weight corresponding to different static pressure is found to be parabolic in nature.
What is dynamic replacement?
Dynamic Replacement (DR) is an extension of Dynamic Compaction (DC) to compressible soils (such as soft clays, silt, sabkha...) where large diameter columns (up to 2.5 m diameter) of very dense granular materials are constructed by dropping heavy pounders from great heights onto the soft soil.
What does the term compaction mean?
Compaction is what happens when something is crushed or compressed. In many places, garbage undergoes compaction after it's collected, so that it takes up less space. The process of making something more compact, or dense and very tightly packed together, is compaction.
What are the advantages of the compaction of soils?
Compaction of the soil and removing air voids generally increases the soil's sheer strength, decreases its compressibility, and decreases its permeability. It will reduce the voids ratio making it more difficult for water to flow through soil.
What is deep compaction?
Deep soil compaction as a method of ground improvement and to stabilization of wastes and slopes with danger of liquefaction, determining the modulus of deformation and shear strength parameters of loose rock. Waste Manag.
Why is compaction done in layers?
Soil compaction is the practice of applying mechanical compactive effort to densify a soil by reducing the void space between soil particles. Compaction occurs when particles are pressed together to reduce the space between them. Highly compacted soils contain very few spaces resulting in soil with higher unit weight.
What are the advantages of the compaction of soils?
Compaction of the soil and removing air voids generally increases the soil's sheer strength, decreases its compressibility, and decreases its permeability. It will reduce the voids ratio making it more difficult for water to flow through soil.
How soil compaction is achieved on site?
Soil compaction occurs when soil particles are pressed together, reducing pore space between them (Figure 1). Heavily compacted soils contain few large pores, less total pore volume and, consequently, a greater density. A compacted soil has a reduced rate of both water infiltration and drainage.
Why is compaction done in layers?
Soil compaction is the practice of applying mechanical compactive effort to densify a soil by reducing the void space between soil particles. Compaction occurs when particles are pressed together to reduce the space between them. Highly compacted soils contain very few spaces resulting in soil with higher unit weight.
What are the deep compaction techniques?
Articles > Deep Compaction Techniques Heavy tamping. Vibration. Compaction grouting. Vibro-compaction and vibro-replacement.
What is dynamic compaction?
Dynamic compaction is an efficient and cost-effective soil improvement technique that uses the dynamic effect of high energy impacts to densify weak soil. The dynamic effect is generated by dropping a static weight (15-40 tones) from a defined height (10-30 m).
When is dynamic compaction not effective?
Dynamic compaction is not effective when soils have fines content in excess of 20%.
How far away from buildings can you use Dynamic Compaction?
It cannot be used within 30m from buildings and 15m from underground services. Dynamic compaction is not appropriate if water depth is less than 1.5m. It cannot be applied if soft cohesive soils are located in the upper part of the compaction.
Typically used for
Dynamic compaction uses the energy from a falling weight in a pre-determined grid pattern to improve granular soils and fills.
Process
Dynamic compaction is a ground improvement technique that densifies soils and fill materials by using a drop weight. The drop weight, typically steel, is lifted by a crane and repeatedly dropped onto the ground surface. Vibrations transmitted below the surface improve soils at depth.
Advantages
Treated granular soils and fills have increased density, friction angle, and stiffness
Quality assurance
Typically, in situ testing by borehole or static cone penetrometer, allied with measurement of print volume and site surface settlement is performed during the dynamic deep compaction.
What is dynamic compaction?
Dynamic compaction is a ground improvement technique in which a drop weight is used to densify the soils and fill materials. The drop weight is typically made of steel and is lifted by a crane and repeatedly dropped onto the ground surface. The vibrations that are resulted from the repeated drops, are transmitted below the surface which improve soils at depth. These drop locations are generally located on a grid pattern. The subsurface conditions and foundation loading and geometry determines the spacing of the grid pattern.
When soils of depths more than 10-12m are to be compacted, what type of compaction can?
When soils of depths more than 10-12m are to be compacted, High energy dynamic compaction can be carried out. This type of compaction technique employs an equipment which comprises of free falling drop weights needing a specially designed weight release system using hydraulic clamps to avoid cable damping and friction, plus repeat cycle lifting hooks. When the high energy dynamic compaction is used for treatment of greater depths, the design of work phases is important in order to obtain a homogeneous compaction over the thickness of the soil mass. Know Construction cost for building a House
Is dynamic compaction effective in saturated soil?
Dynamic Compaction is effective in both saturated and unsaturated soils. Typically this technique should not be carried out within 15m of existing services and 30m from existing buildings. Specially designed 80-120t cranes are used. The site test areas assess the designs after which they are confirmed.
What is Soil Compaction?
Soil compaction is the practice of applying mechanical compactive effort to densify a soil by reducing the void space between soil particles. Compaction occurs when particles are pressed together to reduce the space between them. Highly compacted soils contain very few spaces resulting in soil with higher unit weight. Maximum density is achieved at an optimum moisture content, or OMC, for short.
What does compaction do to a building?
The process of compaction decreases the likelihood of settlement after a building, roadway, runway or parking lot is constructed. Settlement could result in premature pavement failure, costly maintenance or repairs.
Why is Soil Compaction Necessary?
Soil compaction is necessary to increase the bearing capacity and stiffness of in-situ (natural state) or chemically modified soils. Compaction increases the shear strength of soils by adding friction from the interlocking of particles. Future settlement of soils is reduced by increasing the stiffness and eliminating voids creating a densified soil. The removal of voids reduces the chance of the soil settling or shrinking or expanding and it decreases water seepage that would lead to deleterious shrinking and swelling soil properties. Shrink / swell properties compromise the pavement structure thereby leading to premature failure of the pavement structure.
What Factors Affect Soil Compaction?
Different types of soil respond differently with respect to compaction. Soils are classified by their particle size and, in some soil categories, by their critical water content values or Atterberg limits. Well-graded granular soils that contain a wide range of particles are preferred in construction applications because they can be easily compacted, thus eliminating voids by interlocking the particles and resisting moisture absorption thereby allowing the soil to support heavier loads as a very dense soil. Poorly graded soils contain a narrow range of particle sizes and are less conducive for construction purposes due to the fact that the soil lacks shear strength, not associated with the non-interlocking particles because of their similar sizes.
What are the Different Methods Used to Compact Soil?
There are several methods used to compact soil. All methods involve a static and/or dynamic force along with manipulation of the soil. Static force uses the pressure of a weight to physically and continuously compact soil. Manipulation, such as kneading or shearing the soil in alternating movements, can compact soil at greater depths. In conjunction with pressure and manipulation, dynamic force can be applied by adding a vibrating mechanism. Vibratory compaction methods use different amplitudes (the amount of movement on an axis) and frequencies (the speed of the movement) to apply force in alternating directions, usually by the use of a rotating weight, to deliver rapid blows to the surface. This rearranges the soil particles so compaction not only occurs at the top layers but also in the deeper layers of the soil. Another dynamic method of soil compaction is impact compaction using a falling weight. This method is capable of compacting soil at deeper depths as well.
How do you do a Soil Compaction Test?
Several compaction testing methods can be used to determine the degree of compaction. Preliminary in-situ testing at the project site is important to understand what conditions are present initially. Sand cone testing, the use of a balloon densometer or Shelby Tube are all viable options but most commonly a nuclear density gauge is utilized to test for compaction in the field (ASTM D6938-08a). Laboratory methods generally involve compacting soil into molds at to obtain the soil density. For example the moisture density test (commonly referred to as the Proctor tests) (D698 and D1557) specifies compacting soil in a specified volume mold using standardized weight from a specified height. These requirements make for a controlled and reproducible amount of compacting force and provide the maximum density and optimum moisture content of a soil.
What Does 95 Percent Compaction Mean?
95 percent compaction means that the soil has been compacted to 95 percent of the possible density of the soil through compactive efforts. Maximum dry density, along with optimum moisture content, is determined in the laboratory and provides the target for field compaction. 95 percent is often used as a target compaction threshold to ensure that construction projects are erected on a solid platform. The compactive threshold will be provided by the designing engineer and will be based on the bearing capacity required for the final load to be structurally stable.
What is a compaction wheel?
A compaction wheel penetrates the trench fill with specially designed "feet," and achieves compaction from the bottom up rather than from the top down. Soil mixing and displacement achieved during static compaction also limit the possibility of voids and bridging.
Why use a compactor attachment?
If you don't need or want to make the investment in a large, dedicated compactor, but require something with greater productivity than a walk-behind unit, a compaction attachment may be the answer. One benefit is it gives you flexibility to use the carrier (i.e., excavator, backhoe-loader or skid-steer loader) for other tasks.
What attachments do Rockland use to compaction slopes?
Compaction on slopes can also be accomplished with attachments such as the Thompson Slope Packer offered by Rockland. The excavator-mounted attachment consists of a self-cleaning drum with dozer cleats, and it uses the down pressure of the excavator to pack slopes in any condition and grade.
What is boom mounted plate compactor?
According to Neikirk, a boom-mounted plate compactor provides greater amounts of impulse energy compared to static compaction methods. "And they are economically priced compared to [dedicated machines]," he notes. " [Attachments] allow the user to maximize the capabilities of the carrier, and they are generally simple to install or remove, since they replace the bucket. They are excellent tools for compaction in the trench, on inclines or any other application where impulse forces from 3,000 to over 20,000 lbs., as well as 2,000+ cycles per minute, can come in handy."
What is a vibratory plate compactor?
Vibratory plate compactors are a great choice for granular material, since vibration can readily move these particles.
What is the best wheel for soil compacting?
For cohesive soils, such as clay and silt, manufacturers may direct you to a sheepsfoot/roundfoot wheel, which compacts the soil with penetrating, manipulating and mixing actions. For granular soils, such as sand and gravel, a wheel with hexpad or tamper feet is often the better choice.
What is compaction?
Soil compaction occurs when soil particles are pressed together, reducing pore space between them (Figure 1). Heavily compacted soils contain few large pores, less total pore volume and, consequently, a greater density.
How does soil compaction affect soil strength?
Soil compaction changes pore space size, distribution and soil strength. One way to quantify the change is by measuring the bulk density. As the pore space decreases within a soil, the bulk density increases. Soils with a higher percentage of clay and silt, which naturally have more pore space, have a lower bulk density than sandier soils.
How much compaction does a load of 10 tons per axle cause?
Combining heavy axle loads and wet so il conditions increase compaction’s depth in the soil profile. For example, a load of 10 tons per axle or more on wet soils can extend compaction to depths of two feet or more. Because this is well below the depth of normal tillage, the compaction is more likely to persist compared to shallow compaction that can largely be removed by tillage.
Why is compaction increasing in the early season?
Increased potential for compaction early in the cropping season, due to more tillage activity and field traffic.
Why does soil compaction decrease yield?
As soil compaction increases beyond optimum, yields begin to decline. In dry years, soil compaction can lead to stunted, drought-stressed plants due to decreased root growth. Without timely rains and well-placed fertilizers, yields will reduce.
Why is it important to compact corn?
A slightly compacted soil can speed up the rate of seed germination because it promotes good seed-to-soil contact. This is why corn planters have been specifically designed to provide moderate compaction with planter-mounted packer wheels that follow seed placement.
What causes soil to compact?
Causes of compaction. There are several forces, natural and man-induced, that compact a soil (Figure 3). This force can be great, such as from a tractor, combine or tillage implement, or it can come from something as small as a raindrop. Listed below are causes of soil compaction.
Why is compaction done?
Compaction is done purposely in order to get maximum dry density of soil. Consolidation of soil occurs naturally due to structural loads from foundations. It is done before the construction of structure. It begins naturally along with the construction work.
What causes a reduction in the volume of soil?
Both Compaction and consolidation are responsible to cause a reduction in the volume of soil which is due to the compressibility characteristics of the soil. The differences between these two are tabulated below.
Can soil be compacted?
Any type of soil either it is cohesion or Cohesionless can be compacted . Consolidation applies to cohesive soils only especially for low permeable clay. Degree of saturation of soil to be compacted should be less than 100%. Degree of saturation of soil to be consolidated should be 100%.
Is compaction a slow process?
Compaction is the compression of soil by the expulsion of air from the voids of the soil. Consolidation is the compression of soil by the expulsion of water from voids of the soil. 2. It is a quick process. It is a slow process.

Purpose
Dynamic Compaction Process
- The concept of Dynamic compaction is simple but experienced engineers and good planning is essential. Dynamic compaction process includes lifting and dropping a heavy weight several times in one place. It is repeated on a grid pattern across the site. The spacing of grid patterns is determined based on underground condition, foundation loading, and...
Advantages
- Densify and compact soil to a depth of 12m
- Effective in various soil conditions
- Cost effective
- Dramatic cost savings in excess of deep foundations and most undercut and replace options
Disadvantages
- It cannot be used within 30m from buildings and 15m from underground services.
- Dynamic compaction is not appropriate if water depth is less than 1.5m.
- It cannot be applied if soft cohesive soils are located in the upper part of the compaction.
- Dynamic compaction is not effective when soils have fines content in excess of 20%.
Applications
- Densification of weak soil; fills, mine refuse, collapsible soils, sanitary landfills, and soils loosened by sinkholes.
- Reclamation projects.
- Treatment of industrial warehouses, port and airport platforms, roads and railways embankments, heavy storage tanks.