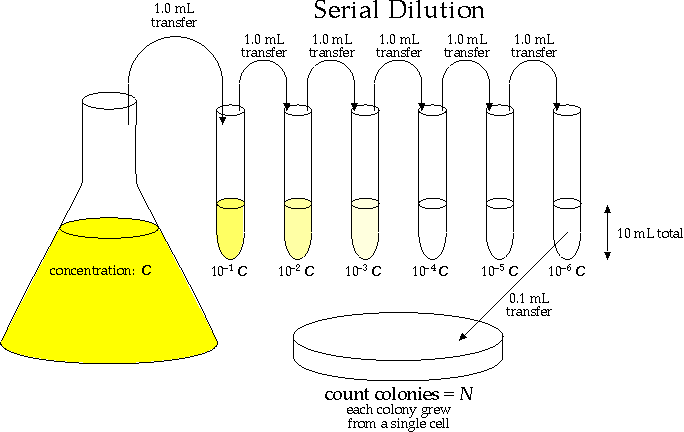
What does 1 100 dilution mean in chemistry?
Apr 13, 2020 · A dilution is a solution made by adding more solvent to a more concentrated solution (stock solution), which reduces the concentration of the solute. An example of a dilute solution is tap water, which is mostly water (solvent), with a small amount of dissolved minerals and gasses (solutes).
How do you do 100 dilution times?
Mar 28, 2022 · What does a 1/100 dilution mean? For a 1:100 dilution, one part of the solution is mixed with 99 parts new solvent. Mixing 100 µL of a stock solution with 900 µL of water makes a 1:10 dilution. The final volume of the diluted sample is 1000 µL (1 mL), and the concentration is 1/10 that of the original solution.
What is an example of dilution?
A 1:4 dilution ratio means that a simple dilution contains one part concentrated solution or solute and four parts of the solvent, which is usually water. For example, frozen juice that requires one can of frozen juice plus four cans of water is a 1:4 simple dilution. Similarly, it is asked, what does a dilution factor of 1 mean?
What is the dilution factor for the first 1000 shares?
Jul 04, 2017 · A 1% solution literally means there is 1gram per 100mls. In terms of dilution, 1% is the same as a 1:100 solution dilution. So, if there is 1g per 100mls there is also 1000mg per 100mls. If we divide this down there will be 10mg in 1ml. 5ml of lidocaine will have 5 x 10mg = 50mg in a 5ml vial.

What is a 1000 fold dilution?
For example, if a solution with a concentration of 1 mUnit/mL is diluted to yield a solution with a concentration of 1 μU/mL, the resulting dilution factor is 1000. For this particular dilution, it can also be said that the stock solution was diluted 1000-fold.Dec 31, 2018
What does 100X dilution mean?
The “X” factor simply indicates that the solution is in a concentrated form that must. usually be diluted to a “1X” concentration for use. For example, a 5X concentrated solution must. be diluted 5-fold, while a 100X concentrated solution must be diluted 100-fold.
How do you make a 1 to 1000 dilution?
You could make 1/1,000 by adding 1 microliter of sample to 0.999 ml diluent. Why is that a poor choice? Because you can't measure 1 microliter (or even 10 microliters) accurately with ordinary pipeters. So, make three serial 1/10 dilutions (0.1 ml [100 microliters] into 0.9 ml): 1/10 x 1/10 x 1/10 = 1/1,000.
How do you do a 1000x dilution?
Reason is, it's already diluted once. If you start with pure copper for example, and stuck it in a beaker, then you would have to add 1000mL to dilute it 1000 fold. But if the copper is already dissolved in 1mL, then you would have to add 999mL to dilute to 1000 fold.Jan 10, 2019
How do you do a 1 10000 dilution?
Another way is to dilute the stock 1/10 twice and then perform a further 1/100 dilution: 1/10 x 1/10 x 1/100 = 1/10,000 dilution This would yield 100 ml of a 1/10,000 dilution of stock in water.
What does a 1/100 dilution mean?
For a 1:100 dilution, one part of the solution is mixed with 99 parts new solvent. Mixing 100 µL of a stock solution with 900 µL of water makes a 1:10 dilution. The final volume of the diluted sample is 1000 µL (1 mL), and the concentration is 1/10 that of the original solution.
What does a 1 1000 dilution mean?
1:1000 means there is 1gram in 1000mls. This is the same as 1g per 1 litre (or 1000mg per 1000mls) Taking this down to actual therapeutic doses that are used in real life clinical practice we 'divide by 1000' – so there will be 1mg per 1ml.
How do you calculate dilution ratio?
The way that I do this is that I simply add the ratio numbers together. So for example: a dilution ratio of 4:1 would be 4+1=5 then I take the total ounces, which in this case is 32 and divide that by 5....To recap:4:1 ratio in a 32oz bottle.4+1 = 5.32oz divided by 5 = 6.4oz.Feb 19, 2020
What is a 2x dilution?
Dilution by Adding Solvent to an End Volume: Consider the case of the alcohol above. Since 50mL of the alcohol was diluted to a final volume of 100mL, we say the alcohol was diluted “two times,” “twice,” or “2x.” For the acid, 20mL was diluted to 500mL, so it would be described as being diluted 25 times (500/20 = 25).
How do you make a 0.1% solution?
and to prepare a 0.1% solution you can take 20 ml of the 0.5 % solution and dilute it to 100 ml by adding 80 ml of water. also to prepare a 0.025% solution you can take 5 ml of the 0.5% solution and dilute it to 100 ml by adding 95 ml of water.
What is a 10000 fold dilution?
In the above example, one could take 0.1 ml (100 μl) and add that volume to 9.9 ml of dilute. This mixture is then mixed well and 0.1 ml is removed from it into 9.9 ml of fresh diluent. Together this makes a 100 × 100-fold dilution, or 10,000-fold dilution.Jan 23, 2016
How do you make a 10mm solution?
take 700 uL from the solution (your org comp dissolved in water) and pour it in a separate vial (2 mL) and add 300 uL of water in it. Now you have 1 mL of your stock with a molarity of 10 mM. you can use this link to calculate in future.Jun 4, 2015
What is 1:1000 dilution?
1:1000 dilution – When a low volume is needed, e.g. Anaphylaxis and Nebulized Epinephrine for severe asthma. The 1:1000 is more concentrated and is good for situations where you want to give a good dose of medicine in a small volume.
What is the density of water?
It is equivalent to the units gram per milliliter (g/mL) and kilogram per liter (kg/L). The density of water is about 1 g/cm 3 or 1000 kg/m 3 since the gram was originally defined as the mass of one cubic centimeter of water at its maximum density at 4 °C.
Is lidocaine a solvent?
Preservatives are also added as well. Sodium chloride is one of the substances added to make it isotonic. As such, in a sense, one could say normal saline is the solvent. But there are more substances than that, again for preservation as well as to create the ideal P H for the body and for isotonicity.
What is 1:1000?
1 percent, 1:1000 and 1:10000 refers to the concentration of dilute drugs like adrenaline (epinephrine) 1 percent is the same as a 1:100 Solution. 1:1000 is the same as 0.1% Solution. 1:10000 is the same a 0.01% Solution.
What is 1% lidocaine?
Lignocaine (lidocaine) – 1%. Lignocaine 1% is commonly used for topical local anaesthesia.
How much lignocaine should I take for anaesthesia?
Lignocaine Dosing for Local Anaesthesia. The safe dose for Lignocaine is 3 – 5mg/kg for ‘plain’ lignocaine. The safe dose is 7mg/kg when adrenaline is added. This means than in a 70kg health man we could safely use 3mg x 70kg = 210mg.
Popular Answers (1)
That depends on PCR efficiency. Actually, when you search the internet a bit, you will immediately come up with some good search hits that will explain you the relation between the slope of a standard curve (made by e.g. 10-fold dilution of standards) and the PCR efficiency.
All Answers (2)
That depends on PCR efficiency. Actually, when you search the internet a bit, you will immediately come up with some good search hits that will explain you the relation between the slope of a standard curve (made by e.g. 10-fold dilution of standards) and the PCR efficiency.
Similar questions and discussions
Why do I get similar Ct values with different dilutions in the standard curve for RT-qPCR?
What is stock dilution?
Stock dilution occurs when a company's action increases the number of outstanding shares and therefore reduces the ownership percentage of existing shareholders. Although it is relatively common for distressed companies to dilute shares, the process has negative implications for a simple reason: A company's shareholders are its owners, ...
What is a dilutive stock?
When it happens, and the numbers of company shares increases, the newer shares are the "dilutive stock.".
What is an exercised option?
Exercising Options. When exercised, certain derivatives instruments are exchanged for shares of stock that are issued by the company to its employees. These employee stock options are often granted instead of cash or stock bonuses and act as incentives. When the option contracts are exercised, the options are converted to shares and ...
What does convertible debt mean?
#N#When a company issues convertible debt, it means that debt holders who choose to convert their securities into shares will dilute current shareholders' ownership. In many cases, convertible debt converts to common stock at some preferential conversion ratio. For example, each $1,000 of convertible debt may convert to 100 shares of common stock, thus decreasing current stockholders' total ownership.
How do employee stock options work?
When the option contracts are exercised, the options are converted to shares and the employee can then sell the shares in the market, thereby diluting the number of company shares outstanding. The employee stock option is the most common way to dilute shares via derivatives, but warrants, rights, and convertible debt and equity are sometimes ...
