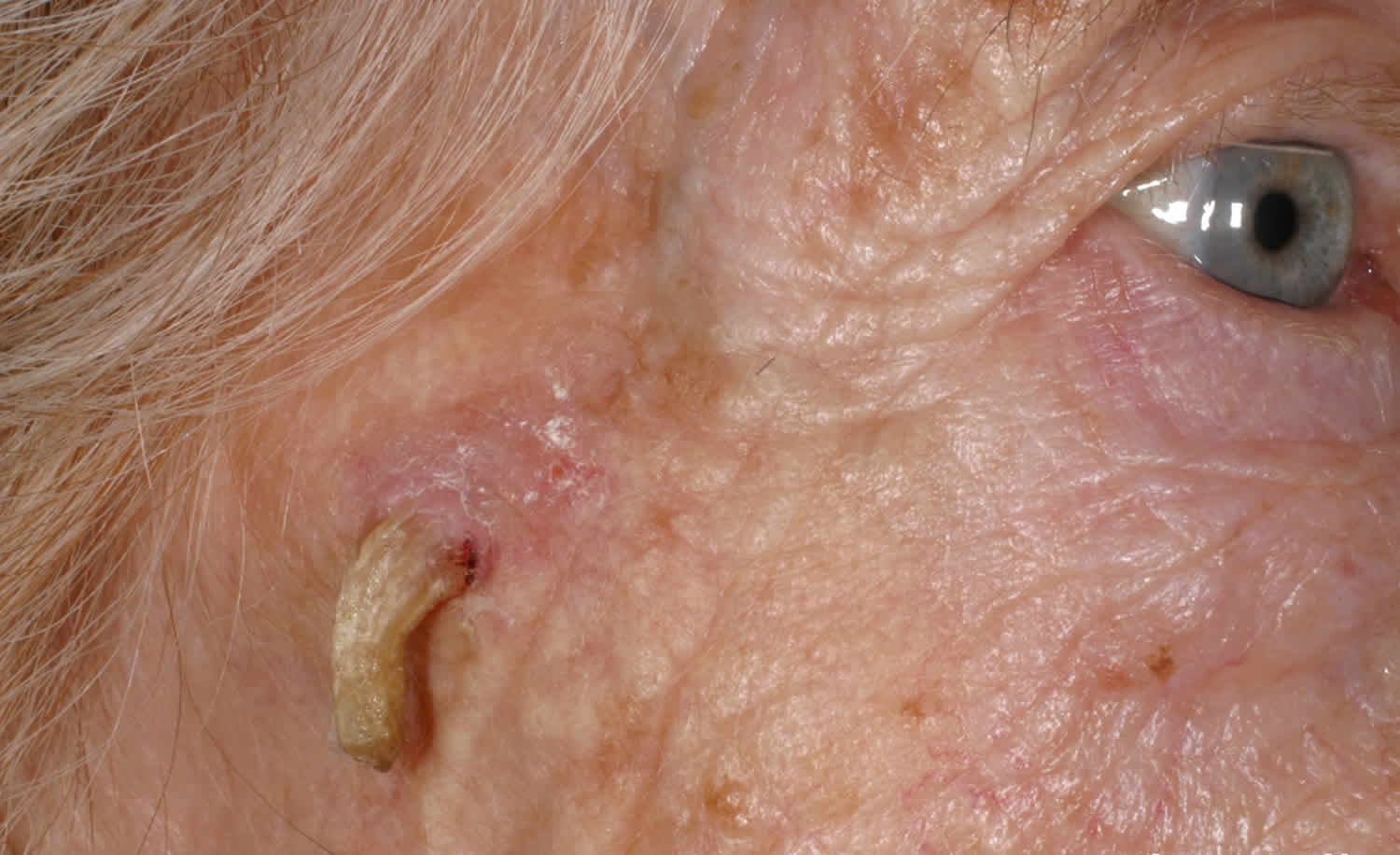
What is a cutaneous horn?
Medically reviewed by Judith Marcin, MD on August 22, 2017 — Written by Lana Bandoim. A cutaneous horn is a type of lesion or growth that appears on the skin. It’s made of keratin, which is a protein that makes up the top layer of the skin. The growth may look like a cone or horn, and it can vary in size.
What does a horse's horn look like?
It can appear as a large bump, cone, spike, or horn. The growth may be the same color as the skin or it may be a different color. The color of the growth can vary and may be: Most cutaneous horns are curved, and the curvature can get worse as they grow.
What does it mean when you have horns on your skin?
Occasionally, the growths look like coral or wood. These tumors develop from the skin’s keratin, particularly in people with very sun-damaged skin. Cutaneous horns may be harmless, precancerous, or cancerous. There may be an underlying cyst.
What does a horn-like growth on the skin look like?
The horn-like growth on the skin’s surface is typically brownish yellow and curved. The growths usually appear on the face, hands, forearms, or ears. The surrounding skin may be unchanged or slightly thickened. The growth is usually a few millimeters or centimeters long, or twice as long as the base is wide.

Can you pull a cutaneous horn off?
Cutaneous Horn Removal If the lesion that is the underlying cause of a skin horn is benign (noncancerous), it is often treated by excision (surgical removal or resection) or with a procedure called curettage. This is a medical procedure involving the removal of tissue by scraping or scooping.
What does the cutaneous horn look like when it first starts?
Symptoms of a cutaneous horn A cutaneous horn looks like a growth on the outside of the skin. This is the most common symptom. It can appear as a large bump, cone, spike, or horn. The growth may be the same color as the skin or it may be a different color.
Are cutaneous horns cancerous?
Cutaneous horns are predominantly benign lesions; however, the possibility of nearly one-third of them harboring malignant or premalignant skin lesions should be borne in mind.
What are cutaneous horns made of?
The horn is composed of compacted keratin. A number of skin lesions can be found at the base of this keratin mound. Cutaneous horns most frequently occur in sites that are exposed to actinic radiation or burns, and hence, are typically found on upper parts of the face.
What does a cancerous horn look like?
The horn-like growth on the skin's surface is typically brownish yellow and curved. The growths usually appear on the face, hands, forearms, or ears. The surrounding skin may be unchanged or slightly thickened. The growth is usually a few millimeters or centimeters long, or twice as long as the base is wide.
How fast do cutaneous horns grow?
The duration of growth or persistence of GCH has been reported from six weeks to seventy-five years. The largest horn was reported by Michal M et al (2002)[4] had a length of 25 cm. The most common histopathological findings at the base of GCH include squamous cell carcinoma[7,8] and verruca vulgaris.
How common is a cutaneous horn?
A cutaneous horn, or cornu cutaneum, is a relatively uncommon, hyperkeratotic epithelial lesion resembling an animal horn defined as having a height that is more than half of the diameter of its base.
What causes a person to grow a horn?
New research in biomechanics suggests that young people are developing hornlike spikes at the back of their skulls — bone spurs caused by the forward tilt of the head, which shifts weight from the spine to the muscles at the back of the head, causing bone growth in the connecting tendons and ligaments.
What is the most common cutaneous malignancy?
Basal cell carcinoma (also called basal cell skin cancer) is most common type of skin cancer. About 8 out of 10 skin cancers are basal cell carcinomas (also called basal cell cancers).
Is cutaneous horn rare?
A cutaneous horn is a rare tumour, often conical, circumscribed, and composed of dead keratin usually derived from base keratinocytes. It occurs mainly in association with underlying benign, premalignant, and malignant cutaneous diseases. The commonest malignancy is squamous cell carcinoma.
Are horns bone or keratin?
Where antlers grow out of a bony stub, horns have a full core of bone. Instead of skin, horns are covered in a tough coating of keratin, the same substance that makes up human fingernails. Horns are also more likely to be a unisex accessory, with males and females of a species both sporting the appendages.
Are cutaneous horns hard?
A cutaneous horn (cornu cutaneum) is a hard conical projection from the skin, made of compact keratin. They are so named as they resemble an animal's horn. They arise from benign, premalignant or malignant skin lesions.
How quickly does basal cell appear?
The cancer is the result of cumulative damage of years spent in the sun, and may take 20 years to manifest. Although it's often more common in older people, it can occur in younger adults, too. Basal cell carcinoma spreads very slowly and very rarely will metastasize, Dr.
Do horns grow from the base?
Horns are made of keratin that grows from the base. Horns are never shed but instead are kept by the animal for its entire life. Pronghorns are unique in that they alone have keratin horns in both sexes that are shed and regrown each year.
How common is a cutaneous horn?
A cutaneous horn, or cornu cutaneum, is a relatively uncommon, hyperkeratotic epithelial lesion resembling an animal horn defined as having a height that is more than half of the diameter of its base.
How do horns develop?
True hair grows from follicles that extend into the dermis, whereas rhino horns grow from dermal papillae which extend up into the horn. The rhino horn is situated over the nasal bones. In species that have two horns, the second horn lies over the frontal bones. Rhino horns commonly curve posteriorly.
What are the characteristics of a cutaneous horn?
Most cutaneous horns share the following characteristics: a curved brown or yellow horn-like growth on the surface of the skin. surrounded by normal or slightly thickened skin. usually at least twice as tall as it is wide. often only one appears, though in rare occasions they may grow in groups.
What is a cutaneous horn?
Image credit: Jojo (2013, May 27). Cutaneous horns are skin tumors that resemble an animal’s horn. It is hard and yellowish-brown in color. To be called a horn, the height must be at least one half of the largest diameter. In very rare cases, a horn may be large, like the horn of an animal. However, a cutaneous horn is very different ...
Why do you have to biopsy a horn?
Almost all cutaneous horns will be biopsied to rule out malignancies. A doctor will take a sample of the horn that includes a piece of the base. After the procedure, the horn will then be sent to a laboratory for further testing and examination to verify the diagnosis and determine whether it is cancerous or benign.
What percentage of cutaneous horns are benign?
When to see a doctor. Associated conditions and complications. Treatment. Outlook. Developing a growth on the skin, such as a cutaneous horn, can be a cause for concern. While around 60 percent of cutaneous horns are benign. Trusted Source.
How to tell if a horn is malignant?
To determine whether a cutaneous horn is malignant, a doctor usually orders a biopsy. This involves taking a sample of the horn that includes a piece of the base.
How to remove a horn from the skin?
During the procedure, the person receives a local anesthetic to numb the horn and the area around the horn. Once the area is numb, a doctor will cut away the horn from its base to remove it from the skin.
Where do cutaneous horns grow?
However, a cutaneous horn is very different from an animal’s horn. Animal horns form around a centrally located bone, while cutaneous horns, including giant cutaneous horns, do not. Usually, only a single horn will grow. They are most likely to appear on the face, ears, and the back of the hand in older people.
How to tell if a horn is cancerous?
Symptoms. Symptoms that a cutaneous horn may be cancerous include the following: Inflammation or pain or redness at the base of the horn. A short cutaneous horn with a large base. Horn located at on the penis- this may be an indicator of skin cancer (squamous cell carcinoma) Hard and thickened skin at the base of the horn.
Why do cutaneous horns hurt?
They can also be painful if they occur in areas prone to physical irritation.
How can you Treat Cutaneous Horns?
It is important to note that treatment cannot continue until a biopsy has been conducted to determine the condition of the cells causing the cutaneous horn.
What is the procedure to burn a horn?
1,2,3. A doctor may scrape and burn the cutaneous horn a process known as curettage and electrodesiccation.
What does it mean when your horn is red?
Hard and thickened skin at the base of the horn. Tenderness at the base of the cutaneous horn. A large sized horn. Lack of terraces on the side of the horn, which is usually an indicator of rapid formation of the horn due to cancer. Redness at the base of the cutaneous horn as well as swelling may be an indicator of cancer (squamous cell carcinoma).
What is the treatment for horn cancer?
Radiation therapy is also recommended, and it follows after the surgical removal of the cutaneous horn) to destroy cancerous cells.
Is a cutaneous horn painful?
Cutaneous horns are not painful unless they have been bruised, or if the horn is of cancerous origin, which is usually a low occurrence. Although the majority of cases involving cutaneous horns are benign or premalignant, early treatment may help alleviate any risk of cancer.
What is a cutaneous horn?
A cutaneous horn (cornu cutaneum) is a hard conical projection from the skin, made of compact keratin. They are so named as they resemble an animal’s horn. They arise from benign, premalignant or malignant skin lesions.
What are the clinical features of a cutaneous horn?
A cutaneous horn generally presents as a straight or curved, hard, yellow-brown projection from the skin .
How is a cutaneous horn treated?
Cutaneous horns are usually excised with appropriate margins, dependent of the nature of the lesion.
Why is horn base examination important?
Histological examination of the horn base is crucial to rule out malignancy, as there are no certain clinical features that can definitively distinguish benign lesions from skin cancer.
What age group is the most likely to have a cutaneous horn?
A cutaneous horn is more common in older patients, with the peak incidence in those between 60 and 70.
What is the thickening of the stratum corneum?
On histology, there is a thickening of the stratum corneum or hyperkeratosis . Orderly horizontal parallel layers of keratin are associated more with benign lesions. Rapidly growing malignant lesions exhibit more erratic growth. Acanthosis is often noted. The base of the lesion shows features of the underlying lesion.
What are the features of a horn?
Squamous cell carcinoma is also likely if the horn has the following features: Painful. Large size. Induration at the base. The anatomic site on the nose, ears, backs of hands, scalp, forearms, face and penis. Wide base or low height to base ratio. Redness at the base of the horn base.
What does a horn look like?
Some characteristics of a cutaneous horn include: 3. It looks cone-shaped or appears as a spike or a large bump. It may be pink, red, whitish, or skin-colored, but most often it is a yellowish-brown color.
How to diagnose a cutaneous horn?
Diagnosis of a cutaneous horn is usually made by conducting a visual inspection as part of an examination. Often, a biopsy is performed once the skin horn is removed, because of the high incidence of pre-malignant and malignant lesions. 4
What is cutaneous horn removal?
Cutaneous Horn Removal. If the lesion that is the underlying cause of a skin horn is benign (noncancerous), it is often treated by excision (surgical removal or resection) or with a procedure called curettage. This is a medical procedure involving the removal of tissue by scraping or scooping.
What is a skin horn?
Diagnosis. Treatment. Prognosis. A skin horn (also known as a cutaneous horn or cornu cutaneum) is a lesion that resembles an animal horn. The horn is a hard outgrowth of abnormally shaped tissue made of keratin—the primary protein of the surface layer of skin that forms its rigidity and provides barrier protection.
Why do some people have skin horns?
Causes. The reason some people get skin horns and others don’t is unknown. A 2010 study found that women were slightly more likely than men to get a cutaneous horn. The study also reported that the skin irregularity occurs most often in people between 60 and 70 years of age.
What is the prognosis of skin horn?
Prognosis. The prognosis of a disease is an estimate of its treatment outcome , based on medical research studies that evaluate many others having been treated for the same disease. The prognosis of skin horn treatment depend s largely on the type of underlying lesion linked with the anomaly.
What color is a sandbox?
It may be pink, red, whitish, or skin-colored, but most often it is a yellowish-brown color. Its height is described as being more than half the diameter of its base. The growth can be found on different areas of the body, but according to a 2010 study, it is most commonly present in areas exposed to the sun, such as the face and head. 4. ...
What Are Cutaneous Horns?
Cutaneous horns are uncommon lesions made of compact keratin. They resemble an animal’s horn. They can occur anywhere on the body but are mostly seen in sun-exposed areas like the face, ear, nose, forearms, and hands. Though 60% of the cutaneous horns are non-cancerous, some may turn cancerous, too ( 1 ).
Where do cutaneous horns occur?
Cutaneous horns are uncommon lesions made of compact keratin. They resemble an animal’s horn. They can occur anywhere on the body but are mostly seen in sun-exposed areas like the face, ear, nose, forearms, and hands. Though 60% of the cutaneous horns are non-cancerous, some may turn cancerous, too ( 1 ).
What are small bumps on someone's skin called?
Have you ever noticed small horn-like bumps on someone’s skin? Those projections are called cutaneous horns. They occur on one’s body and grow up to a few millimeters or centimeters long. Such growths are usually benign but may be harmful too. But how can you know for sure?
How long does it take for a horn to grow?
The growth of cutaneous horns depends on the underlying disease. Non-cancerous horns may grow slowly over a few months or years. However, cancerous horns tend to grow rapidly.
How big can a horn grow?
The base skin may get slightly thickened, and the horn can grow up to a few millimeters or centimeters. One may experience pain and infection if the horn is damaged.
Is a cutaneous horn cancerous?
Cutaneous horns are often benign. But they can be cancerous too. For example, they could occur due to squamous cell carcinoma (skin cancer developing in the cells in the middle and outer skin layers) or basal cell carcinoma (cancer that grows on the skin areas exposed to the sun).
Can a man have a horn?
Both men and women can develop cutaneous horns. However, men are more likely to develop a cancerous horn ( 3 ).
What is a cutaneous horn?
A cutaneous horn, also known as cornu cutaneum, refers to a specific appearance of a skin lesion in which a cone-shaped protuberance arises on the skin caused by overgrowth of the most superficial layer of skin (epidermis). A cutaneous horn is not a particular lesion but is a reaction pattern of the skin. Approximately 40% of cutaneous horns represent precancerous lesions called actinic keratoses. Cutaneous horns may also overlie skin cancer. When overlying cancerous skin, squamous cell carcinoma is typically at the base of the cutaneous horn, but basal cell carcinoma is also possible.
Can a cutaneous horn cause cancer?
Cutaneous horns may also overlie skin cancer. When overlying cancerous skin, squamous cell carcinoma is typically at the base of the cutaneous horn, but basal cell carcinoma is also possible.

Skin Horn Symptoms
- A cutaneous horn is a growth on the skin that can appear like a horn. Some characteristics of a cutaneous horn include:3 1. It looks cone-shaped or appears as a spike or a large bump. 2. It may be pink, red, whitish, or skin-colored, but most often it is a yellowish-brown color. 3. Its height is described as being more than half the diameter of its...
Causes
- A cutaneous horn may arise from various lesions, including:5 1. A viral wart 2. Bowen's disease 3. Seborrheic keratosis 4. Actinic keratosis 5. A benign (noncancerous) lesion 6. A pre-malignant (precancerous) lesion 7. A malignant (cancerous) skin lesion The reason some people get skin horns and others don’t is unknown. A 2010 study found that women were slightly more likely tha…
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis of a cutaneous horn is usually made by conducting a visual inspection as part of an examination. Often, a biopsy is performed once the skin horn is removed, because of the high incidence of pre-malignant and malignant lesions.4 A biopsy includes removing the skin horn, then sending it to the lab to be examined under a microscope for the presence of cancerous cells.
Prognosis
- The prognosis of a disease is an estimate of its treatment outcome, based on medical research studies that evaluate many others having been treated for the same disease. The prognosis of skin horn treatment depends largely on the type of underlying lesion linked with the anomaly.
A Word from Verywell
- If you have a skin horn associated with cancer, such as squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), be sure to discuss treatment options with your healthcare provider. The exact type of cancer treatment depends on many factors, including your age, overall health, and the size, location, and depth of the lesion, as well as whether the cancer is localized or has metastasized (spread) to other area…