
A murmur that occurs when the heart muscle relaxes between beats is called a diastolic murmur. A systolic murmur occurs when the heart muscle contracts. Systolic murmurs are graded by intensity (loudness) from 1 to 6, with a stethoscope slightly removed from the chest. A grade 1 out of 6 is faint, heard only with a special effort.
What does a systolic murmur indicate?
What are the four types of heart murmurs?
- Systolic murmur. A heart murmur that occurs during a heart muscle contraction.
- Diastolic murmur. A heart murmur that occurs during heart muscle relaxation between beats.
- Continuous murmur. A heart murmur that occurs throughout the cardiac cycle.
What is a Grade 2 6 systolic murmur?
Systolic murmurs can also be functional (benign). GRADES Systolic murmurs are graded on a six-point scale. A grade 1 murmur is barely audible, a grade 2 murmur is louder and a grade 3 murmur is...
When to evaluate heart murmurs?
Structural heart disease is more likely when the murmur is holosystolic, diastolic, grade 3 or higher, or associated with a systolic click; when it increases in intensity with standing; or when it has a harsh quality. Chest radiography and electrocardiography rarely assist in the diagnosis of heart murmurs in children.
What valves are affected WIHT a systolic murmur meaning?
Typically, the stenosis arises from senile calcification or a congenital anomaly, such as a bicuspid aortic valve. Less commonly, rheumatic heart disease can affect the aortic valve. The characteristic crescendo-decrescendo systolic murmur is auscultated at the right upper sternal border and may radiate to the carotid arteries. Aortic Regurgitation
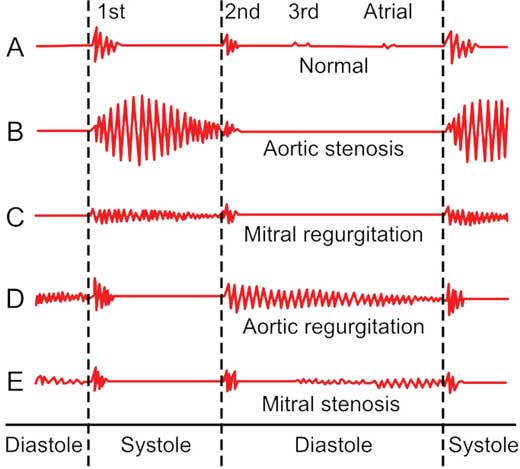
What does a systolic heart murmur mean?
What is a systolic murmur? A systolic (sis-TOL-ic) heart murmur is an unusual heart sound that occurs when your heart contracts (systole, pronounced SIS-tah-lee). This sound is a result of turbulent blood flow. Your heart beat is the sound of the valves in your heart closing.
Is a systolic heart murmur serious?
Most heart murmurs aren't serious. If you're concerned about a heart murmur, make an appointment to see your primary care provider. Your provider can tell you if follow-up care is needed. There is a problem with information submitted for this request.
What causes the sound of a systolic murmur?
A heart murmur is a blowing, whooshing, or rasping sound heard during a heartbeat. The sound is caused by turbulent (rough) blood flow through the heart valves or near the heart.
Which is worse diastolic or systolic murmur?
Providers grade diastolic heart murmurs on a scale of one through four, with one being the faintest and four being the loudest. They grade systolic murmurs on a scale of one through six, with one being the faintest murmur and six being the loudest.
What is the most common cause of a heart murmur?
A murmur is caused by turbulent or abnormal blood flow across your heart valves. If blood is flowing more rapidly than normal, it can cause an innocent heart murmur (also called normal or physiologic). This type of murmur is common during: Childhood.
What should you avoid if you have a heart murmur?
Eat heart-healthy foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, fish, lean meats, and low-fat or non-fat dairy foods. Limit sodium, sugars, and alcohol. If your doctor recommends it, get more exercise.
What are two possible causes for heart murmurs?
CausesFlow murmurs: Exercise, pregnancy, and anemia can all cause a high blood flow, as can hyperthyroidism, fever, and rapid growth spurts. ... Valve disease-related murmurs: Problems with a valve in the heart, such as aortic stenosis or a bicuspid aortic valve, can lead to a heart murmur.More items...
When should I worry about a heart murmur in adults?
If you have been told you have a heart murmur and you think you have symptoms of heart valve disease, you should: Talk to your doctor and ask if you should see a cardiologist, especially if you've had shortness of breath, palpitations or chest pain. See a cardiologist.
What is the difference between a diastolic and systolic murmur?
Types of murmurs include: Systolic murmur - occurs during a heart muscle contraction. Systolic murmurs are divided into ejection murmurs (due to blood flow through a narrowed vessel or irregular valve) and regurgitant murmurs. Diastolic murmur - occurs during heart muscle relaxation between beats.
When does a systolic murmur occur?
Types of murmurs are: Systolic murmur. This happens during a heart muscle contraction. Systolic murmurs are divided into ejection murmurs (because of blood flow through a narrowed vessel or irregular valve) and regurgitant murmurs (backward blood flow into one of the chambers of the heart).
Does a heart murmur make you tired?
People with an abnormal heart murmur may have symptoms of the problem causing the murmur. Symptoms can include: Feeling weak or tired. Shortness of breath, especially with exercise.
Can heart murmur cause stroke?
Abnormal heart murmurs themselves don't cause complications, but underlying conditions may cause serious complications such as heart attack or stroke, heart failure, poor growth (in infants and children) and other serious issues.
When should I be concerned about a heart murmur?
If you have been told you have a heart murmur and you think you have symptoms of heart valve disease, you should: Talk to your doctor and ask if you should see a cardiologist, especially if you've had shortness of breath, palpitations or chest pain. See a cardiologist.
Can you live a long life with a heart murmur?
Living with a heart murmur If you or your child has an innocent heart murmur, you can live a completely normal life. It will not cause you any problems and is not a sign of an issue with your heart. If you have a murmur along with any of the following symptoms, see your doctor: You are very tired.
What causes a heart murmur to develop in adults?
Adults may develop such a hole after a heart attack or surgery. If blood is leaking through an abnormal opening between heart chambers, it can lead to shortness of breath or other symptoms. The abnormal blood-flow pattern also causes a heart murmur. Certain infectious diseases.
Do heart murmurs get worse with age?
Likewise, murmurs can get worse if a condition goes untreated or becomes more serious. Your heart is unique, and some heart murmurs can change over time.
What is an early systolic murmur?
An early systolic murmur is a feature of TR with normal RV systolic pressure. When the RV systolic pressure is elevated, a holosystolic murmur results. Early systolic murmurs may occur in a neonate with a large VSD and in children or adults with a very small VSD or with a large VSD and pulmonary hypertension. View chapter Purchase book.
Where is the systolic murmur audible?
An ejection systolic murmur might be audible in the upper left sternal border or covered by the systolic murmur of VSD . Right ventricular heave may be present.
What is a diamond shaped systolic ejection murmur?
Systolic ejection murmurs associated with ventricular obstructive lesions or conditions associated with increased flow are diamond shaped. Examples include semilunar valvular, subvalvular, or supravalvular stenosis; coarctation; anemia; hyperthyroidism; fever; and increased flow across the pulmonary valve associated with an atrial septal defect. As semilunar valve stenosis progresses, the murmur peaks later in systole and extends to the component of S2 of the affected valve. Holosystolic murmurs associated with ventricular septal defects (other than small muscular defects) or atrioventricular valve regurgitation have a plateau shape. Decrescendo diastolic murmurs have maximal intensity early and then become softer; they are characteristic of semilunar valve regurgitation.
How many children have systolic murmurs?
Nonsignificant systolic murmurs can be heard in more than 60% of children. The systolic murmur of aortic valve sclerosis without stenosis is heard in more than 50% of individuals older than 50 years. Systolic murmurs can be classified as early systolic, midsystolic, late systolic, or holosystolic (occurring all through the systolic time interval; Fig. 2 ).
What causes a short regurgitant murmur?
Early systolic murmurs (or short regurgitant murmurs) begin with the S1, diminish in decrescendo, and end well before the S2, generally at or before midsystole (see Fig. 2-11 ). Only the three conditions that cause holosystolic murmurs (VSD, MR, and TR) are the causes of an early systolic murmur. An early systolic murmur is a feature of TR with normal RV systolic pressure. When the RV systolic pressure is elevated, a holosystolic murmur results. Early systolic murmurs may occur in a neonate with a large VSD and in children or adults with a very small VSD or with a large VSD and pulmonary hypertension.
What is the physiologic ejection murmur?
The physiologic ejection murmur, also called the innocent pulmonic systolic murmur, is identical in quality to the murmur of an atrial septal defect, comprising a murmur caused by flow through the normal pulmonic valve but associated with a normal second sound.
Why is it important to perform an echocardiographic examination in patients with pathologic or possibly pathologic murmurs?
In addition to the prognostic information obtained by having the correct cardiac diagnosis, the echocardiographic data resulted in significant changes in patient management. Such changes included recommendation of endocarditis prophylaxis at delivery for structural heart disease, surgical closure of an ASD postpartum, and genetic counseling in patients with inherited diseases in the study described previously. 185
How do you know if you have a heart murmur?
An abnormal heart murmur may cause the following signs and symptoms, depending on the cause of the murmur: Skin that appears blue, especially on your fingertips and lips. Swelling or sudden weight gain. Shortness of breath.
What is the sound of a heart murmur?
Heart murmurs are sounds — such as whooshing or swishing — made by turbulent blood in or near your heart. Your doctor can hear these sounds with a stethoscope. A normal heartbeat makes two sounds like "lubb-dupp" (sometimes described as "lub-DUP") when your heart valves are closing.
What is a shunt in the heart?
Cardiac shunts. Cardiac shunts occur when there's an abnormal blood flow between the heart chambers or blood vessels , which may lead to a heart murmur.
Why do older people have abnormal heart murmurs?
In older children and adults, causes of abnormal heart murmurs include infections and conditions that damage the structures of the heart. For example:
Why do children murmur?
In children, abnormal murmurs are usually caused by structural problems of the heart (congenital heart defects). Common congenital defects that cause heart murmurs include: Holes in the heart. Known as septal defects, holes in the heart may or may not be serious, depending on the size of the hole and its location. Cardiac shunts.
Can a heart murmur go away?
While there's not much you can do to prevent a heart murmur, it is reassuring to know that heart murmurs are not a disease and are often harmless. For children, many murmurs go away on their own as children grow. For adults, murmurs may disappear as the underlying condition causing them improves.
Is a heart murmur a sign of heart disease?
An innocent heart murmur is not a sign of heart disease and doesn't need treatment. Abnormal heart murmurs require follow-up testing to determine the cause. Treatment is directed at the cause of your abnormal heart murmur.
How loud is a systolic murmur?
Systolic murmurs are graded by intensity (loudness) from 1 to 6. A grade 1 is faint, heard only with a special effort. It's softer than the normal heart sounds. A grade 6 is extremely loud, and can be heard with no contact between stethoscope and the chest.
What causes a murmur in the heart?
Certain congenital defects and other conditions such as pregnancy, fever, anemia or thyrotoxicosis (a condition caused by an overactive thyroid gland) can also cause murmurs. A murmur that occurs when the heart muscle relaxes between beats is called a diastolic murmur.
What is it called when a child's heart rate changes?
These heart murmurs are also called “normal” or “physiological” murmurs. Innocent heart murmurs are so common that most children are likely to have one at some time. Innocent murmurs may disappear and then reappear. When a child’s heart rate changes, such as during excitement or fear, these innocent murmurs may become louder or softer.
What is an innocent heart murmur?
Innocent heart murmurs are sounds made by blood circulating through the heart’s chambers and valves, or through blood vessels near the heart. Innocent murmurs are common in children and are harmless. These heart murmurs are also called “normal” or “physiological” murmurs.
When do murmurs disappear?
Most innocent murmurs disappear when a child reaches adulthood, but in some adults the murmur remains for life.
Can a child have a heart murmur?
With an innocent heart murmur, your child won’t need medication, and doesn't have a heart problem or heart disease. You will not need to restrict your child’s activities or diet. They can lead an active, healthy life! Most innocent murmurs disappear when a child reaches adulthood, but in some adults the murmur remains for life.
Do innocent heart murmurs disappear?
Innocent heart murmurs are so common that most children are likely to have one at some time. Innocent murmurs may disappear and then reappear. When a child’s heart rate changes, such as during excitement or fear, these innocent murmurs may become louder or softer. This still doesn’t signal that the murmur is cause for concern.
What causes a late systolic murmur?
Mitral valve prolapse. This is the most common cause of late systolic murmurs. It can be heard best over the apex of the heart, usually preceded by clicks. The most common cause of mitral valve prolapse is "floppy" valve (Barlow's) syndrome. If the prolapse becomes severe enough, mitral regurgitation may occur.
What causes a systolic murmur to start at S1?
Causes include mitral valve prolapse, tricuspid valve prolapse and papillary muscle dysfunction. Holosystolic (pansystolic) murmurs start at S1 and extend up to S2. They are usually due to regurgitation in cases such as mitral regurgitation, tricuspid regurgitation, or ventricular septal defect (VSD).
What is a mid systolic ejection murmur?
Mid-systolic ejection murmurs are due to blood flow through the semilunar valves. They occur at the start of blood ejection — which starts after S1 — and ends with the cessation of the blood flow — which is before S2. Therefore, the onset of a midsystolic ejection murmur is separated from S1 by the isovolumic contraction phase;
Why does my mitral regurgitate?
Usually due to acute myocardial infarction or ischemia, which causes mild mitral regurgitation.
Can aortic valve stenosis cause a murmur?
Can be due to aortic valve stenosis or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), with a harsh and rough quality. ** Valvular aortic stenosis can produce a harsh, or even a musical murmur over the right second intercostal space which radiates into the neck over the two carotid arteries.
Is aortic valve sclerosis a hemodynamic instability?
Aortic valve sclerosis. This is due to degenerative thickening of the roots of the aortic cusps but produces no obstruction and no hemodynamic instability and thus should be differentiated from aortic stenosis. It is heard over right second intercostal space with a normal carotid pulse and normal S2.
Is S2 a normal shunt?
It is associated with normal pulmonary artery pressure and thus S2 is normal. This fact can be used to distinguish from pulmonary stenosis, which has a wide splitting S2. When the shunt becomes reversed (" Eisenmenger syndrome "), the murmur may be absent and S2 can become markedly accentuated and single.
Why does murmur occur in the systole?
pansystolic murmura regurgitant murmurheard throughout systole, due to blood flow between two chambers normally of very different pressures in systole; the most common causes are mitral regurgitation, tricuspid regurgitation, and ventricular septal defects.
Where is systolic murmur prominent?
Systolic murmurprominent at aortic area was noted on auscultation.
What is a seagull murmur?
seagull murmur a raucous murmur resembling the call of a seagull, frequently heard in aortic sten osis or mitral regurgitation. Still's murmur a functional heart murmur of childhood, with a buzzing or vibratory tone heard in midsystole; it usually disappears by puberty. systolic murmur a heart murmur heard at systole, ...
What is the meaning of murmur in blood?
blood murmur one due to an abnormal, commonly anemic, condition of the blood.
Why does my heart murmur at diastole?
diastolic murmura heart murmurheard at diastole, due to mitral obstruction or to aorticor pulmonic regurgitationwith forward flow across the atrioventricular valve; it has a rumbling quality.
Why does murmurone occur before diastole?
prediastolic murmurone occurring just before and with diastole, due to aortic regurgitationor pulmonic regurgitation.
What is a blood murmur?
blood murmur one due to an abnormal, commonly anemic, condition of the blood. Called also hemic murmur. cardiac murmur heart murmur. cardiopulmonary murmur one produced by the impact of the heart against the lung. continuous murmur a humming heart murmur heard throughout systole and diastole.
What does it mean when your heart murmurs?
A heart murmur is an unusual sound heard between heartbeats. If your doctor hears a “murmur” or any other abnormal sounds coming from your heart, it may be an early indicator of a serious heart condition.
Why do babies murmur?
An abnormal murmur in a child is due to congenital heart malformations, which means they’re present at birth. It may need to be corrected with surgery.
What does a stethoscope do during a heart checkup?
Outlook. During a checkup, your doctor will use a stethoscope to listen to your heartbeat to determine whether your heart is beating properly and has a normal rhythm. This gives your doctor information concerning the health of your heart. A heart murmur is an unusual sound heard between heartbeats. If your doctor hears a “murmur” ...
What is the most common abnormal heart sound?
Heart murmurs. The most common abnormal heart sound is a heart murmur. A murmur is a blowing, whooshing, or rasping sound that occurs during your heartbeat. There are two kinds of heart murmurs : innocent (also called physiological) abnormal. An innocent murmur can be found in children and adults.
Why does my heart click?
Heart clicks are caused by problems with your mitral valve.
Why does my left atrium make a rubbing sound?
Rubbing sounds may be heard in people with certain kinds of infections. A rubbing sound is usually caused by an infection in your pericardium (a sac that surrounds your heart) due to a virus, bacteria, or fungus.
What is the sound of a heartbeat called?
A normal heartbeat has two sounds, a lub (sometimes called S1) and a dub (S2). These sounds are caused by the closing of valves inside your heart. If there are problems in your heart, there may be additional or abnormal sounds.
What causes heart murmurs?
HEART MURMURS. Murmurs are caused by the blood flow across the valve (either from increased blood flow or defective valve). 1. TIMING. It refers to the timing of the murmur in relation to the cardiac cycle. 2. DURATION. It refers to the length of the murmur in relation to the phase of the cardiac cycle. 3.
What is the meaning of "unique" in murmur?
It refers to unusual characteristics of the murmur which makes it unique in quality.
How to hear heart sounds with stethoscope?
Use your stethoscope for cardiac auscultation. Apart from the 3rd and 4th heart sounds and the mid-diastolic murmur of Mitral Stenosis, all the other heart sounds are best heard with the diaphragm of your stethoscope. You should firmly press your “diaphragm” to chest wall whereas apply only light pressure when you are auscultating with the “bell” of your stethoscope.
What pitch is the murmur on a stethoscope?
It can be low, medium or high pitches. Depending on the pitch you select the chestpeice of the stethoscope you place to hear the murmur best.
Where does the sound of a murmur radiate?
It refers to where the sound of the murmur radiates from the main location of it . As a rule of thumb, the murmur radiates in the direction of the blood flow.
Does the opening of a cardiac valve make a sound?
Usually, the opening of cardiac valves does not make any sound. Opening snap occurs due to forceful “Opening” of a stenosed valve and it is described in Mitral stenosis (Refer MS). Hence it is always pathological. It is a high-pitched sound that occurs after S2.
Can you hear murmurs when you auscultate?
Some murmurs are best heard using some maneuvers which should be performed when you auscultate .
