A venous duplex is used to:
- Search for deep vein thrombosis (blood clots)
- Examine varicose veins (veins with an unusual pooling of blood)
- Determine the cause of leg swelling
- Locate and map veins to assist with the placement of a needle or catheter, or for surgery
- Examine blood vessel grafts used for dialysis
Full Answer
What is the difference between duplex and Doppler ultrasound?
Duplex:
- Doppler ultrasonography is a medical non-invasive study of the heart and blood vessels, using ultrasound with high-frequency waves.
- Duplex ultrasonography is a medical non-invasive study, which combines traditional ultrasonography and Doppler ultrasonography.
- Doppler ultrasonography provides a color picture detecting the blood flow. ...
What doctor treats vein problems?
Who Treats Varicose Veins?
- Vascular Surgeon — Specialist in Treating Vascular Conditions. ...
- Interventional Radiologist – Imaging Specialist for Minimally Invasive Treatments. ...
- Dermatologist and Dermatologic Surgeon - Skin Specialist. ...
- Phlebologist — Vein Disorder Specialist. ...
- Treatment Options for Varicose Veins and Spider Veins. ...
What is duplex vs condo?
- Increased security since the condos are managed by the homeowners’ association
- Shared responsibility in terms of house maintenance and repair
- Non-payment of insurance for exteriors
- More affordable
What is duplex and half duplex?
Types of transmission mode
- Simplex. Simplex is also called one-way or unidirectional. ...
- Half-duplex. Half-duplex allows communication in both directions but not at the same time. ...
- Full-duplex. Full-duplex is also called two-way or bidirectional. ...
- Auto-sensing. ...
- Differences between simplex, half-duplex, and full-duplex. ...

Why do you need a duplex ultrasound?
Venous duplex ultrasound is frequently used to check vein health due to varicose veins, pain in the leg, or leg swelling; it is also used to search for blood clots in the veins of the legs. A blood clot can be very dangerous, as it can break away and travel to your lungs, causing a potentially fatal pulmonary embolism.
Who is the best vein doctor in Kansas City?
Dr. Darling is widely considered to be the best vein doctor in Kansas City. To schedule an appointment here at Missouri Vein Specialists, call us today at (816) 792-3400 or fill out our online request form. We look forward to serving you!
What does a radiologist see during a blood scan?
What the scan will show is the movement of your blood through your veins. Pictures will be taken during the scan, and these images will be reviewed by the radiologist. The radiologist, who is a physician who specializes in bodily scans, will write a short report about the findings for your doctor.
What to do if you have a blood clot?
If a blood clot is found, you can start treatment immediately. This usually involves taking blood thinners.
Who is the doctor for bulging veins in legs?
If you are experiencing significant discomfort in one or both of your legs along with bulging varicose veins, our triple-board-certified vein specialist Dr. Scott Darling is here to help. Dr. Darling can conduct an accurate and efficient assessment and provide effective treatment for symptom relief, and he can restore the smooth, clear skin on your legs once again.
Can you get a duplex ultrasound if you have veins?
If you have issues with the veins in one or both of your legs, your vein doctor may recommend that you get a venous duplex ultrasound in order to check your vein health. Ultrasound is a safe technology that does not use radiation, which is why it is utilized in pregnant women.
What is a venous duplex?
A venous duplex combines two types of ultrasounds to produce images that show how blood is moving. Your physician is able to see the speed and direction of your blood flow and where your blood flow may be blocked. This test is commonly used to search for blood clots and to examine varicose veins. The ultrasounds used during this procedure are:
How long does it take to do a venous duplex?
The technician will apply a gel to the area of your body being examined. A transducer (ultrasound probe) is moved gently over the area being tested. This test takes approximately 30 minutes to complete.
What is the procedure used to find deep veins?
The ultrasounds used during this procedure are: B mode ultrasound – High-frequency sound waves create pictures of the veins within your arms and legs. Doppler ultrasound – High-frequency sound waves determine the speed and direction of blood flow in the veins and arteries. A venous duplex is used to: Search for deep vein thrombosis (blood clots)
Is Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center a vascular lab?
The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center's vascular lab offers more advanced testing than most other hospitals in Ohio. We are accredited by ICAVL (Intersocietal Commission for the Accreditation of Vascular Laboratories) and are actively involved in clinical research for vascular disease.
Who reviews vascular studies?
Your study will be reviewed by a vascular surgeon and the results sent to your physician. Your physician will discuss these results with you and explain what they mean in relation to your health.
What is the ultrasound of the right sapheno-femoral junction?
During Your Exam. An image from a venous duplex vascular ultrasound scan of the right Sapheno-femoral junction in the leg showing blood flow. You will be lying on the exam table on your back with your hands at your sides. The technologist will apply a warm gel to your legs and a transducer or a small microphone will be used to examine your arteries.
What is leg ultrasound?
Your doctor has requested an ultrasound of your leg veins. Ultrasound is a procedure that uses sound waves to "see" inside your body. This procedure is performed to evaluate symptoms including leg pain or swelling, excessive varicose veins, shortness of breath, or suspected blood clots in your legs and/or lungs.
Why do we do a venous duplex study?
A venous duplex study was performed for concern for deep venous thrombosis of the lower extremities.
What is the purpose of a venous blood flow test?
Common use. To assess venous blood flow in the upper and lower extremities toward diagnosing disorders such as deep vein thrombosis, venous insufficiency, causation of pulmonary embolism, varicose veins, and monitor the effects of therapeutic interventions.
How does ultrasound work?
Ultrasound (US) procedures are used to obtain information about the patency of the venous vasculature in the upper and lower extremities to identify narrowing or occlusions of the veins or arteries. In venous Doppler studies, the Doppler identifies moving red blood cells (RBCs) within the vein. The US beam is directed at the vein and through the Doppler transducer while the RBCs reflect the beam back to the transducer. The reflected sound waves or echoes are transformed by a computer into scans, graphs, or audible sounds. Blood flow direction, velocity, and the presence of flow disturbances can be readily assessed. The velocity of the blood flow is transformed as a “swishing” noise, audible through the audio speaker. If the vein is occluded, no swishing sound is heard. For diagnostic studies, the procedure is done bilaterally. The sound emitted by the equipment corresponds to the velocity of the blood flow through the vessel occurring with spontaneous respirations. Changes in these sounds during respirations indicate the possibility of abnormal venous flow secondary to occlusive disease; the absence of sound indicates complete obstruction. Compression with a transducer augments a vessel for evaluation of thrombosis. Noncompressibility of the vessel indicates a thrombosis. Plethysmography may be performed to determine the filling time of calf veins to diagnose thrombotic disorder of a major vein and to identify incompetent valves in the venous system. An additional method used to evaluate incompetent valves is the Valsalva technique combined with venous duplex imaging.
What is DVT in medical terms?
Aid in the diagnosis of superficial thrombosis or deep vein thrombosis (DVT) leading to venous occlusion or obstruction, as evidenced by absence of venous flow, especially upon augmentation of the extremity; variations in flow during respirations; or failure of the veins to compress completely when the extremity is compressed
What is the Doppler stethoscope used for?
A Doppler stethoscope is used to obtain the systolic pressure in either the dorsalis pedis or the posterior tibial artery. This ankle pressure is then divided by the highest brachial systolic pressure acquired after taking the blood pressure in both of the patient’s arms. This index should be greater than 1.
Who will discuss the results with the patient?
Inform the patient that a report of the results will be made available to the requesting HCP, who will discuss the results with the patient.
Can smoking cigarettes cause vasoconstriction?
Cigarette smoking, because nicotine can cause constriction of the peripheral vessels. Cold extremities, resulting in vasoconstriction that can cause inaccurate measurements. Occlusion proximal to the site being studied, which would affect blood flow to the area.
What is a venous duplex scan?
During an upper extremity venous duplex scan, the veins in your neck, shoulders, arms, and wrists are viewed. During a lower extremity venous duplex scan, the veins in the legs and ankles are viewed. A special jelly is placed on the area being examined while a wand-like device called a transducer is passed lightly over the skin over the vein.
What is a lower extremity duplex?
WHAT IS A LOWER EXTREMITY VENOUS DUPLEX? Lower extremity venous duplex scan is a painless exam that uses high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound) to capture images of internal veins that return blood to the heart. During an upper extremity venous duplex scan, the veins in your neck, shoulders, arms, and wrists are viewed.
What is the purpose of Doppler ultrasound?
A Doppler ultrasound may also be performed to capture images of the movement of blood through your veins. This test helps to determine how the blood is flowing through your veins .
What is the lower extremity venous system?
The lower extremity venous system arises from the inferior vena cava (IVC) which bifurcates into bilateral common iliac veins (CIV) .
What is DVT in medical terms?
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is the development of a thrombus in a deep vein.
Why do veins have valves?
Veins have lower internal pressure than arteries , they also have valves. Forward blood flow in the artery is maintained by the heart, which acts as a pump propelling the blood onward with each beat. In the veins, especially in the extremities, the limb muscles act as this pump. With each step we take the blood is ejected upward toward the heart, when the muscles relax as we lift our leg in stride, the blood descends caudally due to gravity, that is where the venous valves come into play. They prevent the back-flow of blood. Faulty valves lead to pooling of blood in the veins which overtime dilates them leading to varicose veins.
What is the protocol for bilateral EIV?
The American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine (AIUM) protocol calls for at the very least inclusion of bilateral EIV’s. If symptoms are in the calf the soleal and gastrocnemious veins may be monitored as well as the small saphenous vein.
What is the most common long term complication of VTE?
The most frequent long-term complication is post-thrombotic syndrome, which can cause pain, swelling, a sensation of heaviness, itching, and in severe cases, ulcers. [5] . Also, recurrent VTE occurs in about 30% of those in the 10 years following an inital VTE.
What are the layers of the arteries?
Veins and arteries are made up of the same 3 layers. tunica intima: Inner most layers comprised of endothelial cells. tunica media: middle layer comprised of smooth muscle. tunica adventitia/externa: external layer made up of fibrous connective tissue.
Where does the EIV extend?
We follow the EIV which extends caudally into the common femoral vein (CFV) via the inguinal canal where just below we encounter the saphenofemoral junction, (CFV and great saphenous vein).
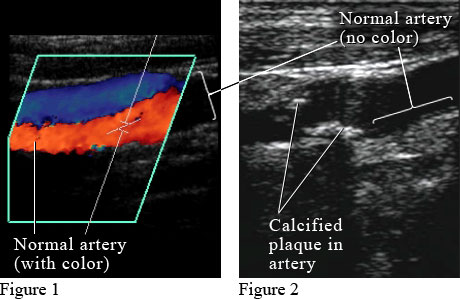
Why do you need an arterial duplex?
Your physician would order an arterial duplex when he/she suspects problems with your blood flow in your arteries or with the arteries themselves. Some of the common reasons for ordering an arterial duplex are: An aneurysm: An aneurysm in basic terms is a bulge in an artery. It could be dangerous if left unchecked.
How long does a vascular test last?
Duration. The duration of the test depends on the type of study. In general, it could last anywhere from 15 minutes to an hour and may be longer. If you have additional questions about your test, you can always ask the ordering physician or the technologist at the vascular lab where you are having your test done.
What is ultrasound study?
It is a non-invasive diagnostic medical imaging study. An ultrasound machine is used to perform the study, similar to the machine used to check on babies in pregnancy.
Can you see through gas on an ultrasound?
As we breath and talk, we start developing gas in our bowels and eating increases the build up of gas in the belly area. Ultrasound machines cannot see through gas and therefore patients are asked to fast. However, medications with a sip of water are usually fine to have before the test.
Can you have a study done on your legs?
If you are having the study done on your legs or arms, then there is no specific preparation other than having the skin of the areas of interest exposed. So you would typically be asked to remove your clothings over that area.
Can a doctor order an arterial duplex?
High blood pressure . For certain people with high blood pressure, the doctor might order an arterial duplex of the renal arteries (the arteries supplying the kidneys). These are just some of the examples where an arterial duplex can be used to help with the diagnosis of a condition. There are other reasons for ordering the study as well.
