
Full Answer
What is the meaning of allostatic load?
Definition of allostatic load : the cumulative adverse effect on the body when allostasis occurs too frequently (as when the body is subjected to repeated stressors) or is inadequate Over weeks, months, or years, exposure to increased secretion of stress hormones can result in allostatic load and its pathophysiologic consequences.
What is the definition of allostasis?
Definition of allostasis. : the process by which a state of internal, physiological equilibrium is maintained by an organism in response to actual or perceived environmental and psychological stressors Therefore, allostasis is the process that keeps the organism alive...
What is Allostatic regulation?
Allostatic regulation reflects, at least partly, cephalic involvement in primary regulatory events, in that it is anticipatory to systemic physiological regulation. This is different from homeostasis, which occurs in response to subtle ebb and flow.
What is the difference between homeostasis and allostasis?
: the process by which a state of internal, physiological equilibrium is maintained by an organism in response to actual or perceived environmental and psychological stressors Therefore, allostasis is the process that keeps the organism alive and functioning, i.e. maintaining homeostasis or “maintaining stability through change” and promoting ...
What is meant by allostatic load?
Introduction: Allostatic load refers to the cumulative burden of chronic stress and life events. It involves the interaction of different physiological systems at varying degrees of activity.
What are the 4 types of allostatic load?
The remaining panels illustrate four conditions that lead to allostatic load, namely, repeated “hits,” lack of adaptation, prolonged response, and inadequate response (McEwen, 2006a) .
What are examples of allostasis?
Some examples of allostatic states are chronic hypertension; a flattened cortisol rhythm in major depression or after chronic sleep deprivation; chronic elevation of inflammatory cytokines accompanied by low cortisol in chronic fatigue syndrome; and the lower cortisol, higher corticotropin-releasing factor and elevated ...
What is allostatic state?
An allostatic state is defined by chronic deviation of regulatory systems away from their normal state of operation, to establish a new set point (Koob and Le Moal, 2001). The limbic system, including the hippocampus and amygdala, is evidenced to mediate many neurodevelopmental consequences of childhood abuse.
How do you heal allostatic loads?
Interventions to alleviate allostatic load include improving diet, promoting regular physical activity, increasing access to social support and integration, and changing policies of the government and private sector to improve quality of life, particularly for the disadvantaged.
How do you recover from allostatic load?
Movement: Physical activity counteracts stress by increasing endorphins, supporting cognitive function, and altering blood flow to stress-affected areas of the brain. Exercise also shifts us into the present moment, focusing our attention on what we're doing right now rather than worrying about the future.
Which behaviors are an indication of allostatic overload?
Poor sleep patterns, inadequate social interaction, and altered eating patterns occur as a result of allostatic overload.
What happens during allostatic overload?
Allostatic overload occurs when the cumulative effects of physiological stress response lead to health problems, disease, or death. This is why it's estimated that stress plays a role in anywhere from 50 to 70 percent of all physical illnesses.
Does exercise increase allostatic load?
Meeting Physical Activity Guidelines Is Associated with Lower Allostatic Load and Inflammation in Mexican Americans - PMC. The .
Is allostatic load a disease?
Recap. Allostatic load refers to the damage that stress can do to the body over time. While the physical reactions that stress creates play a role in protecting the body in the short term, they exert a serious and lasting toll over the long term. This can contribute to an increased vulnerability to disease.
How do you say allostatic?
0:051:02How To Say Allostasis - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipA los tres portales a los tres esos ases a los 13 sustancias a los 3 esos ases a los tres esos ases.MoreA los tres portales a los tres esos ases a los 13 sustancias a los 3 esos ases a los tres esos ases.
Can allostatic load be reversed?
The affects of allostatic load on your body can be reversed if interventions are used early enough.
What is the difference between allostasis and allostatic load?
Allostasis is the extension of the concept of homeostasis and represents the adaptation process of the complex physiological system to physical, psychosocial and environmental challenges or stress. Allostatic load is the long-term result of failed adaptation or allostasis, resulting in pathology and chronic illness.
What increases allostatic load?
Several factors are associated with higher allostatic load, including psychosocial factors such as risky health-related behaviors and socioeconomic status. Damaging health behaviors can also increase allostatic load. Such behaviors include lack of exercise, alcohol consumption, poor sleep, smoking, and diet.
What is the importance of allostatic load?
In summary, allostatic load provides an overall and a body system-specific mechanistic link between exposures to stressors and health outcomes that may help explain health disparities among minority populations.
What are the concepts of allostasis and allostatic load?
Allostasis and allostatic load are terms which supplement the classic terms homeostasis and stress. Allostasis is the active process that leads to adaptation to a stressor, and mediators of allostasis include stress hormones as well as the autonomic nervous systems and pro-inflammatory cytokines and metabolic hormones.
How does allostatic load theory affect health?
article continues after advertisement. Allostatic load theory reminds us that the effects of stress accumulate over time and lead to poor health. But building your resilience can reduce health impacts. Review the stressors in your life and if possible, take actions to reduce them.
Why are people more vulnerable to allostatic overload?
Some people are more vulnerable to allostatic overload due to genetics or past trauma and abuse. Long-term exposure to environmental stressors like noise and crowding and to personal stressors like financial, family, or health problems, also increases vulnerability to health impacts from allostatic overload.
What is the difference between allostasis and allostatic load?
McEwan, PhD, “Whereas allostasis refers to the process of adaptation to challenges, ‘allostatic load’ refers to the price the body pays for being forced to adapt to adverse psychosocial or physical situations, and it represents either the presence of too much allostasis or the inefficient operation of the allostasis response systems, which must be turned on and then turned off again after the stressful situation is over.”
What is allostasis load?
Allostatic load refers to the wear and tear on the body that accumulates when we are exposed to repeated or chronic stressors. These stressors can be internal, external, or both. While allostasis has been traditionally examined in individuals, it undoubtedly impacts couples.
What is the effect of allostatic load on relationships?
On an interpersonal level, increased allostatic load may result in individuals experiencing difficulty in starting or maintaining relationships.
Why is it important to understand the impact of allostatic load on relationships?
Now more than ever, it is vital for PACT therapists to understand the impact of allostatic load on relationships so that we can help couples to identify and manage stressors, return to their window-of-tolerance, and resume the sensation of safety within the couple bubble. The use of these concepts will remain valuable in our work with both individuals and couples long after the COVID-19 pandemic has subsided.
What are the consequences of allostatic load?
Historically, the consequences of allostatic load have been observed as those conditions that directly impact an individual: illness, physical strain, hypertension. Undoubtedly a link exists between the individual and interpersonal consequences. Allostatic load can create concerns related to relationships, intimacy, ...
Is the LGBTQIA+ population immune to allostatic load?
COVID-19 has increased the majority of the population’s susceptibility to prolonged stress. While no one is immune to the impacts of allostatic load, it may be particularly heavy for specific populations. Women, people of color, and members of the LGBTQIA+ community often carry a uniquely dense allostatic load due to the inherent systemic challenges that they face.
What is the definition of allostasis?
The concept was named by Sterling and Eyer in 1988. Allostasis was coined from the Greek allo, which means "variable; " thus, "remaining stable by being variable". Allostatic regulation reflects, at least partly, cephalic involvement in primary regulatory events, in that it is anticipatory to systemic physiological regulation. This is different from homeostasis, which occurs in response to subtle ebb and flow. Both homeostasis and allostasis are endogenous systems responsible for maintaining the internal stability of an organism. Homeostasis is formed from the Greek adjective homoios, meaning "similar," and the noun stasis, meaning "standing;" thus, "standing at about the same level."
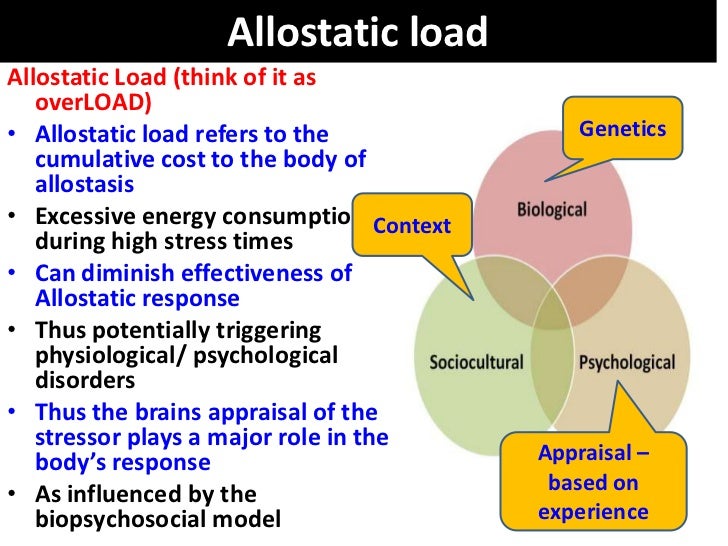
What is allostatic load?
Allostatic load refers to the cumulative cost to the body of allostasis, with allostatic overload... being a state in which serious pathophysiology can occur... Using the balance between energy input and expenditure as the basis for applying the concept of allostasis, two types of allostatic overload have been proposed.
What is allostasis compensation?
Allostasis provides compensation for various problems, such as in compensated heart failure, compensated kidney failure, and compensated liver failure. However, such allostatic states are inherently fragile, and decompensation can occur quickly, as in acute decompensated heart failure .
What is type 2 allostatic overload?
Type 2 allostatic overload begins when there is sufficient or even excess energy consumption accompanied by social conflict and other types of social dysfunction. The latter is the case in human society and certain situations affecting animals in captivity. In all cases, secretion of glucocorticosteroids and activity of other mediators of allostasis such as the autonomic nervous system, CNS neurotransmitters, and inflammatory cytokines wax and wane with allostatic load. If allostatic load is chronically high, then pathologies develop. Type 2 allostatic overload does not trigger an escape response, and can only be counteracted through learning and changes in the social structure.
How is allostasis carried out?
Mechanism. Allostasis can be carried out by means of alteration in HPA axis hormones, the autonomic nervous system, cytokines, or a number of other systems , and is generally adaptive in the short term. Allostasis is essential in order to maintain internal viability amid changing conditions.
What is the goal of allostasis?
Allostasis proposes that efficient regulation requires anticipating needs and preparing to satisfy them before they arise, as opposed to homeostasis, in which the goal is a steady state.
Who said that allostasis is no more than a renaming of the original concept of homeost?
In 2005, Trevor A. Day has argued that the concept of allostasis is no more than a renaming of the original concept of homeostasis.
What is allostatic load?
Allostatic load is defined as the cost of chronic exposure to elevated or fluctuating endocrine or neural responses resulting from chronic or repeated challenges that the individual experiences as stressful .
What are the effects of allostatic overload?
There are two distinctly different outcomes of an allostatic state in terms of allostatic load or overload. First, if energy demands exceed energy income, and also exceeds what can be mobilized from stores, then type 1 allostatic overload occurs. For example, breeding birds use increasing food abundance in spring to reproduce and raise their young. If inclement weather then increases costs of maintaining homeostasis and the allostatic load of breeding, and at the same time reduces food available to fuel that allostatic load, then negative energy balance results in loss of body mass and suppression of reproduction. Another example is the mass movement of seabirds to islands in the face of a severe storm that limit access to food. Second, if energy demands are not exceeded and the organism continues to take in or store as much or even more energy than it needs, perhaps as a result of stress-related food consumption, choice of a fat-rich diet, or metabolic imbalances (prediabetic state) that favor fat deposition, then type 2 allostatic overload occurs. Besides fat deposition, there are other cumulative changes in other systems that can result from repeated stress, for example, neuronal remodeling or loss in hippocampus, atherosclerotic plaques, left ventricular hypertrophy of the heart, glycosylated hemoglobin and other proteins by advanced glycosylation end products as a measure of sustained hyperglycemia, high cholesterol with low high-density lipoprotein (HDL), increased oxidative stress, elevated proinflammatory mediators, and chronic pain and fatigue, for example, in arthritis or psoriasis, associated with imbalance of immune mediators.
What is the term for the physiological impact of cumulative and chronic stress that results in neurological and neuroendocrinological?
Allostatic load. The physiological impact of cumulative and chronic stress that results in neurological and neuroendocrinological changes that can negatively affect tissues and organ systems of the individual.
How does allostatic load theory help us?
Allostatic load theory reminds us that the effects of stress accumulate over time and lead to poor health. But building your resilience can reduce health impacts. Review the stressors in your life and if possible, take actions to reduce them.
Why are people more vulnerable to allostatic overload?
Some people are more vulnerable to allostatic overload due to genetics or past trauma and abuse. Long-term exposure to environmental stressors like noise and crowding and to personal stressors like financial, family, or health problems, also increases vulnerability to health impacts from allostatic overload.
What is the importance of allostatic load?
Allostatic load minimizes an organism's ability to cope with and reduce uncertainty in the future.
What determines the level of allostatic load which affects the body?
Frequent stress: the magnitude and frequency of response to stress is what determines the level of allostatic load which affects the body.
What happens to an animal in type 1 allostasis?
Type 1 allostatic load occurs when energy demand exceeds supply, resulting in activation of the emergency life history stage. This serves to direct the animal away from normal life history stages into a survival mode that decreases allostatic load and regains positive energy balance. The normal life cycle can be resumed when the perturbation has passed. Typical situations ending up in type 1 allostasis are starvation, hibernation and critical illness. Of note, the life-threatening consequences of critical illness may be both cause and consequences of allostatic load.
Why is homeostasis important?
The importance of homeostasis is to regulate the stress levels encountered on the body to reduce allostatic load. Dysfunctional allostasis causes allostatic load to increase which may, over time, lead to disease, sometimes with decompensation of the allostatically controlled problem. Allostatic load effects can be measured in the body.
How does low socioeconomic status affect allostatic load?
Low socio-economic status (SES) affects allostatic load and therefore, focusing on the causes of low SES will reduce allostatic load levels. Reducing societal polarisation, material deprivation, and psychological demands on health helps to manage allostatic load. Support from the community and the social environment can manage high allostatic load. In addition, healthy lifestyle that encompasses a broad array of lifestyle change including healthy eating and regular physical exercise may reduce allostatic load. Empowering financial help from the government allows people to gain control and improve their psychological health. Improving inequalities in health decreases the stress levels and improves health by reducing high allostatic load on the body.
How to reduce the onset of high allotment?
Interventions can include encouraging sleep quality and quantity, social support, self-esteem and wellbeing, improving diet, avoiding alcohol or drug consumption and participating in physical activity. Providing cleaner and safer environments and the incentive towards a higher education will reduce the chance of stress and improve mental health significantly, therefore, reducing the onset of high allostatic load.
Does allostatic load affect thyroid homeostasis?
Whereas both types of allostatic load are associated with increased release of cortisol and catecholamines, they differentially affect thyroid homeostasis: Concentrations of the thyroid hormone triiodothyronine are decreased in type 1 allostasis, but elevated in type 2 allostasis.
