What is ABA and how does it work?
ABA at its core is a way to teach, maintain, or reduce behaviors. ABA is an umbrella term that can cover many specific and unique strategies. Some examples include Incidental Teaching, Discrete Trial Training, and Verbal Behavior.
What are the different types of ABA?
ABA is an umbrella term that can cover many specific and unique strategies. Some examples include Incidental Teaching, Discrete Trial Training, and Verbal Behavior. Most classrooms and many non-ABA practitioners utilize ABA strategies such as shaping, visual schedules, First/Then schedules, prompting, video modeling, or A-B-C data collection.
What is the difference between an ABA and a bcaba?
In many states or with insurance companies, only BCBAs are recognized as being properly authorized to oversee, manage, or supervise ABA programs. The BCaBA denotes the person is at an associate level, and must work under a BCBA. BCaBA's usually have less training or experience, although this isn’t always the case.
What are the certification levels for ABA services?
Many of the common questions asked about our services relate to certification levels. BCBA stands for Board Certified Behavior Analyst. This is the highest level of certification in the field of ABA. To be eligible for this certification, a Master’s degree (or a PhD) is required and 1,000 hours of experience working in the field.

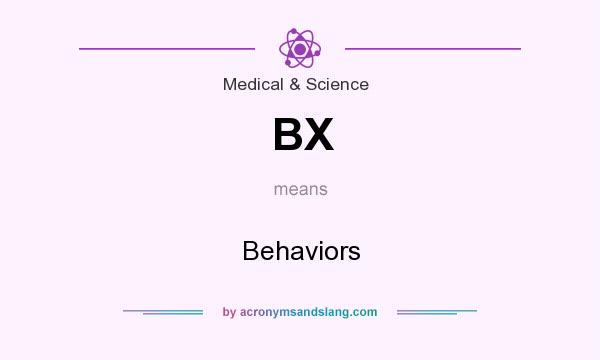
What does BX mean in mental health?
BehaviorBx. Behavior. CACF. California Alliance of Children and. Families.
What is BX therapy?
In Therapy, "Bx" is shorthand for "Behaviors". And that's exactly what Bx Builders is about—using proven therapy techniques to build prosocial behavior skills for all types of learners. Parents can access the social skills app through their therapist, or directly through the app store. READ MORE ABOUT BX FOR PARENTS.
What does it stand for in ABA?
Applied Behavior AnalysisApplied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is a therapy based on the science of learning and behavior.
What is PD in ABA?
Professional Development - ABA Pro & RBT.
What does BX modification involve?
Behavior modification is based on the idea that good behavior should lead to positive consequences and bad behavior should lead to negative consequences. Behavior modification involves positive punishment, negative punishment, positive reinforcement, and negative reinforcement.
What is an example of behavioral activation?
Increasing pleasure and meaning One of the main ways people use behavioral activation is to increase pleasurable feelings and create a sense of meaning. For example, a person who usually loves gardening may struggle with motivation when they have a depressive episode. This may mean that they stop gardening entirely.
What are the 7 components of ABA?
It is important that an individual's treatment plan has goals following these 7 dimensions: 1) Generality, 2) Effective, 3) Technological, 4) Applied, 5) Conceptually Systematic, 6) Analytic, 7) Behavioral.
What are the 4 principles of ABA?
The principles of ABA applied behavior analysis target the four functions of behavior, which include: escape or avoidance, attention seeking, access to tangibles or reinforcements, and instant gratification (or “because it feels good”).
What are the 4 functions of ABA?
They describe the 4 primary functions of behavior as access, attention, escape and automatic reinforcement.
What does pp mean in ABA?
2. Full Physical Prompt. Physically guiding the learner's hands to complete the task thoroughly. Also known as hand-over-hand assistance and is considered the most intrusive prompt.
What is PM in ABA?
Performance Management. • Performance management. – The branch of ABA that focuses on the workplace (Daniels and Bailey, 2014) – Focuses on the identification, measurement, and improvement of key aspects of employee. performance.
What is CBS in ABA?
Our program is administered as a supplementary after-school ABA therapy program.
What does a CBT therapist actually do?
CBT aims to help you deal with overwhelming problems in a more positive way by breaking them down into smaller parts. You're shown how to change these negative patterns to improve the way you feel. Unlike some other talking treatments, CBT deals with your current problems, rather than focusing on issues from your past.
What is best CBT treatment?
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a form of psychological treatment that has been demonstrated to be effective for a range of problems including depression, anxiety disorders, alcohol and drug use problems, marital problems, eating disorders, and severe mental illness.
What is MBT therapy used for?
While MBT was originally developed for the treatment of borderline personality disorder, its use has been extended to treat antisocial personality disorder, substance use disorders, eating disorders, and anxiety disorders.
What type of treatment is CBT?
Cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) is a type of talking therapy. It is a common treatment for a range of mental health problems. CBT teaches you coping skills for dealing with different problems. It focuses on how your thoughts, beliefs and attitudes affect your feelings and actions.
What is ABA in autism?
ABA- Applied Behavior Analysis is an established science that goes MUCH farther than Autism. If all you know of ABA is a treatment for young children with Autism, I highly recommend you further your reading and study of the field. ABA at its core is a way to teach, manage, or reduce behaviors. ABA is an umbrella term that can cover many specific and unique strategies. Some examples include Incidental Teaching, Discrete Trial Training, and Verbal Behavior. There are many ways to implement or carry out ABA.
What is ABA therapy?
ABA is an umbrella term that can cover many specific and unique strategies. Some examples include Incidental Teaching, Discrete Trial Training, and Verbal Behavior. There are many ways to implement or carry out ABA. ABA Therapist- This is a term I use often on my blog to describe a professional who provides ABA therapy to a learner/client/student, ...
What is a RBT?
RBT - Registered Behavior Technician. For direct level staff, this is a credential that denotes the person has met specific education and experience standards, and starting in 12/2015, that the person has passed a rigorous exam. RBT's typically implement a treatment plan designed by a BCBA or BCaBA.
What is a consultant in ABA?
Consultant- Describes anyone who creates the treatment/behavioral plans, trains and supervises staff, and may or may not assist with hiring staff. Typically this is a BCBA level individual with extensive experience and training in running an ABA program, who works independently of an agency or company.
What is an ABBLS-R?
ABBLS-R - (pronounced A-Bulls) This is an assessment tool created by Dr. Partington to help guide instruction, curriculum planning, and to target critical learning skills for Autistics or other Developmental Disabilities.
What is the ABC of behavior?
ABC's of Behavior- Also known as the Three Term Contingency, ABC's of behavior is a tool used to determine the function of any behavior. The A is for antecedent, the B is the actual behavior, and C is the consequence.
What is the preferred term for autism?
Autistic- Although some professionals continue to use person first language (e.g. individual with Autism), many advocates and Autistic support groups have stated that the preferred term is "Autistic". However, there can be variability within the Autistic community of which term is preferred.
What is ABA in psychology?
A Guide to the Acronyms of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) Applied behavior analysis is commonly referred to as ABA. That’s fairly straightforward but since it seems that everything related to ABA has its own acronym, it can get confusing from there. This blog will serve as a guide to explaining the acronyms of ABA.
What does RBT stand for in ABA?
RBT stands for Registered Behavior TechnicianTM. A RBT is a paraprofessional who practices under the close, ongoing supervision of a BCBA or BCaBA. The RBT is primarily responsible for the direct implementation of ABA services.
What is a BCBA?
Many of the common questions asked about our services relate to certification levels. BCBA stands for Board Certified Behavior Analyst. This is the highest level of certification in the field of ABA. To be eligible for this certification, a Master’s degree (or a PhD) is required and 1,000 hours of experience working in the field. At least 10% of these hours must be supervised by a current BCBA who provides feedback and ensures that services are conducted properly. There are certain Master-level programs approved by the certification board as containing adequate classwork to ensure the proper level of academic proficiency in the subject. BCBA’s may complete one of these programs or comparable schoolwork in a non-approved program. Once these requirements are complete, you must pass a certification exam which tests knowledge of principles, real-world applications, and ethics. BCBA’s can provide therapy, conduct assessments and write behavior plans, conduct program updates and supervise therapists, among other duties. BCBA’s must complete 36 hours of continuing education every three years to ensure they stay up to date on current research and practices.
What is VB in BCOTB?
VB stands for verbal behavior. This pertains to B. F. Skinner’s analysis which separated verbal behavior into categories based on function. These categories include mands (requests), labels (tacts), receptive/listener behavior (following directions), intraverbals (conversational speech), and echoics (vocal imitation). A VB program is a program like BCOTB’s which utilizes Skinner’s analysis to more effectively teach communication skills.
What is VB-MAPP?
The VB-MAPP is the Verbal Behavior Milestones Assessment and Placement Program. This is an assessment and curriculum guide which breaks verbal behavior into categories based on function and further breaks each of those categories down into individual skills. These skills are organized in the order in which a typically-developing child would develop them. This allows the assessor to evaluate the child’s current skill level as compared to the appropriate skill level for their age. From this information, the assessor can determine which skills should be targeted during therapy.
How many hours of continuing education do you need for a BCBA?
BCBA’s must complete 36 hours of continuing education every three years to ensure they stay up to date on current research and practices.
What Is Priming?
Priming is an antecedent strategy. Although we do not have a crystal ball and cannot predict the future, one strength of behavioural analysis is data collection: use data collected from past performances from similar situations.
Why Use Priming?
As an antecedent strategy, priming is used to set the stage for a desired response, or to reduce the likelihood of a challenging response.
How To Use Priming?
As an antecedent strategy, priming occurs before the event. Immediately before the triggering event, so it is fresh in mind, take the learner aside and review what is going to happen.
Remember
Use an antecedent log to record triggers to challenging behaviours. This will be informative for identifying situations where priming can be used.
blind biopsy
A biopsy taken without radiographic guidance or strong evidence of localized disease.
cone biopsy
Removal of a cone shaped piece of tissue from the uterine cervix to diagnose or treat cervical diseases. The procedure may be performed with a scalpel, carbon dioxide (CO2) laser, or Loop Electrosurgical Excision Procedure (LEEP).
endometrial biopsy
The removal of a sample of uterine endometrium for microscopic study. The procedure is commonly used in fertility assessment to confirm ovulation and to determine the cause of dysfunctional or postmenopausal bleeding.
fine needle aspiration biopsy
The removal of cells or tissue through a long, narrow-gauge needle with or without radiological guidance.
liver biopsy
1. The percutaneous removal of tissue from the liver with a large-bore needle that captures a core of tissue.
muscle biopsy
The removal of muscle tissue for microscopic examination and chemical analysis.
needle biopsy
The withdrawal of fluid or tissue by means of negative pressure applied with needle and syringe.