
the special, normal, or proper action of any part or organ. bowel function in the omaha system, the ability of the intestine to digest food and evacuate waste. genitourinary function in the omaha system, the ability of the sexual organs to reproduce and of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra to produce and excrete urine.
What are body functions?
Body functions are the physiological or psychological functions of body systems. The body's functions are ultimately its cells' functions.
What does function” mean?
At each organizational level in the body, structures are describable by different characteristics: area, thickness, macroscopic form or shape, microscopic arrangement of the parts, sequence of amino acids, etc. “Function” is defined (biologyonline.com) as “ ( biology) The special, normal, proper physiologic activity of a body part or an organ.”
What is the medical definition of anatomy?
Medical Definition of anatomy 1 : a branch of morphology that deals with the structure of organisms — compare physiology sense 1 2 : a treatise on anatomic science or art 3 : the art of separating the parts of an organism in order to ascertain their position, relations, structure, and function : dissection
What is functional anatomy?
» The BioMechanics Method What Is Functional Anatomy? Most textbooks on traditional anatomy tell us that ‘Muscle A’ goes from ‘Bone 1’ to ‘Bone 2’, and when it contracts it pulls these two bones together.
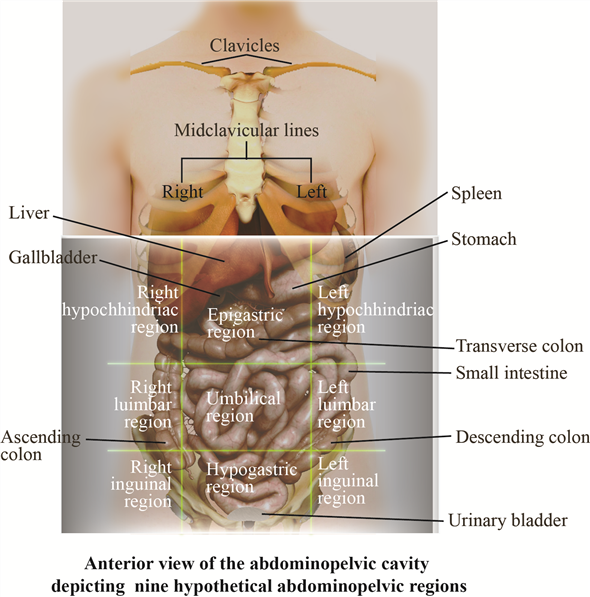
What is the function of anatomy?
Anatomy is the study of the body's structure. It is a branch of science that investigates organs, bones, structures, and cells that exist in animals and people.
What is structure and function in anatomy?
Structure refers to something's form, makeup, or arrangement. Function refers to something's job, role, task, or responsibility.
What does function mean in biology?
Definition. The activity, role, value or purpose of a part, activity, or trait of an organism.
What does function mean in physiology?
In physiology, a function is an activity or process carried out by a system in an organism, such as sensation or locomotion in an animal.
What is an example of structure and function?
This fundamental physical relationship (a relationship between structure and function) can then be applied to a number of other phenomena. For example, the movement of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs and in the tissues must meet the metabolic needs of the body.
What was the difference between structure and function?
Functions are reusable codes that perform a specific task when they are called. Derived data types are formed from fundamental data types. Structures are one such user-defined data type. The structures can have many fundamental data types known as structure members grouped into a single user-defined data type.
What means of function?
noun. the kind of action or activity proper to a person, thing, or institution; the purpose for which something is designed or exists; role. any ceremonious public or social gathering or occasion.
What is form and function in biology?
Form and function in biology describe the relationship between the shape, size, and structure of an organism, and how that structure allows for actions that aid the organism in survival.
What are the 4 functions of a structure?
25.2 The Four Structural Functions in MusicExpository function.Transitional function.Developmental function.Terminative function.
What is the cell structure and function?
Cells are the basic building blocks of all living things. The human body is composed of trillions of cells. They provide structure for the body, take in nutrients from food, convert those nutrients into energy, and carry out specialized functions.
What is an example of a physiological function?
It plays an important role in a variety of physiological functions including structural (skeletal and teeth) and signaling functions (muscle contraction, nerve impulse conduction, hormone and enzyme secretion, and as a secondary messenger in several pathways).
How are structure and function related in cells?
Research in cell structure and function seeks to determine mechanisms by which parts of cells undergo change and interact with one another in carrying out basic cellular functions. The field encompasses cell morphology, physiology, biochemistry, and molecular biology.
What is structure of anatomy?
Definitions of anatomical structure. a particular complex anatomical part of a living thing. synonyms: bodily structure, body structure, complex body part, structure.
What is a body structure?
Definition. Body structures describe the anatomic parts of the body like organs, limbs, and their components. Body structures are classified in the WHO's International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health (ICF).
Is human structure and function the same as anatomy and physiology?
Whereas anatomy is about structure, physiology is about function. Human physiology is the scientific study of the chemistry and physics of the structures of the body and the ways in which they work together to support the functions of life.
What is an example of a structure/function relationship in the human body?
The heart consists of four hollow chambers (atria and ventricles) and is made of cardiac muscle cells (Figure 18.5). This structure allows the heart to have the function of pumping blood around the body.
What is the function of the body?
Body Functions. Body functions are the physiological or psychological functions of body systems. The body's functions are ultimately its cells' functions. Survival is the body's most important business. Survival depends on the body's maintaining or restoring homeostasis, a state of relative constancy, of its internal environment.
When does the body perform its functions?
In general, the body performs its functions least well at both ends of life - in infancy and in old age. During childhood, body functions gradually become more and more efficient and effective. During late maturity and old age the opposite is true.
What is homeostasis in biology?
In his words, homeostasis "means a condition that may vary, but which is relatively constant.". Homeostasis depends on the body's ceaselessly carrying on many activities. Its major activities or functions are responding to changes in the body's environment, exchanging materials between the environment and cells, metabolizing foods, ...
What is the process of differentiation?
Differentiation is a developmental process by which unspecialized cells change into specialized cells with distinctive structural and functional characteristics. Through differentiation, cells develop into tissues and organs.
What is the term for the chemical reactions that occur in the body?
Metabolism . Metabolism is a broad term that includes all the chemical reactions that occur in the body. One phase of metabolism is catabolism in which complex substances are broken down into simpler building blocks and energy is released.
What is the act of sensing a stimulus and responding to it?
Responsiveness or irritability is concerned with detecting changes in the internal or external environments and reacting to that change. It is the act of sensing a stimulus and responding to it.
What is the term for an increase in the number of cells?
Growth. Growth refers to an increase in size either through an increase in the number of cells or through an increase in the size of each individual cell. In order for growth to occur, anabolic processes must occur at a faster rate than catabolic processes.
What is the function of the bowel?
function. the special, normal, or proper action of any part or organ. bowel function in the omaha system, the ability of the intestine to digest food and evacuate waste.
What is the definition of a physiological property?
2. Something closely related to another thing and dependent on it for its existence, value, or significance, such as growth resulting from nutrition. The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company.
What is neuromusculoskeletal function?
neuro-musculo-skeletal function in the omaha system, a client problem in the physiologic domain, defined as the ability of nerves, muscles, and bones to perform or coordinate specific activities.
What is the PSF function?
point-spread function (PSF) The mathematical description of the light distribution across the image of a point source. The shape and width of the function depends upon the amount of diffraction, aberrations and scatter and in the eye, the shape of the pupil. Its shape, which resembles a normal distribution, is conventionally defined by its 'half-width', being the width of the curve at half the peak luminance. If only diffraction is considered the point-spread function is known as Airy's disc.See Fig. D5
What is the meaning of "general properties"?
2. General properties of any substance, depending on its chemical character and relation to other substances.
How does structure determine function?
In biology, a key idea is that structure determines function. In other words, the way something is arranged enables it to play its role, fulfill its job, within an organism (a living thing). Structure-function relationships arise through the process of natural selection. But before explaining how that process works, let’s get our heads around the structure-function connection.
What determines function in engineering?
Structure determines function is also a key idea in engineering. In this human realm, structure/function relationships are often more obvious and easier to grasp than they are in the biological realm. Let’s use a hammer as an example:
What is the structure to function relationship of bats?
Structure to function relationship : The huge ears catch the echoes of the bat’s squeaks, and direct the sound to the inner ear.
What is the function of bats?
Function: Echolocation (locating objects though echoes). Bats can “see” with sound. They emit high frequency squeaks, which bounce off objects and back into the bat ’s ears . The bat’s brain can turn the sound into the equivalent of an image, and use that image to track and catch flying prey (such as moths).
What is the function of the webbing between the toes?
Structure to function relationship : The webbing between the toes acts as a fin, enabling the duck to efficiently kick in the water, moving it forward.
How do biological structures come about?
Biological structures come about as a species adapts to its environment. The result is an adaptation : a trait that helps the members of a species to survive and reproduce. Adaptation comes about through evolution, which we’ll study later in this course. But for now, let’s look at some structure function relationships in living things.
What are the functions of a nail tool?
Function: This tool has two functions. Pounding nails in, and pulling them out.
What is the macula responsible for?
It is responsible for all of our central vision and most of our color vision. The fine detail we see is made possible by the macula. Because it is responsible for our central vision, diseases involving the macula, such as macular degeneration, cause loss of central vision.
How does the macula work?
Much like film in a camera, images come through the eye's lens and are focused on the retina. The retina then converts these images to electric signals and sends them to the brain. The macula has a diameter of about 5 mm. 1 The macula can be seen with the use of an ophthalmoscope or a retinal camera.
Which part of the eye is the most important?
In the center of the macula is the fovea, perhaps the most important part of the eye. The fovea is the area of best visual acuity. It contains a large amount of cones—nerve cells that are photoreceptors with high acuity.
What is the macula in the eye?
Symptoms of Macular Damage. The macula is part of the eye's retina. Located in the center of the retina, the macula is responsible for giving us clear vision and the ability to see fine detail. Although it is small, it enables us to see " 20/20 " and to see our world in color. Learn more about the important role the macula plays inside the eye.
WHAT DO I MEAN WHEN I USE THE “STRUCTURE/FUNCTION” CORE CONCEPT?
The “structure/function” core concept is one of five core concepts that Michael and McFarland ( 5) have described as being “ways of looking at the world.” They serve as thinking tools used by physiologists when they confront any problem or question about a living organism. These concepts often represent a kind of tacit (or implicit) knowledge ( 5 ); “knowledge that usually is not openly expressed or taught” but is used in practice ( 13 ). This seems an apt description for “structure/function” for most physiology teachers.
WHAT MIGHT A CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK FOR “STRUCTURE/FUNCTION” LOOK LIKE?
My colleagues and I ( 15) have argued that when students understand a core concept, can recognize where it is applicable, and can successfully apply the concept to making sense of a physiological phenomenon, this facilitates their mastery of physiology. We also argued that one key to helping students use core concepts is to explicitly invoke them whenever they are applicable to the physiology topic at hand.
What is the definition of anatomy?
Definition of anatomy. 1 : a branch of morphology that deals with the structure of organisms. 2 : a treatise on anatomical science or art. 3 : the art of separating the parts of an organism in order to ascertain their position, relations, structure, and function : dissection.
What is anatomy for kids?
Kids Definition of anatomy. 1 : a science that has to do with the structure of living things. 2 : the structural makeup especially of a person or animal the anatomy of the cat. anatomy. noun. anat·o·my | ə-ˈnat-ə-mē. How to pronounce anatomy (audio) .
What is the meaning of "dissection"?
2 : a treatise on anatomic science or art. 3 : the art of separating the parts of an organism in order to ascertain their position, relations, structure, and function : dissection.

Organization
Metabolism
Responsiveness
Movement
Reproduction
Growth
Differentiation
Respiration
- Respiration refers to all the processes involved in the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the cells and the external environment. It includes ventilation, the diffusionof oxygen and carbon dioxide, and the transport of the gases in the blood. Cellular respiration deals with the cell's utilization of oxygen and release of carbon dioxide ...
Digestion
Excretion