Why does a chromosome have two sister chromatids
- Chromatid pairs are normally genetically identical, and said to be homozygous. ...
- Sister chromatids present at metaphase II might not be genetically identical to each other because... ...
- I presume there exists a similar argument for sister chromatids, in that they are identical. ...
What is a sister chromatid?
Sister chromatids are two identical copies of the same chromosome formed by DNA replication, attached to each other by a structure called the centromere. During cell division, they are separated from each other, and each daughter cell receives one copy of the chromosome. Differences between Sister Chromatids and Non-Sister Homologous Chromatids
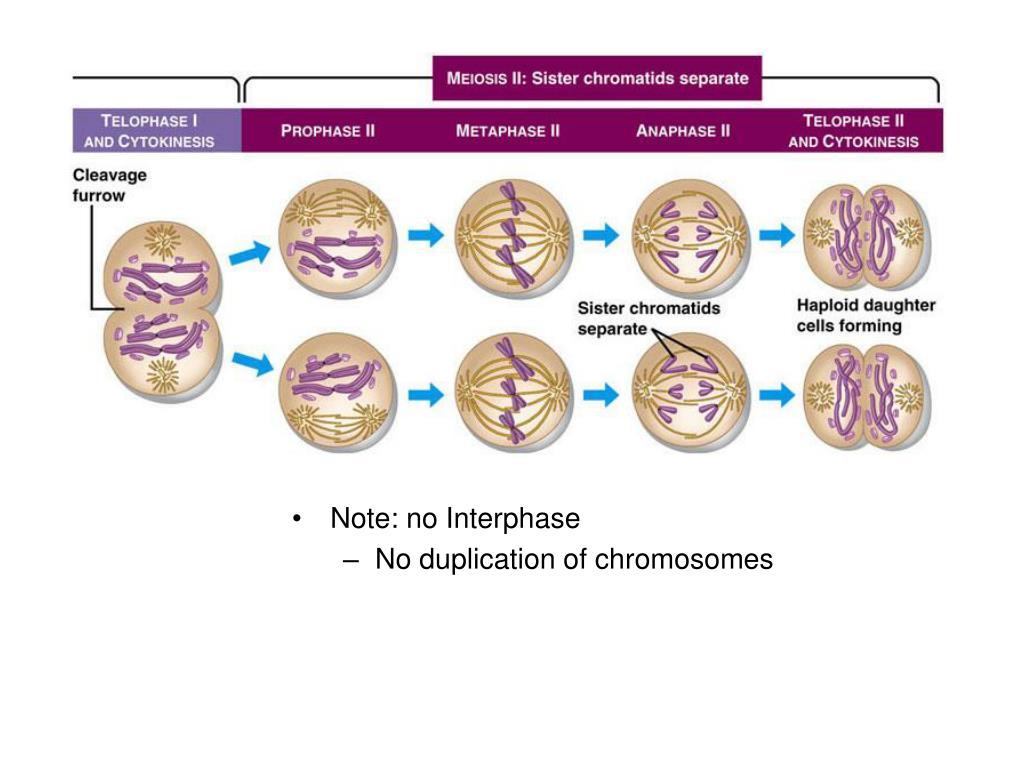
When do sister chromatids separate during meiosis?
Sister chromatids do not separate until anaphase II. Meiosis results in the production of four daughter cells, each with one half the number of chromosomes as the original cell. Sex cells are produced by meiosis.
How are sister chromatids attached to each other during prophase?
Sister chromatids are attached to each other from the time DNA is duplicated till anaphase, through the action of proteins called cohesins. Initially, cohesins are present along the entire length of the chromosome, especially around heterochromatin regions. Therefore, at prophase, sister chromatids are stuck to each other along their entire length.

Why do chromosomes contain 2 chromatids?
These chromosome copies are chromatids that have a special structure that connects the two and allows for this careful separation into new daughter cells to maintain a correct number of chromosomes in each cell.
Do chromosomes always have two sister chromatids?
Chromosomes and cell division After DNA replication, each chromosome now consists of two physically attached sister chromatids. After chromosome condensation, the chromosomes condense to form compact structures (still made up of two chromatids).
What is the purpose of sister chromatids?
Sister chromatids play an important role in meiosis in that they provide a structure for the exchange of genetic information in synapsis and ensure that the correct genetic material gets into the four genetically different cells that result from meiosis.
Why do chromosomes come in pairs?
Answer and Explanation: Your chromosomes come in pairs because humans are diploid. This means we get two copies of each chromosome, one copy from our mom and one copy from... See full answer below.
Can a chromosome have only one chromatid?
Yes, the chromosome contains one chromatid. After replication during the S-phase of the cell cycle, the chromosome consists of two identical sister chromatids.
What is the difference between a chromosome and a sister chromatid?
A chromosome is made up two Identical Sister Chromatids. And each sister chromatids are joined at the centromere....Difference between Chromosome and ChromatidChromosomes have centromeresIt is the Sister Chromatids only who have centromeres5 more rows
Why is the separation of sister chromatids important?
Sister chromatid separation in anaphase is an important event in the cell's transmission of genetic information to a descendent.
What holds 2 chromatids together?
centromeres. … that holds together the two chromatids (the daughter strands of a replicated chromosome). The centromere is the point of attachment of the kinetochore, a structure to which the microtubules of the mitotic spindle become anchored.
How many sister chromatids are in a chromosome?
2 sister chromatidsEach chromosome consists of 2 sister chromatids. The daughter cells now move in to the third and final phase of meiosis: meiosis II. At the end of meiosis I there are two haploid cells.
Is a sister chromatid a chromosome?
Sister chromatids are two identical chromatids resulting in DNA replication during the S phase of interphase. They are joined together by the centromere. A sister chromatid is a one-half of a replicated chromosome. Hence, each replicated chromosome is composed of two sister chromatids.
How many sister chromatids are there in a duplicated chromosome?
two sister chromatidsA single part of the duplicated chromosome is known as the chromatid which is separated during the cell division and each cell gets one chromatid. Thus, the duplicated chromosome has two sister chromatids.
How many chromatids are there in one duplicated chromosome?
twoBecause each duplicated chromosome consists of two identical sister chromatids joined at a point called the centromere, these structures now appear as X-shaped bodies when viewed under a microscope.
What is sister chromatid?
Updated January 23, 2019. Definition: Sister chromatids are two identical copies of a single replicated chromosome that are connected by a centromere. Chromosome replication takes place during interphase of the cell cycle. DNA is synthesized during the S phase or synthesis phase of interphase to ensure that each cell ends up with ...
How does sister chromatid separation work?
Sister chromatid separation ensures that each daughter cell gets the appropriate number of chromosomes after division.
What is the process of meiosis?
Meiosis is a two-part cell division process that is similar to mitosis. In prophase I and metaphase I of meiosis, events are similar with regard to sister chromatid movement as in mitosis. In anaphase I of meiosis, however, sister chromatids remain attached after homologous chromosomes move to opposite poles. Sister chromatids do not separate until anaphase II. Meiosis results in the production of four daughter cells, each with one half the number of chromosomes as the original cell. Sex cells are produced by meiosis.
Why is DNA synthesized during the S phase?
DNA is synthesized during the S phase or synthesis phase of interphase to ensure that each cell ends up with the correct number of chromosomes after cell division. The paired chromatids are held together at the centromere region by a special protein ring and remain joined until a later stage in the cell cycle.
How many daughter cells are produced in meiosis?
Meiosis results in the production of four daughter cells, each with one half the number of chromosomes as the original cell. Sex cells are produced by meiosis. Chromatid - one-half of two identical copies of a replicated chromosome. Chromatin - DNA and protein complex that forms chromosomes.
What is the name of the DNA strands that contain genes that code for the production of proteins?
Chromatin - DNA and protein complex that forms chromosomes. Chromosomes - DNA strands containing genes that code for the production of proteins. Daughter Chromosome - single-stranded chromosome resulting from the separation of sister chromatids. Cite this Article.
What is the structure of a chromosome that replicates before cell division?
Prior to cell division, single-stranded chromosomes replicate forming double-stranded, X-shaped structures known as sister chromatids. In preparation for cell division, chromatin decondenses forming the less compact euchromatin. This less compact form allows the DNA to unwind so that DNA replication can occur.
When DNA is transferred to the daughter cells, one of each of those chromatids is transferred to each of?
Then during mitosis, when the DNA is transferred to the two daughter cells, one of each of those chromatids is transferred to each of the two cells .
What is a chromatid in mitosis?
Then during mitosis, when the DNA is transferred to the two daughter cells, one of each of those chromatids is transferred to each of the two cells. So a chromatid is one copy of a chromosome after DNA replication.
What is a chromatid?
Chromatid. Chromatid. =. A chromatid is one of two identical halves of a replicated chromosome. During cell division, the chromosomes first replicate so that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes. Following DNA replication, the chromosome consists of two identical structures called sister chromatids, ...
What is the sister chromatid?
A sister chromatid refers to the identical copies ( chromatids) formed by the DNA replication of a chromosome, with both copies joined together by a common centromere. In other words, a sister chromatid may also be said to be 'one-half' of the duplicated chromosome. A pair of sister chromatids is called a dyad.
What is the difference between sister chromatids and homologous chromatids?
Compare sister chromatids to homologous chromosomes, which are the two different copies of a chromosome that diploid organisms (like humans) inherit, one from each parent. Sister chromatids are by and large identical (since they carry the same alleles, also called variants or versions, of genes) because they derive from one original chromosome.
What is mitotic recombination?
Mitotic recombination is primarily a result of DNA repair processes responding to spontaneous or induced damages. Homologous recombinational repair during mitosis is largely limited to interaction between nearby sister chromatids that are present in a cell subsequent to DNA replication but prior to cell division.
What is the blue chromosome?
Following chromosomal DNA replication, the blue chromosome is composed of two identical sister chromatids and the pink chromosome is composed of two identical sister chromatids. In mitosis, the sister chromatids separate into the daughter cells, but are now referred to as chromosomes (rather than chromatids) much in the way ...
Why is sister chromatid cohesion important?
Sister chromatid cohesion is essential for the correct distribution of genetic information between daughter cells and the repair of damaged chromosomes.
When are sister chromatids separated?
The two sister chromatids are separated from each other into two different cells during mitosis or during the second division of meiosis .
Does inter sister recombination occur during meiosis?
Studies with the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae indicate that inter-sister recombination occurs frequently during meiosis, and up to one-third of all recombination events occur between sister chromatids.

Chromosomes
Sister chromatids in Mitosis
- In prophase of mitosis, sister chromatids begin to move toward the cell center. In metaphase, sister chromatids align along the metaphase plate at right angles to the cell poles. In anaphase, sister chromatids separate and begin moving toward opposite ends of the cell. Once the paired sister chromatids separate from one another, each chromatidis considered a single-stranded, ful…
Sister chromatids in Meiosis
- Meiosis is a two-part cell division process that is similar to mitosis. In prophase I and metaphase I of meiosis, events are similar with regard to sister chromatid movement as in mitosis. In anaphase I of meiosis, however, sister chromatids remain attached after homologous chromosomes move to opposite poles. Sister chromatids do not separate until...
Related Terms
- Chromatid- one-half of two identical copies of a replicated chromosome.
- Chromatin- DNA and protein complex that forms chromosomes.
- Chromosomes - DNA strands containing genes that code for the production of proteins.
- Daughter Chromosome- single-stranded chromosome resulting from the separation of sister chromatids.