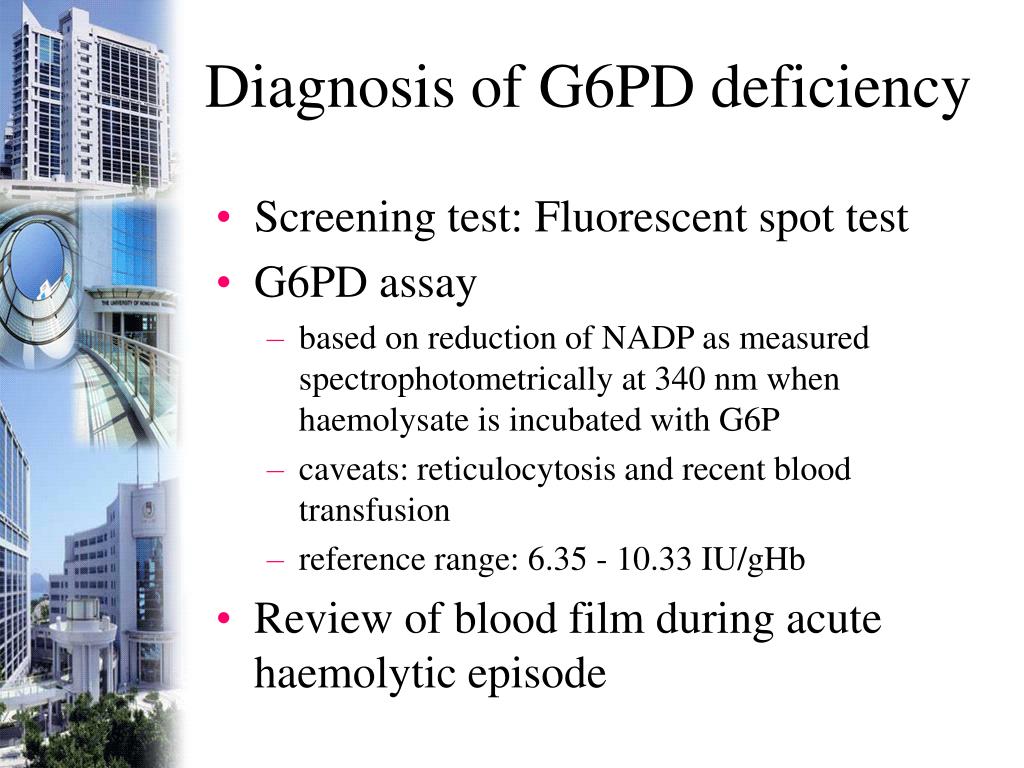
How to diagnose G6PD deficiency?
These include:
- Fatigue
- Pale skin or jaundice, a condition that causes your skin and eyes to turn yellow
- Rapid heart rate
- Shortness of breath
- Dark or yellow-orange colored urine
What causes G6PD deficiency?
Triggers can include:
- medicines such as some antibiotics, malaria medications (both for the prevention and treatment of malaria), aspirin, some anti-cancer drugs and large doses of vitamin C
- some chemicals, including mothballs (naphthalene)
- some foods, particularly fava beans (broad beans), tonic water or blueberries
- certain infections
What to avoid with G6PD deficiency?
You should avoid these antibiotics if you have G6PD deficiency:
- Sulfa drugs, including Septra and Bactrim
- Quinolones, including Cipro and Levaquin.
- Nitrofurantoin
- Dapsone
What to do with a G6PD deficiency diagnosis?
What is G6PD deficiency?
- Symptoms. G6PD is needed to replenish the antioxidant glutathione. ...
- Types. Classes 1 to 3 are clinically significant. ...
- Diagnosis. To diagnose G6PD deficiency, a healthcare professional will take a blood sample to determine the level of G6PD in your blood.
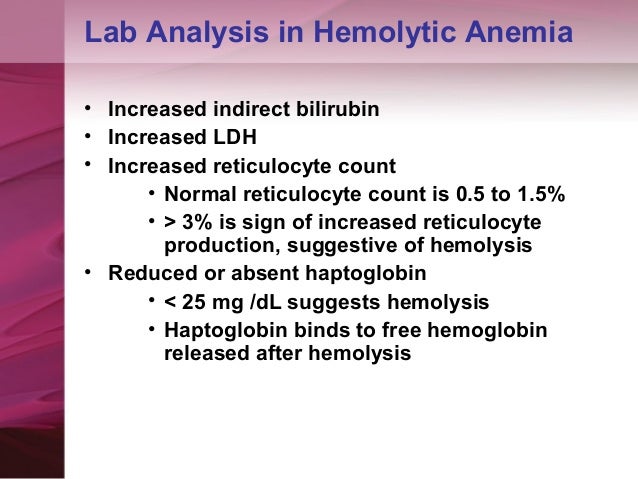
Is G6PD serious?
G6PD is a genetic disorder that happens when your body doesn't have enough glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) enzyme. G6PD helps red blood cells work and protects them from harmful substances. G6PD can cause life-threatening hemolytic anemia that requires blood transfusions.
What does a positive G6PD test mean?
A G6PD test is a blood draw to check levels of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. G6PD is an enzyme that helps your red blood cells function correctly. Low G6PD can lead to a condition called hemolytic anemia. You may need a G6PD test if you have symptoms of hemolytic anemia.
Can G6PD be treated?
There is no cure for G6PD deficiency, and it is a lifelong condition. However, most people with G6PD deficiency have a completely normal life as long as they avoid the triggers.
Is G6PD normal?
G6PD deficiency occurs most often in men. It is rare in women. The disorder affects about 10 to 14 out of 100 African-American men in the U.S. It is also common in people from the Mediterranean area, Africa, or Asia. The severity of the disorder varies, depending on the group.
Can G6PD lead to leukemia?
The results have shown that G6PD activity strongly increases in G6PD normal leukemic cells as well as in G6PD deficient leukemic cells when compared to peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC). Higher levels of G6PD gene expression were observed in leukemic cells from G6PD deficient patients compared to G6PD normal.
What are the symptoms of G6PD?
Most people with G6PD deficiency don't have any symptoms. Others might have symptoms of hemolytic anemia if many RBCs are destroyed. These can include: paleness (in darker-skinned kids, paleness is sometimes best seen in the mouth, especially on the lips or tongue)
Does G6PD affect brain?
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiencies are globally prevalent. Brain deficiencies enhance G6pd gene dose-dependent oxidative DNA damage. Deficient brains exhibit lower Purkinje cell numbers and synaptic dysfunction. G6PD-deficient mice exhibit cognitive and motor abnormalities.
Can G6PD take Covid 19 vaccine?
G6PD deficiency and COVID-19 vaccines Like routine vaccines, COVID-19 vaccines can be safely administered to people with G6PD deficiency. Clinical trials and real-world evidence have not identified any specific concerns regarding COVID-19 vaccines and people with G6PD deficiency.
Is G6PD a disability?
The medical evidence shows that the veteran's diagnosed G6PD deficiency is not a disease or disability for VA compensation purposes and there is no evidence of a superimposed disease or injury related to the veteran's G6PD deficiency during service. Service connection for a G6PD deficiency is not warranted. 38 U.S.C.A.
How do you get G6PD?
G6PD deficiency is inherited. This means it is passed down from parents through their genes. Women who carry one copy of the gene can pass G6PD deficiency to their children. Men who get the gene have G6PD deficiency.
Does G6PD affect weight?
These results reveal a complex interplay between diet-induced metabolic effects and G6PD deficiency, where G6PD deficiency decreases weight gain and hyperinsulinemia with DIO, but elevates serum free fatty acids, without affecting glucose tolerance.
What happens if G6PD is high?
Levels of G6PD are higher in the newborn than they are in the adult. When high levels are seen in older patients, it invariably reflects the presence of a young red blood cell population with reticulocytosis.
What is G6PD disease?
G6PD deficiency is an inherited condition. It is when the body doesn't have enough of an enzyme called G6PD (glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase). This enzyme helps red blood cells work properly. A lack of this enzyme can cause hemolytic anemia. This is when the red blood cells break down faster than they are made.
How do you read G6PD test results?
Here are some general results: A normal test result tells your healthcare provider about G6PD activity in your blood cells. A normal—or no G6PDD—result for adults is 5.5 to 20.5 units/gram of hemoglobin. Less than 10% of normal means that you have severe deficiency and chronic hemolytic anemia.
What is the normal result of G6PD for baby?
Results: G6PD enzyme activity was negatively correlated with age (R = -0.212, p = 0.01). For infants under 30 days of age, the G6PD enzyme activity levels were 1.4 ± 0.9 U/g Hb in hemizygotes (n = 76), 6.5 ± 2.0 U/g Hb in heterozygotes (n = 47), and 13.6 ± 3.7 U/g Hb in those without G6PD mutations (n = 70).
How do you interpret a G6PD quantitative test?
G6PD Test Results A normal measurement is 5.5 to 20.5 units/gram of hemoglobin for adults. Moderate deficiency. A moderate deficiency means the amount of G6PD enzyme in your blood is at 10% to 60% of the normal range. Someone with a moderate deficiency might have hemolytic anemia that comes and goes.
What is the G6PD test?
G6PD blood test Results Explained. A G6PD deficiency is an inherited condition. It occurs when the body does not have enough of a specific enzyme, called glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase. This enzyme helps the red blood cells be able to function in a normal way. When this deficiency is present, it may cause hemolytic anemia after exposure ...
What are the symptoms of G6PD?
These include unexplained issues with weakness or fatigue, pale skin, fainting, shortness of breath, a rapid heart rate, and an enlarged spleen.
How long does it take for a blood test to be ordered for G6PD?
As the red blood cells age, they lose up to 75% of this enzyme. Because of this, the blood test may not be ordered until several weeks after an episode with hemolytic anemia.
Can a G6PD test be duplicated?
If the blood test was performed during an episode of hemolytic anemia, however, then the test should be duplicated several weeks later to confirm the result. Women can be carriers of the genetic causes of a G6PD deficiency. This means they may have some red blood cells that are G6PD deficient and others that are not.
Can a G6PD deficient woman have anemia?
Some women, though rare, have two mutated gene copies and will always have low test results, but typically not experience anemia .
Can low G6PD be used as an indication of how someone will react?
Because of this, low test results cannot be used as an indication of how someone will react in any given set of circumstances. The signs and symptoms of a G6PD deficiency can vary from person to person and even from episode to episode. Normal test results in men are typically indicative that a deficiency is not present.
Can a blood transfusion mask G6PD?
Your medical provider may need to have your test examined by a specific laboratory and this may delay test results by several days. Blood transfusions are known to mask G6PD deficiencies. The G6PD blood test is designed to shed light on episodes of hemolytic anemia and what is causing them.
What does it mean if your G6PD result is too low?
G6PD deficiency is inherited, passed from parent to child, due to mutations or changes in the G6PD gene that cause decreased enzyme activity.
Welcome to Healthmatters Pro
Save time on interpreting lab results with the largest database of biomarkers online. In-depth research on any test at your fingertips, all stored and tracked in one place.
We implement proven measures to keep your data safe
At HealthMatters, we're committed to maintaining the security and confidentiality of your personal information. We've put industry-leading security standards in place to help protect against the loss, misuse, or alteration of the information under our control.
What is the G6PD test?
The G6PD test is a blood test that measures how much of this enzyme you have in your blood. If you have low amounts, you have a condition called G6PD deficiency.
What is the function of G6PD?
It is responsible for stopping your cells from being damaged by compounds called reactive oxygen species. Reactive oxygen species are also called free radicals.
What happens if you don't have G6PD?
When your body can’t make up for the quick loss, you can get hemolytic anemia . . Hemolytic anemia can be dangerous because it causes a loss of oxygen to your organs and tissues.
What does it mean when you have a severe G6PD deficiency?
Severe deficiency. A severe deficiency means you have less than 10% of the normal range of G6PD enzymes in your blood.
What is the normal G6PD level?
A normal test result means you have enough of the enzyme and don’t have G6PD deficiency. A normal measurement is 5.5 to 20.5 units/gram of hemoglobin for adults. Moderate deficiency. A moderate deficiency means the amount of G6PD enzyme in your blood is at 10% to 60% of the normal range. Someone with a moderate deficiency might have hemolytic ...
Does vitamin E help with G6PD?
While antioxidants do fight free radicals, they may not be helpful to this condition. Antioxidants like vitamin E don’t help G6PD deficiency. If you have G6PD deficiency, make sure to talk to your doctor about your medical history and any symptoms you’re having.
Can G6PD cause anemia?
Not everyone who has G6PD deficiency has other health problems. The deficiency alone is not enough to cause anemia or problems with your red blood cells. However, individuals who already have this mutation can have new symptoms triggered by outside sources.
What is the G6PD deficiency?
– G6PD is found in all cells, including red blood cells (RBCs) and helps protect them from certain toxic by-products of cellular metabolism. – G6PD deficiency is the lack of the G6PD enzyme in the blood.
Can G6PD cause jaundice?
G6PD deficiency is a common cause of persistent jaundice in newborns. If left untreated, this can lead to significant brain damage and mental retardation. Most people with G6PD deficiency can lead fairly normal lives, but there is no specific treatment apart from prevention.
How is G6PD passed down?
G6PD deficiency is inherited. This means it is passed down from parents through their genes. Women who carry one copy of the gene can pass G6PD deficiency to their children. Men who get the gene have G6PD deficiency. Women who get the gene are carriers. They often don’t have symptoms.
What is the G6PD deficiency?
G6PD deficiency is an inherited condition. It is when the body doesn’t have enough of an enzyme called G6PD (glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase). This enzyme helps red blood cells work properly. A lack of this enzyme can cause hemolytic anemia.
Can G6PD cause blood problems?
In most cases, G6PD defici ency does not cause problems. Problems may occur if you are exposed to medicines or foods that may harm your blood cells. Depending on your gene flaw, you may be able to handle a small amount of these exposures. Your healthcare provider will figure out the best treatment based on:
How to tell if you have G6PD?
Common symptoms of G6PD deficiency include: Rapid heart rate. Shortness of breath. Dark or yellow-orange coloured urine. Fever. Fatigue and dizziness. Paleness. Jaundice or yellowing of skin. Pain in the abdomen or back.
What does low G6PD mean?
Lower than normal levels of G6PD enzyme indicates a deficiency. G6PD protects the erythrocytes against reactive oxygen species. The deficiency can leave the RBCs vulnerable to toxic substances and may lead to their premature and rapid destruction resulting in hemolytic anemia. Low levels of G6PD in blood also lead to neonatal hyperbilirubinemia.
What to avoid with G6PD?
To manage G6PD deficiency, avoiding food and medications that may trigger the condition is often advised. Foods such as fava beans and some legumes, medications such as anti-malarial drugs, aspirin, antibiotics with sulfonamides, anti-inflammatory drugs, etc. can trigger the deficiency and hence, must be avoided. Reducing stress levels may also help in managing the symptoms of the condition.
Why does G6PD cause enzyme loss?
It is caused due to a mutation in the G6PD gene that leads to decreased enzyme activity. The condition is triggered when affected individuals are exposed to triggers such as stress, infection, fava beans, certain medications such as anti-malarial drugs, etc.
What are the symptoms of G6PD?
Common symptoms of G6PD deficiency include: 1 Rapid heart rate 2 Shortness of breath 3 Dark or yellow-orange coloured urine 4 Fever 5 Fatigue and dizziness 6 Paleness 7 Jaundice or yellowing of skin 8 Pain in the abdomen or back 9 Sudden rise in body temperature 10 Enlarged spleen 11 Gastrointestinal problems such as diarrhoea, nausea, etc.
Why do you need a follow up appointment for G6PD?
Follow-up appointments to discuss test results are often recommended. G6PD test is ordered to determine the exact causes of hemolytic anemia. This test is often ordered after the doctor has ruled out all the other causes of anemia and persistent jaundice.
Is G6PD a side effect?
A G6PD test is a simple blood test that rarely leads to any side effects. There are, however, certain minor risks associated with this test. These include heamatoma, excessive bleeding, swelling at the area from where the blood was drawn, fainting, infection at the site of puncture, etc. These side effects rarely cause any complications ...
What is the G6PD gene?
Listen. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency is caused by mutations in the G6PD gene. This gene gives the body instructions to make an enzyme called G6PD, which is involved in processing carbohydrates. This enzyme also protects red blood cells from potentially harmful molecules called reactive oxygen species.
Why is G6PD more common in males?
Because G6PD deficiency is inherited in an X-linked recessive manner, it is more common for males to have symptoms. This is because males have only one copy of the G6PD gene. If this one copy has a mutation, they will definitely have G6PD deficiency.
What is the G6PD association?
The G6PD Deficiency Association, which is an advocacy group that provides information and supportive resources to individuals and families affected by G6PD de ficiency, provides a list of drugs and food ingredients that individuals with this condition should avoid.
What is MedlinePlus Genetics?
MedlinePlus Genetics contains information on Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency.
What is the name of the enzyme that breaks down red blood cells?
It occurs when a person is missing or has low levels of the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. This enzyme helps red blood cells work properly.
Is G6PD inherited?
G6PD deficiency is inherited in an X-linked recessive manner and symptoms are more common in males (particularly African Americans and those from certain parts of Africa, Asia, and the Mediterranean). It is caused by mutations in the G6PD gene.
What do doctors look for in a diagnosis?
Healthcare professionals typically look at a person’s medical history, symptoms, physical exam, and laboratory test results in order to make a diagnosis.
What is the G6PD enzyme?
Answer: For some background, Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) is an enzyme essential for the health of red blood cells. Levels can be measured in the blood to help rule out or gauge the severity of a genetic metabolic disorder called G6PD Deficiency.
Can G6PD cause hemolysis?
Many people with G6PD feel fine but certain events (viral or bacterial infections, certain sulfa medications, certain antibiotics or eating fava/broad beans – a condition called favism) can trigger hemolysis. Less than 10% of normal indicates severe deficiency.
How to diagnose G6PD?
How’s G6PD deficiency diagnosed? Your doctor can diagnose G6PD deficiency by performing a simple blood test to check G6PD enzyme levels. Other diagnostic tests that may be done include a complete blood count, serum hemoglobin test, and a reticulocyte count.
How to tell if you have G6PD?
Symptoms of G6PD deficiency can include: rapid heart rate. shortness of breath. urine that is dark or yellow-orange. fever. fatigue. dizziness. paleness. jaundice, or yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes.
What is the role of G6PD in the body?
G6PD is also responsible for keeping red blood cells healthy so they can function properly and live a normal life span. Without enough of it, red blood cells break down prematurely. This early destruction of red blood cells is known as hemolysis, and it can eventually lead to hemolytic anemia.
What is G6PD in genetics?
G6PD deficiency is a genetic condition that is passed along from one or both parents to their child. The defective gene that causes this deficiency is on the X chromosome, which is one of the two sex chromosomes. Men have only one X chromosome, while women have two X chromosomes. In males, one altered copy of the gene is enough to cause G6PD ...
How long does it take for G6PD to go away?
Once the underlying cause is treated or resolved, symptoms of G6PD deficiency usually disappear within a few weeks.
What are the risks of G6PD?
You may have a higher risk of having G6PD deficiency if you: 1 are male 2 are African-American 3 are of Middle Eastern descent 4 have a family history of the condition
What is the G6PD?
G6PD deficiency is a genetic abnormality that results in an inadequate amount of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) in the blood. This is a very important enzyme (or protein) that regulates various biochemical reactions in the body. G6PD is also responsible for keeping red blood cells healthy so they can function properly ...