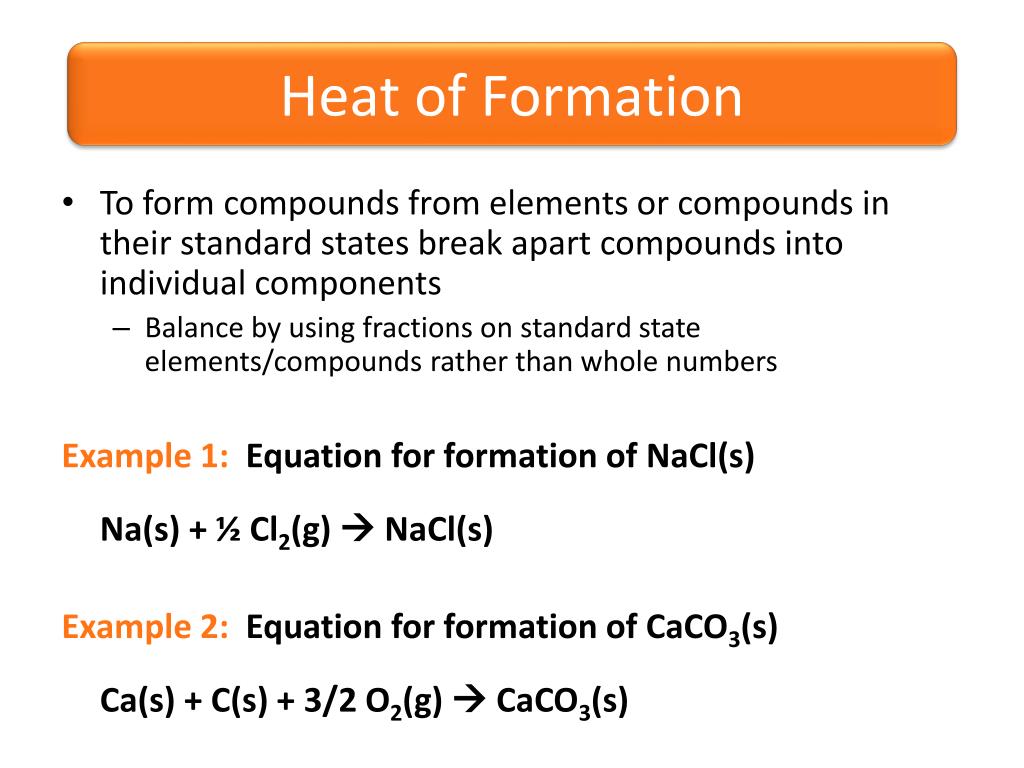
Remember, heat of formation will tell you whether heat was absorbed or released and the quantity of heat. Problem 1 Calculate ΔH for the following reaction: 8 Al (s) + 3 Fe 3 O 4 (s) → 4 Al 2 O 3 (s) + 9 Fe (s) Solution
How to calculate the standard heat of formation?
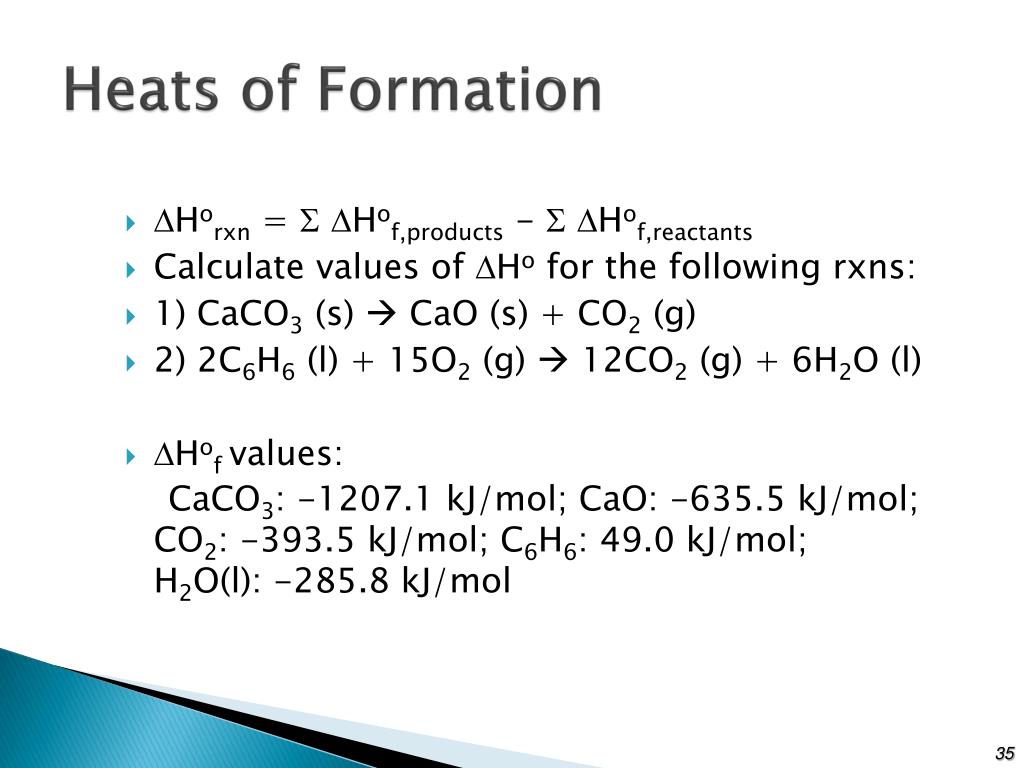
ΔH = Σ ΔHf products - Σ ΔHf reactants. Remember, the heat of formation of H + is zero. The equation becomes: ΔH = ΔHf Br - (aq) - ΔHf HBr (g) The values for ΔHf may be found in the Heats of Formation of Compounds of Ions table. Plugging in these numbers: ΔH = -120.9 kJ - (-36.2 kJ) ΔH = -120.9 kJ + 36.2 kJ.
What is the standard energy of formation?
• The standard Gibbs free energy of formation (ΔG° f ) is the free energy change for a reaction producing one mole of a substance from the elements, with all components in standard state. • As temperature changes, ΔG also changes.
What is standard enthalpy of formation?
The standard enthalpy of formation is defined as the change in enthalpy when one mole of a substance in the standard state (1 atm of pressure and 298.15 K) is formed from its pure elements under the same conditions.
What is standard molar enthalpy?
standard molar enthalpy of formation: the enthalpy change of a chemical reaction in which one mole of a pure substance is formed from the free elements in their most stable states under standard state conditions. Why is molar enthalpy used? Molar enthalpy is the energy released when the substance undergoes combustion.
What does heat of formation tell you about stability?
The heats of formation therefore permit precise comparison of the stability of isomeric compounds. The more negative the heat of formation, the greater is the stability.
What does high heat of formation mean?
Enthalpy of formation (heat of formation; ΔHfo): The hypothetical enthalpy change (ΔH) when a substance is synthesized from the corresponding elements in their standard states. A more negative (or less positive) enthalpy of formation indicates a more stable isomer.
What does heat of reaction tell us?
The heat of reaction is the energy that is released or absorbed when chemicals are transformed in a chemical reaction. It describes the change of the energy content when reactants are converted into products.
What does negative heat of formation indicate?
Negative heat of formation indicates the energy of products is lower than the energy of reactants. Hence, during the reaction, energy is released and the reaction is exothermic.
Does less heat of formation mean more stable?
The heats of formation therefore permit precise comparison of the stability of isomeric compounds. The more negative the heat of formation, the greater is the stability.
Is higher or lower heat of formation more stable?
For example, if equal quantities of two isomeric hydrocarbons burn to produce equal amounts of carbon dioxide and water, the one releasing more energy (i.e., with the higher heat of combustion) is the less stable, since it was the more energetic in its compounded form.
What does a positive heat of reaction mean?
endothermic reactiona positive value indicates the products have greater enthalpy, or that it is an endothermic reaction (heat is required) a negative value indicates the reactants have greater enthalpy, or that it is an exothermic reaction (heat is produced)
How does heat affect a chemical reaction?
When the reactants are heated, the average kinetic energy of the molecules increases. This means that more molecules are moving faster and hitting each other with more energy. If more molecules hit each other with enough energy to react, then the rate of the reaction increases.
What does it mean if the ΔH value for a chemical reaction is positive?
What does it mean if the ΔH of a process is positive? It means that the system in which the chemical reaction is occurring is gaining energy.
Is heat of formation always positive?
Is the standard enthalpy of formation always non-positive? The answer is no.
What does a formation equation show?
This equation essentially states that the standard enthalpy change of formation is equal to the sum of the standard enthalpies of formation of the products minus the sum of the standard enthalpies of formation of the reactants.
What is heat of formation in chemistry?
heat of formation, also called standard heat of formation, enthalpy of formation, or standard enthalpy of formation, the amount of heat absorbed or evolved when one mole of a compound is formed from its constituent elements, each substance being in its normal physical state (gas, liquid, or solid).
What affects heat of formation?
Standard Enthalpies of Formation. The magnitude of ΔH for a reaction depends on the physical states of the reactants and the products (gas, liquid, solid, or solution), the pressure of any gases present, and the temperature at which the reaction is carried out.
How is heat of formation related to heat of combustion?
They can be related to one another by using the sum of the heat of formation for the products and the sum of the heat of formation for the reactants and taking the difference (Hess's law) will give you the heat of combustion.
Is heat of formation endothermic or exothermic?
exothermicNote that while the majority of the values of standard enthalpies of formation are exothermic, or negative, there are a few compounds such as NO(g) and N2O4(g) that actually require energy from its surroundings during its formation; these endothermic compounds are generally unstable.
What is the meaning of enthalpy of formation?
The enthalpy of formation is the standard reaction enthalpy for the formation of the compound from its elements (atoms or molecules) in their most stable reference states at the chosen temperature (298.15K) and at 1bar pressure.
What does heat of formation tell you?
Remember, heat of formation will tell you whether heat was absorbed or released and the quantity of heat.
What is the symbol for the heat of formation?
The symbol for the standard heat of formation (also known as the standard enthalpy of formation) is ΔH f or ΔH f ° where:
What is the enthalpy change that occurs when a pure substance forms from its elements under conditions of constant?
Heat of formation is the enthalpy change that occurs when a pure substance forms from its elements under conditions of constant pressure. These are worked example problems calculating the heat of formation .
What is the measure of energy of a reaction?
Heat of formation is a measure of energy of a reaction.
How is the enthalpy of formation measured?
The standard enthalpy of formation is measured in units of energy per amount of substance, usually stated in kilojoule per mole (kJ mol −1 ), but also in kilocalorie per mole, joule per mole or kilocalorie per gram (any combination of these units conforming to the energy per mass or amount guideline).
What is the standard enthalpy of formation?
The standard enthalpy of formation or standard heat of formation of a compound is the change of enthalpy during the formation of 1 mole of the substance from its constituent elements, with all substances in their standard states. The standard pressure value p⦵ = 10 5 Pa (= 100 kPa = 1 bar) is recommended by IUPAC, ...
How to calculate the standard enthalpy of a reaction?
The standard enthalpy change of any reaction can be calculated from the standard enthalpies of formation of reactants and products using Hess's law. A given reaction is considered as the decomposition of all reactants into elements in their standard states, followed by the formation of all products. The heat of reaction is then minus the sum of the standard enthalpies of formation of the reactants (each being multiplied by its respective stoichiometric coefficient, ν) plus the sum of the standard enthalpies of formation of the products (each also multiplied by its respective stoichiometric coefficient), as shown in the equation below:
What is the enthalpy of all elements in their standard state?
All elements in their standard states ( oxygen gas, solid carbon in the form of graphite, etc.) have a standard enthalpy of formation of zero, as there is no change involved in their formation.
What is Hess's law?
Hess's law. For many substances, the formation reaction may be considered as the sum of a number of simpler reactions, either real or fictitious. The enthalpy of reaction can then be analyzed by applying Hess's Law, which states that the sum of the enthalpy changes for a number of individual reaction steps equals the enthalpy change ...
What is the formula for combustion of methane?
For example, for the combustion of methane, CH 4 + 2 O 2 → CO 2 + 2 H 2 O:
Can carbon and hydrogen react directly?
The formation reactions for most organic compounds are hypothetical. For instance, carbon and hydrogen will not directly react to form methane (CH 4 ), so that the standard enthalpy of formation cannot be measured directly. However the standard enthalpy of combustion is readily measurable using bomb calorimetry.
Enthalpy of formation and stability
How is the enthalpy of formation of a substance connected to the stability of the substance?
Re: Enthalpy of formation and stability
The larger the entropy, the more that the substance is going to be favored in a reaction. By itself, the entropy doesn't fully describe the stability of a molecule. Remember that entropy is connected to the number of states available (or the number of possible configuration a system can align with).
Why Do I Need to Understand the Heat of Reaction?
Industrial associations and federal authorities, such as CSB, OSHA (US), HSE (UK), EU-OSHA, EPSC (EU) or IPE and the State Administration of Work Safety (SAWS) in China, require chemical and pharmaceutical industries to comply with regulations that assure safe production . The directives provided focus on avoiding incidents and accidents in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries.
What Is the Heat of Reaction?
The heat of reaction, or reaction enthalpy, is an essential parameter to safely and successfully scale-up chemical processes. The heat of reaction is the energy that is released or absorbed when chemicals are transformed in a chemical reaction. It describes the change of the energy content when reactants are converted into products. While a reaction can be exothermic (heat releasing) or endothermic (heat absorbing), most of the reactions performed in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries are exothermic. Among others, the heat of reaction is one of the thermodynamic properties used in chemical development, scale-up, and safety to scale processes from the lab scale to manufacturing. The heat of reaction or reaction enthalpy is typically expressed as molar enthalpy in kJ/mol, or as specific enthalpy in kJ/kg or kJ/L.
How to find the heat of reaction enthalpy?
While the heat release rate and the heat of reaction provide information how the heat is released in function of time, the heat of reaction enthalpy is obtained by integrating the heat of reaction trend between start and end of the reaction. As all of the individual heat flow terms are relevant for the overall heat balance, care has to be taken to determine them as accurately as possible.
What are the key parameters necessary to create cooling failure scenarios of the desired reaction?
The accumulation of starting material, the heat of reaction, the enthalpy of reaction and the specific heat are some of the key parameters necessary to create cooling failure scenarios of the desired reaction. However, more advanced studies, such as the evaluation of worst case scenarios, criticality class or the criticality matrix, use the information from the heat of reaction to the same extent.
How to calculate heat of reaction?
The heat of reaction can be calculated based on the standard heat of formation of all reactants involved. However, it is usually determined by measuring the heat production over time using a reaction calorimeter, such as a heat flow calorimeter.
Why is heat flow calorimetry important?
Immune and robust against external influence, heat flow calorimetry allows to accurately and precisely measure the evolution of heat under process conditions. Measuring the "true" heat of reaction is the basis to understanding the progress of chemical reactions, their kinetics and its hazard potential.
Why is the heat release rate needed?
Thus, the heat release rate of a chemical process needs to be designed to be within a certain range of heat production rate to ensure that the reaction can be run safely, irrespective of the total heat of reaction.
Why do chemical bonds form?
Chemical bonds form because they're thermodynamically favorable, and breaking them inevitably requires adding energy. For this reason, bond enthalpy values are always positive, and they usually have units of or . The higher the bond enthalpy, the more energy is needed to break the bond and the stronger the bond. To determine how much energy will be released when we form a new bond rather than break it, we simply make the bond enthalpy value negative.
What happens to the energy of a chemical reaction?
During chemical reactions, the bonds between atoms may break, reform or both to either absorb or release energy. The result is a change to the potential energy of the system. The heat absorbed or released from a system under constant pressure is known as enthalpy, and the change in enthalpy that results from a chemical reaction is the enthalpy of reaction. The enthalpy of reaction is often written as .
How do bond enthalpy and enthalpy of reaction help us understand how a chemical system?
Bond enthalpy and enthalpy of reaction help us understand how a chemical system uses energy during reactions. The bond enthalpy describes how much energy is needed to break or form a bond, and it is also a measure of bond strength. By combining the bond enthalpy values for all of the bonds broken and formed during a reaction, it's possible to estimate the total change in potential energy of the system, which is for a reaction at constant pressure. Depending on whether the enthalpy of reaction is positive or negative, we can determine whether a reaction will be endothermic or exothermic.
Why are average bond enthalpies available?
Because bond enthalpy values are so useful, average bond enthalpies for common bond types are readily available in reference tables. While in reality the actual energy change when forming and breaking bonds depends on neighboring atoms in a specific molecule, the average values available in the tables can still be used as an approximation.
How to find the enthalpy of a reaction?
In order to quantify the enthalpy of reaction for a given reaction, one approach is to use the standard enthalpies of formation for all of the molecules involved. These values describe the change in enthalpy to form a compound from its constituent elements. Subtracting the standard enthalpies of formation for the reactants from the standard enthalpies of the products approximates the enthalpy of reaction for the system. To learn more about enthalpies of formation (which are also called heats of formation) and how to use them to calculate the enthalpy of reaction, you can check out our video on standard heat of formation and the video on using heats of formation to calculate reaction enthalpies.
What is the energy of chemical bonds?
Chemical bonds represent potential energy. Quantifying the energy represented by the bonds in different molecules is an important part of understanding the overall energy implications of a reaction. In this article, we'll explore two different concepts that help describe that energy: enthalpy of reaction and bond enthalpy.
Is hydrogenation endothermic or exothermic?
Reactions where the products have a lower potential energy than the reactants, such as the hydrogenation of propene described above, are exothermic. Reactions where the products have a higher potential energy than the reactants are endothermic.
/GettyImages-1030583994-adf7d29a0f994f2f9301ca1e1acf92d7.jpg)