
X-linked recessive inheritance is a mode of inheritance in which a mutation in a gene on the X chromosome
X chromosome
The X chromosome is one of the two sex-determining chromosomes (allosomes) in many animal species, including mammals (the other is the Y chromosome), and is found in both males and females. It is a part of the XY sex-determination system and X0 sex-determination …
Zygosity
Zygosity is the degree of similarity of the alleles for a trait in an organism. Most eukaryotes have two matching sets of chromosomes; that is, they are diploid.
Full Answer
What is the meaning of X linked recessive inheritance?
Freebase(0.00 / 0 votes)Rate this definition: X-linked recessive inheritance. X-linked recessive inheritance is a mode of inheritance in which a mutation in a gene on the X chromosome causes the phenotype to be expressed in males and in females who are homozygous for the gene mutation.
Why do X-linked recessive conditions occur more frequently in males?
Because it's less likely that females will have a variant on both X chromosomes, X-linked recessive conditions tend to occur more frequently in males than in females. We'll use an X-linked recessive condition called G6PD deficiency as an example.
What is an example of X-linked recessive anemia?
We'll use an X-linked recessive condition called G6PD deficiency as an example. G6PD deficiency is a common genetic condition characterized by episodes of anemia.
What is meant by X-linked recessive?
X-linked recessive inheritance is a way a genetic trait or condition can be passed down from parent to child through mutations (changes) in a gene on the X chromosome. In males (who only have one X chromosome), a mutation in the copy of the gene on the single X chromosome causes the condition.
What is an example of an X-linked recessive trait?
Examples of X-linked recessive conditions include red-green color blindness and hemophilia A: Red-green color blindness. Red-green color blindness simply means that a person cannot distinguish shades of red and green (usually blue-green). Their visual acuity (ability to see) is normal.
What is the difference between X-linked recessive and dominant?
Sex-linked diseases are passed down through families through one of the X or Y chromosomes. X and Y are sex chromosomes. Dominant inheritance occurs when an abnormal gene from one parent causes disease, even though the matching gene from the other parent is normal.
How do you know if a trait is X-linked recessive?
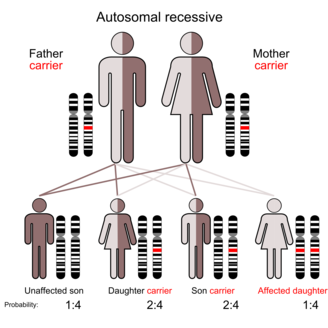
Determine if the chart shows an autosomal or sex-linked (usually X-linked) trait. For example, in X-linked recessive traits, males are much more commonly affected than females. In autosomal traits, both males and females are equally likely to be affected (usually in equal proportions).
What genes are inherited from mother only?
Our mitochondrial DNA accounts for a small portion of our total DNA. It contains just 37 of the 20,000 to 25,000 protein-coding genes in our body. But it is notably distinct from DNA in the nucleus. Unlike nuclear DNA, which comes from both parents, mitochondrial DNA comes only from the mother.
How do you know if you have dominant or recessive genes?
The way people write out dominant and recessive traits is the dominant one gets a capital letter and the recessive one a lower case letter. So for eye color, brown is B and blue is b. As I said above, people have two versions of each gene so you can be BB, Bb, or bb--BB and Bb have brown eyes, bb, blue eyes.
What genes do fathers pass on?
Genetics of Inheritance While moms pass down an X chromosome to their children—since women have two x chromosomes—dads pass down either an X or Y chromosome. The presence of a Y chromosome determines whether your baby's a boy or a girl.
Is Down's syndrome recessive or dominant?
Like cystic fibrosis, Down's Syndrome is autosomal recessive. This means that the condition is genetic and passed down by the mother and/or the father but the condition is not shown in the parents. An autosomal recessive disorder requires two copies of the abnormal gene for the disease or trait to develop.
What is inherited from father?
We inherit a set of 23 chromosomes from our mothers and another set of 23 from our fathers. One of those pairs are the chromosomes that determine the biological sex of a child – girls have an XX pair and boys have an XY pair, with very rare exceptions in certain disorders.
What is X-linked recessive inheritance?
X-linked recessive inheritance occurs with a variety of IMDs, for example: OTC deficiency; pyruvate dehydrogenase complex deficiency; Hunter syndrome (mucopolysaccharidosis type II); Lesch–Nyhan syndrome (a purine disorder); Fabry disease (sphingolipidosis), and ALD. This pattern of inheritance is characterized by carrier females (unaffected, as they have a normal copy of the gene on their other X chromosome) passing the gene to their affected sons (the Y chromosome does not carry the gene so there is no normal copy) (Fig. 24.3 A). The chance of a son being affected is 1 in 2 in each pregnancy, the same as the risk of a daughter being a carrier. As the affected gene lies on the X chromosome, affected fathers can only pass it to their daughters, who will be obligate carriers.
Which royal family has X-linked recessive disease?
No doubt the most famous family to be afflicted with an X-linked recessive condition is the House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha, the British Royal family . Queen Victoria, apparently a carrier of a new hemophilia A mutation, had one affected son, Prince Leopold, and two daughters who were carriers of the disease.
What are the characteristics of X chromosomes?
No special characteristics of the X chromosome distinguish it from an autosome other than size and the genes found on the chromosome , but these features distinguish all chromosomes from each other. X chromosome inheritance, often called X-linked or sex-linked, is remarkable because there is only one X chromosome in males. Most of these alleles are therefore hemizygous, or present in only one copy, in the male because there are no corresponding homologous alleles on the Y chromosome, with the exception of those in the pseudoautosomal pairing region (see Chapter 11, Fig. 11-1 ). Presence of a mutant allele on the X chromosome in a male is expressed, whereas in the female a single mutant allele may have a corresponding normal allele to mask its effects, as expected in the situation of dominance versus recessiveness.
How is X linked inheritance distinguished?
As noted, X-linked inheritance is distinguished by the presence of one chromosome in males but two in females. To explain the appearance of a condensed body in female cells, known as a Barr body, and to justify the possibility of twice as many X chromosome gene products in females as in males, the Lyon hypothesis was proposed. This hypothesis, which has been become well established, recognizes the Barr body in female cells as an inactivated X chromosome. Through inactivation, dosage compensation occurs that generally equalizes the expression between males and females.
How many chances are there of a son being affected?
The chance of a son being affected is 1 in 2 in each pregnancy , the same as the risk of a daughter being a carrier. As the affected gene lies on the X chromosome, affected fathers can only pass it to their daughters, who will be obligate carriers.
Where is the XIST gene located?
This gene is expressed only from the inactive X chromosome and is a key component of the X inactivation center (XIC) found at the proximal end of Xq. The cell recognizes the number of X chromosomes by the number of XICs in the cell.
Can a male transmit X-linked recessive disorder to a grandson?
However, males may transmit the disorder to a grandson through carrier female daughters. It is not uncommon for X-linked recessive disorders to appear in a family such that before a certain generation the disease is not apparent, but is observed to be segregating in the family after that generation.
What is X linked recessive inheritance?
X-linked recessive inheritance is an inheritance pattern that's specific for certain genetic variants found on the X chromosome. Since the number of X chromosomes a person has depends on his or her genetic sex, disease-causing variants found in genes on ...
Why do X-linked recessive conditions occur more frequently in males than females?
Because it's less likely that females will have a variant on both X chromosomes, X-linked recessive conditions tend to occur more frequently in males than in females. We'll use an X-linked recessive condition called G6PD deficiency as an example. G6PD deficiency is a common genetic condition characterized by episodes of anemia. ...
Can a single genetic variant cause recessive disease?
Since the number of X chromosomes a person has depends on his or her genetic sex, disease-causing variants found in genes on the X chromosome have different implications for males and females. For males (who only have one X chromosome), a single genetic variant is sufficient to cause an X-linked recessive condition.
Can a female inherit G6PD?
In most cases, female children who inherit this variant are not expected to develop symptoms of G6PD deficiency unless they also inherit a variant from their father. Males with a variant in the G6PD gene will pass this variant on to their female children but will not pass this variant on to their male children.
What are some of the different types of X-linked recessive conditions?
Examples of X-linked recessive conditions include red-green color blindness and hemophilia A:
How many copies of X-linked recessive genes are there?
X-linked recessive genes are expressed in females only if there are two copies of the gene (one on each X chromosome). However, for males, there needs to be only one copy of an X-linked recessive gene in order for the trait or disorder to be expressed.
What is X linked inheritance?
X-linked inheritance means that the gene causing the trait or the disorder is located on the X chromosome. Females have two X chromosomes; males have one X and one Y. Genes on the X chromosome can be recessive or dominant. Their expression in females and males is not the same.
What is the chance that a daughter will not carry the gene?
There is a 50 percent chance that a daughter will not carry the gene and, therefore, cannot pass it on. There is a 50 percent chance that sons do not have the gene and will be healthy. However, there is a 50 percent chance that a son will have inherited the gene and will express the trait or disorder.
Why are males more likely to be affected by color recognition?
Males are affected more often than females, because the gene is located on the X chromosome.
Can a woman carry a recessive gene?
For example, a woman can carry a recessive gene on one of the X chromosomes unknowingly, and pass it on to a son, who will express the trait: There is a 50 percent chance that daughters carry the gene and can pass it to the next generation.
How many mutations of the WAS gene have been identified?
These individuals also will have absent immunologic responses to polysaccharide antigens, and a subset of patients will develop malignancies, primarily lymphomas and leukemias. More than 300 mutations of the WAS gene on the X chromosome have been identified, with the majority of missense mutations in exons 1–4.
Can a male transmit X-linked recessive disorder to his daughter?
Daughters of normal transmitting males. In most X-linked recessive disorders, such as BMD or DMD, the mutation cannot be passed from a healthy male, such as III:1 in Figure 1, to his daughters. This is because the mutations tend to be fully penetrant as males are hemizygous for X-linked genes.
What is X linked recessive inheritance?
X-linked recessive inheritance is a mode of inheritance in which a mutation in a gene on the X chromosome causes the phenotype to be expressed in males and in females who are homozygous for the gene mutation. X-linked inheritance means that the gene causing the trait or the disorder is located on the X chromosome. Females have two X chromosomes, while males have one X and one Y chromosome. Carrier females who have only one copy of the mutation do not usually express the phenotype, although differences in X chromosome inactivation can lead to varying degrees of clinical expression in carrier females since some cells will express one X allele and some will express the other. The current estimate of sequenced X-linked genes is 499 and the total including vaguely defined traits is 983. Some scholars have suggested discontinuing the terms dominant and recessive when referring to X-linked inheritance due to the multiple mechanisms that can result in the expression of X-linked traits in females, which include cell autonomous expression, skewed X-inactivation, clonal expansion, and somatic mosaicism.
Which hereditary pattern results in the manifestation of characteristics in male offspring and a carrier state in female offspring?
hereditary pattern in which a recessive gene on the X chromosome results in the manifestation of characteristics in male offspring and a carrier state in female offspring
What is X Linked Recessive?
X linked recessive is a condition caused due to recessive mutant genes located in X chromosomes. In females, two mutant gene copies are needed for the disease occurrence. If one mutant copy is present, the normal copy can compensate for the changed copy. She is only a healthy carrier. But in males, one mutant copy is sufficient to cause the X linked recessive disease since males carry only one X chromosome. Males do not carry another copy to compensate the mutant copy like in females.
Why do X linked dominant and X linked recessive disorders occur?
X linked dominant and X linked recessive disorders occur due to the mutations in genes on the X chromosome.
What is the Difference Between X Linked Dominant and X Linked Recessive?
In contrast, X linked recessive is a genetic condition caused due to one or two mutant recessive genes on the X chromosomes. So, this is the key difference between X linked dominant and X linked recessive. Also, X linked dominant disorders are less common than X linked recessive disorders.
How many copies of mutant genes are needed to cause X linked dominant disorder?
But in females, one copy of the mutant gene is enough to cause the X linked dominant disorder while two copies of mutant genes are needed to cause the X linked recessive disorder. Females that carry one recessive mutant gene in one X chromosome are carriers.
Why do males have only one X chromosome?
Females have two X chromosomes, while males have only one X chromosome. In males, one copy of the mutant gene is enough to cause X linked dominant or X linked recessive disorders.
What is X linked dominant?
X linked dominant is a disorder caused by a mutation in genes on the X chromosome. Only one copy of the mutant gene is sufficient for the disease to occur in both males and females. Some X linked dominant disorders are lethal in males. Moreover, males show severe symptoms of the X linked dominant disorder than females.
Is X linked dominant or recessive?
Moreover, in X linked dominant, only one copy is sufficient to cause the disease in both males and females. In X linked recessive, one copy is sufficient to cause the disease in males, but both copies are needed to cause the disease in females. Hence, this is another significant difference between X linked dominant and X linked recessive .
