Explore
If your MCV goes up, it could indicate:
- Low vitamin B12 level
- Folate deficiency ( folic acid is a nutrient)
- Liver disease
- Alcoholism
- Hypothyroidism
- Carbon monoxide poisoning
- Aplastic anemia (a condition where the body stops producing sufficient red blood cells)
- Cold agglutinin disease (a condition where the body’s immune system attacks your red blood cells and destroys them)
What are the causes of high MCV count?
Usually, macrocytosis is caused by nutritional deficiency, specifically of folate or vitamin B12. This can arise from a hereditary condition called pernicious anemia, in which a protein called intrinsic factor is lacking in your gut.
What is the cause of macrocytosis?
Medical Definition of macrocytic. : of or relating to macrocytes specifically, of an anemia : characterized by macrocytes in the blood pernicious anemia is a macrocytic anemia.
What does macrocytic mean in medical dictionary?
Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV)
- Low MCV. A low MCV indicates that the red blood cells are small, or microcytic.
- High MCV. A high MCV implies the red blood cells are larger than normal, or macrocytic.
- Normal MCV. It's important to note that a person can have anemia and have a normal MCV. This is called a normocytic anemia.
What does it mean if your MCV is high?

What is macrocytic anemia caused by?
What causes macrocytic anemia? People may develop macrocytic anemia when they don't get enough vitamin B12 and/or folate (vitamin B9) to create healthy red blood cells, or they have medical conditions that prevent their bodies from absorbing those nutrients.
Is macrocytosis serious?
How serious is macrocytosis? Macrocytosis is usually mild to moderate but can become severe. It can be due to a manageable cause (such as a vegan diet, which can be treated with supplements)3 or be due to a serious illness, such as liver disease or cancer.
What problems does macrocytosis cause?
Macrocytosis can signify an underlying condition, such as nutritional deficiency, liver disease, bone marrow disorders, and more. In severe cases, macrocytosis can lead to neurological symptoms. These include confusion, dementia, depression, loss of balance, and numbness or tingling in the arms and legs.
How do I know if I have macrocytic anemia?
Your doctor will order blood tests to check for anemia and enlarged red blood cells. If your complete blood count indicates anemia, your doctor will do another test known as a peripheral blood smear. This test can help spot early macrocytic or microcytic changes to your red blood cells.
How do you fix macrocytosis?
Management of macrocytosis consists of finding and treating the underlying cause. In the case of vitamin B-12 or folate deficiency, treatment may include diet modification and dietary supplements or injections. If the underlying cause is resulting in severe anemia, you might need a blood transfusion.
Should I be concerned about macrocytosis?
While it isn't a condition of its own, macrocytosis is a sign that you have an underlying health condition and may lead to a severe form of anemia called macrocytic normochromic anemia.
What are the two most common causes of Macrocytic anemia?
Alcohol use accounts for the majority, followed by deficiencies in folate and vitamin B12 and medications. Autoimmune causes are more common in middle-aged women. Hypothyroidism and primary bone marrow disease account for more cases of macrocytic anemia in older patients.
What medications can cause macrocytosis?
Common drugs that cause macrocytosis are hydroxyurea, methotrexate, zidovudine, azathioprine, antiretroviral agents, valproic acid, and phenytoin (Table 1).
What cancers cause high MCV levels?
Liver cancer is the most associated type of cancer with high MCV levels since liver dysfunctions lead to more fats adhering to the membrane of the red blood cells, increasing their surface levels. Other cancers could also lead to macrocytic anemia such as colorectal and esophageal cancers.
Who is at highest risk for Macrocytic anemia?
Common risk factors of megaloblastic anemia include nutritional factors, alcoholism, elderly, pregnant, vegans, and malabsorptive syndromes.
What type of doctor treats Macrocytic anemia?
If you suspect that you have vitamin deficiency anemia, you're likely to start by seeing your family doctor or a general practitioner. However, in some cases, you may be referred to a doctor who specializes in treating blood disorders (hematologist).
What vitamin deficiency can cause macrocytic anemia?
Macrocytic anemia is a blood disorder that causes your bone marrow to make abnormally large red blood cells. It's also a type of vitamin deficiency anemia. This condition happens when you don't get enough vitamin B12 and/or vitamin B9 (folate).
How serious is macrocytosis without anemia?
Macrocytosis without anemia is unlikely to result in specific signs or symptoms, and in many cases, may have minimal clinical significance. Patients should be screened for symptoms of anemia, including fatigue, generalized weakness, dyspnea, palpitations, lightheadedness, and syncopal or near-syncopal events.
Why does macrocytosis occur?
Macrocytosis can occur when there is increased RBC production secondary to peripheral blood cell destruction (i.e., hemolysis) or loss (i.e., hemorrhage), leading to a reticulocytosis. Reticulocytes are incompletely processed RBCs and, therefore, are slightly larger than the average RBC.
Should I worry about high MCV?
Moreover, a high MCV is associated with increased all-cause mortality and cancer mortality in non-anemic cancer-free individuals [3].
How long does it take for MCV to return to normal?
Because the MCV usually returns to normal within 2 to 4 months of abstinence, the increase in RBC size apparently is a direct effect of alcohol on RBC production.
What are the two types of macrocytic anemia?
Macrocytic anemia can be broken into two main types: megaloblastic and nonmegaloblastic macrocytic anemias.
What test can you do to check for anemia?
Blood tests. Your doctor will order blood tests to check for anemia and enlarged red blood cells. If your complete blood count indicates anemia, your doctor will do another test known as a peripheral blood smear. This test can help spot early macrocytic or microcytic changes to your red blood cells.
What is the difference between macrocytosis and anemia?
Macrocytosis is a term used to describe red blood cells that are larger than normal. Anemia is when you have low numbers of properly functioning red blood cells in your body. Macrocytic anemia, then, is a condition in which your body has overly large red blood cells and not enough normal red blood cells.
How do you know if you have macrocytic anemia?
You may not notice any symptoms of macrocytic anemia until you’ve had it for some time. Symptoms include: loss of appetite or weight. brittle nails. fast heartbeat. diarrhea. fatigue. pale skin, including lips and eyelids.
Why is it important to have a blood test for macrocytosis?
Additional blood tests can also help find the cause of your macrocytosis and anemia. This is important because treatment depends on the underlying cause. While nutrient deficiencies cause most macrocytic anemias, other underlying conditions may cause the deficiencies.
What medications are used for HIV?
some medications, such as chemotherapy drugs like hydroxyurea, antiseizure medications, and antiretroviral drugs used for people with HIV
What doctor can diagnose anemia?
They may also do blood tests to check for alcohol use disorder, liver disease, and hypothyroidism. Your primary care doctor may also refer you to a hematologist. Hematologists specialize in blood disorders. They can diagnose the cause and specific type of your anemia.
What is the term for red blood cells that are larger than normal?
Macrocytosis is a term used to describe red blood cells that are larger than normal. Also known as megalocytosis or macrocythemia, this condition typically causes no signs or symptoms and is usually detected incidentally on routine blood tests.
What causes macrocytosis?
Common causes of macrocytosis include: Vitamin B-12 deficiency. Folate deficiency. Liver disease. Alcoholism. Hypothyroidism. A side effect of certain medications, such as those used to treat cancer, seizures and autoimmune disorders. Increased red blood cell production by the bone marrow to correct anemia, for example, after blood loss.
What causes increased red blood cell production in the bone marrow?
Increased red blood cell production by the bone marrow to correct anemia, for example, after blood loss. An underlying bone marrow cancer called myelodysplastic syndrome. If you have macrocytosis, blood tests can help determine its cause.
What is macrocytic anemia?
Macrocytic anemia refers to macrocytosis (mean corpuscular volume (MCV) greater than 100 fL) in the setting of anemia (hemoglobin less than 12 g/dL or hematocrit (Hct) less than 36% in nonpregnant females, hemoglobin less than 11 g/dL in pregnant females, or hemoglobin less than 13 g/dL or Hct less than 41% in males). It is divided into two forms, megaloblastic (hypersegmented neutrophils) and non-megaloblastic. The megaloblastic form is due to impaired DNA synthesis from folate and/or vitamin B12 deficiencies, while the non-megaloblastic moiety occurs from multiple mechanisms.There are many etiologies for macrocytic anemia, decreased hemoglobin with elevated mean corpuscular volume (>100 fL), several of which are easily treatable and some that that are life-threatening. This activity describes the evaluation, diagnosis, and management of macrocytic anemia and highlights the role of team-based interprofessional care for affected patients.
How to calculate corpuscular volume?
The equation for mean corpuscular volume [MCV (fL) = Hct (%) X 10 / RBC (106/microgram)] explains how macrocytic anemia represents large red blood cells (RBCs) in comparison to total amount. Folate and vitamin B12 are necessary for RBC nucleic acid synthesis. Without DNA or RNA, erythropoiesis is ineffective with nuclear/cytoplasmic asynchrony, resulting in larger erythrogenic precursors with abnormal nuclei (ex. hypersegmentation) but normal cytoplasms. Anemia occurring in the presence of macrocytosis and hypersegmented neutrophils is known as megaloblastic anemia. The absence of hypersegmented neutrophils characterizes non-megaloblastic anemia. This occurs from mechanisms discussed earlier: abnormalities involving the RBC membrane, excess erythrocytic precursors, increased cell volume, or RBC toxicity.
What is the mean corpuscular volume of anemia?
Macrocytic anemia refers to macrocytosis (mean corpuscular volume (MCV) greater than 100 fL) in the setting of anemia (hemoglobin less than 12 g/dL or hematocrit (Hct) less than 36% in nonpregnant females, hemoglobin less than 11 g/dL in pregnant females, or hemoglobin less than 13 g/dL or Hct less than 41% in males). It is divided into two forms, megaloblastic (hypersegmented neutrophils) and non-megaloblastic. The megaloblastic form is due to impaired DNA synthesis from folate and/or vitamin B12 deficiencies, while the non-megaloblastic moiety occurs from multiple mechanisms.[1][2]
What does a physical exam reveal?
Physical exam may reveal nonspecific anemia findings (conjunctival pallor), neurologic deficits if vitamin B12 deficient (impaired proprioception or vibration, positive Romberg sign), and stigmata of underlying diseases (glossitis from autoimmune atrophic gastritis, hepatosplenomegaly from familial hemolytic anemias, hypopigmentation from vitiligo, or jaundice and spider angiomata from alcohol abuse).
What is non-megaloblastic anemia?
Non-megaloblastic anemia, the absence of hypersegmented neutrophils, occurs in a variety of settings . Benign conditions are alcohol consumption (RBC toxicity), hereditary spherocytosis (impaired volume regulation increases red cell size), hypothyroidism and liver disease (due to lipid deposition in the cell membrane), and marked reticulocytosis from states of excess RBC consumption such as hemolysis or turnover in pregnancy or primary bone marrow disease (reticulocytes are larger than the average RBCs).
What is the Creative Commons 4.0 license?
This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, duplication, adaptation, distribution, and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, a link is provided to the Creative Commons license, and any changes made are indicated.
What is NCBI bookshelf?
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
What is the name of the condition that causes redness on the tongue?
redness or swelling of the tongue (glossitis) diarrhea. low appetite. depression. confusion. infertility. Macrocytic anemia is just one type of anemia. The symptoms of anemia are similar across all types, so it is important to use blood tests to diagnose the specific anemia a person has.
Why is macrocytic anemia rare?
In very rare cases, macrocytic anemia can be caused by a bone marrow disorder that prevents the body from producing enough healthy blood cells.
What is the name of the protein that transports oxygen around the body?
Hemoglobin is an iron-containing protein that transports oxygen around the body. Deficiencies in vitamin B-12 or folate often cause macrocytic anemia, so it is sometimes called vitamin deficiency anemia.
Why do animals have macrocytic anemia?
Macrocytic anemia is usually caused by a deficiency of folate or vitamin B-12, which is abundant in animal products. Macrocytic anemia is almost always due to a deficiency of folate or vitamin B-12.
What is the first line of treatment for macrocytic anemia?
They may also ask questions about a person’s diet, lifestyle, and other symptoms. In most cases, vitamin injections are the first line of treatment.
What is the most common form of macrocytosis?
Megaloblastic macrocytosis is the most common form. It occurs when DNA cannot be produced because of a vitamin deficiency.
Can macrocytic anemia be diagnosed?
Macrocytic anemia often goes undiagnosed until it becomes severe. People who have symptoms of anemia, a family history of anemia, or who have or are at risk of a condition linked to macrocytic anemia should see a doctor for a blood test.
A Red Blood Cell Deficiency With Enlarged Red Blood Cells
Heidi Moawad is a neurologist and expert in the field of brain health and neurological disorders. Dr. Moawad regularly writes and edits health and career content for medical books and publications.
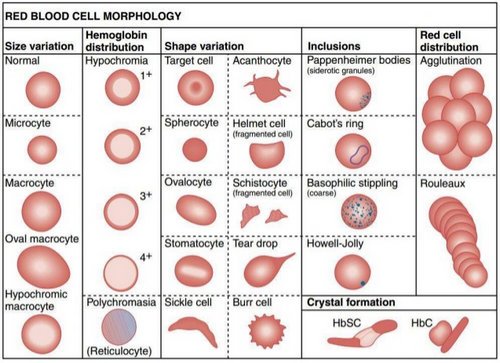
Types of Macrocytic Anemia
Macrocytic anemia is characterized by macrocytosis, which is large red blood cells. Types of macrocytic anemia are categorized by the shape of the red blood cells.
What Are the Symptoms of Macrocytic Anemia?
Macrocytic anemia usually develops slowly over time. Red blood cells normally live for several months. It takes a while for the enlarged red blood cells to have an impact, because there are usually many healthy red blood cells in circulation as well.
Causes of Macrocytic Anemia
There are several causes of macrocytic anemia. You can develop the condition due to just one of the causes, but you can also have more than one cause.
How Macrocytic Anemia Is Diagnosed
Macrocytic anemia doesn’t usually cause physical signs that are detected with a clinical examination. You might have other signs that are associated with the underlying cause.
Treatment for Macrocytic Anemia
The treatment of macrocytic anemia depends on the cause. Treatment and prevention are closely linked together.
Prognosis: What to Expect
Generally, macrocytic anemia is expected to improve with treatment. It can take weeks or longer for symptoms to resolve and for the blood tests to normalize. It is important to maintain consistent treatment and to have your red blood cell measurements monitored at regular intervals as directed by your doctor.
What happens if you have a B12 deficiency?
If you have a B12 or folate deficiency, your doctor completes additional testing to determine the cause of your deficiencies. By addressing the underlying cause, you can increase your vitamin levels and improve your macrocytosis. Management of macrocytosis consists of finding and treating the underlying cause.
What is macrocytosis in blood?
Understanding Macrocytosis. Macrocytosis is also called megalocytosis or macrocythemia. When you complete blood tests, the size of red blood cells is reported in your complete blood count. Because macrocytosis often develops into severe anemia, called macrocytic anemia, it is important to pay attention to these blood test results..
What is the diagnosis of macrocytosis?
Diagnosing Macrocytosis. Treating Macrocytosis. Macrocytosis is a condition in which your red blood cells are larger than they should be. While it isn’t a condition of its own, macrocytosis is a sign that you have an underlying health condition and may lead to a severe form of anemia called macrocytic normochromic anemia.
What to do if you have anemia?
If the underlying cause is resulting in severe anemia, you might need a blood transfusion. Addressing a vitamin B12 deficiency. If you’re not getting enough vitamin B12 or folate in your diet, eat foods rich in these nutrients. If you’re still not getting enough, you may need to take supplements.
What is a peripheral smear?
Peripheral smear, also known as a blood smear. Vitamin B12 and folate levels. Following a blood test, your doctor may want to assess the severity of your anemia. Your doctor will assess your health history to determine the likelihood of macrocytic anemia.
What is the treatment for macrocytosis?
In the case of vitamin B-12 or folate deficiency, treatment may include diet modification and dietary supplements or injections. If the underlying cause is resulting in severe anemia, you might need a blood transfusion.
How many fluid liters per cell for macrocytosis?
When macrocytosis is fully developed, your MCV levels are 100 fluid liters per cell if you don’t also have an iron deficiency, thalassemia trait, or kidney disease. Other indicators include: Keep in mind that if you do have an iron deficiency, macrocytosis may be overlooked.
Overview
- Macrocytosis is a term used to describe red blood cells that are larger than normal. Anemia is w…
Different types of macrocytic anemia can be classified depending on what’s causing it. Most often, macrocytic anemias are caused by a lack of vitamin B-12 and folate. Macrocytic anemia can also signal an underlying condition. - You may not notice any symptoms of macrocytic anemia until you’ve had it for some time.
loss of appetite or weight
Megaloblastic macrocytic anemia
- Most macrocytic anemias are also megaloblastic. Megaloblastic anemia is a result of errors in y…
some medications, such as chemotherapy drugs like hydroxyurea, antiseizure medications, and antiretroviral drugs used for people with HIV
Nonmegaloblastic macrocytic anemia
- Nonmegaloblastic forms of macrocytic anemia may be caused by a variety of factors. These ca…
chronic alcohol use disorder (alcoholism)
Blood tests
- Your doctor will order blood tests to check for anemia and enlarged red blood cells. If your com…
Additional blood tests can also help find the cause of your macrocytosis and anemia. This is important because treatment depends on the underlying cause. - While nutrient deficiencies cause most macrocytic anemias, other underlying conditions may ca…
Your primary care doctor may also refer you to a hematologist. Hematologists specialize in blood disorders. They can diagnose the cause and specific type of your anemia.
For healthier red blood cells
- Add more red meat and chicken to your diet to increase your vitamin B-12 intake.
If you’re a vegetarian or vegan, you can add beans and dark, leafy greens for folate. Try fortified breakfast cereals for vitamin B-12. - Reduce the amount of alcohol you drink.
Talk to your doctor if you take antiretrovirals for HIV, antiseizure medications, or chemotherapy drugs. These may increase your risk of developing macrocytic anemia.