Precipitation hardening, also called age or particle hardening, is a heat treatment process that helps make metals stronger. The process does this by producing uniformly dispersed particles within a metal's grain structure that help hinder motion and thereby strengthen it—particularly if the metal is malleable. The Precipitation Hardening Process
Full Answer
What is the abbreviation for precipitation hardening?
- Coherency strain hardening;
- Chemical hardening;
- Dispersion hardening.
How does precipitation hardening work?
What is Precipitation Hardening – Age Hardening – Definition
- Hardening of Metals. In materials science, hardness is the ability to withstand surface indentation ( localized plastic deformation) and scratching.
- Precipitation Hardening – Age Hardening. ...
- 17-4PH Stainless Steel. ...
- Example – Aluminium Alloys – 6061 Alloy. ...
What is the difference between temperature and precipitation?
When you step outside, keep in mind the difference between weather and climate! Even in a warming world, cold spells and big snowstorms will strike from time to time. But overall, winter is growing warmer over time. Why does this matter? Warmer winters in ...
What is precipitation hardening stainless steel?
What are its Advantages?
- Machinability becomes significantly easier
- Durability and strength is increased exponentially
- Reduced flexibility
- Materials receive higher yield and tensile strength ratings

What is the meaning of precipitation hardening?
Definition of precipitation hardening : the process of hardening an alloy by a heat treatment or aging method that causes a constituent to precipitate from solid solution.
What happens during precipitation hardening?
Precipitation hardening is the hardening of a material due to the growth of precipitates that impede dislocation motion. Basically, this process involves heating a mixture to a high temperature, then cooling, then heating to a medium temperature, and finally cooling again.
What causes precipitation hardening?
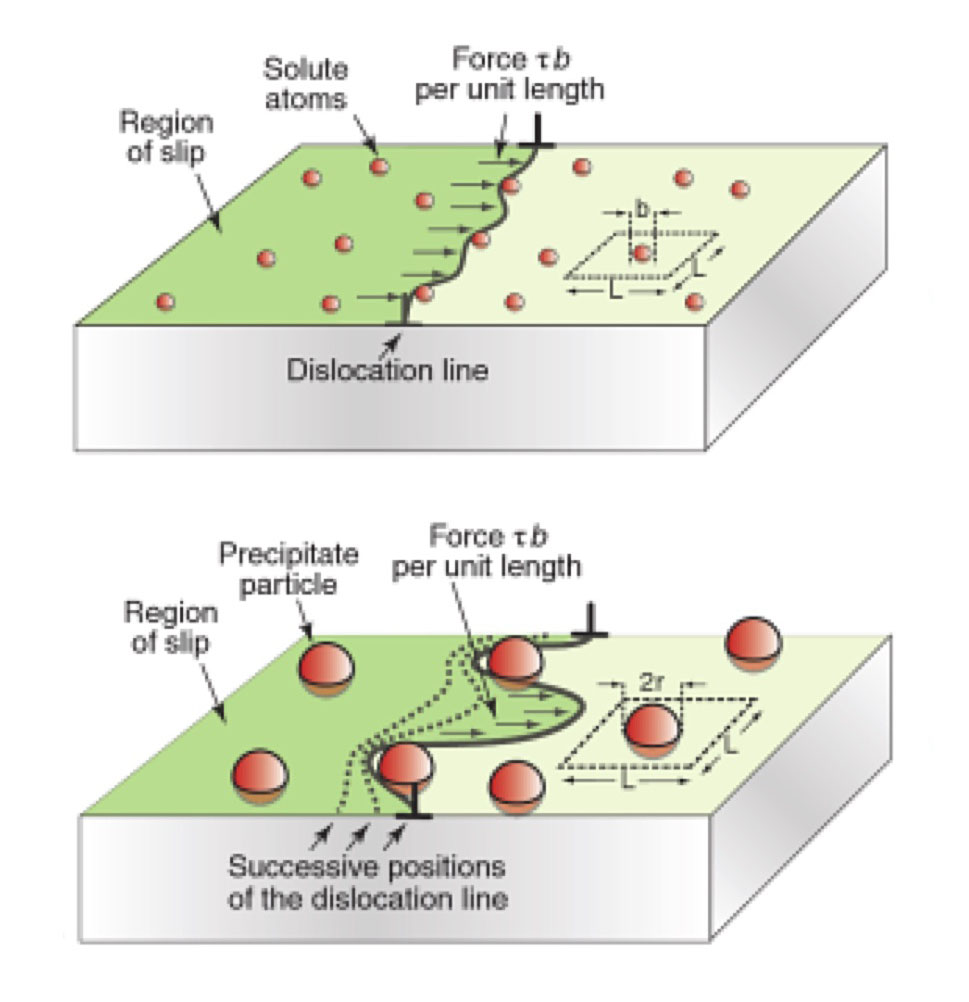
Precipitation hardening relies on changes in solid solubility with temperature to produce fine particles of an impurity phase, which impede the movement of dislocations, or defects in a crystal's lattice. Since dislocations are often the dominant carriers of plasticity, this serves to harden the material.
What is precipitation hardening in heat treatment?
Precipitation hardening is one heat treatment process by which aluminum alloys can be strengthened in a variety of ways. And this process, also known as artificial aging, is actually performed after a previous round of solution heat treatment and quenching.
What is required for precipitation hardening?
In order for an alloy system to be able to be precipitation-strengthened, there must be a terminal solid solution that has a decreasing solid solubility as the temperature decreases. The precipitation-hardening process involves three basic steps: solution treatment, quenching and aging.
What is precipitation hardening stainless steel used for?
Due to the high strength of precipitation hardening stainless steels, most applications are in aerospace and other high-technology industries. Applications include: Gears. Valves and other engine components.
What is the difference between precipitation hardening and age hardening?
BUT: Precipitation hardening is strengthening by precipitates of a second phase during cooling of HOMOGENEOUS solid solution. Age hardening is strengthening by precipitates of a second phase during annealing of a SUPERSATURATED solid solution.
How does precipitation hardening increase yield strength?
Precipitation hardening leads to a gradual increase in yield strength and hardness. This works through a mechanism where the precipitate particles of the low-temperature phase inhibit the movement of dislocations/defects in the lattice structure of an alloy.
What are precipitation hardening steels?
The precipitation hardening (PH) stainless steels are a family of corrosion resistant alloys some of which can be heat treated to provide tensile strengths of 850MPa to 1700MPa and yield strengths of 520MPA to over 1500MPa - some three or four times that of an austenitic stainless steel such as type 304 or type 316.
What is the relationship between precipitation hardening and solution treatment?
Solutionizing: Solutionizing or “solution treatment” is the first part of the process of precipitation hardening. This phase is about dissolving the precipitates and reducing the segregation that might be present in the existing alloy.
Can precipitation hardening be reversed?
Manufacturing processes may result in the premature start of the final precipitation age hardening process, which can be reversed through re-solution treating prior to further processing.
What does precipitation hardening do to microstructure?
What does precipitation hardening do? Precipitation hardening leads to a gradual increase in yield strength and hardness. This works through a mechanism where the precipitate particles of the low-temperature phase inhibit the movement of dislocations/defects in the lattice structure of an alloy.
What is the difference between precipitation hardening and age hardening?
BUT: Precipitation hardening is strengthening by precipitates of a second phase during cooling of HOMOGENEOUS solid solution. Age hardening is strengthening by precipitates of a second phase during annealing of a SUPERSATURATED solid solution.
How does dispersion hardening work?
Dispersion hardening involves the inclusion of small, hard particles in the metal, thus restricting the movement of dislocations, and thereby raising the strength properties. This strengthening process is applied to nickel-based superalloys used in jet engine components.
What is precipitation hardening of metal alloy?
Precipitation hardening is a method that makes use of heat application to a pliable material, like metal alloy, to make it tougher. This technique gives strength to alloys by hardening them and adding fine, solid impurities known as precipitates.
What is precipitation hardening?
Precipitation hardening, also called age hardening or particle hardening, is a heat treatment technique used to increase the yield strength of malleable materials, including most structural alloys of aluminium, magnesium, nickel, titanium, and some steels and stainless steels. In superalloys, it is known to cause yield strength anomaly providing ...
How does coherency hardening occur?
Coherency hardening occurs when the interface between the particles and the matrix is coherent, which depends on parameters like particle size and the way that particles are introduced . Small particles precipitated from supersaturated solid solution usually have coherent interfaces with the matrix. Coherency hardening originates from the atomic volume difference between precipitate and the matrix, which results in a coherency strain. The associated stress field interacts with dislocations leading to an increase in yield strength, similar to the size effect in solid solution strengthening.
How does precipitation affect dislocation?
Dislocations are repulsed by regions of higher stiffness. Conversely, if the precipitate causes the material to be locally more compliant, then the dislocation will be attracted to that region. In addition, there are three types of interphase boundaries (IPBs).
How does order strengthening occur?
Order strengthening occurs when the precipitate is an ordered structure such that bond energy before and after shearing is different. For example, in an ordered cubic crystal with composition AB, the bond energy of A-A and B-B after shearing is higher than that of the A-B bond before. The associated energy increase per unit area is anti-phase boundary energy and accumulates gradually as the dislocation passes through the particle. However, a second dislocation could remove the anti-phase domain left by the first dislocation when traverses the particle. The attraction of the particle and the repulsion of the first dislocation maintains a balanced distance between two dislocations, which makes order strengthening more complicated.
Why does nucleation occur at a high temperature?
Nucleation occurs at a relatively high temperature (often just below the solubility limit) so that the kinetic barrier of surface energy can be more easily overcome and the maximum number of precipitate particles can form. These particles are then allowed to grow at lower temperature in a process called ageing. This is carried out under conditions of low solubility so that thermodynamics drive a greater total volume of precipitate formation.
How does precipitation heat treat?
Precipitation heat treating involves the addition of impurity particles to increase a material's strength.
What are the elements used in precipitation strengthening?
Elements used for precipitation strengthening in typical aluminium and titanium alloys make up about 10% of their composition. While binary alloys are more easily understood as an academic exercise, commercial alloys often use three components for precipitation strengthening, in compositions such as Al (Mg, Cu) and Ti (Al, V ). A large number of other constituents may be unintentional, but benign, or may be added for other purposes such as grain refinement or corrosion resistance. In some cases, such as many aluminium alloys, an increase in strength is achieved at the expense of corrosion resistance.
How long does it take for precipitation to harden?
The process ranges in time from one to several hours, depending on the exact material and characteristics .
What precipitates in a precipitation hardened HSLA steel?
Titanium nitride precipitates in a precipitation hardened HSLA steel. Image copyright: University of Nevada, Reno
How to make metal harder?
Solution Treatment: You heat the metal to a high temperature and treat it with a solution. Quenching: Next, you quickly cool down the solution-soaked metal. Aging: Finally, you heat the same metal to a medium temperature and cool it quickly again. The result: A harder, stronger material.
What is precipitation hardening?
Precipitation hardening, also called age hardening or particle hardening, is a heat treatment technique based on the formation of extremely small, uniformly dispersed particles (precipitates) of a second phase within the original phase matrix to enhance the strength and hardness of some metal alloys.
What is precipitation hardened stainless steel?
For example, precipitation-hardened stainless steel 17-4 PH (AISI 630) have an initial microstructure of austenite or martensite. Austenitic grades are converted to martensitic grades through heat treatment (e.g. throung heat treatment at about 1040 °C followed by quenching) before precipitation hardening can be done. Subsequent ageing treatment at about 475 °C precipitates Nb and Cu-rich phases that increase the strength up to above 1000 MPa yield strength. In all heat treatments performed the predominant microstructure is lath martensite. Unlike austenitic alloys, however, heat treatment strengthens PH steels to levels higher than martensitic alloys. Precipitation-hardening stainless steels are designated by the AISI 600-series. Of all of the available stainless grades, they generally offer the greatest combination of high strength coupled with excellent toughness and corrosion resistance. They are as corrosion resistant as austenitic grades. Common uses are in the aerospace and some other high-technology industries.
What is hardness in metals?
Hardening of Metals. In materials science, hardness is the ability to withstand surface indentation ( localized plastic deformation) and scratching. Hardness is probably the most poorly defined material property because it may indicate resistance to scratching, resistance to abrasion, resistance to indentation or even resistance to shaping ...
Why is hardness important?
Hardness is important from an engineering standpoint because resistance to wear by either friction or erosion by steam, oil, and water generally increases with hardness. Hardening is a metallurgical metalworking process used to increase the hardness of a metal. The hardness of a metal is directly proportional to the uniaxial yield stress at ...
How much strength does precipitation give to aluminium?
In case of aluminium alloys, precipitation strengthening can increase the yield strength of aluminium from about five times up to about fifteen times that of unalloyed aluminium.
What is the process of aging?
This process is known as natural aging . The aging process also can be accelerated to a matter of hours after solution treatment and quenching by heating the supersaturated alloy to a specific temperature and holding at that temperature for a specified time. This process is called artificial aging.
What Does Precipitation Hardening Mean?
Precipitation hardening is a method that makes use of heat application to a pliable material, like metal alloy, to make it tougher. This technique gives strength to alloys by hardening them and adding fine, solid impurities known as precipitates. This can halt dislocation movements within the structure of its crystal lattice.
How long does it take for precipitate to harden?
Another way to achieve precipitate hardening is through natural aging. However, this consumes more time—from days to weeks.
How to get high saturation?
The solution’s high saturation, or supersaturation, is obtained by quenching. This can be accomplished in air or water, or the mixture of these two. It is a vital step in strengthening solution, as it prepares the material for the succeeding step of hardening precipitation.
What can cause disruption to the crystal lattice structure in aluminum, stainless steel and other types of alloys?
Impurities that are built via the precipitation or hardening technique can cause disruption to the crystal lattice structure in aluminum, stainless steel and other types of alloys. These prevent dislocations, making it difficult for lose particles to cut through the material.
What is Precipitation Hardening? What are its Advantages?
The critical thing to remember here is that dislocations are related to plasticity in the material. Therefore, as impurities prevent the movement of dislocations, the material is hardened, making the material more durable. As the hardening process makes the metal stronger, it also leads the way to several other significant manufacturing advantage s.
How many stages of precipitation hardening?
Precipitation hardening metals is not a quick process, hence the name age hardening. The process is accomplished through three phases, and each stage is designed to achieve a different task. Therefore, it is necessary to understand the importance of each stage of the process.
Why is hardening metal more durable?
Therefore, as impurities prevent the movement of dislocations, the material is hardened, making the material more durable. As the hardening process makes the metal stronger, it also leads the way to several other significant manufacturing advantages. Durability and strength is increased exponentially.

Overview
Precipitation hardening, also called age hardening or particle hardening, is a heat treatment technique used to increase the yield strength of malleable materials, including most structural alloys of aluminium, magnesium, nickel, titanium, and some steels and stainless steels. In superalloys, it is known to cause yield strength anomaly providing excellent high-temperature strength.
Kinetics versus thermodynamics
This technique exploits the phenomenon of supersaturation, and involves careful balancing of the driving force for precipitation and the thermal activation energy available for both desirable and undesirable processes.
Nucleation occurs at a relatively high temperature (often just below the solubility limit) so that the kinetic barrier of surface energy can be more easily overcome and the maximum number of preci…
Alloy design
Precipitation strengthening is possible if the line of solid solubility slopes strongly toward the center of a phase diagram. While a large volume of precipitate particles is desirable, a small enough amount of the alloying element should be added so that it remains easily soluble at some reasonable annealing temperature. Although large volumes are often wanted, they are wanted in small particle sizes as to avoid a decrease in strength as is explained below.
Types of hardening
There are several ways by which a matrix can be hardened by precipitates, which could also be different for deforming precipitates and non-deforming precipitates.
Deforming particles (weak precipitates):
Coherency hardening occurs when the interface between the particles and the matrix is coherent, which depends on parameters like particle size and the way that particles are introduced. Coher…
Theory
The primary species of precipitation strengthening are second phase particles. These particles impede the movement of dislocations throughout the lattice. You can determine whether or not second phase particles will precipitate into solution from the solidus line on the phase diagram for the particles. Physically, this strengthening effect can be attributed both to size and modulus effects, and to interfacial or surface energy.
Governing equations
There are two main types of equations to describe the two mechanisms for precipitation hardening based on weak and strong precipitates. Weak precipitates can be sheared by dislocations while strong precipitates cannot, and therefore the dislocation must bow. First, it is important to consider the difference between these two different mechanisms in terms of the dislocatio…
Other Considerations
Grain Size Control
Precipitates in a polycrystalline material can act as grain refiners if they are nucleated or located near grain boundaries, where they pin the grain boundaries as an alloy is solidifying and do not allow for a coarse microstructure. This is helpful, as finer microstructures often outperform (mechanical properties) coarser ones at room temperatures. In recent times nano-precipitates a…
Computational discovery of new alloys
While significant effort has been made to develop new alloys, the experimental results take time and money to be implemented. One possible alternative is doing simulations with Density functional theory, that can take advantage of, in the context of precipitation hardening, the crystalline structure of precipitates and of the matrix and allow the exploration of a lot more alternatives than with experiments in the traditional form.