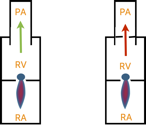
1. Pulmonary artery systolic pressure by TR peak velocity. Continuous wave (CW) Doppler of the tricuspid regurgitation (TR) trace is used to measure the difference in pressures between the right ventricle and right atrium. The simplified Bernoulli equation (P = 4[TRmax]2) is used to calculate this pressure difference using peak TR velocity.
What is the normal pulmonary artery systolic pressure?
- Recurrent syncope secondary to pulmonary hypertension; or
- Right heart failure (same criteria as for heart failure listing); or
- Mean pulmonary artery pressure between 25 and 39 mm Hg; or
- Pulmonary vascular resistance above 3 and below 6 Wood units.
What are the early symptoms of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH)?
the early symptoms of pulmonary arterial hypertension (pah) are: *shortness of breath during normal physical activity *fatigue *chest pains *a racing heartbeat
What causes pulmonary artery pressure?
- Angiosarcoma or other tumor within the blood vessels
- Arteritis
- Congenital pulmonary artery stenosis
- Parasitic infection ( hydatidosis)
What is the normal pulmonary wedge pressure?
What is a normal pulmonary wedge pressure? A normal mean pulmonary artery pressure for a healthy patient is 12-16 mmHg and a normal wedge pressure is 6-12 mmHg. Basically, the pressures in the right side of the heart and the pulmonary arteries are elevated while the pressures in the left side of the heart are normal.
See more

What does pulmonary artery pressure tell you?
Having pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) means that you have high blood pressure in the arteries that go from your heart to your lungs . It's different from having regular high blood pressure. With PAH, the tiny arteries in your lungs become narrow or blocked.
What does it mean if pulmonary artery pressure is high?
Pulmonary hypertension is high blood pressure in the blood vessels that supply the lungs (pulmonary arteries). It's a serious condition that can damage the right side of the heart. The walls of the pulmonary arteries become thick and stiff, and cannot expand as well to allow blood through.
Why do we monitor pulmonary artery pressure?
Hemodynamic congestion can be assessed by measuring pulmonary artery pressure (PAP). A device that accurately measures PAP elevation might thus allow for timely clinician intervention before symptoms appear to avert HF hospitalization.
What do PA pressures measure?
Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure is an integrated measurement of the compliance of the left side of the heart and the pulmonary circulation.
What is the most common cause of pulmonary hypertension?
Problems with the left side of the heart are thought to be one of the most common causes of pulmonary hypertension. These include mitral valve problems, left ventricle problems and aortic valve conditions.
How can I lower my pulmonary hypertension naturally?
9 Tips to Help You Self-Manage Your Pulmonary HypertensionRest. As with any chronic disease, pulmonary hypertension can cause severe fatigue. ... Exercise. ... Don't Smoke. ... Birth Control Pills. ... High Altitudes. ... Avoid Situations That Might Lower Your Blood Pressure Excessively. ... Watch Your Weight. ... Take Your Medications.More items...•
What organ systems are affected by pulmonary hypertension?
Pulmonary hypertension is a type of high blood pressure that affects the arteries in the lungs and the right side of the heart. In one form of pulmonary hypertension, called pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), blood vessels in the lungs are narrowed, blocked or destroyed.
What is normal pulmonary artery systolic pressure on Echo?
In healthy individuals who undergo right heart catheterisation, the average pulmonary artery systolic pressure ranges from 17 mm Hg to 25 mm Hg; on echocardiography, estimated pulmonary artery systolic pressure of more than 30 mm Hg is outside the normal range for most healthy individuals.
What are common complications of pulmonary artery pressure monitoring?
Possible risks include:Abnormal heart rhythms, some of which can be life threatening.Right bundle branch block, which is often temporary.Knotting of the catheter.Rupture of the pulmonary artery.Severely reduced blood flow to part of the lung.Blood clots, which can cause a stroke.More items...
What does the Swan Ganz measure?
Swan-Ganz catheterization is the passing of a thin tube (catheter) into the right side of the heart and the arteries leading to the lungs. It is done to monitor the heart's function and blood flow and pressures in and around the heart. This test is most often done in people who are very ill.
Why is pulmonary artery wedge pressure important?
Clinical significance Because of the large compliance of pulmonary circulation, it provides an indirect measure of the left atrial pressure. For example, it is considered the gold standard for determining the cause of acute pulmonary edema; this is likely to be present at a PWP of >20mmHg.
What is normal pulmonary artery occlusion pressure?
The normal PCWP is 8–12 mmHg (Table 2) and the waveform is similar to RA pressure (Fig. 1). Atrial contraction produces the “a wave” with the “x descent” seen as a fall in pressure during atrial relaxation.
What is the life expectancy with pulmonary hypertension?
For patients treated by experts in PAH, the average survival now exceeds 7 years and may be closer to 10 years.
What are the warning signs of pulmonary hypertension?
Other symptoms that may occur include dizziness, swollen ankles and legs, fainting and a bluish cast to lips and skin. Over time, pulmonary arterial hypertension can damage your heart to the point of danger and result in complications that can interfere with your daily life.
How do you reverse pulmonary hypertension?
There's no cure for pulmonary hypertension, but treatment is available to help improve signs and symptoms and slow the progress of the disease. It often takes some time to find the most appropriate treatment for pulmonary hypertension. The treatments are often complex and require extensive follow-up care.
What should I avoid if I have pulmonary hypertension?
If you have PAH, it may be best to avoid foods that are higher in salt or sodium, including:Canned foods.Soups.Processed foods.Deli meats.Cheeses.Certain seasonings.Frozen dinners.Pickled foods.More items...
What is PAH in pulmonary arteries?
This question gets at a key concept of PAH. Even though PAH is defined by elevated pressures within the pulmonary arteries, how a patient feels is really related to how their right ventricle is able to compensate for the elevated pressures and resistance within the pulmonary arteries.
What are the symptoms of inadequate blood flow?
No one complains that his or her pulmonary artery pressure is too high. What they notice is shortness of breath and fatigue. These are symptoms of inadequate blood flow.
How hot was the house when the AC system ran?
Now the residents of the house began to notice that no matter how long the AC system ran, the temperature in the house never reached a comfortable 78 degrees.
Can pulmonary artery pressure be predictive of exercise?
The pulmonary artery pressure and blood flow at rest may not be predictive of what happens during exercise. Some patients have quite mild appearing disease at rest but with minimal exercise they experience dramatic deterioration in blood flow and elevation of the pulmonary artery pressures.
Is the heart an AC system?
In this analogy, the heart is the AC system and the degree of leakiness of the house for keeping out hot air is analogous to the increasing resistance of the pulmonary arteries in PAH. Thus you feel ok when your heart can keep up with the added demands of diseased pulmonary arteries.
Does AC keep up with added work?
Over the years, the windows and the doors in the house became less airtight and heat was able to enter the house. Initially, the AC system had no problem keeping up with the added work. It simply had to work harder/longer to keep the temperature inside the house comfortable.
How does pulmonary hypertension affect the heart?
Similar to how systemic high blood pressure can cause the heart to work harder to deliver blood to the body, pulmonary hypertension can occur when the arteries in the lungs narrow and thicken, slowing the flow of blood through the pulmonary arteries to the lungs.
How to treat a symtom?
These lifestyle changes can improve your symptoms: 1 Quit smoking. Your doctor can recommend programs and products to help. 2 Follow a healthy diet. Eat a variety of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, plus lean meat, poultry, fish and low-fat/fat-free milk. Your diet should be low in fat, cholesterol, sodium and sugar. 3 Watch your weight. A daily record of your weight can help you be aware of rapid weight gain, which may be a sign that your pulmonary hypertension is worsening. 4 Stay active. Incorporate physical activity such as walking into your lifestyle. Discuss the level of activity with your doctor. Avoid straining or lifting heavy weights. Rest when you need to. 5 Avoid sitting in a hot tub or sauna, or taking long baths, which will lower your blood pressure. 6 Be cautious about air travel or high-altitude locales. You may need to travel with extra oxygen. 7 Get support for the anxiety and stress of living with pulmonary hypertension. Talk with your healthcare team, or ask for a referral to a counselor. A support group for people living with pulmonary hypertension can be invaluable in learning how to cope with the illness.
What is pulmonary hypertension?
Pulmonary Hypertension - High Blood Pressure in the Heart-to-Lung System
What tests are used to diagnose pulmonary hypertension?
Common diagnostic tests include an echocardiograph, chest X-ray, electrocardiogram (EKG) and catheterization of the right heart. Discovering the underlying cause may involve a chest CT scan, chest MRI, ...
What is the difference between pulmonary and systemic blood pressure?
Pulmonary versus systemic blood pressure. Unlike systemic blood pressure, which represents the force of your blood moving through the blood vessels in your body , pulmonary blood pressure reflects the pressure the heart exerts to pump blood from the heart through the arteries of the lungs. In other words, it focuses on the pressure ...
How to get rid of a swollen ear?
Follow a healthy diet. Eat a variety of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, plus lean meat, poultry, fish and low-fat/fat-free milk. Your diet should be low in fat, cholesterol, sodium and sugar.
Is pulmonary blood pressure higher than systemic blood pressure?
Pulmonary blood pressure is normally a lot lower than systemic blood pressure. Normal pulmonary artery pressure is 8-20 mm Hg at rest. If the pressure in the pulmonary artery is greater than 25 mm Hg at rest or 30 mmHg during physical activity, it is abnormally high and is called pulmonary hypertension.
How does PCWP differ from atrial pressure?
The PCWP tracing exhibits several important differences from a directly measured atrial-pressure waveform. The c wave is absent because of the damped nature of the pressure wave. The v wave typically exceeds the a wave on the PCWP tracing. Because the pressure wave is transmitted through the pulmonary capillary bed, a significant time delay occurs between an electrocardiographic event and the onset of the corresponding pressure wave. The delay may vary substantially, depending on the distance the pressure wave travels. Shorter delays are observed when the PCWP is obtained with the catheter tip in a more distal location. Typically, the peak of the a wave follows the P wave on the ECG by about 240 msec, rather than 80 msec as seen in the right-atrial tracing. 8 Similarly, the peak of the v wave occurs after the T wave has already been inscribed on the ECG. The relation between a true left-atrial pressure and the PCWP is shown in Fig. 2.17. Note the time delay between the same physiologic events and the “damped” nature of the PCWP relative to the left-atrial waveform, with a pressure slightly lower than the left atrium it is meant to reflect. In general, the mean PCWP is within a few millimeters of mercury of the mean left-atrial pressure, especially if the wedge and pulmonary artery systolic pressures are low. 9 High pulmonary artery pressure creates difficulty in obtaining a true “wedge,” falsely elevating the PCWP relative to the left-atrial pressure.
What happens to pulmonary pressure during spontaneous breathing?
During spontaneous breathing, the highest pulmonary pressures occur at end-expiration. This is the opposite of mechanical positive pressure ventilation, in which the lowest pulmonary pressures occur at end-expiration. 6 To minimize this artifact, recorded pressures should be made at end-expiration. Even at end-expiration, PAOP measures can still be overestimated if pleural pressures are elevated at end-expiration. Factors such as hyperinflation, air trapping, and PEEP in relation to lung and chest wall compliance increase pleural pressure to varying degrees. 6
How to determine pulmonary wedge pressure?
Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure can be identified from adequate pressure waveforms (see Chapter 3 ). Correct wedge position can be confirmed with oximetry. In cases in which a critical measure of the mitral valvular gradient is required, transseptal left atrial pressure is used. Adequate pulmonary capillary oxygen saturation is difficult to obtain with the balloon inflated. Advancement of the catheter tip with the balloon deflated into the deep wedge position may yield confirmatory oxygen saturation. The best location of the pulmonary wedge pressure has been questioned. But for practical purposes, any of the four locations (left or right upper lobes or left or right lower lobes) within the pulmonary tree are generally acceptable. The right lower lobe is the most common location for positioning of the pulmonary artery balloon-tipped catheter. In patients with high pulmonary artery pressures (>50 mm Hg), an inflated balloon should not be left in place for more than 10 minutes because prolonged balloon inflation may cause pulmonary infarction or damage to the pulmonary artery. The balloon can be inflated for longer periods in other patients. The operator should be careful not to inflate a balloon vigorously in distal portions of the lung where the balloon may tear a small pulmonary vessel. Complications of pulmonary artery catheterization are listed in Table 2-8.
What is a pulmonary capillary wedge pressure?
Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure is a phase-delayed, amplitude-damped version of LA pressure. During diastole with a nonstenotic mitral valve, the pulmonary venous system, LA, and LV is a continuous circuit and the PCWP is then reflective of the LV diastolic pressure. 20 The level of PCWP is important for two reasons. First, it provides the measure of hydrostatic pressure that is responsible for forcing fluid out of the pulmonary vascular space. In addition, the capillary pressure is directly related to diastolic fiber stretch according to Starling's principle, which states that the strength of contraction is proportional to myocardial fiber length/LV volume. 20 When applied to construct a cardiac function curve, it is often called LV filling pressure or preload.
How to measure pulmonary artery occlusion pressure?
Measurements of pulmonary artery occlusion pressure (PAOP) should be performed by slow injection of air into the balloon while watching the pulmonary artery waveform. Over-wedging can lead to falsely high occlusion pressures or pulmonary arterial rupture. Less than 1.5 mL air (balloon volume) may be required. Deflation after PAOP measurement should re-establish the normal pulmonary arterial waveform. If not, distal migration has occurred and the catheter should be withdrawn until the waveform is re-established.
What is the ideal PCWP?
The ideal PCWP trace should have well defined a and v waves, a mean pressure that is equal to or less than the PA diastolic pressure, and an oxygen saturation of ≥95% (in the absence of pulmonary parenchymal diseases that distort normal gas exchange). Accurate measurement of the PCWP may be difficult to obtain as both over inflation and under inflation of the catheter balloon remain common source of errors. Over inflation leads to dampening of the pressure waveforms and underinflation leads to transmittance of the PAP and the overestimation of PCWP.
How much does a wedge pressure overestimate left atrial pressure?
Pulmonary capillary wedge pressures tend to overestimate left atrial pressure by approximately 2 mm Hg. If a wedge pressure is used care must be taken to ensure that the catheter is not partially wedged, which would yield a higher false gradient;
Why is pulmonary hypertension so hard to diagnose?
Pulmonary hypertension is hard to diagnose early because it's not often detected in a routine physical exam. Even when the condition is more advanced, its signs and symptoms are similar to those of other heart and lung conditions. Your doctor will perform a physical exam and talk to you about your signs and symptoms.
What tests can be done to determine if you have pulmonary hypertension?
Tests for pulmonary hypertension may include: Blood tests. Blood tests can help your doctor determine the cause of pulmonary hypertension or look for signs of complications. Chest X-ray. A chest X-ray creates pictures of your heart, lungs and chest.
What is the purpose of a right heart catheter?
Right heart catheterization allows your doctor to directly measure the pressure in the main pulmonary arteries and right ventricle of the heart. It's also used to see what effect different medications may have on your pulmonary hypertension.
What is the purpose of sound waves in a heart?
Echocardiogram. Sound waves are used to create moving images of the beating heart. An echocardiogram lets a doctor see how well the heart and its valves are working. It can show the size and thickness of the right ventricle and the pressure in the pulmonary arteries.
What is the test to see how much air is in your lungs?
Pulmonary function test. This noninvasive test measures how much air your lungs can hold, and the airflow in and out of your lungs. During the test, you'll blow into a simple instrument called a spirometer. Polysomnogram.
How to reduce fatigue related to pulmonary hypertension?
Get plenty of rest. Resting can reduce fatigue related to pulmonary hypertension.
How to diagnose pulmonary hypertension?
To diagnose pulmonary hypertension, a doctor will perform a physical exam and review any signs and symptoms. You'll likely be asked questions about your medical and family history.
What is a pulmonary artery catheter?
Pulmonary artery catheterization is a diagnostic procedure in which an intravascular catheter is inserted through a central vein, such as the femoral, jugular, antecubital or brachial vein, to connect to the right side of the heart and advance towards the pulmonary artery. Pulmonary artery catheterization remains an excellent tool for the assessment of patients with pulmonary hypertension, cardiogenic shock, or unexplained dyspnea. It can be used to assess right-sided cardiac chamber filling pressures, to estimate cardiac output, to evaluate intracardiac shunts, to evaluate cardiac valves, or to assess vascular resistance. This activity describes the indications and techniques involved in pulmonary artery catheterization and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in the care of patients undergoing this procedure.
What is PAC in a shunt?
Pulmonary artery catheterization (PAC) is a procedure in which an intravascular catheter is inserted through a central vein (femoral, jugular, antecubital or brachial) to connect to the right side of the heart and advance towards the pulmonary artery. This diagnostic procedure can be utilized to assess right sided cardiac chamber filling pressures, estimation of cardiac output, intracardiac shunt evaluation, valvular studies, and vascular resistance. Despite the decrease in the use of pulmonary artery catheterization for evaluation and management of critically ill patients, it still remains an excellent tool for assessment of patients with pulmonary hypertension, cardiogenic shock, and unexplained dyspnea[1].
Why is my catheter misplaced?
Misplacement of the catheter can occur due to looping of the catheter in the right chambers. This can be prevented with the placement of the catheter under fluoroscopy and paying attention to the waveforms in the monitor.
Where is the catheter inserted into the pulmonary artery?
Insertion of the catheter from one of the main central veins (subclavian, internal jugular, femoral) traverses into the superior or inferior vena cava and reach the right atrium. From the right atrium through the tricuspid valve, the catheter reaches the right ventricle. From here the catheter is advanced to the right ventricular outflow tract and then to the pulmonary artery after getting across the pulmonary valve. The tip of the catheter lays into the main pulmonary artery, where the balloon can be inflated and deflated for measurement of pressures. Balloon can be inflated here to obtain pulmonary capillary wedge (or occlusive) pressure which gives an indirect assessment of left sided filling pressures.
What is the waveform of a catheter?
During the placement of the catheter, due to the transducer that is in the catheter, a pressure waveform can be seen in the monitor. Each section of the right heart anatomy has a distinctive pattern that can help to assist or helps to determine where is the catheter tips.
How thick is a catheter line?
Within the catheter, there are black lines that help to measure the length of the catheter. One thin line is 10 cm, and a thick black line indicated 50 cm.
What is the etiology of shock based on?
Distinduishing etiology of shock based on mixed venous oxygen saturation (SvO2) measurement such as in septic or cardiogenic shock[4]
How to find right ventricular systolic pressure?
Right Ventricular Systolic Pressure (RVSP) in echo is obtained by simply measuring the pressure gradient of the tricuspid regurgitant jet.
What is a PASP?
As a matter of fact, PHTN is something you should always interrogate in these cases. Ultimately, we want to know what the Pulmonary Artery Systolic Pressure is (PASP). This is the measurement that we’re most interested in.
What is the peak velocity of a tricuspid regurgitant jet?
With your continuous wave Doppler, you measure a peak velocity of the tricuspid regurgitant jet of 3.7 m/s.
What is pulmonary hypertension?
According to the Mayo Clinic, pulmonary hypertension (PHTN) is a type of high blood pressure that affects the arteries in your lungs as well as the right sided chambers of your heart. The Journal of the American Society of Echocardiography states that pulmonary hypertension results in right ventricular pressure overload, ...
How to find the RAP of an IVC?
In short, in order to estimate the RAP, you need to measure the diameter of the IVC and then look to see if the IVC collapses more than 50% of its diameter, or less than 50% of its diameter.
What is the RAP of a patient with an IVC of 1.9 cm?
So if a patient has an IVC that measures 1.9 cm and it collapses more than 50%, they would have an estimated mean RAP of 3 mmHg.
What does a cardiac sonographer do?
Average cardiac sonographers will simply record these measurements and move on without fully understanding or comprehending what it is that they’re measuring.
