How do you solve Pythagorean theorem?
How do you solve Pythagorean theorem problems? Step 1: Draw a right triangle and then read through the problems again to determine the length of the legs and the hypotenuse. Step 2: Use the Pythagorean Theorem (a 2 + b 2 = c 2 ) to write an equation to be solved .
What are the uses of the Pythagorean theorem?
Jobs That Use the Pythagorean Theorem
- Jobs in Management. Many positions that fall under the umbrella term of management use the Pythagorean Theorem regularly.
- Agriculturists Use Math. Agriculturists, such as farmers, gardeners and environmentalists all need this mathematical formula.
- Surveyors and Cartographers. ...
- Production Workers and the Pythagorean Theorem. ...
What is the answer to the Pythagorean theorem?
What is the Pythagorean Theorem step by step?
- Square one leg
- Square the other leg
- Add these together
- Take the square root of the sum
- The answer is equal to the hypotenuse
What is an example of Pythagorean theorem?
The Pythagorean Theorem can be usefully applied because the relationship between the lengths of the sides in any right triangle is consistent. For example, in a baseball field, if the distance between each base is known, then the shortest distance to throw the ball from first base to third base can be calculated using the Pythagorean Theorem.

What is the Pythagoras theorem in simple terms?
Pythagorean-theorem definition A theorem stating that the square of the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other sides. It is mathematically stated as c2 = a2 + b2 , where c is the length of the hypotenuse and a and b the lengths of the other two sides.
What does Pythagoras theorem do?
Pythagoras' theorem states that for all right-angled triangles, 'The square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the other two sides'. The hypotenuse is the longest side and it's always opposite the right angle. In this triangle a 2 = b 2 + c 2 and angle is a right angle.
What do you mean Pythagoras?
Definitions of Pythagoras. Greek philosopher and mathematician who proved the Pythagorean theorem; considered to be the first true mathematician (circa 580-500 BC) example of: mathematician. a person skilled in mathematics.
How is the Pythagorean theorem used in real life?
Some of the important real-life uses of the Pythagorean theorem are as follows: Used in construction and architecture. Used in two-dimensional navigation to find the shortest distance. Used to survey the steepness of the slopes of mountains or hills.
Who proved the Pythagorean Theorem?
The theorem is named for the Greek philosopher Pythagoras, born around 570 BC....Pythagorean theorem.TypeTheoremGeneralizationsLaw of cosines Solid geometry Non-Euclidean geometry Differential geometry5 more rows
What is Pythagoras full name?
Pythagoras of SamosPythagoras / Full namePythagoras of Samos (Ancient Greek: Πυθαγόρας ὁ Σάμιος, romanized: Pythagóras ho Sámios, lit. 'Pythagoras the Samian', or simply Πυθαγόρας; Πυθαγόρης in Ionian Greek; c. 570 – c. 495 BC) was an ancient Ionian Greek philosopher and the eponymous founder of Pythagoreanism.
What were the words of Pythagoras?
“Rest satisfied with doing well, and leave others to talk of you as they please.” “The oldest, shortest words— "yes" and "no"— are those which require the most thought.” “A man is never as big as when he is on his knees to help a child.” “No man is free who cannot control himself.”
How do you speak Pythagoras?
0:120:45How to Pronounce Pythagorean? (CORRECTLY) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipHow do you say it pythagorean you do want to stress on the second syllable on the syllableMoreHow do you say it pythagorean you do want to stress on the second syllable on the syllable pythagorean pretty straightforward once you know pythagorean.
What did Pythagoras study?
Pythagoras studied odd and even numbers, triangular numbers, and perfect numbers. Pythagoreans contributed to our understanding of angles, triangles, areas, proportion, polygons, and polyhedra. Pythagoras also related music to mathematics.
What is the Pythagorean Theorem step by step?
The Pythagorean Theorem rule is that the length of one leg squared plus the length of the other leg squared is equal to the hypotenuse squared. Ste...
What is the Pythagorean Theorem in simple terms?
The Pythagorean Theorem is a rule for right triangles that is used to find the length of one side when two sides are given. The rule is that the su...
What is the general formula for the Pythagorean Theorem?
The general formula for the Pythagorean Theorem is "a squared plus b squared is equal to c squared", where a and b are the lengths of legs of a rig...
How do you solve Pythagorean Theorem?
The Pythagorean Theorem is a rule for right triangles that is used to find the length of one side when two sides are given. To solve a problem usin...
What is the Pythagorean Theorem and what is it used for?
The Pythagorean Theorem is an equation used to find the length of one side of a right triangle when the other two sides are given. It is commonly u...
What is the Pythagorean theorem?
Pythagoras Theorem is an important topic in Maths, which explains the relation between the sides of a right-angled triangle. It is also sometimes called the Pythagorean Theorem. The formula and proof of this theorem are explained here with examples. Pythagoras theorem is basically used to find the length of an unknown side and angle of a triangle.
What is an example of Pythagoras theorem?
An example of using this theorem is to find the length of the hypotenuse given the length of the base and perpendicular of a right triangle.
What is the hypotenuse of a triangle?
The hypotenuse is the longest side of the right-angled triangle, opposite to right angle, which is adjacent to base and perpendicular. Let base, perpendicular and hypotenuse be a, b and c respectively. Then the hypotenuse formula, from the Pythagoras statement will be; c = √ (a2 + b2)
Which side of a triangle has the longest side?
Here, the hypotenuse is the longest side, as it is opposite to the angle 90°. The sides of a right triangle (say a, b and c) which have positive integer values, when squared, are put into an equation, also called a Pythagorean triple.
Which theorem states that the square of the hypotenuse side is equal to the sum of the other two?
Pythagoras Theorem Statement. Pythagoras theorem states that “ In a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse side is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides “. The sides of this triangle have been named as Perpendicular, Base and Hypotenuse.
How to know if a triangle is right angled?
To know if the triangle is a right-angled triangle or not. In a right-angled triangle, we can calculate the length of any side if the other two sides are given. To find the diagonal of a square.
Which theorem is useful to find the sides of a right angled triangle?
Pythagoras theorem is useful to find the sides of a right-angled triangle. If we know the two sides of a right triangle, then we can find the third side.
Who generalized Pythagoras' theorem?
Generalization of Pythagoras' theorem by Tâbit ibn Qorra. Lower panel: reflection of triangle CAD (top) to form triangle DAC, similar to triangle ABC (top).
Who discovered the Pythagorean theorem?
A generalization of the Pythagorean theorem extending beyond the areas of squares on the three sides to similar figures was known by Hippocrates of Chios in the 5th century BC, and was included by Euclid in his Elements:
How to prove Pythagorean proof?
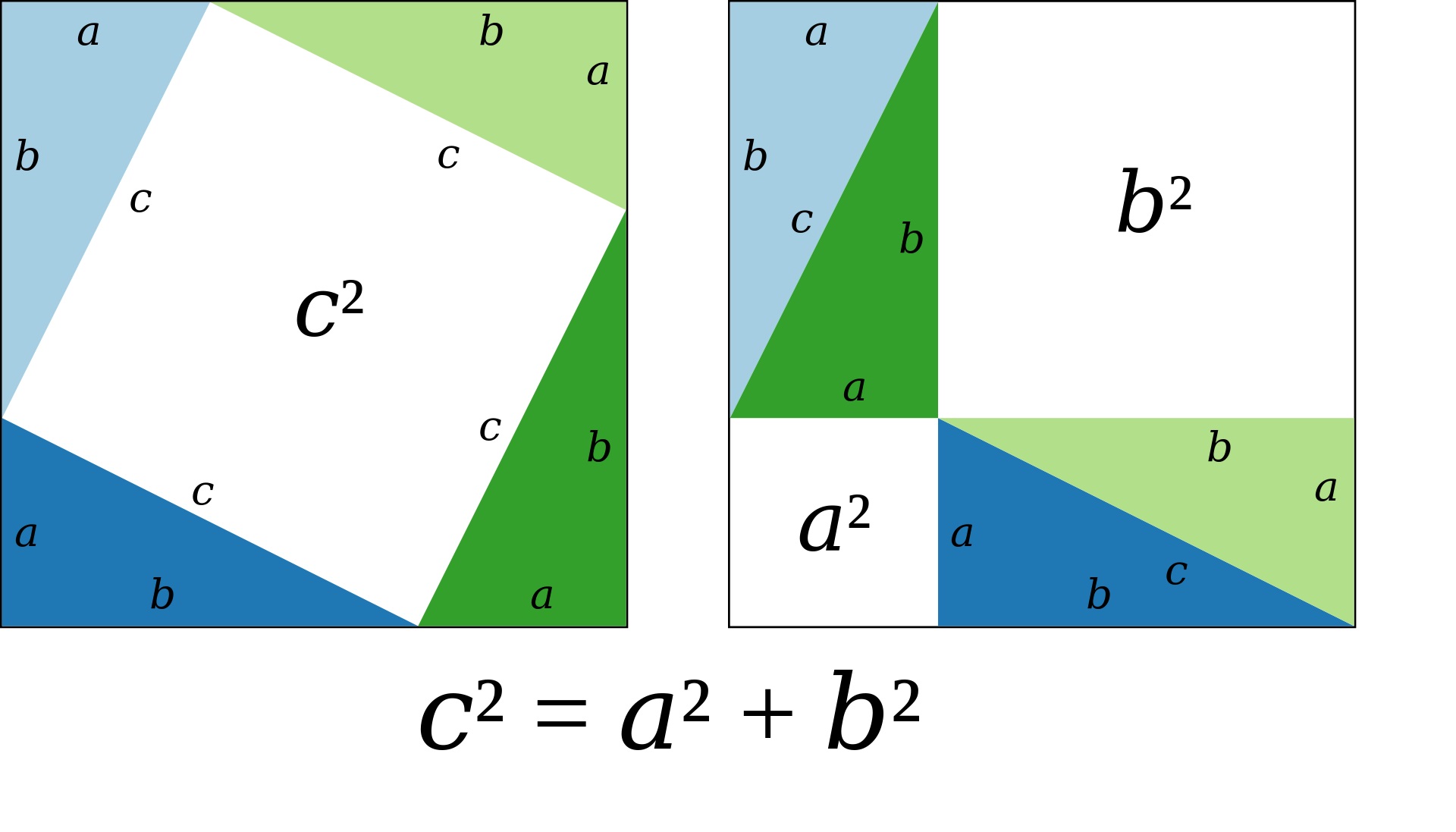
We have already discussed the Pythagorean proof, which was a proof by rearrangement. The same idea is conveyed by the leftmost animation below, which consists of a large square, side a + b, containing four identical right triangles. The triangles are shown in two arrangements, the first of which leaves two squares a2 and b2 uncovered, the second of which leaves square c2 uncovered. The area encompassed by the outer square never changes, and the area of the four triangles is the same at the beginning and the end, so the black square areas must be equal, therefore a2 + b2 = c2.
What is a Pythagorean triple?
A Pythagorean triple has three positive integers a, b, and c, such that a2 + b2 = c2. In other words, a Pythagorean triple represents the lengths of the sides of a right triangle where all three sides have integer lengths. Such a triple is commonly written (a, b, c).
How many proofs does the Pythagorean Theorem have?
This theorem may have more known proofs than any other (the law of quadratic reciprocity being another contender for that distinction); the book The Pythagorean Proposition contains 370 proofs.
What is the law of cosines?
A generalization of this theorem is the law of cosines, which allows the computation of the length of any side of any triangle, given the lengths of the other two sides and the angle between them. If the angle between the other sides is a right angle, the law of cosines reduces to the Pythagorean equation.
Which tablet records Pythagorean triples from Babylonian times?
The Plimpton 322 tablet records Pythagorean triples from Babylonian times.
How to prove Pythagorean Theorem?
The Pythagorean Theorem can be proved geometrically by using the squares of the sides of the right triangle. The squares are formed from the lengths a, b, c as shown.
What is the Pythagorean Theorem for a triangle?
For the triangle provided, the Pythagorean Theorem is {eq} {a^ {2}+b^ {2}}=c^ {2} {/eq}
How to find the length of a right triangle?
The Pythagorean Theorem is a rule for right triangles that is used to find the length of one side when two sides are given. To solve a problem using the Pythagorean first square the lengths of each leg. Add these results together. Take the square root of the answer. If the hypotenuse is given, then square the length of the hypotenuse and subtract the side squared. The square root of this result is the length of the other leg.
Which theorem is used for any triangle, not just a right triangle?
The Pythagorean Theorem is a specific case of the Law of Cosines which is used for any triangle, not just a right triangle. The Law of Cosines states that
What is the area of all four triangles?
The area of each triangle is 1/2 ab, therefore the area of all four triangles is 2ab
What are the sides of a hypotenuse called?
where c is the hypotenuse, or the side opposite the right angle, and the other sides, a and b, are called the legs.
Can the legs be rearranged to form the squares?
The squares formed by the legs can be rearranged to form the square formed by the hypotenuse.
What does Pythagorean numerology mean?
Pythagorean Numerology Number Meaning: Master Numbers. Final Words: Pythagorean Numerology analysis is the ancient art of decoding the secrets behind your birth date and name, which can be extremely helpful in unlocking the future course of your life.
Who created the Pythagorean numerology?
Back in the age-old days, it was created by a Greek scientist Pythagoras. Hence, the name Pythagorean numerology!
Where did the Pythagorean numerology system originate?
The Origin of Pythagorean Numerology System. To know about the origin of Pythagorean numerology, we must go back to the ancient days because the Pythagorean system was formed way before our forefather’s time. Back in the age-old days, it was created by a Greek scientist Pythagoras.
What is the master number in Pythagorean numerology?
All numbers are not created equal. Some numbers have a special place in Numerology. These numbers are called the master numbers. Generally speaking, 11, 22, and 33 are said to be the master numbers in the world of Numerology.
What does Pythagorean theorem mean?
meaning. The theorem that the sum of the squares of the lengths of the sides of a right triangle is equal to the square of the length of the hypotenuse.
Which theorem only applies to right triangles?
The Pythagorean theorem only applies to right triangles.
What is the sum of the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other sides?
It is mathematically stated as c2 = a2 + b2 , where c is the length of the hypotenuse and a and b the lengths of the other two sides.
What is the Pythagorean theorem?
In mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem — or Pythagoras' theorem — is a relation in Euclidean geometry among the three sides of a right triangle. In terms of areas, it states: In any right-angled triangle, the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares whose sides are the two legs. The theorem can be written as an equation relating the lengths of the sides a, b and c, often called the Pythagorean equation: where c represents the length of the hypotenuse, and a and b represent the lengths of the other two sides. The Pythagorean theorem is named after the Greek mathematician Pythagoras, who by tradition is credited with its discovery and proof, although it is often argued that knowledge of the theorem predates him. There is evidence that Babylonian mathematicians understood the formula, although there is little surviving evidence that they used it in a mathematical framework. The theorem has numerous proofs, possibly the most of any mathematical theorem. These are very diverse, including both geometric proofs and algebraic proofs, with some dating back thousands of years. The theorem can be generalized in various ways, including higher-dimensional spaces, to spaces that are not Euclidean, to objects that are not right triangles, and indeed, to objects that are not triangles at all, but n-dimensional solids. The Pythagorean theorem has attracted interest outside mathematics as a symbol of mathematical abstruseness, mystique, or intellectual power; popular references in literature, plays, musicals, songs, stamps and cartoons abound.
What is the numerical value of Pythagorean theorem in Chaldean numerology?
The numerical value of pythagorean theorem in Chaldean Numerology is: 2
Which theorem is generalized to Hilbert spaces?
A generalization of the Pythagorean theorem for Euclidean triangles to Hilbert spaces

Pythagoras Theorem Statement
Pythagoras Theorem Formula
- Consider the triangle given above: Where “a” is the perpendicular, “b” is the base, “c” is the hypotenuse. According to the definition, the Pythagoras Theorem formula is given as: The side opposite to the right angle (90°) is the longest side (known as Hypotenuse) because the side opposite to the greatest angle is the longest. Consider three squares of sides a, b, c mounted o…
Pythagoras Theorem Proof
- Given: A right-angled triangle ABC, right-angled at B. To Prove- AC2 = AB2 + BC2 Construction: Draw a perpendicular BD meeting AC at D. Proof: We know, △ADB ~ △ABC Therefore, Or, AB2 = AD × AC ……………………………..……..(1) Also, △BDC ~△ABC Therefore, Or, BC2= CD × AC ……………………………………..(2) Adding the equations (1) and (2) we get, AB2 + BC2 = AD …
Applications of Pythagoras Theorem
- To know if the triangle is a right-angled triangle or not.
- In a right-angled triangle, we can calculate the length of any side if the other two sides are given.
- To find the diagonal of a square.
Pythagorean Theorem Solved Examples
- Problem 1: The sides of a triangle are 5, 12 & 13 units. Check if it has a right angle or not. Solution:From Pythagoras Theorem, we have; Perpendicular2 + Base2 = Hypotenuse2 P2 + B2 = H2 Let, Perpendicular (P) = 12 units Base (B)= 5 units Hypotenuse (H) = 13 units {since it is the longest side measure} LHS = P2 + B2 ⇒ 122 + 52 ⇒ 144 + 25 ⇒ 169 RHS = H2 ⇒ 132 ⇒ 169 ⇒ …
Overview
In mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem, or Pythagoras' theorem, is a fundamental relation in Euclidean geometry among the three sides of a right triangle. It states that the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides. This theorem can be written as an equation relating the lengt…
Other forms of the theorem
If c denotes the length of the hypotenuse and a and b denote the two lengths of the legs of a right triangle, then the Pythagorean theorem can be expressed as the Pythagorean equation:
If only the lengths of the legs of the right triangle are known but not the hypotenuse, then the length of the hypotenuse can be calculated with the equation
If the length of the hypotenuse and of one leg is known, then the length of the other leg can be c…
Proofs using constructed squares
In one rearrangement proof, two squares are used whose sides have a measure of and which contain four right triangle whose sides are a, b and c, with c being the hypotenuse. In the first square, the triangles are placed such that the corners of the square correspond to the corners of the right angle in the triangles, forming a square in the center whose sides are length c. Each square has an area of both and , with representing the area of the four triangles. In the second sq…
Other proofs of the theorem
This theorem may have more known proofs than any other (the law of quadratic reciprocity being another contender for that distinction); the book The Pythagorean Proposition contains 370 proofs.
This proof is based on the proportionality of the sides of three similar triangles, that is, upon the fact that the ratio of any two corresponding sides of similar triangle…
Converse
The converse of the theorem is also true:
For any three positive numbers a, b, and c such that a + b = c , there exists a triangle with sides a, b and c, and every such triangle has a right angle between the sides of lengths a and b.
An alternative statement is:
For any triangle with sides a, b, c, if a + b = c , then the angle between a and b measures 90°.
Consequences and uses of the theorem
A Pythagorean triple has three positive integers a, b, and c, such that a + b = c . In other words, a Pythagorean triple represents the lengths of the sides of a right triangle where all three sides have integer lengths. Such a triple is commonly written (a, b, c). Some well-known examples are (3, 4, 5) and (5, 12, 13).
A primitive Pythagorean triple is one in which a, b and c are coprime (the greate…
Generalizations
The Pythagorean theorem generalizes beyond the areas of squares on the three sides to any similar figures. This was known by Hippocrates of Chios in the 5th century BC, and was included by Euclid in his Elements:
If one erects similar figures (see Euclidean geometry) with corresponding sides on the sides of a right triangle, then the sum of the areas of the ones on the two smaller sides equals the area of t…
History
There is debate whether the Pythagorean theorem was discovered once, or many times in many places, and the date of first discovery is uncertain, as is the date of the first proof. Historians of Mesopotamian mathematics have concluded that the Pythagorean rule was in widespread use during the Old Babylonian period (20th to 16th centuries BC), over a thousand years before Pythagoras w…