Which factors affect blood flow resistance?
Resistance to blood flow within a vascular network is determined by the size of individual vessels (length and diameter), the organization of the vascular network (series and parallel arrangements), physical characteristics of the blood (viscosity, laminar flow versus turbulent flow), and extravascular mechanical forces acting upon the vasculature.Of the above factors, changes in vessel ...
Which blood vessel offer most resistance to blood flow?
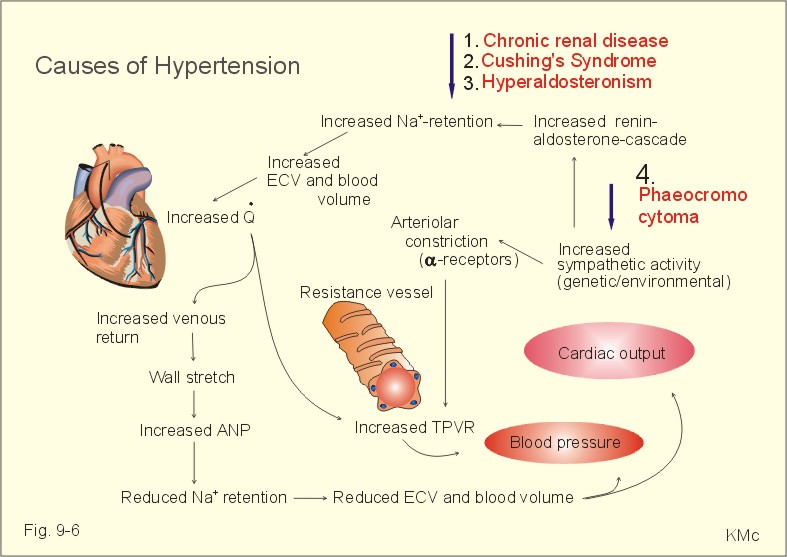
the amount of opposition that the blood vessels offer to the flow of blood; most resistance is caused by the arterioles (resistance vessels) vasoconstriction narrowing of blood vessels; usually refers to arterioles
What would decrease peripheral resistance to blood flow?
Peripheral resistance is the resistance of the arteries to blood flow. As the arteries constrict, the resistance increases and as they dilate, resistance decreases. Peripheral resistance is determined by three factors: Autonomic activity: sympathetic activity constricts peripheral arteries.
What causes increased systemic vascular resistance?
α-1 receptors are responsive to stimulation by the autonomic nervous system. Stimulation of the α-1 receptor causes vasoconstriction and increased systemic vascular resistance.
How does resistance relate to blood flow?
Resistance to flow must be overcome to push blood through the circulatory system. If resistance increases, either pressure must increase to maintain flow, or flow rate must reduce to maintain pressure.
What factors determine resistance to blood flow?
There are three primary factors that determine the resistance to blood flow within a single vessel: vessel diameter (or radius), vessel length, and viscosity of the blood. Of these three factors, the most important quantitatively and physiologically is vessel diameter.
What will happen to blood flow if the resistance to flow increases?
In the arterial system, as resistance increases, blood pressure increases and flow decreases. In the venous system, constriction increases blood pressure as it does in arteries; the increasing pressure helps to return blood to the heart.
What is the most significant source of blood flow resistance?
Blood vessel diameterAnswer and Explanation: Blood vessel diameter is the most significant source of blood flow resistance. A decrease in vessel diameter increases contact and friction between the blood and vessel wall, thus increasing blood flow resistance and blood pressure.
What causes low vascular resistance?
Although many clinical conditions can cause a low SVR, septic shock remains the most common cause and usually results in a severe decrease in SVR. In more than 90% of patients with septic shock who are aggressively volume loaded, the CO is initially normal or elevated.
What is the relationship between blood flow and resistance quizlet?
As the resistance decreases, the blood flow increases. The larger the radius of a vessel, the less the resistance. Blood flow to an organ will decrease with vasoconstriction.
What factors affect blood flow?
You need to know the factors that affect blood flow through the cardiovascular system: blood pressure, blood volume, resistance, disease and exercise.
How does exercise affect the blood flow?
Skeletal muscle blood flow increases dramatically, while blood flow to other tissues, especially the abdominal viscera and kidneys, is reduced. During heavy exercise, the vast increase in cardiac output is directed almost exclusively to contracting skeletal and cardiac muscles.
What are the factors of resistance?
There are four factors affecting resistance which are Temperature, Length of wire, Area of the cross-section of the wire, and nature of the material. When there is current in a conductive material, the free electrons move through the material and occasionally collide with atoms.
Which vessels are most important for controlling resistance to blood flow quizlet?
Explain your answer. - Arterioles play the largest role in determining peripheral resistance because they have small, have muscular walls that can constrict and dilate and since there are SO many of them, small changes result in large changes in resistance and pressure.
What are the two main factors that directly influence blood pressure quizlet?
The three main factors that determine blood pressure are peripheral resistance, cardiac output, and blood volume, all of which are directly proportional to blood pressure.
What are the three primary variables affecting blood pressure?
Increases in peripheral resistance, blood volume, and cardiac output result in higher blood pressure. Conversely decreases in any of these factors lead to lower blood pressure. Three main sources of peripheral resistance: Blood vessel diameter, blood viscosity, and total vessel length.
How does length affect flow?
The length of a vessel is directly proportional to its resistance: the longer the vessel, the greater the resistance and the lower the flow. As with blood volume, this makes intuitive sense, since the increased surface area of the vessel will impede the flow of blood. Likewise, if the vessel is shortened, the resistance will decrease and flow will increase.
How does viscosity affect flow?
Viscosity is the thickness of fluids that affects their ability to flow. Clean water, for example, is less viscous than mud. The viscosity of blood is directly proportional to resistance and inversely proportional to flow; therefore, any condition that causes viscosity to increase will also increase resistance and decrease flow. For example, imagine sipping milk, then a milkshake, through the same size straw. You experience more resistance and therefore less flow from the milkshake. Conversely, any condition that causes viscosity to decrease (such as when the milkshake melts) will decrease resistance and increase flow.
What is the difference between systolic pressure and diastolic pressure?
As shown in Figure 6.7.1, the difference between the systolic pressure and the diastolic pressure is the pulse pressure. For example, an individual with a systolic pressure of 120 mm Hg and a diastolic pressure of 80 mm Hg would have a pulse pressure of 40 mmHg.
How does the respiratory pump work?
The respiratory pump aids blood flow through the veins of the thorax and abdomen. During inhalation, the volume of the thorax increases, largely through the contraction of the diaphragm, which moves downward and compresses the abdominal cavity. The elevation of the chest caused by the contraction of the external intercostal muscles also contributes to the increased volume of the thorax. The volume increase causes air pressure within the thorax to decrease, allowing us to inhale. Additionally, as air pressure within the thorax drops, blood pressure in the thoracic veins also decreases, falling below the pressure in the abdominal veins. This causes blood to flow along its pressure gradient from veins outside the thorax, where pressure is higher, into the thoracic region, where pressure is now lower. This in turn promotes the return of blood from the thoracic veins to the atria. During exhalation, when air pressure increases within the thoracic cavity, pressure in the thoracic veins increases, speeding blood flow into the heart while valves in the veins prevent blood from flowing backward from the thoracic and abdominal veins.
What are the factors that affect cardiac output?
These factors include sympathetic stimulation, the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, thyroid hormones, and increased calcium ion levels. Conversely, any factor that decreases cardiac output, by decreasing heart rate or stroke volume or both, will decrease arterial pressure and blood flow. These factors include parasympathetic stimulation, elevated or decreased potassium ion levels, decreased calcium levels, anoxia, and acidosis.
How does the heart pump blood?
The pumping action of the heart propels the blood into the arteries, from an area of higher pressure toward an area of lower pressure. If blood is to flow from the veins back into the heart, the pressure in the veins must be greater than the pressure in the atria of the heart. Two factors help maintain this pressure gradient between the veins and the heart. First, the pressure in the atria during diastole is very low, often approaching zero when the atria are relaxed (atrial diastole). Second, two physiologic “pumps” increase pressure in the venous system. The use of the term “pump” implies a physical device that speeds flow. These physiological pumps are less obvious.
What is the sound of blood pressure?
Blood pressure is one of the critical parameters measured on virtually every patient in every healthcare setting. The technique used today was developed more than 100 years ago by a pioneering Russian physician, Dr. Nikolai Korotkoff. Turbulent blood flow through the vessels can be heard as a soft ticking while measuring blood pressure; these sounds are known as Korotkoff sounds. The technique of measuring blood pressure requires the use of a sphygmomanometer (a blood pressure cuff attached to a measuring device) and a stethoscope. The technique is as follows:
Components of Arterial Blood Pressure
Arterial blood pressure in the larger vessels consists of several distinct components: systolic and diastolic pressures, pulse pressure, and mean arterial pressure.
Pulse
After blood is ejected from the heart, elastic fibers in the arteries help maintain a high-pressure gradient as they expand to accommodate the blood, then recoil. This expansion and recoiling effect, known as the pulse, can be palpated manually or measured electronically.
Measurement of Blood Pressure
Blood pressure is one of the critical parameters measured on virtually every patient in every healthcare setting. The technique used today was developed more than 100 years ago by a pioneering Russian physician, Dr. Nikolai Korotkoff.
Variables Affecting Blood Flow and Blood Pressure
Recall that blood moves from higher pressure to lower pressure. It is pumped from the heart into the arteries at high pressure. If you increase pressure in the arteries (afterload), and cardiac function does not compensate, blood flow will actually decrease. In the venous system, the opposite relationship is true.
Venous System
The pumping action of the heart propels the blood into the arteries, from an area of higher pressure toward an area of lower pressure. If blood is to flow from the veins back into the heart, the pressure in the veins must be greater than the pressure in the atria of the heart.
Chapter Review
Blood flow is the movement of blood through a vessel, tissue, or organ. The slowing or blocking of blood flow is called resistance. Blood pressure is the force that blood exerts upon the walls of the blood vessels or chambers of the heart.
Self Check
Answer the question (s) below to see how well you understand the topics covered in the previous section.
What is BFR in medical terms?
Unfortunately, most individuals do not have access to this sophisticated device, which has led our lab to complete extensive research on what is known as practical blood flow restriction (BFR). Practical BFR involves the use of an elastic wrap to restrict blood flow. In studies, we have used knee and elbow wraps. However, cotton elastic bandages can also be used.
What is BFR in a cuff?
Blood flow restriction, also known as BFR, involves wrapping a device such as a pressure cuff, occlusion training bands, or even knee wraps around the top portion of a limb to restrict blood flow out of the working muscle. During properly performed BFR, blood is able to enter the muscle via arterial flow; however, the veins are restricted so that blood is partially prevented from leaving the working muscle.
Why does my BFR go numb?
To us, this indicates that several of the BFR training sessions that led to numbness could have been a result of improper wrapping techniques. Learn to do it right, and you should have nothing to fear.
Does BFR increase muscle size?
In fact, some research found that individuals who walked with BFR at low intensities could actually increase muscle size. However, we have found that resistance training results in greater benefits in muscle and strength than walking.
Does blood flow restriction cause muscle growth?
This arrangement allows for a swelling effect of the muscle, which is the first mechanism of muscle growth. Blood flow restriction also causes a buildup of metabolites, such as lactic acid, that have been shown to directly stimulate muscle growth. And the direct fatigue caused to the muscle forces the nervous system to recruit the largest fast-twitch muscle fibers, which have the greatest capacity to grow.
IS BLOOD FLOW RESTRICTION SAFE FOR MY NERVOUS SYSTEM?
This leads to the implication that BFR could be too taxing on the nervous system; however, further studies looking at nerve conduction velocity (speed at which a nerve impulse is transmitted) saw no change following four weeks of BFR at 30 percent of 1RM.
You are more than your score
For the longest time, I felt numb about my MCAT score. Sure, I didn't do awful whatsoever. However, I did feel as if I underperformed to my standards. Thanks to the advice I received from several doctors, med students, and peers, I decided to go with it anyways.
PRO TIP: TAKE CELL BIOLOGY IF YOU CAN BEFORE THE MCAT
holy fuck. The class was hell. But holy shit. Saved my ass for bio/biochem. Made it a lot easier to study. just a pro tip bc I would’ve been behind mcat studying if it weren’t for that class
Shoutout to all my Jan test takers. Spain with no S
The #1 social media platform for MCAT advice. The MCAT (Medical College Admission Test) is offered by the AAMC and is a required exam for admission to medical schools in the USA and Canada. /r/MCAT is a place for MCAT practice, questions, discussion, advice, social networking, news, study tips and more.