
What is Reverse Osmosis
Reverse osmosis
Reverse osmosis (RO) is a water purification technology that uses a semipermeable membrane to remove ions, molecules, and larger particles from drinking water. In reverse osmosis, an applied pressure is used to overcome osmotic pressure, a colligative property, that is driven by c…
What are the pros and cons of reverse osmosis water?
- Wastes as much as 6x the amount of clean water produced
- Requires professional maintenance to ensure effectiveness and safety
- Removes healthy minerals including calcium, magnesium, potassium and bicarbonates
- Relatively expensive starting from $300 + maintenance and replacements
What are the advantages of reverse osmosis?
Benefits of Reverse Osmosis
- Removes 95% – 99% of total dissolved solids (TDS) Reverse osmosis is the most effective way to drop the unwanted amounts of total dissolved solids in water.
- Improves the taste and odor of your water. ...
- Allows people to drink more water. ...
- Better for the environment. ...
- Comes with additional filtration levels. ...
- Improves the taste of your hot drinks and food. ...
What do I need to know about reverse osmosis?
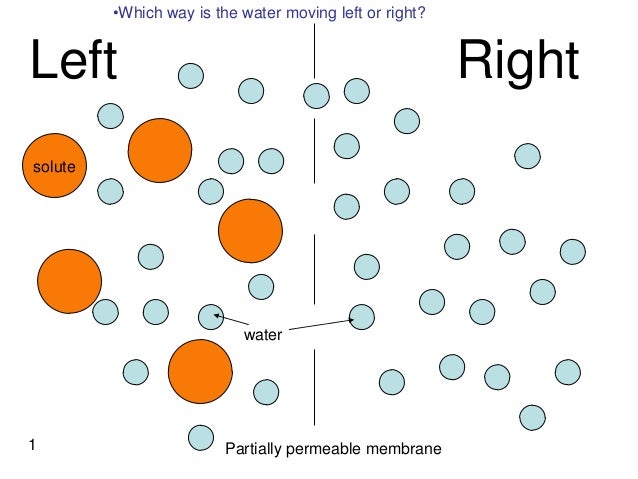
Reverse osmosis or RO is a filtration method that is used to remove ions and molecules from a solution by applying pressure to the solution on one side of a semipermeable or selective membrane. Large molecules (solute) can't cross the membrane, so they remain on one side. Water (solvent) can cross the membrane.
Why is reverse osmosis bad?
Disadvantages of Reverse Osmosis system
- The time it takes to purify water. Reverse Osmosis is not a very fast way to get clean water. ...
- Water wasting. RO systems are known to produce wastewater and some people get notoriously angry about that. ...
- Possible clogging. ...
- Ongoing filter replacement. ...
- Removal of beneficial minerals. ...
- Dropping the pH scale. ...
What are the benefits of drinking reverse osmosis water?
6 Key Benefits Of Reverse Osmosis Water#1. RO is Highly Effective at Removing Contaminants. ... #2. RO is Energy Efficient, Too. ... #3. RO Provides Clean Water On Demand. ... #4. RO Also Removes Minerals. ... #5. RO Will Save You Money. ... #6. RO Results In Better-Tasting Food. ... #1. You May Need To Get Used To The Taste. ... #2.More items...
Is it good to drink reverse osmosis water?
According to the World Health Organization, low mineral (TDS) drinking water produced by reverse osmosis or distillation is not suitable for long term human consumption and in fact, can create negative health effects to those consuming it. This lack of minerals may also impact the taste negatively for many people.
Are there any disadvantages to drinking reverse osmosis water?
Wastes Significantly More Water Than It Produces One of the biggest disadvantages to reverse osmosis water systems is wasted water. Studies show various reverse osmosis systems can waste between 3 and 20 times as much water as they produce.
What is not removed by reverse osmosis?
There are some contaminants not removed from water by RO systems. Reverse osmosis units do not effectively remove most organic compounds, bacterial microorganisms, chlorine by-products, or dissolved gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and radon.
What is the healthiest water to drink?
What Is The Healthiest Water To Drink? When sourced and stored safely, spring water is typically the healthiest option. When spring water is tested, and minimally processed, it offers the rich mineral profile that our bodies desperately crave.
Is reverse osmosis water better than filtered water?
The difference between reverse osmosis and carbon filtration is the presence of the high-quality reverse osmosis membrane. Activated carbon filtration is most effective at removing or reducing impurities and contaminants such as chlorine, sediment, volatile organic compounds, poor taste and odour from water.
Does RO water cause kidney stones?
RO filtration removes the unhealthy, inorganic minerals that the body cannot process. The build-up of these kinds of minerals, especially calcium salts, leads to problems such as gallstones and kidney stones.
Does reverse osmosis water dehydrate you?
It Doesn't Hydrate as Well as Alkaline Water Meanwhile, all indications cite how reverse osmosis water is less hydrating than even untreated water. This is because RO water has zero electrolytes. When the machines filter the water, they also remove them.
What are the pros and cons of reverse osmosis water?
The Benefits of Reverse Osmosis water FiltrationPro #1: Reverse Osmosis filters the most contaminants.Pro #2: Reverse Osmosis is a safe, environmentally friendly alternative to bottled water.Pro #3: Reverse osmosis provides better water for cooking.Con #1: More water wasted.Con #2: Some noticeable pressure drop.More items...
Can bacteria grow in RO water?
Reverse osmosis is not designed to remove bacteria. In fact, we now know that bacteria can grow inside the tank and that in some cases, such bacteria can be very detrimental to some individuals. RO tanks can literally become "incubators" for bacteria.. that's scary!
Should I add minerals to reverse osmosis water?
No, not necessarily. Although the minerals in water are important for health, avoiding chemicals, bacteria and contamination are also very beneficial too. The solution isn't to avoid reverse osmosis but instead adding minerals to the water.
What is the best home water filtration system?
Our RecommendationsBest Overall: Big Berkey Gravity Fed Water Filter.Best Under Sink: Frizzlife Under Sink Water Filter System.Best for Faucets: Pur Plus Faucet Mount Water Filtration System.Best Whole House: Express Water 3 Stage Whole House Water Filtration System.Best Pitcher: Pur Classic 11 Cup Water Filter.More items...•
Do you need to add minerals to reverse osmosis water?
No, not necessarily. Although the minerals in water are important for health, avoiding chemicals, bacteria and contamination are also very beneficial too.
What does the World Health Organization say about reverse osmosis water?
After analyzing hundreds of scientific studies concerning demineralized or reverse osmosis water, the World Health Organization released a report stating that such water "has a definite adverse influence on the animal and human organism."
How does reverse osmosis work?
Reverse osmosis is a process which uses a membrane under pressure to separate relatively pure water (or other solvent) from a less pure solution. When two aqueous solutions of different concentrations are separated by a semi-permeable membrane, water passes through the membrane in the direction of the more concentrated solution as a result of osmotic pressure (Figure 1). If enough counter pressure is applied to the concentrated solution to overcome the osmotic pressure, the flow of water will be reversed (Figure 2).
What is reverse osmosis?
Reverse osmosis (RO) has been known for more than a century, but it did not become a commercial process until the early sixties when a special membrane was developed (1,2,3,4). Because RO operates at a comparatively low temperature and is relatively energy efficient, it is employed in various applications, e.g., desalination, treatment of waste water, reclamation of minerals, concentration of whey and other food products, and purification of water (5,6). In recent years, RO has been used increasingly in making processed water for dialysis in hospitals and for certain cosmetics and drugs by pharmaceutical manufacturers (7,8). In addition to these applications, RO is capable of producing water of sufficient purity to be used as Water For Injection (WFI) and for the preparation of parenteral solutions (9,10,11,12). This ITG will focus on the chemical and microbiological quality of water produced by reverse osmosis.
What is fouling in RO systems?
A major problem in operating RO systems is concentration polarization or fouling which is the gradual build up of rejected solute on the feed side, immediately adjacent to the membrane. A flush cycle is often used to reduce build up. The spiral wound construction is less susceptible to fouling than that of the hollow fiber unit. A membrane module lasts two to three years on the average. The shut down procedure for non-working hours should assure that minimum flow and operating pressures are continued with a timed internal flush cycle.
What is the active barrier in RO?
The skin is the active barrier and primarily allows water to pass through. Two types of RO construction are commonly used: 1. spiral wound ---sheets of membrane sandwiched with mesh spacers are connected and wound around a permeate tube; and 2. hollow fiber. Either of these modules is assembled into a pressure housing.
How are salt ions rejected?
Salt ions, on the other hand, are rejected by a mechanism related to the valence of the ion. Ions are repelled by dielectric interactions; ions with higher charges are repelled to a greater distance from the membrane surface. Monovalent ions such as chloride ions will not be rejected as efficiently as, for example, divalent sulfate ions. The nominal rejection ratio of common ionic salts is 85 - 98%.
When should feed water be disinfected?
Feed water and product water should be monitored for microbiological quality. The system should be disinfected when microbiological quality levels are exceeded.
Can bacteria grow in RO water?
It has been reported that bacteria can "grow" through membranes. The mechanism by which bacteria pass through a RO membrane is not known and no correlation exists between a dye leak test of the membrane and its bacterial retention efficiency. Researchers at the Center for Disease Control (CDC) conducted extensive investigations on the bacterial contamination of RO systems used in producing purified water for dialysis (15). They reported: 1. certain naturally occurring Gram- negative bacteria can multiply in relatively pure RO water; 2. thorough periodic disinfection of the entire RO system is essential in producing water with acceptable bacterial counts; 3. stagnant water in pipes down stream of the membrane is the major source of bacteria and endotoxin in the product water; and 4. the efficiency of a membrane in rejecting bacteria is better in continuous operation than in intermittent use.
What is reverse osmosis?
Though reverse osmosis sounds like a biology class you might’ve missed, in reality, it’s just a type of filtration process. In reverse osmosis, untreated water, like saltwater, flows through a semipermeable membrane and carbon filters. The size of the membrane lets the water flow through the filter, but leaves behind salt, chemicals, ...
How much water is wasted in reverse osmosis?
There’s not as much pressure in these as there are in huge, industrial-size systems, so more energy is needed. In total, up to 85 percent of the water can be wasted to produce 15 percent of drinkable water. ( 3)
How much magnesium is lost in reverse osmosis water?
For example, when using demineralized water, like reverse osmosis water, you can lose up to 60 percent of magnesium or 70 percent of manganese in your food. ( 1) Water wants to bond to everything, and it will take the minerals where it can — like in your food. In fact, the World Health Organization released a report about its concerns ...
Why is water scarce in California?
In places like California, water is scarce thanks to drought. In third-world countries, there’s a lack of infrastructure to provide potable water. And even in our own homes, tap water toxicity is a real concern, as toxins like lead and arsenic have been found flowing through the tap. It’s just one of the reasons that reverse osmosis water ...
What is the result of the size of the membrane?
The result is “pure” water that’s free from bacteria and minerals.
Is reverse osmosis better than filtration?
If the water supply in your area is really sub par, and you feel that the reverse osmosis system is a better option than other filtration systems, it’s definitely better than ingesting ingredients like lead or arsenic. However, if you’re merely curious about a reverse osmosis water system, definitely do your research.
Is reverse osmosis water drinkable?
Water that’s been treated through reverse osmosis is drinkable! Some cities use reverse osmosis when there’s an abundance of saltwater but not enough fresh water, like this plant in Australia. You might have used even reverse osmosis in a water filter on a camping trip to ensure you had safe drinking water.
What is reverse osmosis?
Reverse osmosis ( RO) is a water purification process that uses a partially permeable membrane to separate ions, unwanted molecules and larger particles from drinking water. In reverse osmosis, an applied pressure is used to overcome osmotic pressure, a colligative property that is driven by chemical potential differences of the solvent, ...
How does osmosis work?
In the normal osmosis process, the solvent naturally moves from an area of low solute concentration (high water potential ), through a membrane, to an area of high solute concentration (low water potential). The driving force for the movement of the solvent is the reduction in the Gibbs free energy of the system when the difference in solvent concentration on either side of a membrane is reduced, generating osmotic pressure due to the solvent moving into the more concentrated solution. Applying an external pressure to reverse the natural flow of pure solvent, thus, is reverse osmosis. The process is similar to other membrane technology applications.
How does solar desalination work?
A solar-powered desalination unit produces potable water from saline water by using a photovoltaic system that converts solar power into the required energy for reverse osmosis. Due to the extensive availability of sunlight across different geographies, solar-powered reverse osmosis lends itself well to drinking water purification in remote settings lacking an electricity grid. Moreover, solar energy overcomes the usually high-energy operating costs as well as greenhouse emissions of conventional reverse osmosis systems, making it a sustainable freshwater solution compatible to developing contexts. For example, a solar-powered desalination unit designed for remote communities has been successfully tested in the Northern Territory of Australia.
Why is pretreatment important in reverse osmosis?
Pretreatment is important when working with reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes due to the nature of their spiral-wound design. The material is engineered in such a fashion as to allow only one-way flow through the system. As such, the spiral-wound design does not allow for backpulsing with water or air agitation to scour its surface and remove solids. Since accumulated material cannot be removed from the membrane surface systems, they are highly susceptible to fouling (loss of production capacity). Therefore, pretreatment is a necessity for any reverse osmosis or nanofiltration system. Pretreatment in sea water reverse osmosis systems has four major components:
When was osmosis first discovered?
A process of osmosis through semipermeable membranes was first observed in 1748 by Jean-Antoine Nollet. For the following 200 years, osmosis was only a phenomenon observed in the laboratory. In 1950, the University of California at Los Angeles first investigated desalination of seawater using semipermeable membranes. Researchers from both University of California at Los Angeles and the University of Florida successfully produced fresh water from seawater in the mid-1950s, but the flux was too low to be commercially viable until the discovery at University of California at Los Angeles by Sidney Loeb and Srinivasa Sourirajan at the National Research Council of Canada, Ottawa, of techniques for making asymmetric membranes characterized by an effectively thin "skin" layer supported atop a highly porous and much thicker substrate region of the membrane. John Cadotte, of FilmTec Corporation, discovered that membranes with particularly high flux and low salt passage could be made by interfacial polymerization of m -phenylene diamine and trimesoyl chloride. Cadotte's patent on this process was the subject of litigation and has since expired. Almost all commercial reverse-osmosis membrane is now made by this method. By 2019, there were approximately 16,000 desalination plants operating around the world, producing around 95 million cubic metres per day (25 billion US gallons per day) of desalinated water for human use. Around half of this capacity was in the Middle East and North Africa region.
What is a second sediment filter?
optionally, a second sediment filter with smaller pores. an activated carbon filter to trap organic chemicals and chlorine, which will attack and degrade certain types of thin-film composite membrane. a reverse osmosis filter, which is a thin-film composite membrane.
What is the purpose of drinking water purification?
Around the world, household drinking water purification systems, including a reverse osmosis step, are commonly used for improving water for drinking and cooking. Such systems typically include a number of steps: a sediment filter to trap particles, including rust and calcium carbonate.
What does Reverse Osmosis Remove?
With a pore size of around 0.0001 microns , an RO’s system membrane is quite efficient. So, when you use reverse osmosis, what does it remove?
Why is reverse osmosis better than tap water?
This is mainly because tap water contains traces of lead, nitrates, sulfur, and many other compounds, giving it a different taste. Therefore, reverse osmosis helps to provide people with clean, fresh, and tastier water. No Added Chemicals.
What is the membrane used in reverse osmosis?
The semi-permeable membrane used in reverse osmosis allows water to pass through, trapping back the undesired particles. This brings the impurity levels in the water down to 0.0009 microns, making the purified water safe to drink or use for other purposes.
How does RO work?
Through the RO process, applied pressure helps overcome the osmotic pressure, forcing a more concentrated liquid through a semi-permeable membrane to a lesser concentrated one. In essence, it’s osmosis taking place backward, hence, reverse osmosis. Instead of water moving towards a concentrated solute, it moves to a lower solute concentration ...
What percentage of Americans use reverse osmosis?
With over 40 percent of Americans using reverse osmosis purified water, it’s only fair to answer this crucial question in detail; what does reverse osmosis remove from tap water?
Why is purified water important?
Purified water is always in demand for various purposes, including drinking, manufacturing, beverage industries, medical and pharmaceutical fields, etc. Tap water contains many contaminants making it inadequate for domestic or industrial use. For this reason, water purification becomes paramount to help remove these dangerous impurities from ...
What are the pros and cons of reverse osmosis?
Pros of Reverse Osmosis. Clean water with Fewer Contaminants. As the process removes up to 99% of contaminants in tap water, it means that this water is suitable for drinking. Fewer contaminants mean fewer diseases and health issues.
How Does Reverse Osmosis System Work?
The process takes place when there is the center of the semi-permeable membrane and pressure is applied by the side where the more concentrated water is present that will soon pass to the less contaminated side and now that water is a minor contaminant. That’s how the reverse osmosis process is done.
How effective is reverse osmosis water treatment?
You might be wondering if the reverse osmosis water treatment is effective in removing bacteria because bacteria are almost too small to be filtered out, but you might be surprised at the advanced technology of reverse osmosis water filtration systems, and I’m glad to say that they are 99.9% effective in removing bacteria from your drinking water.
What do reverse osmosis filters remove from water?
Reverse osmosis is one of the best cleaning techniques to remove all the harmful substances like chlorides, fluoride, poisonous impurities like Nickle, barium, cadmium, lead, arsenic sulfates, cyanide, selenium, mercury, phosphate, nitrates & nitrites.
How many stages of filtration are there in a reverse osmosis system?
Many of the reverse osmosis systems are four filtered, which means they have 4 stage filtration. Each filter has its purpose in removing the contaminants from water. The whole house reverse osmosis water filters have extensive filtration mechanisms, whereas water filter pitchers with reverse osmosis filters are simplified, compact, and portable.
What is reverse osmosis water filtration?
Reverse osmosis water filtration systems use a semi-permeable membrane to push contaminants out of the water making the water safe and purified to access clean water in your homes.
What minerals are removed from a reverse osmosis filter?
The reverse osmosis filters also remove some of the essential minerals like iron, magnesium, sodium, zinc (95 – 98%), potassium (85 – 95%), sodium (85 – 94%), calcium (94 – 98%).
How many microns are in a reverse osmosis membrane?
The reverse osmosis membrane has tiny pores about 0.001 microns in size, and trust me when I say this, it can filter out all the bacteria in your drinking water, and you can access clean water any time anywhere you want.
How does reverse osmosis work?
Using a semi-permeable filter membrane, reverse osmosis filtration systems allow water to flow through them, while many contaminants are prevented from going any further. The water mole cules are pushed through the filter’s membrane by way of reverse osmosis, which separates the water from the contaminants. Now that you understand better how the ...
What is Reverse Osmosis?
As touched upon above, reverse osmosis filtration systems involve the process of removing or reducing the volume of contaminants present in water. It does this by forcing water to move in the opposite direction to its natural flow. Although it may feel like a relatively new technology to some, it’s been around for over 45 years.
What are the contaminants that can be removed from reverse osmosis?
Some of the most common contaminants that reverse osmosis systems can remove include: Protozoa, like Giardia and Cryptosporidium. Bacteria, such as E-coli, Shigella, Salmonella, and Campylobacter to name a few. Viruses, like Rotavirus, Norovirus and Hepatitis B. Chemical contaminants including: Lead. Chromium.
What is the most effective way to absorb chlorine?
Carbon-based filtration is the most effective method to absorb (and adsorb) chlorine from water. It just so happens that home reverse osmosis water filtration systems will always have a carbon stage incorporated for this reason.
What is the most effective method of filtration against harmful bacteria and viruses?
The answer is ultraviolet light filtration. This is the most effective method of filtration against harmful bacteria and viruses and works as a disinfectant treatment, much like how water chlorination was designed. The big difference is that there are no harmful by-products added to the water like with chlorination.
Why was the salt water system first used?
It began being used commercial once it was realized it could remove other contaminants too and not just salt. And as far back as the 70s, these kinds of systems were installed in people’s homes to help clean and sanitize the water consumed and used for various applications.
Is reverse osmosis filtration effective?
Some reverse osmosis set-ups come equipped with UV lights built-in. This is an example of one. The truth is RO filtration is very effective. In fact, it’s probably the most effective form of water filtration available in the home.

Overview
Fresh water applications
Around the world, household drinking water purification systems, including a reverse osmosis step, are commonly used for improving water for drinking and cooking.
Such systems typically include a number of steps:
• a sediment filter to trap particles, including rust and calcium carbonate
History
A process of osmosis through semipermeable membranes was first observed in 1748 by Jean-Antoine Nollet. For the following 200 years, osmosis was only a phenomenon observed in the laboratory. In 1950, the University of California at Los Angeles first investigated desalination of seawater using semipermeable membranes. Researchers from both University of California at Los Angeles an…
Landfill leachate purification
Treatment with reverse osmosis is limited, resulting in low recoveries on high concentration (measured with electrical conductivity) and fouling of the RO membranes. Reverse osmosis applicability is limited by conductivity, organics, and scaling inorganic elements such as CaSO4, Si, Fe and Ba. Low organic scaling can use two different technologies, one is using spiral wound membra…
Desalination
Areas that have either no or limited surface water or groundwater may choose to desalinate. Reverse osmosis is an increasingly common method of desalination, because of its relatively low energy consumption.
In recent years, energy consumption has dropped to around 3 kWh/m (11,000 J/L), with the development of more efficient energy recovery devices and impro…
Disadvantages
Household reverse-osmosis units use a lot of water because they have low back pressure. Earlier they used to recover only 5 to 15% of the water entering the system. However, the latest RO water purifiers can recover 40 to 55% of water. The remainder is discharged as wastewater. Because wastewater carries with it the rejected contaminants, methods to recover this water are not practical for household systems. Wastewater is typically connected to the house drains and will …
New developments
Since the 1970s, prefiltration of high-fouling waters with another larger-pore membrane, with less hydraulic energy requirement, has been evaluated and sometimes used. However, this means that the water passes through two membranes and is often repressurized, which requires more energy to be put into the system, and thus increases the cost.
Other recent developmental work has focused on integrating reverse osmosis with electrodialysis to …
See also
• Electrodeionization
• ERDLator
• Forward osmosis
• Microfiltration
• Reverse osmosis plant