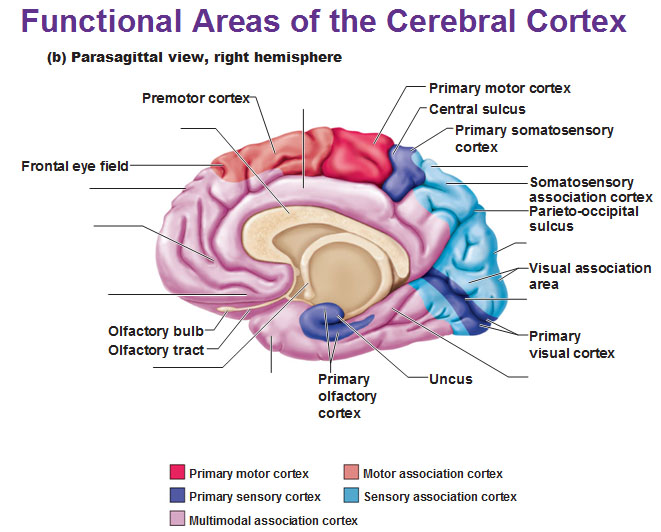
What are the 4 parts of the cerebrum?
http://www.interactive-biology.com - In this video, I talk about the 4 lobes of the Cerebrum: The frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal lobes. I also tal...
What happens if the cerebrum is damaged?
These symptoms include, but not are limited to, the following:
- Difficulty in planning basic tasks, such as making a cup of coffee or restocking toilet paper.
- Apathy or a complete loss of interest in life.
- Loss of thinking flexibility.
- Difficulty focusing or a complete lack of attention.
- Difficulty speaking in social settings.
- Often repeating actions without any awareness of doing so.
What are the parts of the cerebrum and their functions?
- Frontal lobe. The largest lobe of the brain, located in the front of the head, the frontal lobe is involved in personality characteristics, decision-making and movement. ...
- Parietal lobe. ...
- Occipital lobe. ...
- Temporal lobe. ...
What are the responsibilities of the cerebrum?
There are several key functions of the cerebellum, including: 3
- Balance and posture
- Mental function
- Movement
- Motor learning
- Vision
See more

What is the anterior part of the brain responsible for?
Frontal Lobe: most anterior, right under the forehead; the frontal lobe controls intellectual activities, such as the ability to organize, as well as personality, behavior, and emotional control.
What does the cerebrum control?
The largest part of the brain, the cerebrum initiates and coordinates movement and regulates temperature. Other areas of the cerebrum enable speech, judgment, thinking and reasoning, problem-solving, emotions and learning.
What three things does the cerebrum control?
Cerebrum. The largest part of the brain, the cerebrum has two hemispheres (or halves). The cerebrum controls movement, speech, intelligence, emotion, and what we see and hear.
What part of the cerebrum controls reasoning?
They also have language functions. Cerebral cortex: The cerebral cortex controls your thinking, voluntary movements, language, reasoning, and perception.
Which of the following is controlled by the cerebrum?
Cerebrum. The largest part of the brain, the cerebrum has two hemispheres (or halves). The cerebrum controls movement, speech, intelligence, emotion, and what we see and hear.
Which part of the brain controls balance?
CerebellumCerebellum: Sensing how to balance.
What part of the brain controls speech and motor skills?
frontal lobesThe frontal lobes are the largest of the four lobes responsible for many different functions. These include motor skills such as voluntary movement, speech, intellectual and behavioral functions.
What part of the brain controls moods and emotional behavior?
Amygdala: Limbic structure involved in many brain functions, including emotion, learning and memory. It is part of a system that processes "reflexive" emotions like fear and anxiety.
Which side of the brain controls logical thinking?
left brainAccording to Sperry's dated research, the left brain helps you with: logic. sequencing. linear thinking.
What side of the brain controls emotions?
right brainAt Ghent University, Guy Vingerhoets, Ph. D., Celine Berckmoes, M.S., and Nathalie Stroobant, M.S., knew that the left brain is dominant for language, and the right brain is dominant for emotion.
What is controlled by the cerebellum?
Maintenance of balance and posture. The cerebellum is important for making postural adjustments in order to maintain balance. Through its input from vestibular receptors and proprioceptors, it modulates commands to motor neurons to compensate for shifts in body position or changes in load upon muscles.
What does the cerebrum control quizlet?
The cerebrum is the most highly developed part of the human brain and is responsible for thinking, perceiving, producing and understanding language.
What is the main function of cerebellum?
The cerebellum is located in the back of your brain. It helps with the coordination and movement related to motor skills, especially involving the hands and feet. It also helps maintain posture, balance, and equilibrium.
What happens if cerebrum is damaged?
Effects of a left hemisphere stroke in the cerebrum The effects of a left hemisphere stroke may include: Right-sided weakness or paralysis and sensory impairment. Problems with speech and understanding language (aphasia) Visual problems, including the inability to see the right visual field of each eye.
What is the cerebrum responsible for?
The cerebrum is responsible for processing sensory functions like vision, hearing, and touch; and it is involved in movement of your body. It's also the source of intellect and enables you to think, plan, read, hold memories, and process emotions—among many other tasks.
How does the cerebrum affect the way you think?
Brain injuries and diseases can affect how the cerebrum functions and, by extension, can impact the way you think, move your body, or feel sensations. This article will give you an introduction to the structure of the cerebrum and its functions plus common conditions that can affect this brain region.
What is the largest part of the brain?
The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain and it's what most people envision when thinking of the brain. It is divided into two halves, or hemispheres, and its outer layer has large folds and creases of tissue that give the brain its characteristic wrinkly appearance.
How is the cerebrum divided?
The cerebrum is divided lengthwise into two halves, separated by a deep crease called the longitudinal fissure. From side-to-side, a crease called the central sulcus divides each hemisphere in half again.
Which layer of the brain is responsible for most of the information processing?
This outer layer of gray matter is the cerebral cortex and it is associated with most information processing, including language, perception, and thought. White matter is an inner core of brain tissue that's mostly composed of axons, or nerve fibers, that are covered by myelin (a type of fat).
How many halves are there in the cerebral cortex?
The gray matter of the cerebral cortex is divided lengthwise into two halves, separated by a deep crease called the longitudinal fissure.
Where are the parietal lobes located?
Parietal lobes are located near the middle of the brain behind the frontal lobes and are sensory areas that process pain, taste, temperature, and textures along with spatial relationships (such as the distance between your car and the one in front of you).
What happens if you clot the anterior cerebral artery?
In particular, clotting of this artery can lead to stroke, a dangerous “brain attack” caused by inadequate oxygen supply. In addition, due to the regions supplied, problems here can affect gait, ...
Which ACA branch delivers blood to the gyrus rectus?
Orbital Branches: Branches arising from the A2 section of the ACA deliver blood to the gyrus rectus (thought to be related to higher cognitive function) as well as the olfactory complex and the medial orbital gyrus, associated with perception of scent.
What is fenestration in ACA?
Fenestration of ACA: In 0 to 4% of cases, the A1 section of the ACA displays fenestration, in which segments of the artery are duplicated. 1 This anomaly raises the risk of an aneurysm (bleeding in the brain).
What is the ACA?
Supplying the medial portions of the frontal and parietal lobes, the anterior cerebral artery, also known as the ACA, is one of a pair of arteries that play an essential role in delivering oxygen to the brain. Arising at the termination of the internal carotid artery, its course curves upward and towards the middle ...
What is the third segment of the ACA?
A3: The third segment of the ACA, called the precallosal segment, ...
Which arteries are part of the circle of Willis?
One of the larger arteries tasked with supplying blood to important brain regions, the right and left ACAs are major components of the circle of Willis. These are mainly divided into three sections, some of which have important branches:
What is the anterior part of the brain?
The cerebrum is the anterior part of the brain. As large as a cantaloupe, this region accounts for about 85% of the total brain weight.
What Is The Main Function Of The Cerebellum?
Moving clockwise from the cerebrum we find the cerebellum, another vital region of the brain.
What is the outer part of the brain called?
The outside of the cerebrum is covered with a thin layer of gray matter called the cerebral cortex . This part of the cerebrum is in charge of your motor skills and helps the brain control voluntary movements.
How to make your cerebrum work?
To ensure that your cerebrum is working to its full potential, you need to give your brain a good mental workout every day. The best way to do this is by constantly learning new things.
What are the two parts of the brain stem?
The brain stem consists of two parts – the medulla oblongata on the bottom and the pons on the top. Together, they are responsible for several vital functions including breathing, coronary health, and deep sleep regulation. In addition, the medulla is in charge of reflexive actions like coughing and sneezing.
Which part of the brain controls voluntary movements?
While the motor area of the cerebral cortex plans and controls your voluntary movements, the cerebellum is in charge of carrying them out. Namely, this part of the brain activates all the muscles in your body needed to make the movement that you want to make. In addition to this, the cerebellum also ensures that your muscles are well-synchronized ...
What is the cerebellum responsible for?
What’s more, the cerebellum is also responsible for maintaining your balance and posture while you’re moving.

Anatomy of The Cerebrum
Function
- The role of the cerebrum is to coordinate and process sensory and motor functions required by the body, as well as to provide reasoning functions, process emotions, and contribute the unique personality traits that make each human being an individual. The cerebrum performs these functions using communication between nerve cells. Some of these proce...
Associated Conditions
- Traumatic injury and an array of medical conditions can affect the cerebrum. Each can lead to many different types of problems with brain function depending on which regions of the cerebrum are affected or have the most damage. Conditions that affect the cerebrum may include: 1. Brain trauma occurs if a high-force accident shakes the brain inside the skull or if a projectile penetrat…
Tests
- Some brain conditionsare not diagnosed primarily through medical testing. For example, diagnosing Alzheimer's disease may rely on a person's individual and family medical histories and cognitive function testing. Other cerebral conditions may be diagnosed through different types of medical testing—alone, or in combination. Common types include: 1. Lumbar puncture (spinal ta…
Summary
- The cerebrum is a major part of the brain and its upper layer called the cerebral cortex is responsible for a range of complex functions. The cerebrum is the source of intellect and personality. It helps you move and understand what you see, hear, touch, and smell. Due to the cerebrum's many important roles, damage to any of its lobes from injuries, illnesses, or chronic c…