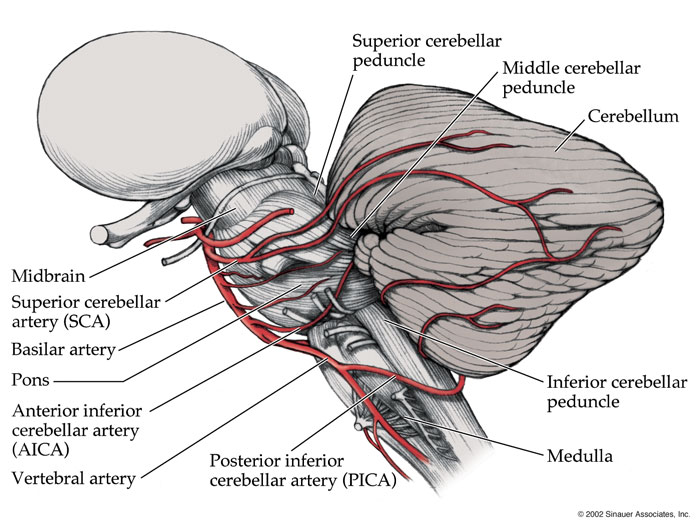
The anterior inferior cerebellar artery is one of three arteries that provide oxygenated blood to the cerebellum. The other arteries supplying the cerebellum are the superior cerebellar artery and the posterior inferior cerebellar artery.
What is anterior inferior?
Superior and Inferior
- The nose is superior to the mouth.
- The lungs are superior to the liver.
- The appendix is (usually) inferior to the transverse colon.
What are the anterior cerebral arteries?
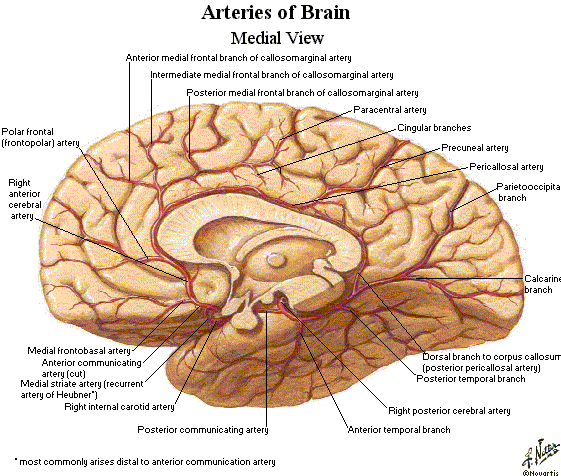
The anterior cerebral artery ( ACA) is one of a pair of arteries on the brain that supplies oxygenated blood to most midline portions of the frontal lobes and superior medial parietal lobes. The two anterior cerebral arteries arise from the internal carotid artery and are part of the circle of Willis.
Is anterior same as frontal?
The anterior cranial fossa consists of three bones: the frontal bone, ethmoid bone and sphenoid bone. It is bounded as follows: Anteriorly and laterally it is bounded by the inner surface of the frontal bone. Posteriorly and medially it is bounded by the limbus of the sphenoid bone. The limbus is a bony ridge that forms the anterior border of the prechiasmatic sulcus (a groove running between the right and left optic canals).
What is the difference between the anterior and the posterior?
is that anterior is (anatomy) nearer the forward end; nearer the head of an animal or the front of a human while posterior is (anatomy) nearer the back end; nearer the caudal end of the body in quadrupeds or the dorsal end in bipeds. As adjectives the difference between anterior and posterior is that anterior is before in place while posterior is located behind, or towards the rear of an object. As a noun posterior is

What supplies the anterior inferior cerebellar artery?
The anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA) is one of three pairs of arteries that supplies blood to the cerebellum. It arises from the basilar artery on each side at the level of the junction between the medulla oblongata and the pons in the brainstem.
What happens if the anterior inferior cerebellar artery is damaged?
Syndrome of Anterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery Occlusion Usual symptoms are nausea, vertigo, tinnitus, and hearing loss. Other features include vomiting, ipsilateral facial numbness, facial palsy, Horner syndrome, and contralateral loss of pain and temperature.
Does the anterior inferior cerebellar artery supply the medulla?
It arises from the basilar artery on each side at the level of the junction between the medulla oblongata and the pons in the brainstem....Anterior inferior cerebellar arterySourceBasilar arteryBranchesLabyrinthine arteryVeinInferior cerebellar veins10 more rows
What does the posterior inferior cerebellar artery supply?
The posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) is the largest branch of the vertebral artery. It is one of the three main arteries that supply blood to the cerebellum, a part of the brain.
What areas of the brain does the anterior cerebral artery supply?
To summarize, the ACA supplies the medial and superior parts of the frontal lobe, and the anterior parietal lobe.
What is anterior inferior cerebellar artery infarction?
Conclusions—Infarction in the anterior inferior cerebellar artery territory can present with a broad spectrum of audiovestibular dysfunctions. Unlike a viral cause, labyrinthine dysfunction of a vascular cause usually leads to combined loss of both auditory and vestibular functions. (Stroke.
What do the cerebellar arteries supply?
The anteroinferior cerebellar artery (AICA) supplies the pons, the facial and spinal trigeminal nucleus and tract, as well as the inferior and middle cerebellar peduncles and spinothalamic tract.
What artery supplies medulla?
The blood supply to the medulla can divide into two groups, which are the paramedian bulbar and lateral bulbar arteries. The paramedian bulbar arteries arise from the vertebral arteries and supply the medial aspect of the medulla.
Which arteries will supply the insula?
The prefrontal, precentral, and central arteries, and, in 22.5% of the hemispheres, the anterior and posterior parietal arteries fanned out over the insula from the superior trunk. They predominantly supplied the anterior portion of the insula.
What happens if posterior cerebral artery is blocked?
Symptoms of posterior cerebral artery stroke include contralateral homonymous hemianopia (due to occipital infarction), hemisensory loss (due to thalamic infarction) and hemi-body pain (usually burning in nature and due to thalamic infarction) 3. If bilateral, often there is reduced visual-motor coordination 3.
What does posterior cerebral artery supply?
The Posterior Cerebral Artery (PCA) supplies the occipital lobe, the inferior part of the temporal lobe, and various deep structures including the thalamus and the posterior limb of the internal capsule.
What is a Wallenberg stroke?
Wallenberg syndrome is a rare condition in which an infarction, or stroke, occurs in the lateral medulla. The lateral medulla is a part of the brain stem. Oxygenated blood doesn't get to this part of the brain when the arteries that lead to it are blocked. A stroke can occur due to this blockage.
What causes Circle Willis?
Overview. The Circle of Willis is the joining area of several arteries at the bottom (inferior) side of the brain. At the Circle of Willis, the internal carotid arteries branch into smaller arteries that supply oxygenated blood to over 80% of the cerebrum.
What causes a PICA stroke?
PICA may arise from the vertebral artery (the usual case), or as a separate branch of the basilar artery. Because of the far more common origin from the vertebral artery, most "PICA" syndrome strokes actually are due to vertebral artery occlusion (Kim 2003).
What is a PICA stroke?
The Posterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery (PICA) carries blood to this part of the brain. This stroke (Wallenberg's Syndrome) causes the person to have balance problems and lean to one side. They may also have numbness on one side of the face and body and an eye droop. They may have hoarseness and trouble swallowing.
What is stroke Syndrome?
a symptom complex caused by a disorder of the blood vessels serving the brain, with impaired blood supply and ischemia. Called also stroke, cerebral vascular accident, and cerebrovascular accident.
Where is the anterior inferior cerebellar artery located?
The anterior inferior cerebellar artery is located in the cerebellum of the brain. The cerebellum is just above the brainstem and controls coordination of movement and balance, among other important functions. The anterior inferior cerebellar artery originates at the basilar artery of the brainstem.
Which artery supplies the cerebellum?
The other arteries supplying the cerebellum are the superior cerebellar artery and the posterior inferior cerebellar artery. Regions served by the anterior inferior cerebellar artery include the internal acoustic meatus (an opening in the temporal bone that is part of the inner ear) and the biventral lobule, superior semilunar lobule, ...
What are the three arteries that supply the cerebellum?
The other arteries supplying the cerebellum are the superior cerebellar artery and the posterior inferior cerebellar artery.
Can an aneurysm occur in the anterior inferior cerebellar artery?
In rare cases, an aneurysm can occur in the anterior inferior cerebellar artery. An aneurysm is a ballooning of the blood vessel, and can be fatal if it ruptures. Last medically reviewed on April 14, 2015.
How many segments are there in the anterior cerebral artery?
Due to the distinct features of different parts of the anterior cerebral artery, its course is divided into five segments (A1-A5). In some classical anatomical textbooks the last three segments (A3-A5) are considered as one. The five segments include:
What are the segments of the cerebral artery?
Due to the distinct features of different parts of the anterior cerebral artery, its course is divided into five segments (A1-A5). In some classical anatomical textbooks the last three segments (A3-A5) are considered as one. The five segments include: 1 Precommunicating segment (A1): situated between the internal carotid bifurcation and the anterior communicating artery. It usually lies superior to the optic chiasm/ optic nerves and inferior to the anterior perforated substance. 2 Infracallosal (A2) segment (a.k.a. vertical/postcommunicating segment): courses around the rostrum of the corpus callosum, extending from the anterior communicating artery to the genu of corpus callosum (as far as the origin of the callosomarginal artery). 3 Precallosal (A3) segment: originates at the origin of the callosomarginal artery, arching around the genu of corpus callosum. It runs posteriorly to rise above the rostral part of the body of corpus callosum. 4 Supracallosal (A4) segment: runs from the body of the corpus callosum anterior to the coronal suture. 5 The postcallosal (A5) segment continues its way superior to the corpus callosum after passing the plane of the coronal suture.#N#Anterior cerebral artery in the circle of Willis
What are the symptoms of cerebral artery stroke?
Some of the most common symptoms of the anterior cerebral artery stroke are the motor deficits of the contralateral lower limb, contralateral face and arm paresis, urinary incontinence, sensory deficits, tremor, altered psychiatric status (e.g. memory impairments, emotional lability), etc.
What is the A2 segment?
Infracallosal (A2) segment (a.k.a. vertical/postcommunicating segment): courses around the rostrum of the corpus callosum, extending from the anterior communicating artery to the genu of corpus callosum (as far as the origin of the callosomarginal artery). Precallosal (A3) segment: originates at the origin of the callosomarginal artery, ...
What are the cortical branches?
The cortical branches bear the names of the corresponding areas of which they supply (orbito frontal and parietal). The orbitofrontal branches supply the olfactory cortex, gyrus rectus and medial orbital gyrus. The branches that ramify into the frontal lobe supply the corpus callosum (with the exception of the splenium), cingulate gyrus, medial frontal gyrus and paracentral lobule, while the parietal branches vascularize the precuneus. Note that several small frontal and parietal branches also cross onto the superolateral cerebral surface to supply the superior parts of the precentral and postcentral gyri. These areas are responsible for motor and sensory functions in the lower limb.
Which artery supplies the corpus callosum, frontal, parietal, and cingulate
Being located in the anterior and medial aspects of the interhemispheric fissure, the anterior cerebral artery supplies a large portion of the medial cerebral hemispheric surfaces namely the corpus callosum, frontal, parietal, and cingulate cortex. Through the anterior communicating artery, it anastomoses with its contralateral counterpart.
What are the structures of the corpus callosum?
These structures include: Rostrum of the corpus callosum. Septum pellucidum. Anterior part of the putamen. Head of the caudate nucleus. Anteromedial aspect of the anterior limb of the internal capsule. Since the anterior cerebral artery has a broad supply territory in the brain, it gives off many branches.
What happens if you clot the anterior cerebral artery?
In particular, clotting of this artery can lead to stroke, a dangerous “brain attack” caused by inadequate oxygen supply. In addition, due to the regions supplied, problems here can affect gait, ...
Which arteries are part of the circle of Willis?
One of the larger arteries tasked with supplying blood to important brain regions, the right and left ACAs are major components of the circle of Willis. These are mainly divided into three sections, some of which have important branches:
What is the ACA?
Supplying the medial portions of the frontal and parietal lobes, the anterior cerebral artery, also known as the ACA, is one of a pair of arteries that play an essential role in delivering oxygen to the brain. Arising at the termination of the internal carotid artery, its course curves upward and towards the middle ...
Where does the ACA originate?
Along with the middle cerebral artery, the ACA is a terminal branch of the internal carotid artery, which is the primary source of blood to the brain. It originates from the termination of the internal carotid artery, quickly coursing upward and towards the middle to cross the front of the brain on its way to the corpus callosum (the bundle of nerves in the middle of the brain that divides the right and left hemispheres) above the optic nerve .
What is the third segment of the ACA?
A3: The third segment of the ACA, called the precallosal segment, ...
Which branch of the ACA is responsible for sensory, motor, and cognitive functions?
Cortical Branches: Via its frontal branches, the ACA supplies the corpus callosum, which integrates sensory, motor, and cognitive function between the hemispheres as well as the cingulate and medial frontal gyri, which are associated with behavior regulation and emotion.
Where does the primary supply for the ACA come from?
Azygos ACA: In these cases, the primary supply for the ACA comes from a single trunk in the A2 section. This occurs in roughly 2% of cases. 1 . Bihemispheric ACA: In cases where the A2 segment never properly forms (called “hypoplasia”), the corresponding segment from the other side’s ACA supplies both sides.
What is the anterior cerebral artery?
The anterior cerebral artery (ACA) is a much smaller branch of the internal carotid artery (when compared to the middle cerebral artery). It begins at the terminal portion of the internal carotid artery (after the ophthalmic branch is given off) on the medial part of the Sylvian fissure.
Which segment of the cerebral artery gives off the anterior cerebral artery?
The ophthalmic segment (C6) gives of the ophthalmic artery and the superior hypophyseal artery. The communicating segment (C7) gives off the anterior cerebral (ACA), middle cerebral (MCA) and the anterior choroidal (AChA) arteries.
What is the anterior circulation?
Anterior circulation. The anterior circulation involves all the arteries that originate from the internal carotid arteries. It is responsible for the blood supply of the anterior and middle aspect of the brain. The arteries of this anterior circuit are: The internal carotid arteries. The anterior cerebral arteries.
How many pairs of primitive branchial arch arteries are there?
There are six pairs of primitive branchial arch arteries that appear during the early stages of development via vasculogenesis (formation of new blood vessels from stem cells). During the third week (around day 24), the internal carotid artery is the first of the cerebral vessels to arise.
What is the MCA?
The middle cerebral artery (MCA) is the largest terminal branch of the internal carotid artery. It travels through the Sylvian (lateral) fissure before coursing in a posterosuperior direction on the island of Reil ( insula ). It subsequently divides to supply the lateral cortical surfaces along with the insula.
What is the arterial system of the brain?
Owing to the high oxygen and nutrient demand of the organ, it is supplied by two arterial systems: The posterior circuit is supplied by the vertebrobasilar system .
Which part of the artery is considered the lacerum segment?
The part of the artery that was considered the lacerum segment is now referred to as a continuation of the petrous segment . The intracranial part involves the clinoid, ophthalmic and communicating portions (i.e. C5, C6, and C7) The petrous part (C2) gives off the caroticotympanic and Vidian arteries.
What is the posterior inferior cerebellar artery?
The posterior inferior cerebellar artery (or PICA) is an artery that provides blood flow to the cerebellum, a part of the brain located behind the top of the brain stem, ...
Which cerebral artery is the most variable?
Out of all the cerebral arteries, the posterior inferior cerebellar artery is considered the most variable. It is mostly made up of the supratonsillar segment and parts of the medulla.