
What does the nucleus contain?
What Does the Nucleus Contain? The nucleus is a collection of particles called protons, which are positively charged, and neutrons, which are electrically neutral. Protons and neutrons are in turn made up of particles called quarks.
Which part of a plant does not contain nucleus?
There are many parts of plant which do not contain nucleus. ●Sclerenchymatous cells get deposited by lignin and lose nucleus & cytoplasm at maturity. ●Xylem vessels consist of series of elongated dead cells for quick conduction of water and salts. ●Sieve tubes which also conduct food, don't have nucleus in them.
What is the difference between nucleus and nucleoplasm?
The nucleus houses chromosomes containing DNA. DNA holds heredity information and instructions for cell growth, development, and reproduction. When a cell is "resting", or not dividing, its chromosomes are organized into long entangled structures called chromatin . Nucleoplasm is the gelatinous substance within the nuclear envelope.
What is the shape of the nucleus?
The shape of a nucleus varies from cell to cell but is often depicted as spherical. To understand more about the role of the nucleus, read about the structure and function of each of its parts.
What is the nucleus?
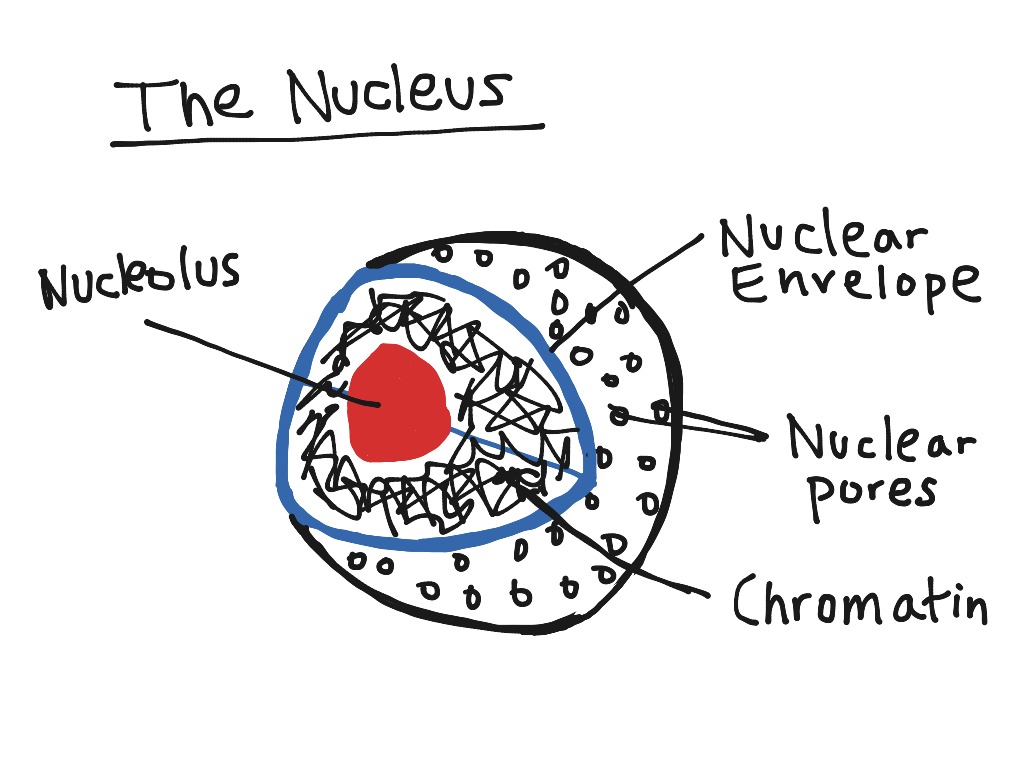
Nucleus. =. A nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle that contains the cell's chromosomes. Pores in the nuclear membrane allow for the passage of molecules in and out of the nucleus.
Why is the nucleus important?
So this is really an important part of the cell to protect. The nucleus has a membrane around it that keeps all the chromosomes inside and makes the distinction between the chromosomes being inside the nucleus and the other organelles and components of the cell staying outside.
What is the most important part of a cell?
The nucleus is one of the most obvious parts of the cell when you look at a picture of the cell. It's in the middle of the cell, and the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes, which encode the genetic material. So this is really an important part of the cell to protect. The nucleus has a membrane around it that keeps all ...
What is a Nucleus?
The most integral component of the cell is the nucleus (plural: nuclei). It is derived from a Latin word which means “ kernel of a nut ”.
What is the structure of the nucleus?
Structure Of Nucleus. Typically, it is the most evident organelle in the cell. The nucleus is completely bound by membranes. It is engirdled by a structure referred to as the nuclear envelope. The membrane distinguishes the cytoplasm from the contents of the nucleus. The cell’s chromosomes are also confined within it.
What are the functions of the nucleus?
Following are the important nucleus function: 1 It contains the cell’s hereditary information and controls the cell’s growth and reproduction. 2 The nucleus has been clearly explained as a membrane-bound structure that comprises the genetic material of a cell. 3 It is not just a storage compartment for DNA, but also happens to be the home of some important cellular processes. 4 First and foremost, it is possible to duplicate one’s DNA in the nucleus. This process has been named DNA Replication and produces an identical copy of the DNA. 5 Producing two identical copies of the body or host is the first step in cell division, where every new cell will get its own set of instructions. 6 Secondly, the nucleus is the site of transcription. Transcription creates different types of RNA from DNA. Transcription would be a lot like creating copies of individual pages of the human body’s instructions which may be moved out and read by the rest of the cell. 7 The central rule of biology states that DNA is copied into RNA, and then proteins.
What is the classification of every cell?
Mostly, every type of cell that exists is categorized on the basis of the absence or presence of the nucleus within its cell (categorized either as a prokaryotic or eukaryotic cell.)
Which organelle contains genetic material?
The nucleus is a double-membraned organelle that contains the genetic material and other instructions required for cellular processes. It is exclusively found in eukaryotic cells and is also one of the largest organelles.
What is the rule of biology?
The central rule of biology states that DNA is copied into RNA, and then proteins.
Which organisms have a nucleus diagram?
A nucleus diagram highlighting the various components. Moreover, only eukaryotes have the nucleus, prokaryotes have the nucleoid
What type of cell does not have a nucleus?
There are two types of cells- Prokaryotic without a well defined nucleus and Eukaryotic with a well defined nucleus. Prokaryotic organisms do not have their DNA surrounded by a nuclear membrane and are present in a single loop in the nucleoid region of the cell hence they do not completely lack the nucleus but they lack a “true nucleus that is membrane bound”.They have the major component important for the functioning. The reason for this might be because they evolved much before the eukaryotic organisms and did not have the membrane bound organelles . Lacking a nucleus also acts as an advantage for adaptation.
Why is the absence of nuclei in cells important?
The absence of nuclei in such cells is an adaptation that helps to serve its specialized function.
Why is the nucleus important?
Because the nucleus serves as the information processing and administrative center of every cell. With which it stores the cell's hereditary material, DNA, and it coordinates the cell's activities, which include growth, intermediary metabolism, protein synthesis, and reproduction (cell division) its absence means no cellular division for real.
Which organelle is made absent to accommodate more hemoglobin?
The best and the most famous example is that of the Red Blood Cells (RBCs or Erythrocytes). RBCs are specialized to carry oxygen. To serve this function, it would be helpful to have a large surface area. So the nucleus, being a large organelle is made absent to accommodate more Hemoglobin, and hence more oxygen.
What is the most famous example of a nucleus?
The best and the most famous example is that of the Red Blood Cells ( RBCs or Erythrocytes). RBCs are specialized to carry oxygen. To serve this function, it would be helpful to have a large surface area. So the nucleus, being a large organelle is made absent to accommodate more Hemoglobin, and hence more oxygen.
How do red blood cells lose their nucleus?
Mammalian red blood cells lose its nucleus by a process called enucleation, it occurs roughly when the cell has reached maturity.
How many proton is in hydrogen?
Simple hydrogen. Hydrogen has only one proton. However, Hydrogen has three isotopes (variations). They are call Protium (1 proton, H1), Deuterium (1 proton, 1 neutron, H2) and Tritium (1 proton and 2 neutrons, H3). The most common isotope by far is Protium. All three isotopes are stable at STP, but when H2 and H3 are subjected to extreme heat they fuse together as Helium (He4) and shed their neutrons which releases the energy that bound them together. This is how a thermonuclear weapon works.
