
What are the main functions of the pharynx?
The pharynx, commonly called the throat, is a passageway that extends from the base of the skull to the level of the sixth cervical vertebra. It serves both the respiratory and digestive systems by receiving air from the nasal cavity and air, food, and water from the oral cavity.
Where is the pharynx and what is its function?
pharynx, (Greek: “throat”) cone-shaped passageway leading from the oral and nasal cavities in the head to the esophagus and larynx. The pharynx chamber serves both respiratory and digestive functions. Thick fibres of muscle and connective tissue attach the pharynx to the base of the skull and surrounding structures.
What is the role of the pharynx and larynx in breathing?
The Larynx and Vocal Cords Allow Us to Breathe and Talk and Sing. The larynx connects the lower part of the pharynx, the laryngopharynx, to the trachea. It keeps the air passages open during breathing and digestion and is the key organ for producing sound.
What happens in the pharynx?
The pharynx, or throat, is the passageway leading from the mouth and nose to the esophagus and larynx. The pharynx permits the passage of swallowed solids and liquids into the esophagus, or gullet, and conducts air to and from the trachea, or windpipe, during respiration.
What is the function of the pharynx quizlet?
the pharynx is a fibrous muscular tube that lies behind the oral and nasal cavity. It transports air and food to the larynx and oesophagus respectively.
Is pharynx the throat?
More Information. Anatomy of the pharynx (throat). The pharynx is a hollow tube that starts behind the nose, goes down the neck, and ends at the top of the trachea and esophagus. The three parts of the pharynx are the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and hypopharynx.
What is the function of pharynx Brainly?
The function of the pharynx is to transfer food from the mouth to the oesophagus and to warm, moisten and filter air before it moves into the trachea. The pharynx is a part of both the digestive and respiratory systems.
What is the difference between pharynx and larynx?
The pharynx is a membrane-lined cavity present behind the nose and the mouth, connecting them to the larynx and esophagus respectively. The larynx is a muscular organ that forms an air passage for the lungs and vocal cord. It is a part of the respiratory system. Both oral and the nasal cavities open into the pharynx.
Where is the pharynx and how did it become an important part of human sound production?
Where is the pharynx and why did it become an important part in the human sound production? The pharynx is above the larynx (or the voice box of the oral box). When the larynx moved lower, the pharynx became longer and acted as a resonator, resulting in increased range and clarity of sounds produced via the larynx.
What does the pharynx secrete?
The lining of the pharynx secretes mucus to lubricate the pharynx and helps in smooth propulsion of food down to the esophagus and reduce throat irritation. It provides drainage to the nose, oral cavity, and middle ear.
How does food pass through the pharynx?
Food is forced into the pharynx by the tongue. When food reaches the opening, sensory receptors around the fauces respond and initiate an involuntary swallowing reflex. This reflex action has several parts.
What roles do the the pharynx and esophagus play in the digestive tract?
The only role in digestion played by the pharynx and esophagus is to move food through the GI tract. The mouth and stomach, in contrast, are organs where digestion, or the breakdown of food, also occurs.
What is the role of the pharynx in the respiratory system?
The pharynx acts as a passageway for food on its way to the stomach and for air en route to the lungs. The mucosal epithelium in the pharynx is thicker than elsewhere in the respiratory tract as it has to protect the tissues from any abrasive and chemical trauma caused by food.
What is the function of the pharynx?
Its function is to regulate the passage of air to the lungs and food to the esophagus. The pharynx, or throat, is the passageway leading from the mouth and nose to the esophagus and larynx.… Two small tubes (eustachian tubes) connect the middle ears to the pharynx and allow air pressure on the eardrum to be equalized.
What is the pharynx?
The pharynx is the body cavity that connects the nasal and oral cavities with the larynx and esophagus. It is commonly referred to as the throat. For the digestive system, its muscular walls function in the process of swallowing, and it serves as a pathway for the movement of food from the mouth to the esophagus.
What is the function of the pharynx?
Functions – What Does the Pharynx Do. Since it works as the connecting tube between the nasal cavity and larynx, as well as the oral cavity and esophagus, the pharynx is an integral part of both the respiratory and digestive systems.
Where is the pharynx located?
Located just below the nasal and oral cavities and before the larynx and esophagus, the pharynx starts at the human skull base, extending to the lower end of the cricoid cartilage [4].
What are the symptoms of a pharynx?
Conditions Associated with Pharynx 1 Pharyngitis, an inflammatory condition causing swelling, pain during swallowing, redness, and scratchiness, along with white patches in the throat [13] 2 Tonsillopharyngitis, a viral (or bacterial) throat infection causing pain and difficulty swallowing [14] 3 Pharynx cancer, causing a lumpy feeling in the throat or neck, bleeding, nasal obstruction, ear and throat pain, problems with swallowing and even deafness [15]. 4 Throat paralyses resulting from infectious diseases like diphtheria, rabies, and polio [12] 5 Pharynx ‘cobblestoning’ due to allergic rhinitis, characterized by streaks of lymphatic tissue, marking the back of the pharynx [16] 6 Laryngopharyngeal reflux (LRP), common in those suffering from GERD, occurs when the stomach acids get up to the throat from the esophagus
Why does my pharynx have a cobblestone?
Pharynx ‘cobblestoning’ due to allergic rhinitis, characterized by streaks of lymphatic tissue, marking the back of the pharynx [16] Laryngopharyngeal reflux (LRP), common in those suffering from GERD, occurs when the stomach acids get up to the throat from the esophagus.
Which muscles help the esophagus to pass through?
The consecutive contractions of the circular muscles of the pharynx help the ingested foods to pass through the lumen into the esophagus [10]. The longitudinal muscles contribute to widening the pharynx, elevating the larynx during the process of swallowing [3].
How many longitudinal muscles are there in the human pharynx?
There are three paired longitudinal muscles in the human pharynx [10]:
Where is the middle pharyngeal constrictor located?
Middle pharyngeal constrictor, located in the laryngopharynx. Inferior pharyngeal constrictor, also located in the Laryngopharynx, divided into the superior (having oblique fibers attaching to thyroid cartilage) and inferior (having horizontally placed fibers attaching to cricoid cartilage) components [3].
How does the pharynx help the respiratory system?
Because of its location, the pharynx helps the respiratory system by allowing air to make its way to the respiratory tract. For digestion, the use of the muscles surrounding the pharynx (both circular constrictive muscles and longitudinal muscles) work together to send food and drink down to the esophagus. The circular muscles push food and drink ...
What is the pharynx?
The pharynx is most commonly referred to as the throat, a muscular tube that starts at the base of the skull behind the nasal cavity and extends down to the larynx and esophagus. Its primary function serves both the respiratory system by taking in air from the nasal cavity as well as the digestive system by taking food and drink from ...
What are the three parts of the pharynx?
The pharynx consists of three major sections: the nasopharynx, the oropharynx , and the laryngopharynx. These sections are in order down the pharynx, as the nasopharynx is the top part of the throat, located behind the nasal cavity, the oropharynx makes up the middle part behind the oral cavity, and the laryngopharynx as the bottom piece, which is behind the larynx (commonly referred to as the voice box). The pharynx as a whole is about 5 centimeters (cm) in length. While the tube is largely hard tissues, some areas like the oropharynx consist of soft tissue. 2
Why does air travel through the pharynx?
Because the pharynx is an enclosed space that can change shape thanks to its musculature structure, air is able to travel through the pharynx to the larynx (the voice box). As vocal cords work to make sound the pharynx is able to amplify that sound as the larynx opens up into the pharynx. 7 .
Why is the pharynx in the middle of the neck?
By being in the middle of the neck it is able to assist the respiratory and digestive tracts equally. Any muscular changes in the pharynx may affect its location, whether it be longitudinal muscles attached incorrectly or missing muscles.
Which muscles help push food down into the esophagus?
Last, the laryngopharynx contains two groups of constrictor muscles as well—a middle pharyngeal constrictor and inferior pharyngeal constrictor. Together these muscles help push food down into the esophagus for digestion. 4 . Aside from the constrictor muscles (which are more circular in shape) the pharynx also has several longitudinal muscles ...
What is the nasopharynx made of?
For example, the nasopharynx is made up of respiratory epithelium, a protective mucous membrane that coats the airways and respiratory tract. The nasopharynx is also where the adenoid tonsils are located, a patch of tissue high up in the throat that makes up some of your tonsils.
What is the pharynx?
The pharynx, is a common passageway shared by both the digestive and respiratory systems. The pharynx is a muscular funnel extending about 13 cm (5 in.) from the posterior nasal apertures to the larynx. The pharynx is attached above to the base of the skull and is continuous below, approximately at the level of vertebra CVI (cervical vertebrum C6), ...
What is the function of the larynx?
The larynx is a cartilaginous chamber about 4 cm (1.5 in.) long. Its primary function is to keep food and drink out of the airway, but it evolved the additional role of sound production (phonation) in many animals; hence, we colloquially think of it as the “voice box.”. Figure 2. Larynx anatomy.
How many cartilages are there in the larynx?
The framework of the larynx consists of nine cartilages. The first three are solitary and relatively large. The most superior one, the epiglottic cartilage, is a spoon-shaped supportive plate in the epiglottis. The largest, the thyroid cartilage, is named for its shieldlike shape.
Where is the oropharynx located?
The oropharynx extends between the soft palate and the base of the tongue at the level of the hyoid bone. Like the posterior and inferior portions of the nasopharynx, the posterior portion of the oral cavity communicates directly with the oropharynx. The epithelium changes from a pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium to a nonkeratinized (mucosal type) stratified squamous epithelium at the boundary between the nasopharynx and oropharynx. The posterior margin of the soft palate supports the dangling uvula and two pairs of muscular pharyngeal arches, the posterior arch and the anterior arch.
What is the voice box in infants?
This creates a more or less continuous airway from the nasal cavity to the larynx and allows an infant to breathe continually while swallowing.
What are the three parts of the pharynx?
Muscles of the pharynx play necessary roles in swallowing and speech. The pharynx is subdivided into three regions (Figure 1): the Nasopharynx, the Oropharynx, and. the Laryngopharynx. Figure 1. Pharynx and larynx anatomy. The pharynx connects the nose, mouth, and throat. The digestive and respiratory systems share the pharynx.
What is the name of the tube that opens into the nasopharynx?
The posterior apertures (choanae) of the nasal cavities open into the nasopharynx above the soft palate. The nasopharynx receives the auditory (eustachian ) tubes from the middle ears and houses the pharyngeal tonsil. The nasopharynx passes only air and is lined by pseudostratified columnar epithelium.
What is the function of the pharynx?
For the digestive system, its muscular walls function in the process of swallowing and it serves as a pathway for the movement of food from the mouth to the esophagus . After food is introduced into the mouth and is chewed, the tongue pushes it to the back of the throat to be swallowed.
Where is the pharynx located?
The human pharynx is the part of the throat situated immediately inferior to (below) the mouth and nasal cavity, and superior to the esophagus and larynx. The pharynx extends from the base of the skull down to the inferior border of the cricoid cartilage (around the C6 vertebral level), where it becomes continuous with the esophagus.
What would happen if the pharynx was not functioning?
The function of the pharynx in the digestive system is critical. Without the pharynx, swallowing would not occur, and food could not be digested. The body would starve and eventually cease to function.
What is the pharynx made of?
Despite of the fact that majority of peopleconsider pharynx just as the throat. It resembles a funnel made out of muscles that acts as an intermediary between the nasal cavity, the larynx and esophagus. The nasopharynx simply allows air to travel through it and reach the lower sections.
Which part of the throat connects the upper part of the throat to the nasal cavity?
The nasopharynx (epipharynx) which connects the upper part of the throat with the nasal cavity. The oropharynx (mesopharynx) positioned between the top of the epiglottis and the soft palate. The laryngopharynx (hypopharynx)located below the epiglottis. The pharynx is part of the digestive system and also the respiratory system;
Which structure allows air to travel through the nasopharynx?
The nasopharynx simply allows air to travel through it and reach the lower sections. The oropharynx does something similar, except it is located at the posterior of the oral cavity. Once the air reaches the laryngopharynx, a cartilaginous structure called the epiglottis will divert it to the larynx.
Which flap is responsible for transferring air from the esophagus to the trachea?
The epiglottis is a flap that performs a vital task, by switching access between the esophagus and trachea. This ensures that air will travel through the trachea, but that food which is swallowed and travels through the pharynx is diverted to the esophagus.
What is the function of the pharynx?
Following are the main functions of the pharynx: The pharynx serves both respiratory and digestive functions. It is a 5-inch-long cylindrical tube that involves the passage of food and air into its appropriate chambers. The connection between the oral and nasal regions enables us to breathe through nose and mouth.
What is the pharynx?
Based on the attachments, the pharynx is subdivided into three regions: Nasopharynx: It is situated in the space between the back of the nose and soft palate. It is continuous with the nasal cavity and forms the upper part of the respiratory system. It plays an important role in transferring air from the nose to the larynx.
How do you know if you have cancer of the larynx?
Symptoms and signs of cancer of the larynx, the organ at the front of the neck, include hoarseness, a lump in the neck, sore throat, cough, problems breathing, bad breath, earache, and weight loss. Treatment for larynx cancer depends on the stage (the extent) of the disease. Radiation therapy, surgery, and chemotherapy are all forms ...
Why does my throat hurt?
A sore throat may be caused by bacterial infections, viral infections, toxins, irritants, trauma, or injury to the throat area . Common symptoms of a sore throat include a fever, cough, runny nose, hoarseness, earaches, sneezing, and body aches.
What is the role of the Eustachian tube?
The adenoid tissue in the nasopharynx is the lymphoid tissue that helps fight infections entering through the nasal epithelium or lining. The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx.
What is the connection between the oral and nasal regions?
The connection between the oral and nasal regions enables us to breathe through nose and mouth. The pharyngotympanic tube (Eustachian tube) connecting the middle ear to the pharynx equalizes the air pressure in the ear and drains fluid from the ear, preventing ear infections. It plays an important role in phonation (speech).
What is the function of tonsils?
The tonsils are called as gatekeepers. Their function is to help fight infections that enter through the mouth or nose. They contain a collection of white cells. Laryngopharynx: It extends from the front of the epiglottis to the top of the esophagus at the level of base of the neck.
What are the functions of the respiratory system?
The airways have three main functions: - To act as channels for gases moving to and from the lungs; - To protect the lungs from the entry of any foreign matter; - To control the heat and humidity of the gases.
Which part of the respiratory system is visible externally?
The nose. The nose is the only part of the respiratory system that is visible externally and is the route for air entry into the respiratory system. Air is drawn in via the nostrils or external nares and enters the large nasal cavity, which is divided into two by the nasal septum. The nasal cavity is partitioned from the oral cavity directly below ...
What part of the larynx is closed off?
Another leaf-shaped piece of cartilage, the epiglottis, partly covers the opening of the larynx and acts like a trapdoor, closing off the glottis during swallowing so that food and fluids cannot enter the trachea. If anything other than air enters the larynx, the cough reflex is triggered to try to expel the foreign matter (Marieb, 2006).
Why is the mucosal epithelium thicker than elsewhere in the respiratory tract?
The mucosal epithelium in the pharynx is thicker than elsewhere in the respiratory tract as it has to protect the tissues from any abrasive and chemical trauma caused by food. Two eustachian or auditory tubes connect the middle ears with the nasopharynx and allow pressure in the middle and outer ear to equalise.
What is the nasal cavity?
The nasal cavity is partitioned from the oral cavity directly below it by the palate. Like the rest of the respiratory tract, the nose is lined with mucosal epithelium containing glands that secrete a thick, sticky mucus that helps to moisten the tract.
What are the structures that open into the nose and drain tears from the corner of each eye?
Lacrimal ducts open into the nose and drain tears from the corner of each eye. This also helps to moisten the surface of the nasal cavity. Three shell-like structures, the conchae or turbinates, protrude into each side of the nasal cavity and increase the surface area over which air flows on its way to the lungs (Fig 2).
Where does humidified air pass through?
Warmed, humidified air passes from the nasal cavities through the internal nares into the pharynx, a structure shared by the respiratory and digestive systems.
What is the respiratory system?
Your respiratory system is the network of organs and tissues that help you breathe. This system helps your body absorb oxygen from the air so your organs can work. It also cleans waste gases, such as carbon dioxide, from your blood. Common problems include allergies, diseases or infections.
What are the two parts of the respiratory system that help regulate the temperature and humidity of the air you inhale?
Your airways are a complicated system that includes your: Mouth and nose: Openings that pull air from outside your body into your respiratory system. Sinuses: Hollow areas between the bones in your head that help regulate the temperature and humidity of the air you inhale.
What are the bones and muscles that surround the respiratory system?
Some of the bones and muscles in the respiratory system include your: Diaphragm: Muscle that helps your lungs pull in air and push it out. Ribs: Bones that surround and protect your lungs and heart. When you breathe out, your blood carries carbon dioxide and other waste out of the body.
What does the syringe do to your body?
Besides helping you inhale (breathe in) and exhale (breathe out), it: Allows you to talk and to smell. Warms air to match your body temperature and moisturizes it to the humidity level your body needs. Delivers oxygen to the cells in your body.
Why is it important to clear mucus out of the lungs?
Being able to clear mucus out of the lungs and airways is important for respiratory health.
What is a spirometer?
A spirometer is a device that can tell how much air you inhale and exhale. See your doctor for regular checkups to help prevent serious respiratory conditions and lung disease. Early diagnosis of these issues can help prevent them from becoming severe.
What are the lobes of the lungs?
Lung lobes: Sections of the lungs — three lobes in the right lung and two in the left lung. Pleura: Thin sacs that surround each lung lobe and separate your lungs from the chest wall. Some of the other components of your respiratory system include:
Which part of the pharynx is the only passageway for air?
The pharynx includes three regions: The nasopharynx is posterior to the nasal cavity and serves only as a passageway for air. The oropharynx lies posterior to the oral cavity and contains the palatine tonsils.
Where is the oropharynx located?
The oropharynx lies posterior to the oral cavity and contains the palatine tonsils. Both air and ingested food pass through the oropharynx and through the laryngopharynx below. The laryngopharynx lies posterior to the epiglottis and connects to the larynx (superiorly) and the esophagus (inferiorly).
What part of the pharynx is the cilia?
Finally the filtered, warmed air passes out of the back of the nasal cavities into the nasopharynx, the uppermost part of the pharynx. 2. The Paranasal Sinuses Surround the Nasal Cavities.
How many cartilages are in the larynx?
This larynx is comprised of nine cartilages. One, the epiglottis, is a lifesaver: Located on the posterior side of the larynx, the epiglottis closes like a trap door as we swallow. This action steers food down the esophagus and away from the windpipe.
What are the structures that allow us to breathe and speak?
These structures allow us to breathe and speak. They warm and clean the air we inhale: mucous membranes lining upper respiratory structures trap some foreign particles, including smoke and other pollutants, before the air travels down to the lungs. 1. The Nose and Nasal Cavities Provide Airways for Respiration.
What is the function of the nose?
Nose. The nose detects odor molecules and helps filter and warm the air we inhale. The upper respiratory system, or upper respiratory tract, consists of the nose and nasal cavity, the pharynx, and the larynx. These structures allow us to breathe and speak.
Which organ is responsible for breathing and talking?
4. The Larynx and Vocal Cords Allow Us to Breathe and Talk and Sing. The larynx connects the lower part of the pharynx, the laryngopharynx, to the trachea. It keeps the air passages open during breathing and digestion and is the key organ for producing sound. This larynx is comprised of nine cartilages.
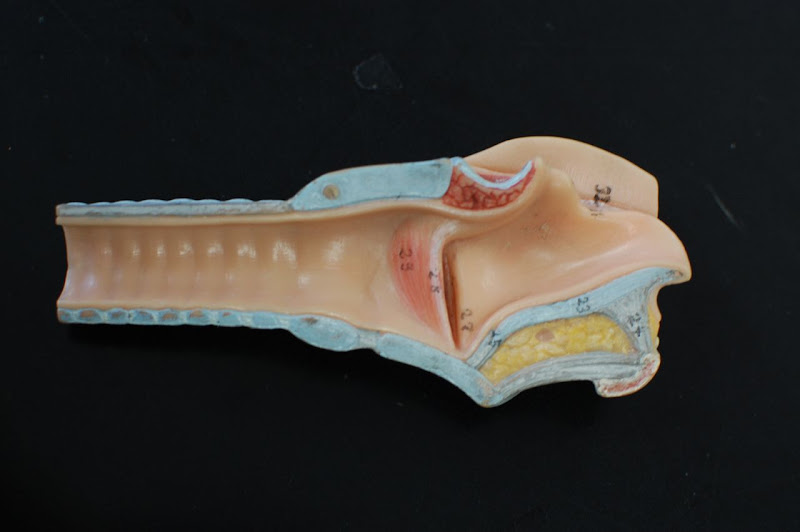
What Is The Pharynx
Where Is The Pharynx Located
Functions – What Does The Pharynx Do
Conditions Associated with Pharynx