What does Kepler's third law imply about planetary motion?
Kepler's third law of planetary motion says that the average distance of a planet from the Sun cubed is directly proportional to the orbital period squared. Newton found that his gravity force law could explain Kepler's laws. Kepler found this law worked for the planets because they all orbit the same star (the Sun).
What are the Three Laws of planetary motion?
Planetary Physics Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion Kepler's three laws describe how planetary bodies orbit the Sun. They describe how (1) planets move in elliptical orbits with the Sun as a focus, (2) a planet covers the same area of space in the same amount of time no matter where it is in its orbit, and (3) a planet’s orbital period is proportional to the size of its orbit (its semi-major ...
What is astronomer proposed three laws of planetary motion?
Kepler’s third law of planetary motion says that the average distance of a Sun’s gravity do the work and take advantage of Kepler’s laws of orbital motion. In the early 1600s, Johannes Kepler proposed three laws of planetary motion. Kepler was able to summarize the carefully collected data of his mentor – Tycho Brahe
What was Johanne Keplers Three Laws of planetary motion?
Kepler’s three laws of planetary motion can be stated as follows: ( 1) All planets move about the Sun in elliptical orbits, having the Sun as one of the foci. ( 2) A radius vector joining any planet to the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal lengths of time.

What does Kepler's third law mean simplified?
The Kepler's third law also known as the Law of Harmonies states that the ratio of the squares of the periods of any two planets is equal to the ratio of the cubes of their average distances from the sun. The third law compares the orbital period and radius of orbit of a planet to those of other planets.
What is Kepler's 3rd law state?
Kepler's third law states that square of period of revolution (T) of a planet around the sun, is proportional to third power of average distance r between sun and planet. i.e T2=Kr3 here K is constant.
Why are the 3 laws of planetary motion important?
Kepler's laws of planetary motion mark an important turning point in the transition from geocentrism to heliocentrism. They provide the first quantitative connection between the planets, including earth. But even more they mark a time when the important questions of the times were changing.
When was the third law of planetary motion?
1618They were derived by the German astronomer Johannes Kepler, whose analysis of the observations of the 16th-century Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe enabled him to announce his first two laws in the year 1609 and a third law nearly a decade later, in 1618.
What is meant by Kepler's law?
Definition of Kepler's law 1 : a statement in astronomy: the orbit of each planet is an ellipse that has the sun at one focus. 2 : a statement in astronomy: the radius vector from the sun to each planet generates equal orbital areas in equal times.
How do you verify Kepler's third law?
1:064:46Verifying Kepler's Third Law - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo the radius i'll call r from here to here is proportional to t to the power of 2 where it is beingMoreSo the radius i'll call r from here to here is proportional to t to the power of 2 where it is being cubed and the proportional constant between these two variables will be represented as k.
How do you use Kepler's third law?
The equation for Kepler's Third Law is P² = a³, so the period of a planet's orbit (P) squared is equal to the size semi-major axis of the orbit (a) cubed when it is expressed in astronomical units.
How do Kepler's laws affect us today?
His descriptions of planetary motions became known as Kepler's laws. Today, these laws not only describe planetary motion but also determine the orbits of satellites and space stations.
What are Kepler's 3 laws of planetary motion quizlet?
Terms in this set (3) The planets orbits in an elliptical [oval] shape. The sun is at one focus. The second focus is not needed because of sun's mass & gravity. A planet spends equal amount of time [in its orbit] perihelion & aphelion.
What are the 3 laws of planetary motion?
There are actually three, Kepler's laws that is, of planetary motion: 1) every planet's orbit is an ellipse with the Sun at a focus; 2) a line joining the Sun and a planet sweeps out equal areas in equal times; and 3) the square of a planet's orbital period is proportional to the cube of the semi-major axis of its ...
Who discovered the three laws of planetary motion quizlet?
29) Tycho Brahe discovered the three laws of planetary motion.
What event actually made it possible for the three laws of planetary motion to be discovered?
What specific event really made it possible for the three laws of planetary motion to be discovered? When NASA and a group of astronomers sent up a spacecraft designed to find planets orbiting other stars, they named it after Kepler.
What does Kepler's second law state?
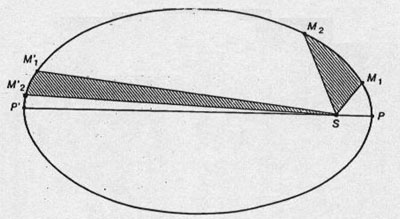
Kepler's Second Law says says that a line running from the sun to the planet sweeps out equal areas of the ellipse in equal times. This means that the planet speeds up as it approaches the sun and slows down as it departs from it.
What is Kepler's law of planetary motion class 9?
The Kepler's Law of planetary motion typically revolves around the periods, orbits, and areas with regard to planet and sun. The principle thus states that the planets revolve around the sun in elliptical orbits with the sun at one focus in a sun-centred solar system.
What is Kepler's law formula?
T = 2 π r 3 G M E . T = 2 π r 3 G M E . For an ellipse, recall that the semi-major axis is one-half the sum of the perihelion and the aphelion. For a circular orbit, the semi-major axis (a) is the same as the radius for the orbit.
What are Kepler's 3 laws of planetary motion quizlet?
Terms in this set (3) The planets orbits in an elliptical [oval] shape. The sun is at one focus. The second focus is not needed because of sun's mass & gravity. A planet spends equal amount of time [in its orbit] perihelion & aphelion.
Johannes Kepler
The first seeds of Kepler’s laws were planted before his 1571 birth in the Free Imperial City of Weil der Stadt, which is now part of the Stuttgart Region in the German state of Baden-Württemberg to father Heinrich Kepler and mother Katharina Guldenmann.
Properties of ellipses laws one and two
One of the keys to understanding Kepler’s laws of planetary motion lies in the properties of ellipses.
What does the third law of planetary motion mean?
The third law states that the ratio of the squares of the orbital period for two planets is equal to the ratio of the cubes of their mean orbit radius. This indicates that the length of time for a planet to orbit the Sun increases rapidly with the increase of the radius of the planet’s orbit.
What does Kepler’s second and third law imply about planetary motion?
Universal gravitation implies that the planets further from the Sun will move more slowly than the planets closer to the Sun ( Kepler’s third law). … Universal gravitation implies that when a planet is closer to the Sun in its orbit , it will move faster than when it is farther from the Sun ( Kepler’s second law).
When a planet is closest to the sun in its orbit?
The place where the planet is closest to the Sun (helios in Greek) and moves the fastest is called the perihelion of its orbit, and the place where it is farthest away and moves the most slowly is the aphelion. For the Moon or a satellite orbiting Earth (gee in Greek), the corresponding terms are perigee and apogee.
What are Kepler’s 3 laws in simple terms?
There are actually three, Kepler’s laws that is, of planetary motion: 1) every planet’s orbit is an ellipse with the Sun at a focus; 2) a line joining the Sun and a planet sweeps out equal areas in equal times; and 3) the square of a planet’s orbital period is proportional to the cube of the semi-major axis of its …
Which law states that the period for a planet to orbit the Sun increases rapidly with the radius of its orbit?
Kepler’s Third Law : the squares of the orbital periods of the planets are directly proportional to the cubes of the semi major axes of their orbits. Kepler’s Third Law implies that the period for a planet to orbit the Sun increases rapidly with the radius of its orbit.
How much stronger is the gravitational pull of the sun on Earth at 1 AU than it is on Saturn at?
Test 1 (part 2)QuestionAnswerAccording to Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation if the moon were three times further from Earth the force by Earth on the Moon would:decreases by a factor of 9How much stronger is the gravitational pull of the Sun on Earth, at 1 AU, than it is on Saturn at 10 AU?100X.
Which law of planetary motion is directly proportional to the cubes of the mean distances from the Sun?
Kepler's third law of planetary motion. The squares of the sidereal periods (P) of the planets are directly proportional to the cubes of their mean distances (d) from the Sun.
Who developed the laws of planetary motion?
See all videos for this article. Kepler’s laws of planetary motion, in astronomy and classical physics, laws describing the motions of the planets in the solar system. They were derived by the German astronomer Johannes Kepler, whose analysis of the observations ...
How many questions are there about Kepler's laws of planetary motion?
Kepler's laws of planetary motion explained in five questions.
How fast is the Earth traveling?
When Earth is closest to the Sun, it is traveling at a speed of 30.3 kilometers (18.8 miles) per second. Kepler’s three laws of planetary motion can be stated as follows: ( 1) All planets move about the Sun in elliptical orbits, having the Sun as one of the foci. ( 2) A radius vector joining any planet to the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal ...
What is Kepler's second law?
Kepler's second law of planetary motion. A radius vector joining any planet to the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal lengths of time. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc./Patrick O'Neill Riley. Kepler's third law. Kepler's third law of planetary motion.
What is the first law of Kepler?
Kepler’s first law means that planets move around the Sun in elliptical orbits. An ellipse is a shape that resembles a flattened circle. How much the circle is flattened is expressed by its eccentricity. The eccentricity is a number between 0 and 1. It is zero for a perfect circle.
What is the eccentricity of an ellipse?
The eccentricity of an ellipsemeasures how flattened a circleit is. It is equal to the square root of [1 - b*b/(a*a)]. The letter a stands for the semimajor axis, ½ the distance across the long axis of the ellipse. The letter b stands for the semiminor axis, ½ the distance across the short axis of the ellipse. For a perfect circle, a and b are the same such that the eccentricity is zero. Earth’s orbit has an eccentricity of 0.0167, so it is very nearly a perfect circle.
What is the third law?
The third law expresses that the farther a planet is from the Sun, the slower its orbital speed, and vice versa. Isaac Newton showed in 1687 that relationships like Kepler's would apply in the Solar System as a consequence of his own laws of motion and law of universal gravitation .
Who wrote the laws of planetary motion?
In astronomy, Kepler's laws of planetary motion, published by Johannes Kepler between 1609 and 1619, describe the orbits of planets around the Sun. The laws modified the heliocentric theory of Nicolaus Copernicus, replacing its circular orbits and epicycles with elliptical trajectories, and explaining how planetary velocities vary. The three laws state that:
What is the orbit of every planet?
The orbit of every planet is an ellipse with the Sun at one of the two foci.
What are the laws of the planets?
The three laws state that: The orbit of a planet is an ellipse with the Sun at one of the two foci. A line segment joining a planet and the Sun sweeps out equal areas during equal intervals of time. The square of a planet's orbital period is proportional to the cube of the length of the semi-major axis of its orbit.
What is the second law of Kepler?
Kepler had two versions, related in a qualitative sense: the "distance law" and the "area law". The "area law" is what became the Second Law in the set of three; but Kepler did himself not privilege it in that way.
What is Kepler's method?
His method involves the solution of a transcendental equation called Kepler's equation .
How many laws did Kepler have?
Figure 1: Illustration of Kepler's three laws with two planetary orbits.
What is Kepler's third law?
Kepler’s third law (in fact , all three) works not only for the planets in our solar system, but also for the moons of all planets, dwarf planets and asteroids, satellites going round the Earth, etc.
Who put the Sun at the center of the Earth?
Copernicus , Kepler, and Newton dealt a one-two-three knockout blow to the idea – thousands of years old – that the Sun (and planets) moved around the Earth. Copernicus put the Sun at the center, Kepler modified Copernicus’ circular motions (and provided a simple, quantitative description of the actual motion), and Newton explained how it all worked (gravity).
What is the square of the orbital period of a planet?
caption]#N#“The square of the orbital period of a planet is proportional to the cube of the semi-major axis of its orbit ” That’s Kepler’s third law. In other words, if you square the ‘year’ of each planet, and divide it by the cube of its distance to the Sun, you get the same number, for all planets.
What is the third law of gravity?
Kepler's Third Law implies that the period for a planet to orbit the Sun increases rapidly with the radius of its orbit. Thus we find that Mercury, the innermost planet, takes only 88 days to orbit the Sun. The earth takes 365 days, while Saturn requires 10,759 days to do the same. Though Kepler hadn't known about gravitation when he came up with his three laws, they were instrumental in Isaac Newton deriving his theory of universal gravitation, which explains the unknown force behind Kepler's Third Law. Kepler and his theories were crucial in the better understanding of our solar system dynamics and as a springboard to newer theories that more accurately approximate our planetary orbits.
What is the second law of the Sun?
Kepler's Second Law: the imaginary line joining a planet and the Sun sweeps equal areas of space during equal time intervals as the planet orbits. Basically, that planets do not move with constant speed along their orbits. Rather, their speed varies so that the line joining the centers of the Sun and the planet sweeps out equal parts of an area in equal times. The point of nearest approach of the planet to the Sun is termed perihelion. The point of greatest separation is aphelion, hence by Kepler's Second Law, a planet is moving fastest when it is at perihelion and slowest at aphelion.
Why did Kepler have difficulty with Mars?
After much struggling, Kepler was forced to an eventual realization that the orbits of the planets are not circles, but were instead the elongated or flattened circles that geometers call ellipses, and the particular difficulties Brahe hand with the movement of Mars were due to the fact that its orbit was the most elliptical of the planets for which Brahe had extensive data. Thus, in a twist of irony, Brahe unwittingly gave Kepler the very part of his data that would enable Kepler to formulate the correct theory of the solar system, banishing Brahe's own theory.
Why is Mars' orbit so problematic?
But the reason Mars' orbit was problematic was because the Copernican system incorrectly assumed the orbits of the planets to be circular.
Why did Kepler set up the Mars orbit?
It is believed that part of the motivation for giving the Mars problem to Kepler was Brahe's hope that its difficulty would occupy Kepler while Brahe worked to perfect his own theory of the solar system, which was based on a geocentric model, where the earth is the center of the solar system. Based on this model, the planets Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn all orbit the Sun, which in turn orbits the earth. As it turned out, Kepler, unlike Brahe, believed firmly in the Copernican model of the solar system known as heliocentric, which correctly placed the Sun at its center. But the reason Mars' orbit was problematic was because the Copernican system incorrectly assumed the orbits of the planets to be circular.
What is the third property of an ellipse?
The third property of an ellipse: the longest axis of the ellipse is called the major axis, while the shortest axis is called the minor axis. Half of the major axis is termed a semi-major axis. Knowing then that the orbits of the planets are elliptical, johannes Kepler formulated three laws of planetary motion, which accurately described the motion of comets as well.
What are Kepler's laws?
Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion. Kepler's three laws describe how planetary bodies orbit about the Sun. They describe how (1) planets move in elliptical orbits with the Sun as a focus, (2) a planet covers the same area of space in the same amount of time no matter where it is in its orbit, and ...
