What enzyme breaks down alcohol into acetaldehyde?
Two liver enzymes - alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) and aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) - begin to break apart the alcohol molecule so that it can eventually be eliminated from the body. ADH helps convert the alcohol to acetaldehyde. The enzymes cytochrome P450 2E1 (CYP2E1) and catalase also break down alcohol to acetaldehyde.
What is acetaldehyde and how is it made?
A product of alcohol metabolism that is more toxic than alcohol itself, acetaldehyde is created when the alcohol in the liver is broken down by an enzyme called alcohol dehydrogenase.
What is acetaldehyde and how can it be reduced?
As mentioned above, in the case of alcohol the toxin in question is acetaldehyde. Research has shown that precise supplementation of a combination of compounds can reduce acetaldehyde toxicity and aid the deficient ALDH2 enzyme in metabolizing alcohol — treating the symptoms immediately, rather than preventing them completely.
What enzyme converts ethanol to acetic acid?
Your liver converts the ethanol to acetaldehyde, a substance that can cause cell damage. Another enzyme called aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) helps convert acetaldehyde to acetic acid (vinegar), which is nontoxic.

What helps the body break down acetaldehyde?
How to reduce acetaldehyde exposureAcetium capsule reduces the amount of acetaldehyde in the stomach. ... Avoid or reduce smoking and alcohol consumption.Do not drink alcohol to the point of intoxication. ... Consume mild alcoholic beverages rather than hard liquor. ... Maintain a high level of oral hygiene.More items...
How do you break down acetaldehyde quickly?
Increased glutathione levels allow the body to break down acetaldehyde more quickly and helps reverse the depletion of glutathione caused by alcohol consumption.
What enzyme can break down alcohol?
An enzyme called alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) helps metabolize (process) the ethanol. Your liver converts the ethanol to acetaldehyde, a substance that can cause cell damage. Another enzyme called aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) helps convert acetaldehyde to acetic acid (vinegar), which is nontoxic.
What foods break down acetaldehyde?
Eggs. They're full of really high-quality complete protein—complete meaning containing all essential amino acids. In particular, Cysteine breaks down acetaldehyde, which is the alcohol-metabolism byproduct that is causing your headache, and taurine, which is especially helpful for liver function.
Does Vitamin C break down acetaldehyde?
Vitamin C is needed to maintain cysteine in the reduced state in which it is effective against acetaldehyde. Vitamin B1 or thiamine and alpha-lipoic acid are also involved in acetaldehyde detoxification but levels of these substances are also reduced by alcohol consumption.
Does taurine break down acetaldehyde?
Our findings suggest that the oral supplementation of taurine prevents ethanol-induced hypertension by decreasing protein bound acetaldehyde and altering the cation handling by the membrane.
What breaks down alcohol the fastest?
The liver is the primary organ responsible for the detoxification of alcohol. Liver cells produce the enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase which breaks alcohol into ketones at a rate of about 0.015 g/100mL/hour (reduces BAC by 0.015 per hour).
What can neutralize alcohol?
For one drink of alcohol, a 28.5% concentration of acetic acid is recommended, or a 2.05g concentration of citric acid. Using these concentrations will allow the alcohol to be most efficiently neutralized in the body.
What helps your body break down alcohol?
There is nothing a person can do to quickly reduce the blood alcohol concentration (BAC) level in their body. The liver needs time to filter blood and remove the alcohol from the system....Appearing soberCoffee. ... Cold showers. ... Eating and drinking. ... Sleep. ... Exercise. ... Carbon or charcoal capsules.
Is coffee high in acetaldehyde?
Ground and instant coffee has some of the highest levels of acetaldehyde of any non-alcoholic foods and vegetables. The research measuring acetaldehyde levels in these foods can be found here and here.
Does coffee have acetaldehyde?
Acetaldehyde occurs naturally in coffee, bread, and ripe fruit, and is produced by plants. It is also produced by the partial oxidation of ethanol by the liver enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase and is a contributing cause of hangover after alcohol consumption.
Can Sprite break down acetaldehyde?
The carbonated lemon-lime drink showed a markedly positive effect on alcohol-related symptoms in a recent study conducted by a team of Chinese scientists. Apparently, Sprite has the ability to breakdown acetaldehyde, a metabolite of ethanol.
Can Sprite break down acetaldehyde?
The carbonated lemon-lime drink showed a markedly positive effect on alcohol-related symptoms in a recent study conducted by a team of Chinese scientists. Apparently, Sprite has the ability to breakdown acetaldehyde, a metabolite of ethanol.
What does acetaldehyde do to the brain?
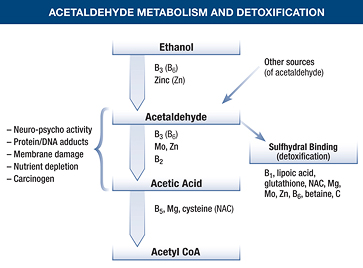
Acetaldehyde Adducts in the Brain An increase in the levels of ROS due to ethanol oxidation leads to the formation of lipid peroxides, which in turn cause modification of proteins and DNA, resulting in injury or damage to tissue within the brain.
Does Sprite break down alcohol?
The researchers found that Sprite was one of the top drinks that sped up the ALDH process, causing the alcohol to be broken down more quickly and shortening how long the hangover lasts.
What alcoholic beverages have high acetaldehyde content?
Clear, non-flavored spirits, such as gin and vodka, tend to have less acetaldehyde than dark, fruity drinks, such as brandy or sherry. Regular beer tends to have lower acetaldehyde content, though higher than clear spirits. Wine, on the other hand, has relatively high acetaldehyde content.
What does alcohol dehydrogenase do in the liver?
In the liver, alcohol dehydrogenase converts ethanol to acetaldehyde, which is then processed by aldehyde dehydrogenase into acetate. Acetate is th...
Is alcohol dehydrogenase good or bad?
Alcohol dehydrogenase can only be considered as good, since all living organisms contain at least one type of alcohol dehydrogenase. Without them,...
How does alcohol dehydrogenase break down alcohol?
Alcohol dehydrogenase binds to ethanol. It performs a redox reaction on the alcohol-containing carbon to create acetaldehyde, also known as ethanol.
What does alcohol dehydrogenase do?
Alcohol dehydrogenase is an enzyme that uses a redox reaction to convert the second carbon or ethanol into an aldehyde group. This reaction convert...
What happens if you don't have alcohol dehydrogenase?
Without alcohol dehydrogenase, even small levels of alcohol in food sources or produced by the gut itself would be toxic. As alcohol dehydrogenase...
What is Acetaldehyde?
Acetaldehyde is a flammable liquid that is commonly used in the manufacture of acetic acid, perfumes, and flavors. [1] It is also found in varying concentrations in plants, fresh fruits, vegetables, cigarette smoke, gasoline and diesel exhaust fumes. [2]
What is the process of producing acetaldehyde?
Acetaldehyde from Alcohol. As mentioned above, acetaldehyde produced by the action of alcohol dehydrogenase when we consume alcohol. Alcohol dehydrogenases are a class of enzymes that play an important role in the oxidation and reduction of various aldehydes such as acetaldehyde.
What happens when you combine acetaldehyde and alcohol?
When combining the acetaldehyde from the wine with the acetaldehyde that is produced during the metabolism of the wine’s alcohol, the result is a heavy load of toxins that the body is required to break down. Couple this with an ALDH2 deficient liver and we have a situation where a large dose of acetaldehyde begins to contribute to some ...
How does alcohol dehydrogenase work?
Firstly, alcohol dehydrogenase enzymes convert the alcohol to acetaldehyde. Then the acetaldehyde is further broken down into a less toxic byproduct called acetate.
What is the main source of acetaldehyde in cigarettes?
Some studies have shown that naturally occurring polysaccharides in tobacco, like cellulose, are the main sources of acetaldehyde in cigarette smoke. [8] . The amount that enters the body is mostly affected by design factors that increase total smoke production such the kinds of filter and paper used.
Where does acetaldehyde enter the body?
Acetaldehyde also gets dissolved into saliva and enters the stomach when it is swallowed. [6] . Once it enters the body, it is broken down by aldehyde dehydrogenase in the blood, liver and elsewhere in the body, including at the blood-brain barrier.
Which food has the highest amount of acetaldehyde?
In this study, some of the foods and beverages containing the highest amount of acetaldehyde included instant coffee and fermented foods such as yogurt.
Which enzyme is attracted to acetaldehyde?
The acetaldehyde is then attacked by another enzyme, acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, and another substance called glutathione, which contains high quantities of cysteine (a substance that is attracted to acetaldehyde). Together, the acetaldehyde dehydrogenase and the glutathione form the nontoxic acetate (a substance similar to vinegar).
What is the drug that blocks acetaldehyde?
In studies that blocked the enzyme that breaks down acetaldehyde (acetaldehyde dehydrogenase) with a drug called Antabuse, designed to fight alcoholism, acetaldehyde toxicity resulted in headaches and vomiting so bad that even alcoholics were wary of their next drink.
What is the chemical that causes a hangover?
Biology of a Hangover: Acetaldehyde. A product of alcohol metabolism that is more toxic than alcohol itself, acetaldehyde is created when the alcohol in the liver is broken down by an enzyme called alcohol dehydrogenase.
Does alcohol run out of glutathione?
Unfortunately, the liver's stores of glutathione quickly run out when larger amounts of alcohol enter the system. This causes the acetaldehyde to build up in the body as the liver creates more glutathione, leaving the toxin in the body for long periods of time.
Is glutathione acetate?
Together, the acetaldehyde dehydrogenase and the glutathione form the nontoxic acetate (a substance similar to vinegar). This process works well, leaving the acetaldehyde only a short amount of time to do its damage if only a few drinks are consumed.
Why is acetaldehyde bad for you?
Since acetaldehyde is regularly entering the body from numerous sources or being created inside the body, it is always present in low concentrations. In those with ALDH2 Deficiency, this is a problem because it can accumulate and cause damage. Acetaldehyde is a reactive compound, and can damage DNA and proteins in the body.
What is ALDH2 in the liver?
ALDH2 ( Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 2), is an enzyme found in the liver. It is responsible for the breakdown of a toxin called acetaldehyde. In addition to being a toxin, acetaldehyde is a carcinogen, which means it can cause cancer.
Who does ALDH2 Deficiency affect?
Over 1 billion people globally have ALDH2 Deficiency. While it affects up to 40% of all people of East Asian descent, including Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Vietnamese, and more, other ethnicities can have ALDH2 Deficiency as well. In fact, people of all ethnicities can have ALDH2 Deficiency. You can find out for sure by taking an ALDH2 DNA test.
How does Essential AD2 help?
By doing so, Essential AD2 reduces the symptoms of alcohol flush reaction, protects from the acetaldehyde toxin, and improves liver health and function.
Is aldh2 a genetic disorder?
ALDH2 Deficiency is a genetic disorder, and so it is passed down from parents to children. Since acetaldehyde is regularly entering the body from everyday sources or is being created inside the body, it is always present in low concentrations. In those with ALDH2 Deficiency, it can accumulate and cause damage and inflammation.
Is acetaldehyde a reactive compound?
Acetaldehyde is a reactive compound, and can damage D NA and proteins in the body. Long term acetaldehyde exposure can have serious health implications, including higher risk of diseases like gastrointestinal cancer and liver cirrhosis. This is why those with ALDH2 Deficiency are at significantly higher risk of these diseases than others.
Is acetaldehyde a carcinogen?
In addition to being a toxin, acetaldehyde is a carcinogen, which means it can cause cancer. Normally, the ALDH2 enzyme quickly and safely breaks down acetaldehyde. ALDH2 Deficiency is a genetic disorder in which the ALDH2 enzyme doesn't work properly. This is caused by a mutation in the ALDH2 Enzyme. This mutation leaves the enzyme unable ...
What enzyme breaks down acetaldehyde into acetate?
Thus, the body has a way of dealing with this toxic compound. Another enzyme called acetaldehyde dehydrogenase comes in to convert acetaldehyde to acetate, a harmless molecule that is further broken down into water and carbon dioxide. These compounds can easily be released from the body.
Where does alcohol dehydrogenase come from?
The answer comes from alcohol dehydrogenase. Alcohol dehydrogenase an enzyme that is found mostly in the liver and stomach. Like its name implies, its job is to start the pathway of alcohol metabolism. Its name also implies the mechanism of action in this process. The prefix 'de' means not, and 'hydro' refers to a hydrogen atom. So, alcohol dehydrogenase works by removing a hydrogen atom from alcohol. The hydrogen atom is bound to part of the enzyme called NAD+ and is later released, regenerating the enzyme for further use.
How is methanol metabolized?
Methanol is metabolized to formaldehyde by alcohol dehydrogenase. Interestingly methanol poisoning can actually be treated by administering intravenous ethanol to the patient. The ethanol competes with methanol for alcohol dehydrogenase activity, thus slowing down how much methanol alcohol dehydrogenase can convert to formaldehyde.
How does ethanol break down?
When we drink ethanol, alcohol dehydrogenase in the stomach is able to get to work breaking it down. Ethanol that continues through the stomach is absorbed into the blood in the small intestine. Blood in capillaries surrounding the small intestine goes directly to the liver. The main job of the liver is to detoxify the blood, so blood goes directly here from the digestive tract. In the liver there is more alcohol dehydrogenase to break down ethanol in the blood.
What is the job of the liver?
The main job of the liver is to detoxify the blood, so blood goes directly here from the digestive tract. In the liver there is more alcohol dehydrogenase to break down ethanol in the blood. But, alcohol dehydrogenase breaks alcohol down to another toxic compound, acetaldehyde.
What is the hydrogen atom of alcohol?
The hydrogen atom is bound to part of the enzyme called NAD+ and is later released, regenerating the enzyme for further use. Although there are many types of alcohol in our environment most of the work done by alcohol dehydrogenase is on ethanol, the type of alcohol we drink in beer, wine, and spirits. We'll talk about the metabolism of other types ...
Is acetaldehyde bad for you?
Although this seems like a bad thing, it's actually beneficial to people as it protects against alcoholism.
How Does Essential AD2 Work to Address ALDH2 Deficiency?
FDA. The proprietary blend enables the body to target acetaldehyde breakdown in two ways: (1) by increasing the activity of the ALDH2 Deficient enzyme to improve the natural breakdown of the acetaldehyde, and (2) by directly counteracting the acetaldehyde toxin. Essential AD2’s efficacy in reducing acetaldehyde accumulation during alcohol consumption has been demonstrated through third party, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical research.
How to reduce aldh2?
The main thing is to keep our body’s acetaldehyde accumulation as low as possible. Limiting our intake of alcohol, coffee, sugary foods and beverages, and exposure to air pollution and cigarette smoke can help reduce acetaldehyde accumulation. Also, taking a daily dietary supplement, such as Essential AD2, can help reduce acetaldehyde accumulation in the body every day.
What is Alcohol Flush Reaction? How Do I Know if I Have ALDH2 Deficiency?
The main indicator of ALDH2 Deficiency is the presence of Alcohol Flush Reaction (known as ‘Asian Flush’ ) when drinking alcohol. Symptoms of Alcohol Flush Reaction may include red facial flushing, raised body temperature, rapid heart rate, inflammation, headache, nausea and dizziness. If you suffer from Alcohol Flush Reaction, there is a very good chance that you have ALDH2 Deficiency.
How Does ALDH2 Deficiency Impact Our Health?
Studies show that people with ALDH2 Deficiency are at higher risk of esophageal cancer, liver cirrhosis and Alzheimer’s. This is due to our weakened ability to break down acetaldehyde in the body. Many people with ALDH2 Deficiency choose not to drink alcohol. This is very helpful because alcohol results in high concentrations of acetaldehyde. But the problem is that acetaldehyde can still enter the body in low levels through other everyday sources such as high sugar foods, coffee, soda, air pollution and cigarette smoke.
What is ALDH2 Deficiency?
ALDH2 stands for Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 2 and is an important enzyme responsible for the breakdown of toxins, primarily acetaldehyde. Approximately 35-40% of the East Asian population has a genetic mutation that is passed from generation to generation and causes many of us to have ALDH2 Deficiency. There are over 1 billion people worldwide with ALDH2 Deficiency. To find out if you have ALDH2 Deficiency, you can take an easy, at-home DNA test.
What happens when acetaldehyde enters the body?
When acetaldehyde enters the body it provokes a histamine release that can cause any of the following short-term ALDH2 deficiency symptoms:
What is the liver enzyme?
The typical human liver contains two major aldehyde dehydrogenase enzymes, a cytosolic ALDH1 component, and a mitochondrial ALDH2 component. Many people, notably about 30% to 40% of East Asian Orientals, have only the ALDH1 enzyme and are deficient in the ALDH2 enzyme. Being deficient in the ALDH2 enzyme means that your body is less able ...
What causes ALDH2 deficiency?
ALDH2 deficiency is a genetic condition thought to be originally caused by the emergence of rice cultivation in Asia between 7,000 to 10,000 years ago.
What are the ALDH2 deficiency symptoms?
The ALDH2 deficiency symptoms can vary depending on the one's sensitivity to the environmental toxin not being broken down.
What happens if you drink alcohol with a low aldh2 level?
The ALDH2 enzyme is responsible for detoxifying acetaldehyde, so if you're ALDH2 deficient your body will undergo acetaldehyde toxicity whenever you drink alcohol. This is commonly referred to as alcohol flush reaction or Asian flush (because of the large proportion of Asian people affected).
What does it mean when you are deficient in ALDH2?
Being deficient in the ALDH2 enzyme means that your body is less able to safely deal with a particular set of toxins that can enter from the external environment. One example is the toxin acetaldehyde that enters our body when we consume alcohol.
How to treat aldh2 deficiency?
One easy way to treat ALDH2 deficiency is to take Asian flush pills, which reduce skin reddening and other issues ALDH2 deficient drinkers suffer from. Let's start by looking at some causes of these issues.
Which enzyme is associated with alcoholism?
That said, one study found variations of the ALDH enzyme, ALDH1A1*2, and ALDH1A1*3 may be associated with alcoholism in African-American people.
Why is acetaldehyde not safe?
Other researchers claim it is not possible for acetaldehyde alone to cause these effects because the brain protects itself from toxic chemicals in the blood with its unique blood-brain barrier.
How Fast Is Alcohol Metabolized?
According to the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, it can take a fasting adult male between two to seven hours to return to a zero blood-alcohol content (BAC), or blood alcohol concentration, level after rapidly consuming one to four standard drinks .
What are the variations of ADH and ALDH?
Variations of ADH and ALDH enzymes have been traced to variations in the genes that produce these enzymes. Some people have ADH and ALDH enzymes that work less efficiently than others, while others have enzymes that work more effectively. Simply put, this means some people have enzymes that can break down alcohol to acetaldehyde or acetaldehyde ...
Why is ADH important?
ADH helps convert alcohol to acetaldehyde. Acetaldehyde is only in the body for a short time because it is rapidly converted to acetate by other enzymes. Although acetaldehyde is present in the body a short period of time, it is highly toxic and a known carcinogen.
How long does it take for alcohol to go down?
According to the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, it can take a fasting adult male between two to seven hours to return to a zero blood-alcohol content (BAC), or blood alcohol concentration, level after rapidly consuming one to four standard drinks .
Which organ is most affected by alcohol?
Because the liver is the organ that metabolizes most of the alcohol in the body and therefore is where most of the acetaldehyde is produced, it is particularly vulnerable to the effects of alcohol metabolism. More than 90% of heavy drinkers develop fatty liver .
Overview
Alcohol intolerance is an inherited metabolic disorder. Metabolic disorders affect your metabolism, the way your body converts and uses energy.
Symptoms and Causes
A genetic metabolic disorder causes alcohol intolerance. When most people ingest alcohol, which contains ethanol:
Diagnosis and Tests
Your healthcare provider will ask you about the symptoms and reactions that occur after you drink alcohol.
Prevention
You cannot prevent alcohol intolerance from developing. It is an inherited disorder, so it was passed down to you from your parents. However, you can take steps to avoid the symptoms.
Living With
The best way to live with this condition is to avoid alcohol as much as possible. Try nonalcoholic beverages as substitutions for your favorite alcoholic drinks. Avoiding alcohol will allow you to live an active, enjoyable life without unpleasant symptoms.
