pH of Seawater — Acidic or Alkaline?
- • There are many rocks and minerals which are basic. The water can easily erode their surfaces, leading to the...
- • The relative amount of carbonate and bicarbonate ions also affects the pH. The buffering mechanism has been discussed...
- • The concentration of carbon dioxide- There is an increase in acidic character when the carbon...
What are the factors that affect pH of water?
There are many factors that affect the pH of water, the first is CO2 concentration. Due to the uprise of global warming carbon dioxide emission have been prominent in our atmosphere.
Why is the pH of seawater less than 7?
Anything higher than 7 is basic (or alkaline) and anything lower than 7 is acidic. The pH scale is an inverse of hydrogen ion concentration, so more hydrogen ions translates to higher acidity and a lower pH. Carbon dioxide and seawater Carbon dioxide, which is naturally in the atmosphere, dissolves into seawater.
How does CO2 affect pH of water?
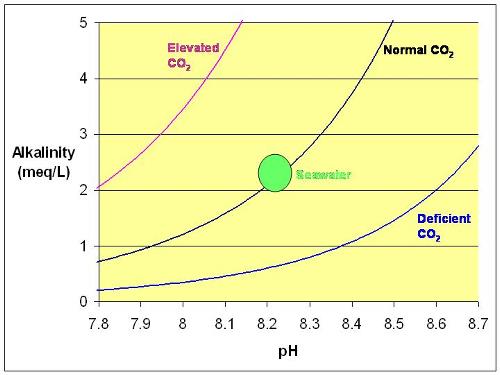
There are many factors that affect the pH of water, the first is CO2 concentration. Due to the uprise of global warming carbon dioxide emission have been prominent in our atmosphere. The graph on the left eximplifies the relationship between increased carbon dioxide emissions and pH level of water.
How has the pH of the ocean changed during the Industrial Revolution?
In the 200-plus years since the industrial revolution began, the concentration of carbon dioxide (CO 2) in the atmosphere has increased due to human actions. During this time, the pH of surface ocean waters has fallen by 0.1 pH units.
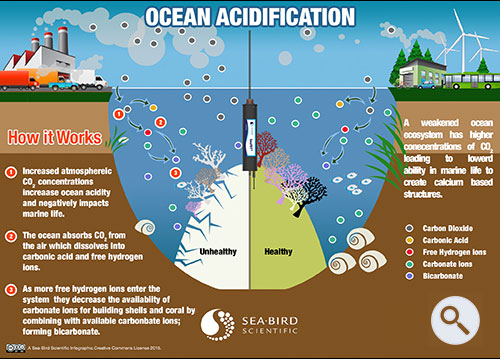
What are 5 things that can affect the pH of the ocean?
Causes of Ocean AcidificationRaised Carbon IV oxide Concentration in the Ocean. ... Raised Carbon IV oxide Concentration in the Atmosphere. ... Higher Concentration of Hydrogen ions in the Water. ... Burning Fossil Fuels. ... Waste Disposal. ... Improper Land Management. ... Industrialization.
What causes high pH in sea water?
If seawater has a big enough deficiency of CO2, the pH can be as high as pH 9 or more. Why Does pH Become Elevated? So there is net consumption of carbon dioxide during the day. This leads to deficient in CO2 during the day, raising their pH.
How does the pH of seawater change with depth?
In the North Atlantic, the pH decreases rapidly in the first 500 m and then stays roughly constant as the depth increases. In the North Pacific, the pH decreases even more rapidly in the first 500 m, but then it increases gradually as the depth increases.
Does sea water affect pH?
Ocean acidification will result in a shift towards a lower pH value, meaning the water will become less basic and therefore more acidic.
What maintains the pH of the ocean?
If too much carbon dioxide is added to seawater, which creates too much carbonate ions, the reaction will shift back to the left (back towards the reactants) to buffer (uptake some of the free hydrogen ions) the solution. This buffering helps to keep the acidity of the seawater from dropping.
How do you increase the pH of seawater?
You can increase the pH by adding calculated amounts of Calcium Carbonate, Magnesium Carbonate and/ or Magnesium Chloride.
What causes high pH?
An increase in alkali (alkaline chemicals) is typically caused by an increase in bicarbonate, a drop in acid levels, or a decrease in carbon dioxide. The cause of the alkalosis determines what type it is.
What causes low pH in water?
Oftentimes, acidic water is due to industrial pollution, with low pH water often being found near mining sites, chemical dumps, power plants, confined animal feeding operations, and landfills (2). Acidic water has a pH of 6.5 or less and can be caused by natural phenomena, as well as industrial pollution.
Does temperature affect ocean acidification?
CO2 concentrations drive rising temperatures and acidification. The rising concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is driving up ocean surface temperatures and causing ocean acidification. Although warming and acidification are different phenomena, they interact to the detriment of marine ecosystems.
What is responsible for changing the pH of the ocean?
Because of human-driven increased levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, there is more CO2 dissolving into the ocean. The ocean's average pH is now around 8.1 , which is basic (or alkaline), but as the ocean continues to absorb more CO2, the pH decreases and the ocean becomes more acidic.
Does temperature affect pH of salt water?
As the temperature increases the bonds holding the protons are broken and the pH increases. As Neal said, an increase in seawater temperature would lead to a decrease in seawater CO2 concentration.
How is pH measured in seawater?
To measure the pH of larger bodies of water, researchers use ships, stationary buoys and floats. Some sensors connected to ships rely on ISFETs, which are lowered into the ocean for a certain period of time so researchers can receive ongoing data on pH levels.
What causes high pH?
An increase in alkali (alkaline chemicals) is typically caused by an increase in bicarbonate, a drop in acid levels, or a decrease in carbon dioxide. The cause of the alkalosis determines what type it is.
What is responsible for changing the pH of the ocean?
Because of human-driven increased levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, there is more CO2 dissolving into the ocean. The ocean's average pH is now around 8.1 , which is basic (or alkaline), but as the ocean continues to absorb more CO2, the pH decreases and the ocean becomes more acidic.
What does high pH in water mean?
In chemistry, pH is a measurement of the concentration of hydrogen ions in a water-based solution. A lower pH means that there are more hydrogen ions in the liquid, whereas a higher pH indicates fewer hydrogen ions in the liquid.
Why is pH important in aqueous solutions?
An important property of aqueous solutions is pH because it affects chemical and biochemical properties such as chemical reactions, equilibrium conditions, and biological toxicity. With the increasing uptake of fossil fuel CO 2 into the oceans, a decrease in pH is important to consider at this time.
What is the pH traceable to the SI system?
A convention used to define pH traceable to the SI system is the Bates–Guggenheim convention that is defined by the Debye–Hückel equation: (15) log γ C l − = − A I 1 / 2 [ 1 + 1.5 I 1 / 2] where A is the Debye–Hückel constant and I is the ionic strength ( Bates and Guggenheim, 1960, Buck et al., 2002 ). Definitions and conventions, as outlined above, can lead to substantially different pH values as we will further examine below.
What are the two types of cells used to measure pH?
There are primarily two cells that are used for measuring pH in aqueous solutions by potentiometric methods. The Harned cell is a gas hydrogen cell that does not have transference (of ions), and is the only cell for state-of the-art assignment of primary pH standards using IUPAC standards ( Buck et al., 2002 ). This is the basis of the primary method, only of concern to metrological institutes and physical-chemistry research groups ( Mariassy et al., 2009 ). Their use only becomes relevant when associated with proper control of the sources of uncertainty, which do not pertain to most practical applications ( Lito et al., 2006, Guiomar et al., 2007 ). Nevertheless they constitute references to which a traceability chain (establishment of a calibration hierarchy) should be ensured (P. de Bièvre, “Metrological traceability of measurement results in chemistry” http://www.iupac.org/projects/2001/2001-010-3-500.html ). Combination glass electrodes, on the other hand, are the preferred cell for practical pH measurements ( UNESCO, 1987, Nordstrom et al., 2000, Buck et al., 2002, ISO, 2007 ). A shortfall of these cells is that they have liquid junction potentials that affect pH measurements. There are experimental ways of minimizing liquid junction potentials ( UNESCO, 1987, Covington and Whitfield, 1988, Millero and Roy, 1997, Millero, 1986, Millero, 2001, Buck et al., 2002, ISO, 2007 ); but the latter problem is a major source of uncertainty in quantifying the pH of aqueous solutions ( Leito et al., 2002 ).
What are the components of natural water?
In this review, we are primarily considering the pH of natural waters (rivers, estuaries, seawater and brines) that are made up of the major components of seawater (Na +, Mg 2+, Ca 2+, K +, Sr 2+ , Cl −, SO 42−, HCO 3−, Br −, CO 32−, B (OH) 4−, F −, OH −, B (OH) 3, and CO 2; Millero et al., 2008 ).
What is the unit of pH?
The pH concentration units are mol/ (kg H 2 O) (molality), mol/ (kg soln), or mol/l (molarity). For example, the definition of pH by UNESCO (1987) distinguished pH SWS by using T m H for the H species in Eq. (4) that have molal (m) concentrations: (5)pHSWS,H = − log [TmH] and T [H] for mol/ (kg soln): (6)pHSWS = − log [T[H]]
What is pH NBS?
What we are calling pH in Eq. (2) (an abstract concept) is sometimes referred to as pH NBS (an operational procedure), where NBS refers to the National Bureau of Standards (now called NIST, National Institute of Standards and Technology). For some, Eq.
Can HCl be measured?
While individual ion activities cannot be measured unambiguously, activity products such as a HCl can be measured or modeled. For example, the activity product for HCl is (10)aHCl = (a ± HCl)1/2 = [ (γH+) (γCl−) (mH+) (mCl−)]1/2 or (11)aHCl = [ (aH+) (γCl−) (mCl−)]1/2
What are the factors that affect the pH of water?
Carbon Dioxide. There are many factors that affect the pH of water, the first is CO2 concentration. Due to the uprise of global warming carbon dioxide emission have been prominent in our atmosphere. The graph on the left eximplifies the relationship between increased carbon dioxide emissions and pH level of water.
What causes pH to rise?
Pollution and Waste Water Contamination. Presence of chemical detergents and cleaning agents that are improperly disposed of can increase the pH. The pH of a body of water is affected by the dumping of chemicals into the water by individuals,industries or communities.
What causes acid rain?
Acid rain is caused by sulfur dioxide in the air combining with water vapor. These pollutants are primarily from automobile and coal-fired power plant emissions. Acid rain is responsible for many of the first order streams becoming acidic. Glacier water has naturally low pH in comparison to ground water.
Why does pH change?
pH changed because of dissolved minerals in water depends on your geographical region. For instance, in areas that depend on groundwater, the result of an alter pH is from limestone bedrock which increases the pH of water.Some rock types have little or no effect on the pH such as granite.
When there is a high temperature the pH is low#N#When there is low temperature the pH is high#?
When there is a high temperature the pH is low#N#When there is low temperature the pH is high#N#This concept has been proven scientifically using distilled water , when pure distilled water is raised in temperature by 25 degrees Celsius, the pH had increased to 0.45, like all experiments this would only be effective depending on the atmosphere. Furthermore, water ionizes as the temperature rises so hydrogen ion concentration increases this mean that the pH decreases however water remains neutral as the number of hydroxyl ions remain equal to the number of hydrogen ions
Does water ionize as temperature increases?
Furthermore, water ionizes as the temperature rises so hydrogen ion concentration increases this mean that the pH decreases however water remains neutral as the number of hydroxyl ions remain equal to the number of hydrogen ions.
Does CO2 affect pH?
CO2 content decreases-> High pH. As well, the pH is affected by the amount of plant growth and organic material within a body of water. When these materials decompose, carbon dioxide is released. The carbon dioxide combines with water to form carbonic acid. Though this is a weak acid, large amount of it will lower pH.
How much has the pH of the ocean changed since the Industrial Revolution?
During this time, the pH of surface ocean waters has fallen by 0.1 pH units. This might not sound like much, but the pH scale is logarithmic, so this change represents approximately a 30 percent increase in acidity.
How does acidification affect corals?
Ocean acidification is already impacting many ocean species, especially organisms like oysters and corals that make hard shells and skeletons by combining calcium and carbonate from seawater. However, as ocean acidification increases, available carbonate ions (CO32-) bond with excess hydrogen, resulting in fewer carbonate ions available for calcifying organisms to build and maintain their shells, skeletons, and other calcium carbonate structures. If the pH gets too low, shells and skeletons can even begin to dissolve.
What happens when carbon dioxide is absorbed by the ocean?
When carbon dioxide is absorbed by the ocean from the atmosphere, the chemistry of the seawater is changed. (NOAA) Download Image. The ocean absorbs about 30% of the carbon dioxide (CO 2) that is released in the atmosphere. As levels of atmospheric CO 2 increase from human activity such as burning fossil fuels (e.g., ...
What is the role of NOAA in the ocean?
NOAA invests in new tools to measure the ocean. Four new research projects are giving a boost to NOAA’s ability to measure, track and forecast ocean acidification, warming and other important ocean health indicators.
What is the chemical that dissolves in water?
Carbon dioxide, which is naturally in the atmosphere, dissolves into seawater. Water and carbon dioxide combine to form carbonic acid (H 2 CO 3 ), a weak acid that breaks (or “dissociates”) into hydrogen ions (H +) and bicarbonate ions (HCO 3- ). Because of human-driven increased levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, ...
Why are algae and seagrasses at risk?
While some species will be harmed by ocean acidification, algae and seagrasses may benefit from higher CO 2 conditions in the ocean, as they require CO 2 for photosynthesis just like plants on land.
What is the pH of a pH scale?
The pH scale. The pH scale runs from 0 to 14, with 7 being a neutral pH. Anything higher than 7 is basic (or alkaline) and anything lower than 7 is acidic. The pH scale is an inverse of hydrogen ion concentration, so more hydrogen ions translates to higher acidity and a lower pH.