
The occurrence of the French revolution is mainly caused by four factors— absolute power of the king, political injustice, economic crisis, and the emergence of new thinkers.
- Absolute Power or Absolute Monarchy
- — Before the last king of France— Louis XVI, the previous king. ...
- Factors that Caused
- Political Iniquity
- — In political factors, the nobles made all the rules and were directly approved by the king. ...
- Factors that Caused
- Economic Crisis
- — The life of the previous king and royal nobles, as well as the consort of King Louis XVI. ...
What are three major causes of the French Revolution?
What were the top 3 causes of the French Revolution?
- Social Inequality in France due to the Estates System.
- Tax Burden on the Third Estate.
- The Rise of the Bourgeoisie.
- Ideas put forward by Enlightenment philosophers.
- Financial Crisis caused due to Costly Wars.
- Drastic Weather and Poor Harvests in the preceding years.
What were some social causes of the French Revolution?
Causes Of French Revolution of 1789
- Social – The social conditions in France in the late 18th century were extremely unequal and exploitative. ...
- Economic – As a result of numerous wars waged by Louis XVI the State coffers were empty. ...
- Political – The Bourbon king of France, Louis XVI was an extremely autocratic and weak-willed king who led a life of obscene luxury. ...
What events led to the French Revolution?
List of 10 Major Events of the French Revolution
- Meeting of the Estates General. ...
- Fall of the Bastille. ...
- March on Versailles. ...
- Flight to Varennes. ...
- Dissolution of the National Assembly. ...
- War. ...
- Attack on the Tuileries Palace. ...
- Declaration of the Republic and the Trial of Louis. ...
- Reign of Terror. ...
- Directory and the Rise of Napoleon. ...
What are the effects of the French Revolution?
- Revolution overthrew the French monarchy, under the slogan of "Liberty, equality, fraternity". ...
- The Abolitionist Thomas Clarkson openly supported the French Revolution
- Abolitionists used the same tactics as radicals to win public support – associations, petitions, cheap publications, public lectures, public meetings, pressure on Parliament
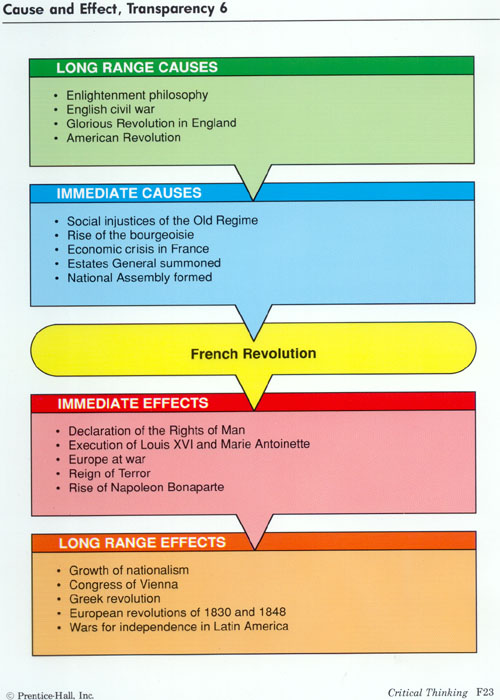
What were the 3 main causes of the French Revolution?
The causes can be narrowed to five main factors: the Estate System, Absolutism, ideas stemming from the Enlightenment, food shortages, and The American Revolution.
What were the six causes of French Revolution?
The 6 Main Causes of the French RevolutionLouis XVI & Marie Antoinette. France had an absolute monarchy in the 18th century – life centred around the king, who had complete power. ... Inherited problems. ... The Estates System & the bourgeoise. ... Taxation & money. ... The Enlightenment. ... Bad luck.
What are 7 causes of the French Revolution?
Here are the 10 major causes of the French Revolution.#1 Social Inequality in France due to the Estates System. ... #2 Tax Burden on the Third Estate. ... #3 The Rise of the Bourgeoisie. ... #4 Ideas put forward by Enlightenment philosophers. ... #5 Financial Crisis caused due to Costly Wars. ... #7 The Rise in the Cost of Bread.More items...•
What are the 5 social Causes of French Revolution?
Social causes of French revolution: - Weak economic policies, poor leadership, and exploitative political and social systems all contributed to the French revolution. The authoritarian monarchy, bankruptcy, and wasteful royal expenditures were among the political causes of the French revolution.
What was the main cause of the French Revolution essay?
[1] The French revolution occurred for various reasons, including poor economic policies, poor leadership, an exploitative political- and social structures. The political causes of the French revolution included the autocratic monarchy, bankruptcy and extravagant spending of royals.
What are the causes and impact of French Revolution?
The primary cause of the French Revolution was the dissatisfaction of the common people with the absolute monarchy of King Louis XVI. Other causes include economic inequality and social injustice. Answer. The French Revolution began on July 14, 1789, with the storming of the Bastille.
What were the main causes of the French revolution quizlet?
What were the main causes of the French Revolution? Enlightenment ideas, Economic Troubles, Weak Leader, Meeting of the Estates General, National Assembly, and Tennis Court Oath.
How did French Revolution start?
A popular insurgency culminated on July 14 when rioters stormed the Bastille fortress in an attempt to secure gunpowder and weapons; many consider this event, now commemorated in France as a national holiday, as the start of the French Revolution.
What are causes of French Revolution Class 9?
Causes of the French Revolution:Despotic rule of Louis XVI: He became the ruler of France in 1774. ... Division of French society: The French society was divided into three estates; first, second and third estates, respectively. ... Rising prices: The population of France had increased.More items...•
What were the main causes of French Revolution Class 9 Brainly?
This is Expert Verified Answer #1 Social Inequality in France due to the Estates System. #2 Tax Burden on the Third Estate. #3 The Rise of the Bourgeoisie. #4 Ideas put forward by Enlightenment philosophers.
What were the main causes of the French revolution quizlet?
What were the main causes of the French Revolution? Enlightenment ideas, Economic Troubles, Weak Leader, Meeting of the Estates General, National Assembly, and Tennis Court Oath.
What were the main causes of French Revolution PDF?
Causes of the French Revolution International: struggle for hegemony and Empire outstrips the fiscal resources of the state 2. Political conflict: conflict between the Monarchy and Aristocrats over the “reform” of the tax system led to paralysis and bankruptcy. 3.
How did the price of bread in France affect the French people?
Louis XVI implemented deregulation of the grain market but it resulted in further increasing the bread prices. The rise in the cost of bread severely affected the common French citizens who resented the monarch for his not being able to solve the food crisis.
What did Louis XVI do to the bread market?
Louis XVI implemented deregulation of the grain market but it resulted in further increasing the bread prices. The rise in the cost of bread severely affected the common French citizens who resented the monarch for his not being able to solve the food crisis.
What were the causes of the French Revolution?
There were various reasons which brought about the Revolution. These include intellectual reasons like the ideas put forward by the philosophers of the Age of Enlightenment; cultural reasons like the rise of the bourgeoisie class; political reasons like the ineffective leadership of French monarch Louis XVI; social reasons like the unjust Estates System; financial reasons like French involvement in expensive wars; and economic reasons like the rise in price of bread. Here are the 10 major causes of the French Revolution.
What happened in 1783?
In June 1783, Laki volcano in Iceland erupted sending volcanic ash high into the atmosphere in Europe. This led to a severe winter in Europe in 1784 and the following summers included extreme droughts that caused poor harvests and famine.
What were the bourgeoisie's main goals in the French Revolution?
The bourgeoisie resented the position of the First and the Second Estate, which they believed was derived from their efforts. Moreover, they aspired to attain political equality with the other two estates. The desire of the bourgeoisie to rid themselves of feudal and royal encroachments on their personal liberty, commercial prospects and ownership of property was one of the reasons which led to the French Revolution.
What were the three estates of France?
In the 1780s, the population of France was around 24 million and 700 thousand and it was divided into three estates. The First Estate was the Roman Catholic clergy, which numbered about 100,000. The Second Estate consisted of the French nobility, which numbered about 400,000. Everyone else in France; including merchants, lawyers, laborers and peasants; belonged to the Third Estate, which comprised around 98% of the French population. The Third Estate was excluded from positions of honor and political power; and was looked down upon by the other estates. It was thus angered and resented its position in French society. This led to them coming together to launch the French Revolution in 1789.
What was the effect of the poor economic condition of the nation on the masses?
The poor economic condition of the nation angered the masses and they became critical of their king. Moreover, both Louis XV and his grandson were aware of anti-monarchist forces that were threatening their family’s rule but they were unable to stop them. Louis XVI – Monarch of France during the Revolution.
What was the second estate of the bourgeois class?
The new bourgeoise class could only make the leap to the Second Estate (the nobility ) through the practice of venality, the buying and selling of offices. Following parlements blocking of reforms, Louis XVI was persuaded to call an assembly known as the Estates General, which had last been called in 1614.
What was the motto of the First Republic?
Many also view the philosophy and ideals of the First Republic as being underpinned by Enlightenment ideas, and the motto most closely associated with the revolution itself – ‘liberté, égalité, fraternité’ – can be seen as a reflection of key ideas in Enlightenment pamphlets.
What were the values of the Enlightenment?
Individuals like Voltaire and Rousseau espoused values of liberty, equality, tolerance, constitutional government and the separation of church and state.
What were the French finances like in the late 18th century?
4. Taxation & money. French finances were a mess by the late 18th century. The taxation system allowed the wealthiest to avoid paying virtually any tax at all, and given that wealth almost always equalled power, any attempt to push through radical financial reforms was blocked by the parlements.
What was the estate system in France?
The Estates System was far from unique to France: this ancient feudal social structure broke society into 3 groups, clergy, nobility and everyone else. In the Medieval period, prior to the boom of the merchant classes, this system did broadly reflect the structure of the world.
How many courtiers were there at Versailles?
The court at Versailles, just outside Paris, had between 3,000 and 10,000 courtiers living there at any one time, all bound by strict etiquette. Such a large and complex social set required management by the king in order to manage power, bestow favours and keep a watchful eye over potential troublemakers.
What was the name of the painting that led to the Enlightenment?
Eugene Delacroix 's allegorical painting, Liberty Leading the People. In 1789, France was the powerhouse of Europe, with a large overseas empire, strong colonial trade links as well as a flourishing silk trade at home, and was the centre of the Enlightenment movement in Europe. The Revolution which engulfed France shocked her European counterparts ...
Why was Louis XVI not respected?
To make matters worse, Louis XVI was not respected as a leader, as he was known to be indecisive and shy. As such, the French citizens resented his authority and the history of the absolute monarchy in France which led to people revolting in 1789 at the outbreak of the French Revolution.
How did the Enlightenment impact the French Revolution?
The impact of the Enlightenment on the French Revolution can be seen in the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen. The document was adopted by the National Assembly on August 26th, 1789. The declaration was vitally important to the French Revolution because it directly challenged the authority of Louis XVI.
What did the French people question before the French Revolution?
Similar to the earlier discussed estates system, in the years before the French Revolution, the people of France began to question the authority of Louis XVI and his absolute monarchy.
Why did bread prices rise in France?
After nearly a decade of dramatic weather and poor harvests, the peasants were suffering to survive day-to-day life in France. This was all made worse when, the poor harvests caused the price of flour to increase dramatically, thus also causing the price of bread to rise.
What is the absolute monarchy?
An absolute monarchy is a form of government that involved society being ruled over by an all-powerful king or queen. The monarch had complete control over all aspects of the society, including: political power, economics, and all forms of authority.
Why did the estate system anger the citizens of the third estate?
By 1789, the estates system had begun to anger the citizens of the third estate as they resented their position within French society. The third estate was forced to pay heavy taxed while the other two did not and many in the peasant class felt as though they were being crushed by the clergy and nobility.
What was the difference between the clergy and the peasant class?
The clergy was divided in that the higher church positions, like bishops, were held by members of the nobility, while positions in lower clergy were often held by members of the peasant class. The Church had many privileges, including the collection of tithes.
Why were the deputies elected in the Assembly of 1789?
It explains why the deputies elected in the Assembly of 1789 went much further than what they were asked: to solve a financial problem. In the summer 1789, the privileges of the church and the nobility were abolished and human rights were proclaimed.
Why were nobles important?
The most important are that they would not pay taxes and they were given top-jobs in the army, the administration and the royal courtyard. The nobles usually felt superior to the commoners and would let them know it. The duke of Orléans, cousin of the king. Painted by Callet, sourced from Wikipedia.
Where is Cahier des Doléances?
Cahier des doléances from Bastia in Corsica. Sourced from Wikipedia
Why was the French monarchy in trouble?
The French monarchy was financially in trouble since the end of the reign of Louis XIV, the Sun-King, in 1715. The wars against many powerful European countries had left the country in a great debt that was even increased by the expenses of the crown.
How were the monks and clergy financed?
Both were financed by a religious tax imposed on the commoners. The clergy did not pay taxes while the church was the main landowner of the country.
What did the contemporaries try to understand?
Since the beginning of the Revolution, the contemporaries tried to understand what happened, which actors and movements were to praise or to blame.
How was the society divided?
The society was strongly divided by the status of the individuals and groups. There were 3 orders in the society. On top, the nobility. The king could give to someone a title of nobility but this status was usually acquired by birth. The nobles had all kind of privileges.
Why did the bourgeoisie gain power?
There were many reasons. The bourgeoisie —merchants, manufacturers, professionals—had gained financial power but were excluded from political power. Those who were socially beneath them had very few rights, and most were also increasingly impoverished. The monarchy was no longer viewed as divinely ordained. When the king sought to increase the tax burden on the poor and expand it to classes that had previously been exempt, revolution became all but inevitable.
What caused the American Revolution?
In North America this backlash caused the American Revolution, which began with the refusal to pay a tax imposed by the king of Great Britain. Monarchs tried to stop this reaction of the aristocracy, and both rulers and the privileged classes sought allies among the nonprivileged bourgeois and the peasants.
What was the impact of the discovery of gold in Brazil?
The discovery of new gold mines in Brazil had led to a general rise in prices throughout the West from about 1730, indicating a prosperous economic situation. From about 1770, this trend slackened, and economic crises, provoking alarm and even revolt, became frequent. Arguments for social reform began to be advanced.
How many deputies were elected in the Third Estate?
There were practically no exclusions from the voting; and the electors drew up cahiers de doléances, which listed their grievances and hopes. They elected 600 deputies for the Third Estate, 300 for the nobility, and 300 for the clergy. Jacques Necker.
What was the French Revolution?
The French Revolution was a period of major social upheaval that began in 1787 and ended in 1799. It sought to completely change the relationship between the rulers and those they governed and to redefine the nature of political power. It proceeded in a back-and-forth process between revolutionary and reactionary forces.
What is an encyclopedia editor?
Encyclopaedia Britannica's editors oversee subject areas in which they have extensive knowledge, whether from years of experience gained by working on that content or via study for an advanced degree. ...
Who is Calonne by?
Calonne, detail of an engraving by Brea, 18th century, after a portrait by Elisabeth Vigee-Lebrun. Courtesy of the Bibliothèque Nationale, Paris. During the spring and summer of 1788, there was unrest among the populace in Paris, Grenoble, Dijon, Toulouse, Pau, and Rennes. The king, Louis XVI, had to yield.
What happened to France during the American Revolution?
As the 18th century drew to a close, France’s costly involvement in the American Revolution, and extravagant spending by King Louis XVI and his predecessor, had left the country on the brink of bankruptcy.
What was the name of the agrarian revolt that led to the end of feudalism?
Known as the Great Fear ( la Grande peur ), the agrarian insurrection hastened the growing exodus of nobles from the country and inspired the National Constituent Assembly to abolish feudalism on August 4, 1789, signing what the historian Georges Lefebvre later called the “death certificate of the old order.”.
What happened on June 12th?
On June 12, as the National Assembly (known as the National Constituent Assembly during its work on a constitution) continued to meet at Versailles, fear and violence consumed the capital.
How much of France's population was non-aristocratic?
France’s population had changed considerably since 1614. The non-aristocratic members of the Third Estate now represented 98 percent of the people but could still be outvoted by the other two bodies.
What did the nobles want from the government?
While all of the orders shared a common desire for fiscal and judicial reform as well as a more representative form of government, the nobles in particular were loath to give up the privileges they enjoyed under the traditional system.
What happened on November 9, 1799?
On November 9, 1799, as frustration with their leadership reached a fever pitch, Bonaparte staged a coup d’état, abolishing the Directory and appointing himself France’s “ first consul .” The event marked the end of the French Revolution and the beginning of the Napoleonic era, in which France would come to dominate much of continental Europe.
What was the Thermidorian reaction?
His death marked the beginning of the Thermidorian Reaction, a moderate phase in which the French people revolted against the Reign of Terror’s excesses.

Louis XVI & Marie Antoinette
Inherited Problems
- By no means did Louis XVI inherit an easy situation. The power of the French monarchy had peaked under Louis XIV, and by the time Louis XVI inherited, France found herself in an increasingly dire financial situation, weakened by the Seven Years War and American War of Independence. With an old and inefficient taxation system which saw large portions of the wealt…
The Estates System & The Bourgeoise
- The Estates System was far from unique to France: this ancient feudal social structure broke society into 3 groups, clergy, nobility and everyone else. In the Medieval period, prior to the boom of the merchant classes, this system did broadly reflect the structure of the world. As more and more prosperous self-made men rose through the ranks, the system’s rigidity became an increa…
Taxation & Money
- French finances were a mess by the late 18th century. The taxation system allowed the wealthiest to avoid paying virtually any tax at all, and given that wealth almost always equalled power, any attempt to push through radical financial reforms was blocked by the parlements. Unable to change the tax, and not daring to increase the burden on those who already shouldered it, Jacq…
The Enlightenment
- Historians debate the influence of Enlightenmentin the French Revolution. Individuals like Voltaire and Rousseau espoused values of liberty, equality, tolerance, constitutional government and the separation of church and state. In an age where literacy levels were increasing and printing was cheap, these ideas were discussed and disseminated far mo...
Bad Luck
- Many of these issues were long term factors causing discontent and stagnation in France, but they had not caused revolution to erupt in the first 15 years of Louis’ reign. The real cost of living had increased by 62% between 1741 and 1785, and two successive years of poor harvests in 1788 and 1789 caused the price of bread to be dramatically inflated along with a drop in wages. …