
When your body goes into anaphylactic shock, your blood pressure suddenly drops and your airways narrow, possibly blocking normal breathing. This condition is dangerous. If it isn’t treated immediately, it can result in serious complications and even be fatal.
What are signs and symptoms of anaphylactic shock?
- trouble breathing
- wheezing
- hoarseness (changes in the way your voice sounds)
- hives (raised reddened rash that may itch)
- severe itching
- swelling of your face, lips, mouth, or tongue
- skin rash, redness, or swelling
- fast heartbeat
- weak pulse
- feeling very anxious
What does anaphylactic shock feel like?
What do the signs and symptoms of anaphylactic shock look like? Hives, flushed skin, or paleness on the skin. Suddenly feeling too hot. Feeling like you have a lump in your throat or difficulty swallowing. Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea. Abdominal pain. A weak and rapid pulse. Runny nose and sneezing. Swollen tongue or lips.
What is anaphylactic shock really looks like?
What is anaphylaxis really like? The first visible symptom of anaphylaxis usually appears on the skin, which gets red. Often, this occurs in the cheeks, and may look like flushing, though it will not include any sweating. Redness can also occur on the chest and neck, or other areas of the body. Next, the person may develop hives. ...
What do you need to know about anaphylactic shock?
What You Need to Know About Anaphylactic Shock via Your Houston Endodontist
- Anaphylaxis. Anaphylaxis is a severe, whole-body reaction to an allergen, which is a substance that causes an allergic reaction.
- Anaphylactic Shock. A person experiencing a severe case of anaphylaxis can go into anaphylactic shock. ...
- Treatment for Anaphylactic Shock. ...

What is the difference between anaphylaxis and anaphylactic shock?
The terms "anaphylaxis" and "anaphylactic shock" are often used to mean the same thing. They both refer to a severe allergic reaction. Shock is when your blood pressure drops so low that your cells (and organs) don't get enough oxygen. Anaphylactic shock is shock that's caused by anaphylaxis.
What are the first signs of anaphylactic shock?
Symptoms of anaphylaxisfeeling lightheaded or faint.breathing difficulties – such as fast, shallow breathing.wheezing.a fast heartbeat.clammy skin.confusion and anxiety.collapsing or losing consciousness.
Why does anaphylactic shock happen?
But sometimes, exposure to an allergen can cause a life-threatening allergic reaction known as anaphylaxis . This severe reaction happens when an over-release of chemicals puts the person into shock. Allergies to food, insect stings, medications and latex are most frequently associated with anaphylaxis.
What are the 3 criteria for anaphylaxis?
ASCIA defines anaphylaxis as: Any acute onset illness with typical skin features (urticarial rash or erythema/flushing, and/or angioedema), plus involvement of respiratory and/or cardiovascular and/or persistent severe gastrointestinal symptoms; or.
How do you survive anaphylactic shock without an EpiPen?
Q: What do you do if someone goes into anaphylactic shock without an EpiPen? A: Make sure that you've called 911. If antihistamines are on-hand, these can be administered and may provide some relief, but antihistamines are never a suitable medication for fully treating anaphylactic shock.
What does anaphylactic shock feel like?
Anaphylaxis causes the immune system to release a flood of chemicals that can cause you to go into shock — blood pressure drops suddenly and the airways narrow, blocking breathing. Signs and symptoms include a rapid, weak pulse; a skin rash; and nausea and vomiting.
How fast does anaphylaxis happen?
It mostly occurs within 20 minutes to 2 hours after exposure to the allergen. Signs and symptoms may be mild at first, but can rapidly worsen. A small number of people suddenly develop signs and symptoms of a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) without any signs of a mild to moderate allergic reaction.
Can you survive anaphylaxis without treatment?
Seek emergency treatment right away. In severe cases, untreated anaphylaxis can lead to death within half an hour. An antihistamine pill, such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl), isn't enough to treat anaphylaxis. These medications can help relieve allergy symptoms, but they work too slowly in a severe reaction.
How long does anaphylaxis take to start?
Anaphylaxis can occur within minutes. It mostly occurs within 20 minutes to 2 hours after exposure to the allergen. Signs and symptoms may be mild at first, but can rapidly worsen.
What does mild anaphylaxis feel like?
Runny or stuffy nose and sneezing. Shortness of breath or trouble breathing and rapid heartbeat. Swollen or itchy lips or tongue. Swollen or itchy throat, hoarse voice, trouble swallowing, tightness in your throat.
Can anaphylactic shock happen slowly?
The symptoms of anaphylaxis can vary. In some people, the reaction begins very slowly, but in most the symptoms appear rapidly and abruptly. The most severe and life-threatening symptoms are difficulty breathing and loss of consciousness.
Can you have a mild anaphylactic reaction?
Anaphylaxis is defined by a number of signs and symptoms, alone or in combination, which occur within minutes, or up to a few hours, after exposure to a provoking agent. It can be mild, moderate to severe, or severe. Most cases are mild but any anaphylaxis has the potential to become life-threatening.
How long does it take for anaphylaxis to show?
Anaphylaxis symptoms usually occur within minutes of exposure to an allergen. Sometimes, however, it can occur a half-hour or longer after exposure. Signs and symptoms include: Skin reactions, including hives and itching and flushed or pale skin. Low blood pressure (hypotension) Constriction of your airways and a swollen tongue or throat, ...
What are the triggers for anaphylaxis?
The most common anaphylaxis triggers in children are food allergies, such as to peanuts, and tree nuts, fish, shellfish and milk. Besides allergy to peanuts, nuts, fish and shellfish, anaphylaxis triggers in adults include: 1 Certain medications, including antibiotics, aspirin and other over-the-counter pain relievers, and the intravenous (IV) contrast used in some imaging tests 2 Stings from bees, yellow jackets, wasps, hornets and fire ants 3 Latex
What happens if you don't have epinephrine?
If you don't have epinephrine, you need to go to an emergency room immediately. If anaphylaxis isn't treated right away, it can be fatal.
What happens if you have an attack and you carry an epinephrine autoinjector?
If you have an attack and you carry an epinephrine autoinjector, administer it right away. Even if symptoms improve after the injection, you still need to go to an emergency room to make sure symptoms don't recur, even without more exposure to the allergen. This second reaction is called biphasic anaphylaxis.
What causes a sudden drop in blood pressure?
Anaphylaxis causes your immune system to release a flood of chemicals that can cause you to go into shock — your blood pressure drops suddenly and your airways narrow, blocking breathing. Signs and symptoms include a rapid, weak pulse; a skin rash; and nausea and vomiting. Common triggers include certain foods, some medications, ...
Can an allergic reaction cause anaphylaxis?
Allergy symptoms aren't usually life-threatening, but a severe allergic reaction can lead to anaphylaxis. Even if you or your child has had only a mild anaphylactic reaction in the past, there's a risk of more severe anaphylaxis after another exposure to the allergy-causing substance. The most common anaphylaxis triggers in children are food ...
Can you get anaphylaxis from jogging?
Although not common, some people develop anaphylaxis from aerobic exercise, such as jogging, or even less intense physical activity, such as walking. Eating certain foods before exercise or exercising when the weather is hot, cold or humid also has been linked to anaphylaxis in some people.
What happens to the body during anaphylaxis?
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, allergies affect more than 50 million Americans every year—and anaphylaxis, the most severe allergic reaction, affects at least 1.6 percent of the general population [ PDF ].
How to stop anaphylaxis in its tracks?
The only way to stop anaphylaxis in its tracks is with epinephrine, more commonly known as adrenaline. Adrenaline is a hormone naturally produced by the adrenal glands to help generate the "fight or flight" response in emergency situations. It works by constricting certain blood vessels, increasing blood pressure, and relaxing airways, counteracting all the reactions produced by histamines.
What happens when mast cells are allergic?
If two or more allergen molecules bind to a sensitized mast cell, the mast cell releases inflammatory mediators that produce an allergic reaction. These mediators include substances like histamine and more of the interleukins that, in turn, activate eosinophils, Th2 cells, and basophils (another type of white blood cell). In a non-allergic reaction, mediators produce helpful inflammation that prevents infection and initiates healing—but those same symptoms can be annoying and even dangerous when the immune system attacks an otherwise benign allergen. Mast cells also release leukotrienes, which recruit more immune cells to the area and speed up the reaction. That leads to what Stanford University researcher Tina Sindher calls a “‘chain reaction’ of allergic inflammation.”
What happens when you are exposed to an antigen?
Being exposed to an antigen "primes" a T-helper cell, turning it into a Th2 cell. Primed Th2 cells release proteins called interleukins, which do two things: First, they interact with another type of immune cell called B cells to produce infection-fighting antibodies that bind to mast cells, which contain chemical particles they'll release in the presence of an antigen. Second, the interleukins activate eosinophils, a type of white blood cell that discharges toxic substances to destroy invading cells (and, occasionally, host cells). In this process, the immune system identifies the "threat" and deploys cells prepared to fight it. The immune system's elevated level of awareness of and preparation against the antigen reclassifies the substance as an allergen —a considerably more dangerous threat.
What happens to the immune system when you have allergies?
An immune system on allergies is a little bit like a brain that can't distinguish a piece of lint from a spider: unable to relax, constantly on guard against every potential threat. After initial exposure, the mast cells activated during the sensitization phase are still equipped with allergen-specific antibodies and remain combat-ready, prepared to respond immediately should a second exposure ever occur. If it does—and it probably will—here’s what you can expect to happen.
How does epinephrine work?
It works by constricting certain blood vessels, increasing blood pressure, and relaxing airways, counteracting all the reactions produced by histamines. According to Sindher, it’s important to use epinephrine immediately if you're at risk for anaphylactic shock. “There’s a general belief out there that epinephrine should only be used in ...
How does the immune system work?
When the body encounters a foreign substance, also called an antigen, immune system cells deliver some of substance's molecules to T-helper cells living in the lymph nodes. Those cells also bring along a type of molecule that informs a T-helper cell it’s time to stage an immune response. Known as a costimulatory molecule, it's ...
What happens during an anaphylactic reaction?
The blood vessels will instantly precipitate hyperdilation, causing a massive drop in blood pressure. Blood volume is not impacted; however, since resistance is distressed, perfusion is greatly affected, leading to low arterial pressure.
What are the two elements that affect anaphylactic shock?
Volume and Resistance. Before going through what anaphylactic shock is, let’s get into the essential factors that influence the different types of shock. With shock, there are only two elements that are affected – volume and resistance .
What is the best medicine for anaphylaxis?
Epinephrine is the best medication used reverse anaphylaxis. Clients who are known to have allergic outbursts usually carry around epinephrine. The body naturally manufactures adrenaline, and epinephrine is the bottled version of it. Epinephrine is a sympathomimetic drug that vasoconstricts the blood vessels, shunting blood to the primary organs like the lungs, heart, and brain to appropriately deliver oxygen.
What happens when blood volume is decreased?
If there is decreased blood volume, the body will compensate by increasing resistance through vasoconstriction; shunting blood to the heart, brain, and lungs.
Why does hypovolemic shock happen?
With a hypovolemic shock, the volume is affected due to rapid blood and fluid loss from the body, which then leads to a decrease in blood pressure, resulting in low oxygen. Pressure is equivalent to blood volume which is why, when a person is bleeding out due to trauma, the body will eventually go into hypovolemic shock if no intervention took place.
What is the fix for shock?
Regarding fixing the type of shock, if it’s caused by volume depletion, the fix is increasing volume. On the other hand, if shock is caused by decreased resistance like anaphylactic shock, constricting the blood vessels through epinephrine is critical.
Why is there not a lot of blood in the body?
There is not a lot of blood circulating through the body due to the huge dilated blood vessels that limit the distribution of blood to different parts of the body. Therefore, the body will compensate through the following: Breathing faster to get more oxygen inside the body, and in the blood.
What is anaphylactic shock?
Anaphylactic Shock: What You Should Know. Anaphylactic shock is a rare but severe allergic reaction that can be deadly if you don't treat it right away. It's most often caused by an allergy to food, insect bites, or certain medications. A shot of a drug called epinephrine is needed immediately, and you should call 911 for emergency medical help.
What is the difference between anaphylactic shock and shock?
Shock is when your blood pressure drops so low that your cells (and organs) don't get enough oxygen. Anaphylactic shock is shock that's caused by anaphylaxis.
How to tell if you have an allergy?
It's a good idea to wear a medical alert bracelet to let people know about your allergy in case you're not able to talk. You also should tell your friends and family so they can help you in an emergency. Be sure they know: 1 Your allergy trigger (s) 2 Signs of an anaphylactic reaction 3 Where you keep epinephrine and how to give you a shot 4 When to call 911
What to wear for anaphylaxis?
Your primary care doctor or allergist can help you with this. It's a good idea to wear a medical alert bracelet to let people know about your allergy in case you're not able to talk.
How to prevent anaphylaxis?
The best prevention is to avoid your triggers. Since you may not be able to do that all the time, make sure you have a plan to spot and treat symptoms of anaphylaxis right away . Your primary care doctor or allergist can help you with this.
How to stop breathing problems?
Other possible treatments include a breathing tube and medications to help you breathe better, and a corticosteroid (a powerful anti-inflammatory drug) to keep symptoms from coming back hours later.
When to call 911 for epinephrine?
A shot of epinephrine in your thigh is needed right away, and you should call 911 because you're at risk for a second reaction (called a biphasic reaction) within 12 hours. At the emergency room, doctors can keep an eye on your symptoms and treat you in case of a second reaction.
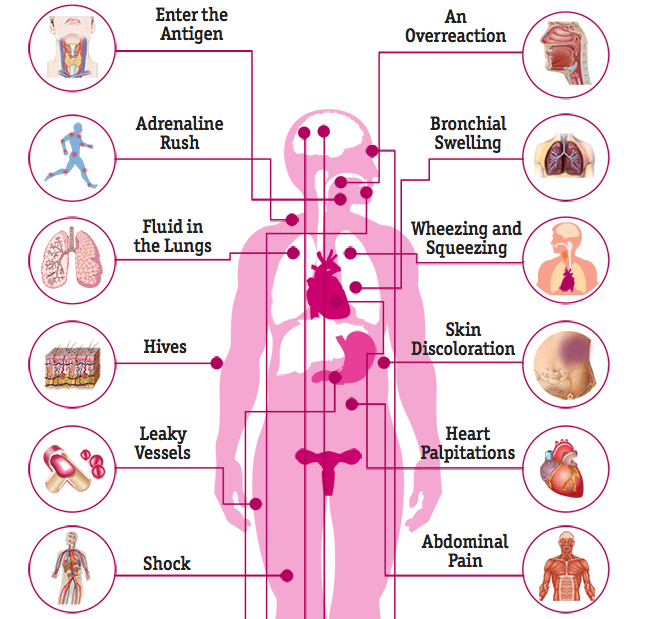
What happens to the body during anaphylactic shock?
During anaphylactic shock, your body goes into overdrive by producing inflammatory chemicals to attack the allergen. In turn, this acute response affects other parts of your body, too. Learn more about the symptoms that occur during anaphylaxis as well as the overall effects on your body. Anaphylaxis isn’t the same as allergies, ...
What happens when you have anaphylaxis?
During anaphylaxis, small blood vessels (capillaries) begin to leak blood into your tissues. This can cause a sudden and dramatic drop in blood pressure. Other symptoms include a rapid or weak pulse and heart palpitations.
How does anaphylaxis affect the immune system?
But with anaphylaxis, your immune system has an exaggerated response when you’re exposed to the substance again. This response affects the whole body and may put your life in danger. Symptoms may begin within seconds.
Why do you need adrenaline injections for anaphylaxis?
In anaphylaxis, an extra dose can help increase blood flow throughout your body and help reverse the immune system’s aggressive response. This is why your doctor will recommend adrenaline (epinephrine) injections in the case of anaphylaxis. It will stop the inflammation from spreading to other body systems.
What happens when you get antigens?
Sometimes, when your body encounters that antigen again, your immune system overreacts. Far too much histamine and other inflammatory chemicals are quickly released into your system. This leads to a wide variety of symptoms throughout the body. It can quickly turn into a medical emergency.
What is the first line of treatment for anaphylaxis?
The first line of treatment is usually adrenaline (epinephrine shots), because it can turn things around quickly. Once you’ve experienced anaphylaxis, you’re always at risk, so you should try to avoid potential allergens as much as possible.
Why is prompt treatment important for anaphylaxis?
slurred speech, hoarse voice, and difficulty talking. As your body goes into shock, loss of consciousness occurs. This is why prompt treatment and medical attention are vital to preventing possible complications of anaphylaxis. Last medically reviewed on June 21, 2018.
What is anaphylactic shock?
Anaphylactic shock. Anaphylactic shock is the direct result of the entrance of a specific foreign material into the bloodstream of a person whose body has become sensitized against it as a result of previous exposure and subsequent formation of antibo dies. During an anaphylactic reaction, lung bronchi constrict intensely, ...
How does venom interact with basophils?
Venom, distributed through the body by the bloodstream, interacts with basophils in the blood and (bottom left) mast cells in tissues. Previous exposure has “primed,” or sensitized, the individual by stimulating these cells to generate immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies, which attach to the surfaces of the mast cells and basophils.
What happens when venom interacts with IgE antibodies?
When the venom interacts with the IgE antibodies, it stimulates the mast cells and basophils to release biologically active chemicals. Within seconds or minutes the chemicals give rise to manifestations of systemic anaphylaxis, which are listed on the right side of the figure. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.
How does nitrous oxide affect circulation?
They are able to decrease the contractility of the heart muscle as well as increase the circulatory capacity by dilating the blood vessels. In addition, the normal postural circulatory reflexes are lost, so pooling of blood in the legs is liable to occur if the affected person is tilted to a head-up position. This is of particular importance after surgery; if a person is made to sit up too soon, it can lead to low blood pressure and an insufficient flow of blood to the brain. Overdosage of certain drugs—notably barbiturates, narcotics, and tranquilizers —blocks normal circulatory reflexes and causes dilation of the blood vessels, leading to a fall in blood pressure that often is accompanied by a slow, full-volume pulse.
Does spinal anesthesia cause blood pressure to drop?
Thus, spinal anesthesia —injection of an anesthetic into the space surrounding the spinal cord —or severance of the spinal cord results in a fall in blood pressure because of dilation of the blood vessels in the lower portion of the body and a resultant diminution of venous return to the heart.
Does neurogenic shock require specific therapy?
Neurogenic shock does not usually require specific therapy ; indeed, spinal anesthetics may be given with a view to producing a low blood pressure so as to diminish bleeding during an operation. If blood pressure becomes critically low, the legs are sometimes elevated and a vasoconstrictor administered.
Is bee venom anaphylactic?
anaphylaxis. Systemic anaphylactic response to bee venom in an individual with type I hypersensitivityIn most people a bee sting is nothing more than an unpleasant, painful experience that is soon forgotten. However, for a minority of individuals who have an allergic predisposition to bee venom, the insect's sting can cause a dangerous, ...
What are the symptoms of anaphylactic shock?
What to Watch For. To identify anaphylactic shock, first look for symptoms of allergy which include: Itching. Red, raised, blotchy skin, seen in 90 percent of cases. Wheezing or shortness of breath, seen in 70 percent of cases.
When does anaphylaxis become anaphylactic shock?
Anaphylaxis becomes anaphylactic shock when a person shows signs of low blood pressure :
How does anaphylaxis cause death?
Anaphylactic shock can cause death by restricting the amount of blood and oxygen that reaches organs, causing unconsciousness, coma, cardiac arrest, and even death. Anaphylaxis can also cause suffocation due to severe swelling of the throat. If left untreated, anaphylaxis can cause death within minutes to hours. 4
What is anaphylaxis in medical terms?
Anaphylaxis is a sudden and severe allergic reaction that involves more than one body system. It is a life-threatening medical emergency. 1 You will often have skin reactions and shortness of breath, which can develop into anaphylactic shock with a drop in blood pressure.
How does anaphylaxis develop?
Anaphylaxis comes on suddenly and the symptoms progress quickly. It will develop most commonly after eating, getting stung by an insect, or taking medications.
How long does it take for anaphylaxis to start?
An episode of anaphylaxis typically begins within 5 to 30 minutes of coming into contact with the allergen to which you are allergic, though it can take more than an hour. 1 However, there are atypical patterns.
What is the first line of treatment for anaphylaxis?
The first line of treatment for anaphylaxis is an injection of epinephrine , which relaxes smooth muscles and increases blood circulation. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) may be needed if the affected person stops breathing. Other treatments may include: 4. High-flow oxygen therapy.
What is anaphylaxis a reaction?
Anaphylaxis is a severe, systemic hypersensitivity reaction that is rapid in onset and characterized by life-threatening airway, breathing, and/or circulatory problems, and that is usually associated with skin and mucosal changes.
Which effector cells are important effectors of anaphylaxis?
B. Mouse models of anaphylaxis suggest that IgG antibodies and FcγR-bearing effector cells (e.g. basophils, macrophages, neutrophils, as well as mast cells) can be important effectors of anaphylaxis induced by large amounts of antigen in the presence of high concentrations of IgG antibodies.
What is the role of IgE in anaphylaxis?
IgE antibodies undeniably can play an important role in conferring immunological specificity to effector cell activation in anaphylaxis and other allergic diseases.15-18IgE is by far the isotype found at the lowest concentrations in the circulation (50-200 ng/ml total circulating IgE in healthy individuals vs. ∼10 mg/ml for IgG);15however, IgE can be found at much higher levels in individuals with allergic diseases.16, 19IgE binds to the high affinity receptor, FcεRI, on the surface of blood basophils and tissue resident mast cells,20and (in humans to a greater extent than in mice) other cell types, including neutrophils, eosinophils, monocytes and dendritic cells, and platelets.20Upon exposure to a bi- or multi-valent allergen, crosslinking of FcεRI-bound IgE induces activation of mast cells and basophils, and the immediate release of preformed mediators such as histamine and various proteases, as well as de novosynthesis of many inflammatory mediators such as certain leukotrienes, prostaglandins, and cytokines.16, 20The importance of that reaction was demonstrated 50 years ago, when different groups realized that purified IgE was capable of transferring skin reactivity from a sensitized human subjects to naive hosts.17, 21-23Similarly, transfer of antigen-specific IgE into naïve mice sensitizes the animals to develop anaphylaxis upon subsequent exposure to that allergen.24, 25Such IgE-mediated anaphylaxis is abrogated in mice lacking the high affinity IgE receptor FcεRI25, as well as in mast cell-deficient mice,26-28highlighting the importance of IgE-mediated mast cell activation in such models of anaphylaxis.
What is evidence from studies of anaphylaxis in humans?
Evidence from studies of anaphylaxis in humans will be discussed, as well as insights gained from analyses of animal models, including mice genetically deficient in the antibodies, antibody receptors, effector cells, or mediators implicated in anaphylaxis, and mice which have been “humanized” for some of these elements.
Why is anaphylaxis considered an aberrant example of an imbalance between the cost and benefit of an immune?
Because it can be triggered in some people by minute amounts of antigen (e.g. certain foods or single insect stings), anaphylaxis can be considered the most aberrant example of an imbalance between the cost and benefit of an immune response.
What is the first line of treatment for anaphylaxis?
Note: As mentioned in the text, first line treatment of anaphylaxis consists of the rapid administration of epinephrine (see Castells et al.6). Although there is evidence that the mediators shown in the figure, particularly histamine and cysteinyl leukotrienes, contribute to some of the various signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis, and anti-histamines are routinely administered to patients with anaphylaxis, pharmacological targeting of such mediators represents second line treatment and should not be considered as an alternative to epinephrine . In red: Strong evidence for the importance of that mediator, in humans, in the development of some of the signs and symptoms listed in the adjacent box; in blue: these elements can be important in mouse models of anaphylaxis but their importance in human anaphylaxis is not yet clear (studies in human subjects suggest that cysteinyl leukotrienes may contribute importantly to the bronchoconstriction and enhanced vascular permeability associated with anaphylaxis [see text]); in grey: elements with the potential to influence anaphylaxis, but their importance in human or mouse anaphylaxis not yet clear. Note that some mediators (underlined) are likely to contribute to the development of late consequences of anaphylaxis.
Which cells play a dominant role in anaphylaxis?
AAntigen-specific IgE antibodies and FcεRI-bearing effector cells (e.g. mast cells, basophils) play a dominant role in anaphylaxis induced (sometimes by very small amounts of antigen) when concentrations of IgG antibodies are low. B.
Volume and Resistance
Pathophysiology
- Anaphylaxis symptoms usually occur within minutes of exposure to an allergen. Sometimes, however, anaphylaxis can occur a half-hour or longer after exposure. In rare cases, anaphylaxis may be delayed for hours. Signs and symptoms include: 1. Skin reactions, including hives and itching and flushed or pale skin 2. Low blood pressure (hypotension) 3. ...
Fixing Anaphylactic Shock
Shock in A Nutshell