What mineral does magma turn into when it cools?
When magma or lava cools, the magma and ore carried within it crystallize to form tiny minerals in the newly-created igneous rock. Minerals found in such rock might include feldspar or mica. Minerals can also be transported and released from water sources, such as seawater, river water, or groundwater.
What size crystals form when magma cools rapidly?
The factor that affects the size of the crystals is the cooling rate of the molten rock or magma. If the magma cools rapidly, the crystal formed is very small, whereas if the magma cools slowly, the crystal formed is large.
What happens to magma when it cools?
When magma cools below ground, it cools more slowly and crystals have time to grow larger. That kind of magma is called ‘intrusive igneous rock’. Examples of such rocks are granite, diorite, and syenite. The liquid cool faster the closer to the surface it is so that if you could take a slice down the volcanic vent you could see a smooth transition.
When magma cools and hardens it becomes?
Magma cools either underground or on the surface and hardens into an igneous rock. As the magma cools, different crystals form at different temperatures, undergoing crystallization. For example, the mineral olivine crystallizes out of magma at much higher temperatures than quartz.

What happens when magma crystallizes?
As magma begins to cool - both below and above ground - mineral crystals in the melt will begin to form and precipitate, in a process called crystallization (the solidification of atoms or molecules into a highly structured form called a crystal).
What would happen when magma will be cooled and crystallized beneath the surface?
As magma cools the elements within the magma combine and crystalize into minerals that form an igneous rock. Magma cools either below the surface or at the surface (magma that reaches the surface is called lava). As magma cools igneous rock is formed.
What happens when magma cools and solidifies?
When magma cools, it solidifies to form rock which is called "igneous rock".
What is cooling and crystallization?
In evaporation, the solvent is removed by heating the solution until the solvent is evaporated; in cooling crystallization, the solution is cooled until the solubility of the compound involved is reduced, causing it to separate from the solvent through crystallization.
What type of rock will be formed when the lava cools and crystallizes?
Igneous rocksIgneous rocks form when magma (molten rock) cools and crystallizes, either at volcanoes on the surface of the Earth or while the melted rock is still inside the crust.
What type of rock is formed when magma cools and solidifies?
Igneous rocksIgneous rocks (from the Latin word for fire) form when hot, molten rock crystallizes and solidifies.
What happens when magma cools quickly?
If the magma cools rapidly on the surface of the earth the rock forms what is called lava. The crystals are much smaller and harder. An extreme example is obsidian or volcanic glass where the crystals are so small that the crystals look like glass.
What is the cooling of magma called?
Igneous Rocks= formed from cooling of magma and lava. 4. Metamorphic Rocks= formed by high temperature and pressure. 5. Sedimentary Rocks= formed by compaction and lithification.
When molten magma cools it solidifies to become?
When the molten magma cools, it becomes solid. Rocks thus formed are called igneous rocks. They are also called primary rocks. There are two types of igneous rocks: intrusive rocks and extrusive rocks.
What happens crystallization?
Crystallization or crystallisation is the process by which a solid forms, where the atoms or molecules are highly organized into a structure known as a crystal. Some of the ways by which crystals form are precipitating from a solution, freezing, or more rarely deposition directly from a gas.
How are minerals formed by crystallization from magma?
Magma heats nearby underground water, which reacts with the rocks around it to pick up dissolved particles. As the water flows through open spaces in the rock and cools, it deposits solid minerals.
Why do crystals in a magma stop growing during cooling?
Why do crystals in a magma stop growing during cooling? They run out of heat.
What happens when magma cools underground?
When magma cools underground, it cools very slowly and when lava cools above ground, it cools quickly. When magma and lava cool, mineral crystals start to form in the molten rock. Plutonic rocks, which cool slowly underground, have large crystals because the crystals had enough time to grow to a large size.
What happens when magma cools either underground or on the surface and hardens?
Crystallization. Magma cools either underground or on the surface and hardens into an igneous rock. As the magma cools, different crystals form at different temperatures, undergoing crystallization. For example, the mineral olivine crystallizes out of magma at much higher temperatures than quartz.
Why do crystals in a magma stop growing during cooling?
Why do crystals in a magma stop growing during cooling? They run out of heat.
How can you tell whether a magma cooled at surface or underground?
It is also determined by the rate that the magma cools. If the magma cools deep underground, it cools slowly. If the magma cools at or very near the surface, it cools quickly.
Formation
- The minerals that make up igneous rocks crystallize at a range of different temperatures. This explains why a cooling magma can have some crystals within it and yet remain predominantly liquid. The sequence in which minerals crystallize from a magma is known as the Bowen reaction series (Figure 3.10 and Who was Bowen). Of the common silicate minera...
Discovery
- Norman Levi Bowen, born in Kingston Ontario, studied geology at Queens University and then at MIT in Boston. In 1912, he joined the Carnegie Institution in Washington, D.C., where he carried out groundbreaking experimental research into the processes of cooling magmas. Working mostly with basaltic magmas, he determined the order of crystallization of minerals as the temperature …
Introduction
- The Bowen reaction series is one of the results of his work, and even a century later, it is an important basis for our understanding of igneous rocks. The word reaction is critical. In the discontinuous branch, olivine is typically the first mineral to form (at just below 1300°C). As the temperature continues to drop, olivine becomes unstable while pyroxene becomes stable. The e…
Mechanism
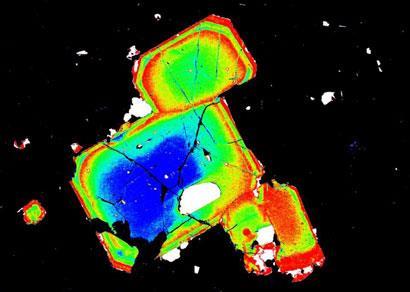
- In cases where cooling happens relatively quickly, individual plagioclase crystals can be zoned from calcium-rich in the centre to more sodium-rich around the outside. This occurs when calcium-rich early-forming plagioclase crystals become coated with progressively more sodium-rich plagioclase as the magma cools. Figure 3.11 shows a zoned plagioclase under a microscope.
Composition
- The composition of the original magma is critical to magma crystallization because it determines how far the reaction process can continue before all of the silica is used up. The compositions of typical mafic, intermediate, and felsic magmas are shown in Figure 3.12. Note that, unlike Figure 3.6, these compositions are expressed in terms of oxides (e.g., Al2O3 rather than just Al). There …
Genetics
- Mafic magmas have 45% to 55% SiO2, about 25% total of FeO and MgO plus CaO, and about 5% Na2O + K2O. Felsic magmas, on the other hand, have much more SiO2 (65% to 75%) and Na2O + K2O (around 10%) and much less FeO and MgO plus CaO (about 5%).