What decreases soil fertility?
Soil fertility decline
- Contributing factors. Nitrogen can also be lost from the soil as a gas by the process of denitrification.
- Effects. Organic matter plays a key role in maintaining soil fertility. ...
- Managing soil fertility decline. Fertility management aims to maintain soil organic matter, soil structure, soil nutrient status and satisfactory soil pH.
How can you preserve the fertility of soil?
Some of the categories and ways to conserve the soil include:
- Agricultural Soil Conservation Agricultural soil conservation involves the practices that can be used by farmers to promote the health and quality of soils. ...
- Home Soil Conservation Methods Home soil conservation methods are the techniques that can be utilized at home to preserve and improve soil quality. ...
- Resource planning
How can the ground lose its fertility?
- Erosion - by wind and erosion by water.
- Percolation down through the soil - rainfall and flooding.
- Over-cropping (i.e., farming).
- A major change in climate - as happened in many places, (the Fertile Crescent - the pre-Columbian droughts of the Americas).
What is the way to maintain soil fertility?
Ways to improve soil fertility
- Organic matter. A diverse range of organic matter is the best method to improve soil fertility. ...
- Biochar. Biochar improves soil fertility by acting as a direct nutrient source or by changing the physiochemical properties in the soil.
- Green Manuring. ...
- Mulching. ...
- Mixed cropping. ...
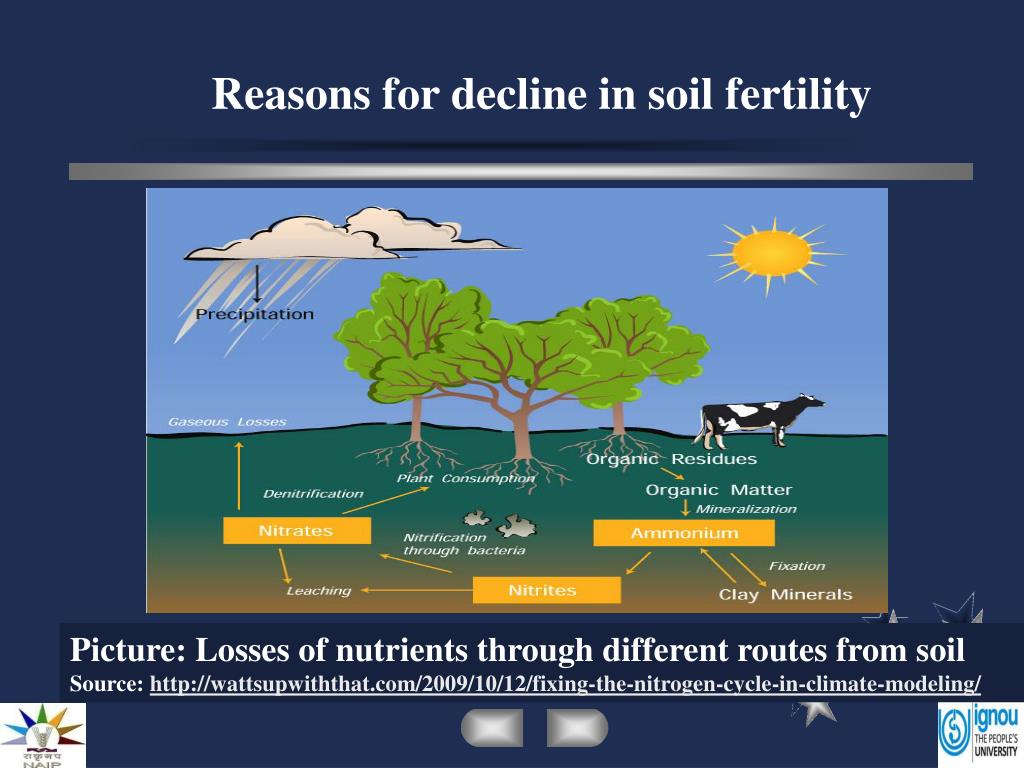
What causes lose of soil fertility?
The major causes of soil fertility depletion are inadequate fertilizer use, complete removal of crop residues, continuous cropping systems, climate and soil types, lack of proper cropping systems and soil erosion and continuous cultivation.
How does fertility affect soil?
What is Soil Fertility? “Soil fertility refers to the ability of the soil to sustain plant growth.” Fertile soil results in high yield and better quality of plants. Fertile soil is rich in fundamental elements and minerals, has good aeration, water holding capacity, and good texture.
Why is soil fertility important?
A fertile soil also provides essential nutrients for plant growth, to produce healthy food with all the necessary nutrients needed for human health. Moreover, fertility has an impact on activities with an economic impact and is therefore related to economic growth and the fight against poverty.
How important is soil fertility in a farm operation?
Crops need nutrients just like people do. A fertile soil will contain all the major nutrients for basic plant nutrition (e.g., nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium), as well as other nutrients needed in smaller quantities (e.g., calcium, magnesium, sulfur, iron, zinc, copper, boron, molybdenum, nickel).
Why do soils lose fertility?
Continue Reading. Soils lose fertility when the qualities that support plant growth and soil health are degraded: Loss of plant nutrients - The nutrients essential for growth (N, P, K, Ca, S, Mg, B, Cl, Mn, Fe, Zn, Cu, Mo, Ni) are unavoidably lost when plants are harvested and removed. But they are also lost when soil erodes or when water leaches ...
What is the loss of soil structure?
Loss of soil structure - The granular, crumb-like structure of topsoil is desired by every farmer or gardener and is the product of adequate levels of organic matter. The subsoil also has structure that is formed over long periods of time by wetting and drying, freezing and thawing, the deposition of clay particles, and the mechanical action of soil organisms. Good soil structure allows air and water to penetrate more easily and provides routes for the growth of plant roots. To maintain soil structure, keep adequate levels of organic matter in the topsoil and take measures to prevent soil compaction by farm or construction equipment.
How to minimize nutrient loss?
To minimize nutrient loss, use effective erosion control practices, and capture nutrients with the use of cover crops before and after the main crop. Loss of organic matter - Organic matter is responsible for imparting many benefits t. Continue Reading. Soils lose fertility when the qualities that support plant growth and soil health are degraded:
What are the benefits of organic matter?
Loss of organic matter - Organic matter is responsible for imparting many benefits to topsoil, including increasing water-holding capacity, maintaining soil structure, ability to hold nutrients until needed by plants, and increasing permeability to rainfall.
How are nutrients recycled?
A lot of nutrients are recycled within an agricultural system when plant material rots down and in the faeces and urine of farm animals , but any time produce leaves the farm it reduces the nutrients available for the next crop. Some nutrients are replaced through the breakdown of minerals in the soil rockbase, and nitrogen can be replaced through fixation of atmospheric nitrogen by a range of plants and cyanobacteria, (actually the plants that fix nitrogen do so through bacteria living within the plant structure).
Why is it important to get soil tested after every crop?
It is a good practice to get the soil tested after every crop so that the farmer can maintain the balanced fertility. Continue Reading. On cultivation plants absorb the nutrients and elements it needs for its growth and yields. So soil deplete and loose its fertility.
Where does soil get its nutrients?
Soil gains most of its nutrients and other beneficial components from the soil, which is common knowledge. What might not be common knowledge is that soil gets those nutrients from trees, or more specifically the roots of trees. In many countries we see an epidemic of deforestation.
Why is soil fertility important?
It is important to safeguard the soil fertility to ensure profitable agribusiness ventures. Below are ways the soil losses fertility and the solutions to curb this losses.
What is volatilization in soil?
Volatilization: Gaseous escape of Nitrogen from the soil.
What is humipower soil?
HUMIPOWER® is a water soluble soil amendment and blend that contains potassium, Iron EDDHA, humates and fulvic acid in granular form.
What happens when nitrogen is converted to plant available form?
Solution- when Nitrogen is converted to plant available form (Nitrates), Humipower will help hold it and avail them to the plants.
How to make sure organic matter doesn't decay faster than it's replenished?
Solution- To make sure that organic matter doesn’t decay faster than it’s replenished, return crop residues to the soil and use cover crops to generate additional plant matter.
Can humipower be applied to fertilizer?
Solution- Apply Humipower in Fertilizer and manure. Only unavoidable leaching will occur.
What was the impact of the 1990s on soil fertility?
In the late 1990’s several studies were done that compared the nutrient levels of today’s food to that of 50 years ago. They found that nutrient levels were lower today. People quickly concluded that this was proof of a decline in soil fertility. Modern agriculture had used up the nutrients in our soil and now our food supply was suffering.
How to measure soil fertility?
One of the best ways to measure soil fertility is to look at plant growth and measure nutrients in plants.
Are Soils Less Nutritious?
The examination of nutrients in food over time does not support the idea that soils are less nutrient rich today compared to the past.
Why are agricultural plants growing bigger?
Agricultural plants are growing bigger and producing more than ever before. This fact alone indicates that they are getting the nutrients they need. The nutrient levels in soil may be going down, but they have not reached a critical point where it becomes important to remineralize the soil above what is currently being done with fertilizers.
How is soil created?
But there is another process at play. Soil was originally created by the decomposition of rocks. As rocks break down they release nutrients into the soil. With the exception of nitrogen, rocks are the source of the nutrients our plants need.
What is the importance of plant growth?
Plants, like animals are programmed by genetics. Their genetics determines which nutrients they need in order to grow and function correctly. A significant decrease in any of the required nutrients results in poor growth, sickness or death.
What are rocks in soil?
Keep in mind that the term rocks includes things like silt and sand, which are just small rocks. Nutrients are also added back to soil through fertilization, increasing soil fertility. The microbes in the soil help break down the rock and make the nutrients available to plants.
What is soil fertility decline?
Soil fertility decline occurs when the quantities of nutrients removed from the soil in harvested products exceed the quantities of nutrients being applied. In this situation, the nutrient requirements of the crop are met from soil reserves until these reserves cannot meet crop demands.
What is the loss of organic matter in a plant?
It holds nitrogen and sulfur in organic forms and other essential nutrients such as potassium and calcium. The loss of organic matter mainly occurs through continuous cropping with stubble removal or burning, and is accelerated by frequent tillage.
Why is the subsoil depleting?
Limited in-season rainfall often causes crops to meet their water (and nutrient) requirements from the subsoil. This has resulted in subsoil depletion of nutrients even though the surface soil may have adequate levels due to redistribution via crop residues.
How can nutrients be removed from soil?
Contributing factors. Nutrients may be removed from the soil by: growing crops. soil erosion. leaching. Nitrogen can also be lost from the soil as a gas by the process of denitrification.
Is Queensland unable to produce crops?
Significant areas of cultivated land in Queensland are now unable to produce economic crop yields and high protein grains without the use of fertilisers.
Why is soil degraded?
Soils are becoming severely degraded due to a combination of intensive farming practices and natural processes. As the layer of fertile topsoil thins, it gets increasingly difficult to grow crops for food.
How much soil did Iowa lose in 2014?
In just one spring in 2014, Iowa lost nearly 14 million tonnes of soil from its cropland in a series of storms, according to environmental groups. A study of 82 sites in 21 counties by Iowa State University showed that in the 50 years from 1959, soil structure and levels of organic matter had degraded while acidity had increased.
How much of the world's soil is degraded?
According to the United Nations’ Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO), a third of the world’s soil is now moderately to highly degraded. The processes that generate high-quality, fertile topsoil can take centuries. But the world is ploughing through that resource at an alarming rate.
How deep is Iowa soil?
But beneath the feet of Iowa’s farmers, a crisis is unfolding. The average topsoil depth in Iowa decreased from around 14-18 inches (35-45cm) at the start of the 20th Century to 6-8 inches (15-20cm) by its end. Relentless tilling and disturbance from farm vehicles have allowed wind and water to whisk away this priceless resource.
Is there a shortage of mud and dirt?
At first glance, it might seem that there is no shortage of mud and dirt around the world. But it's the quality that really counts. “Many types of soil degradation are invisible,” says Ronald Vargas, secretary of the global soil partnership at the FAO in Rome.
How can soil fertility be challenged?
Soil fertility can be severely challenged when land-use changes rapidly. For example, in Colonial New England, colonists made a number of decisions that depleted the soils, including: allowing herd animals to wander freely, not replenishing soils with manure, and a sequence of events that led to erosion.
What is soil fertility?
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Soil fertility refers to the ability of soil to sustain agricultural plant growth, i.e. to provide plant habitat and result in sustained and consistent yields of high quality. A fertile soil has the following properties:
How does soil fertility work?
Soil fertility is a complex process that involves the constant cycling of nutrients between organic and inorganic forms. As plant material and animal wastes are decomposed by micro-organisms, they release inorganic nutrients to the soil solution, a process referred to as mineralization. Those nutrients may then undergo further transformations which may be aided or enabled by soil micro-organisms. Like plants, many micro-organisms require or preferentially use inorganic forms of nitrogen, phosphorus or potassium and will compete with plants for these nutrients, tying up the nutrients in microbial biomass, a process often called immobilization. The balance between immobilization and mineralization processes depends on the balance and availability of major nutrients and organic carbon to soil microorganisms. Natural processes such as lightning strikes may fix atmospheric nitrogen by converting it to (NO 2 ). Denitrification may occur under anaerobic conditions (flooding) in the presence of denitrifying bacteria. Nutrient cations, including potassium and many micronutrients, are held in relatively strong bonds with the negatively charged portions of the soil in a process known as cation exchange .
Why is soil depletion bad?
This leads to poor crop yields. In agriculture, depletion can be due to excessively intense cultivation and inadequate soil management .
What are the properties of fertile soil?
A fertile soil has the following properties: The ability to supply essential plant nutrients and water in adequate amounts and proportions for plant growth and reproduction; and. The absence of toxic substances which may inhibit plant growth. The following properties contribute to soil fertility in most situations: ...
What are the properties of soil fertility?
The following properties contribute to soil fertility in most situations: Sufficient soil depth for adequate root growth and water retention; Good internal drainage, allowing sufficient aeration for optimal root growth (although some plants, such as rice, tolerate waterlogging);
Why is soil conservation important?
This is because soil erosion and other forms of soil degradation generally result in a decline in quality with respect to one or more of the aspects indicated above.
Why is my soil not fertile?
Poor Soil Structure. Soil fertility problems may also be caused by overtilling and poor soil structure. Fertile soil structure has plenty of pores that allow air and water to enter the soil to supply plant roots. If the soil particles are too fine and there is not enough organic material, the soil tends to crust on the top and not allow in air ...
How does crop residue affect soil fertility?
Crop residue also contributes to soil fertility, advises CIMMYT. When the residue is removed by grazing animals or by burning, it cannot replenish the soil. The breakdown of crop residue to help replenish the soil is accomplished by organisms, such as earthworms, termites and some types of fungi and bacteria. Without a food source, such as crop residues, these organisms may die out, further reducing soil fertility.
What are the factors that contribute to soil infertility?
Factors that cause or contribute to soil infertility include nutrient mining, removal of crop residue, erosion, incorrect soil pH, salinity and natural disasters.
Why is clay soil so small?
Clay soil naturally has smaller particles, but small soil particles can also be caused by tilling the ground. Tilling also breaks up the pores in the soil, damages the habitats of earthworms and other biological life, decomposes organic material and contributes to soil compaction.
What causes soil to be infertile?
There are many potential causes of soil infertility, including nutrient mining, incorrect pH levels, salinity and erosion. Natural disasters, such as flooding and forest fires, are also factors affecting soil fertility. Once you diagnose your soil fertility problems, you can take steps to improve soil fertility and the health of your plants.
What is the breakdown of crop residue?
The breakdown of crop residue to help replenish the soil is accomplished by organisms , such as earthworms, termites and some types of fungi and bacteria. Without a food source, such as crop residues, these organisms may die out, further reducing soil fertility.
What is the subsoil that plants reach down into?
With limited topsoil, plants reach down into the subsoil. In many cases, the subsoil is inhospitable to plant roots. Coarse subsoil that consists of gravel and sand particles will not hold enough water to support the plants. Subsoil that has fine particles prevents water drainage and limits oxygen availability to the roots.
