What are some examples of sex linked traits?
- Red-green colorblindness – Inability differentiate between red and green.
- Male Pattern Baldness
- Hemophilia – a condition lacking the enzyme for blood clotting
- Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy – Muscular weakness, progressive deterioration of muscle tissue, and loss of coordination.
What are some examples of sex - linked traits?
- Red-green colorblindness – Inability differentiate between read and green.
- Male Pattern Baldness
- Hemophilia – Causes the blood not to clot. If get a cut it may take a along time to clot or internal bleeding may result from a bruise.
- Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy – Muscular weakness, progressive deterioration of muscle tissue, and loss of coordination.
What is the definition of sex - linked traits?
Sex-linked traits are characteristics other than sex that are carried by the sex chromosomes (coiled structures in a cell's nucleus that carries the cell's genetic information). Sex chromosomes in humans do more than determine whether a person is male or female, and they can carry such traits as the condition color blindness and the disease muscular dystrophy.
What are some examples of X - linked traits?
- The disorder should mostly affect males.
- X-linked recessive disorders transmit through healthy carrier females to their son.
- No male-to-male transmission
What are sex - linked characteristics?
Sex-linked characteristics. In sex chromosomes the Y chromosome is very small compared with the X. The Y chromosome does not have the same number of genes in it as the X and, therefore, most of the genes in the X chromosome will lack matching alleles in males. For females, the normal pairing of alleles will exist. When characteristics located ...

What are sex-linked traits found on?
Sex-linked traits are associated with genes found on sex chromosomes. In humans, the sex chromosomes are X and Y. Because the X-chromosome is larger, X-linked traits are more common than Y-linked traits. An example of a sex-linked trait is red-green colorblindness, which is carried on the X-chromosome.
What are sex-linked traits give an example?
The manifestation of certain traits as an outcome of the expression of particular genes in the sex chromosome is referred to as sex linkage. For example, color blindness is a sex-linked trait whose allele is recessive and located on the X chromosome.
Is eye color a sex-linked trait in humans?
Most sex-linked traits are actually X-linked, such as eye color in Drosophila or color blindness in humans.
Is human height a sex-linked trait?
Samuli Ripatti, a professor at the University of Helsinki and the head researcher of this study, suggests that there is a direct correlation between the two copies of X chromosomes and women and their tendency to be shorter than men.
What genes are sex-linked?
Genes that are carried by either sex chromosome are said to be sex linked. Men normally have an X and a Y combination of sex chromosomes, while women have two X's. Since only men inherit Y chromosomes, they are the only ones to inherit Y-linked traits.
Is tongue rolling a sex-linked character?
Tongue rolling also is a character evenly found in both male and female, a person born with one or two dominant allele of the gene for tongue rolling ends up having the ability. This could be male or female.
Is skin colour sex-linked?
Skin color genes are present on autosomes and do not exhibit sex-linked inheritance. The presence of more than one allele for a gene is called multiple allelism; each gene for skin color has two alleles only.
Is blindness a sex-linked trait?
Mutations in these genes can cause color blindness. Color blindness is a common inherited sex-linked disorder that affects a person's ability to see or recognize certain colors.
Is hair sex-linked?
There are some human traits and health conditions that are determined by the genes passed through the sex chromosomes (X and Y chromosomes). These are called sex-linked traits. The way your hair looks is neither Y-linked or X-linked.
Is hair color sex-linked or autosomal?
Researchers have discovered 124 genes that play a major role in determining human hair color variation. The findings were published online this week in the journal Nature Genetics. Hysi et al identified 123 autosomal and one X-chromosome loci significantly associated with hair color.
What are the 5 biological sexes?
The six biological karyotype sexes that do not result in death to the fetus are:X – Roughly 1 in 2,000 to 1 in 5,000 people (Turner's )XX – Most common form of female.XXY – Roughly 1 in 500 to 1 in 1,000 people (Klinefelter)XY – Most common form of male.XYY – Roughly 1 out of 1,000 people.More items...•
What is a sex linked narrator?
Narration. Sex linked... These are traits that are found on either one of the chromosomes that determine sex, or the sex chromosomes. And in humans this is the X or the Y chromosomes.
Why is the X chromosome larger than the Y chromosome?
This is because the X chromosome is large and contains many more genes than the smaller Y chromosome . In a sex-linked disease, it is usually males who are affected because they have a single copy of X chromosome that carries the mutation. In females, the effect of the mutation may be masked by the second healthy copy of the X chromosome.
When a female parent is homozygous for a recessive X-linked trait, will
When a female parent is homozygous for a recessive X-linked trait, she will pass the trait on to 100 percent of her male offspring , because the males will receive the Y chromosome from the male parent. In humans, the alleles for certain conditions (some color-blindness, hemophilia, and muscular dystrophy) are X-linked.
What was the first trait to be identified?
Eye color in Drosophila, the common fruit fly, was the first X-linked trait to be identified. Thomas Hunt Morgan mapped this trait to the X chromosome in 1910. Like humans, Drosophila males have an XY chromosome pair, and females are XX.
How many homologous pairs of autosomes are there in humans?
Until now, we have only considered inheritance patterns among non-sex chromosomes, or autosomes. In addition to 22 homologous pairs of autosomes, human females have a homologous pair of X chromosomes, whereas human males have an XY chromosome pair.
Do heterozygous females have X-linked traits?
Females who are heterozygous for these diseases are said to be carriers and may not exhibit any phenotypic effects. These females will pass the disease to half of their sons and will pass carrier status to half of their daughters; therefore, X-linked traits appear more frequently in males than females. In some groups of organisms ...
Is the Y chromosome X or X?
Although the Y chromosome contains a small region of similarity to the X chromosome so that they can pair during meiosis, the Y chromosome is much shorter and contains fewer genes. When a gene being examined is present on the X, but not the Y, chromosome, it is X-linked.
67 Sex-Linked Traits
In humans, as well as in many other animals and some plants, the sex of the individual is determined by sex chromosomes—one pair of non-homologous chromosomes. Until now, we have only considered inheritance patterns among non-sex chromosomes, or autosomes.
License
Mt Hood Community College Biology 102 by Lisa Bartee and Christine Anderson is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted.
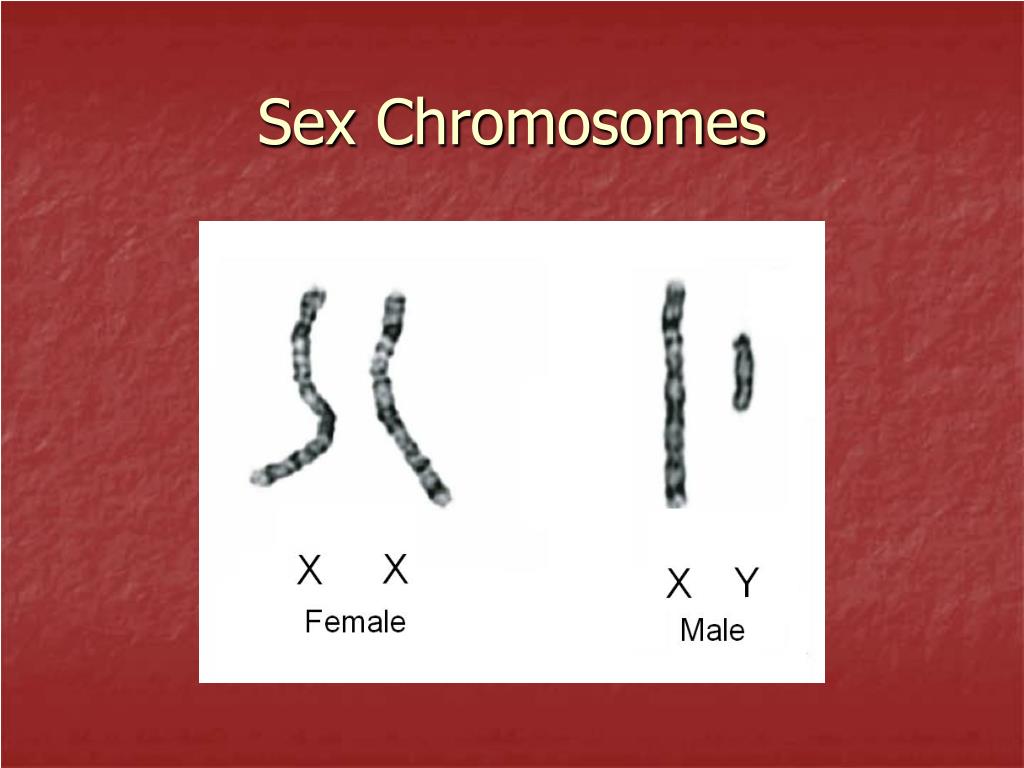
Sex Chromosomes
Sex chromosomes determine whether an individual is male or female. In humans and other mammals, the sex chromosomes are X and Y. Females have two X chromosomes, and males have an X and a Y.
Inheritence of Sex Chromosomes in Mammals
Meiosis is the process of making gametes, also known as eggs and sperm in most animals. During meiosis, the number of chromosomes is reduced by half, so that each gamete gets just one of each autosome and one sex chromosome.
Sex Chromosomes in Pigeons
The way sex determination works in birds is nearly the reverse of how it works in mammals. If you’ve played Pigeonetics, you know that the sex chromosomes in birds are Z and W. Male birds have two Z chromosomes, and females have a Z and a W. Male birds make sperm, which always have a Z chromosome. Female gametes (eggs) can have a Z or a W.
Inheritance of Sex-Linked Genes
For genes on autosomes, we all have two copies—one from each parent. The two copies may be the same, or they may be different. Different versions of the same gene are called “alleles” (uh-LEELZ). Genes code for proteins, and proteins make traits.* Importantly, it’s the two alleles working together that affect what we see—also called a “phenotype.”
Recombination and Sex-Linked Genes
When gametes (egg and sperm) form, chromosomes go through a process called recombination. During recombination, homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange stretches of DNA. Recombination makes new allele combinations, which can then be passed to offspring.
Sex-Linked Genes Can Also Be Genetically Linked
In pigeons, the color and dilute genes are not only sex-linked, they are also genetically linked.
Characteristics of Sex-Linked Inheritance
It has been witnessed that the X-chromosomes are present in paired form (XX) in human females, and a single X and Y chromosome (XY) is present in human males. The X- chromosome has no counterpart in males, so the genes present, either in dominant or recessive form, are always expressed in males.
Sex-Linked Disorders in Humans
In colour blindness, a person cannot distinguish red and/or green colours. The colourful vision of the eye is due to the cone cells present in the retina of the eye. Cone cells are of three types, red, blue, and green. If these cells show mutation, it can lead to different conditions.
Summary
Sex-linked inheritance is the transfer of traits from the sex chromosomes. Female shows XX chromosome while the male has only one X chromosome along with Y chromosome. If the traits are present on the X chromosome, it is called X-linked inheritance, and if it is present on the Y chromosome, it is called Y-linked inheritance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Sex-Linked Inheritance
Q.1. State some examples of sex-linked recessive disorder? Ans: Colour blindness and haemophilia are examples of sex-linked recessive disorders.
