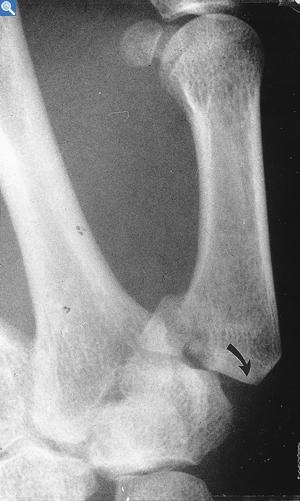
What is Bennett fracture of the thumb?
A Bennett fracture is a fracture of the base of the thumb resulting from forced abduction of the first metacarpal. It is defined as an intra-articular two-part fracture of the base of the first metacarpal bone. Despite a relatively simple appearance on radiographs, Bennett fractures are considered unstable.
What is the mechanism of injury for a Bennett fracture?
Mechanism of injury. The Bennett fracture is an oblique intraarticular metacarpal fracture dislocation, caused by an axial force directed against the partially flexed metacarpal. This type of compression along the metacarpal bone is often sustained when a person punches a hard object, such as the skull or tibia of an opponent, or a wall.
Can a CT scan show a Bennett fracture?
Although X-ray films can be used to diagnose this condition, a CT scan should be ordered to evaluate the extent of the damage. On these CT scans a Bennett fracture will present can as an intra-articular fracture and dislocation of base of the first metacarpal.
What are the signs and symptoms of a Bennett fracture?
Bennett fractures are associated with pain and weakness of the pinch grasp and swelling and ecchymosis over the carpal metacarpal joint of the thumb. The patient will be unable to perform functional tasks such as tying a shoe or using a key.

How serious is a Bennett fracture?
A Bennett's Fracture is a fracture plus dislocation of the Metacarpal bone at the base of the thumb. The fracture involves the joint surface and is often significantly displaced . This is a highly unstable injury and occurs commonly in football.
How long does it take a Bennett's fracture to heal?
The Bennett fracture healed and full recovery of function was found between 4-8 weeks.
Does Bennetts fracture require surgery?
Treatment for Bennett's Fracture The procedure doesn't require surgery and involves bones being reset back into place from the outside. For a more severe break to heal, an open reduction may be needed, which requires surgery to realign the bones using pins and screws.
What does a Bennett fracture feel like?
A Bennett's fracture causes your thumb to feel painful and stiff. Your thumb area will swell. Your thumb may be unstable and therefore difficult to move normally. Over time, it is common for an old poorly treated Bennett's fracture to develop arthritis.
Can you move your thumb with a Bennett fracture?
Bennett's fractures can result from any significant forces placed on the base of the thumb, such as sports, falls and accidents. A Bennett's fracture causes your thumb to feel painful and stiff. Your thumb area will swell. Your thumb may be unstable and therefore difficult to move normally.
How common is a Bennett fracture?
The Bennett's fracture is the most common type of fracture to the thumb metacarpal base. A Bennett's fracture is an intra-articular fracture, or one that extends into the joint between the metacarpal and wrist bone (“trapezium”). This injury most often occurs in contact sports such as football, rugby, and boxing.
How do you fix a Bennett's fracture?
[8] Surgical treatment of Bennett fractures is varied but generally consists of either closed reduction with percutaneous pinning or open reduction with either pins or interfragmentary screws. All methods of fixation have been shown to be effective in case reviews and series.
How is Bennett's fracture diagnosed?
Although X-ray films can be used to diagnose this condition, a CT scan should be ordered to evaluate the extent of the damage. On these CT scans a Bennett fracture will present can as an intra-articular fracture and dislocation of base of the first metacarpal.
Why is it called a Bennett's fracture?
The Bennett fracture is named after Edward Hallaran Bennett, Professor of Surgery (1837–1907) at Trinity College of the University of Dublin, who described it in 1882.
What are 3 signs and symptoms of a fracture?
SymptomsA visibly out-of-place or misshapen limb or joint.Swelling, bruising, or bleeding.Intense pain.Numbness and tingling.Broken skin with bone protruding.Limited mobility or inability to move a limb or put weight on the leg.
Can a 5th metatarsal fracture heal without a cast?
Diagnosis. The base of the fifth metatarsal is divided into three fracture zones. Zone 1 fractures are avulsion or chip fractures that occur at the tip of the base of the fifth metatarsal. These fractures typically are treated without surgery using a cast, boot, or hard-soled shoe and tend to heal within 6-8 weeks.
What does walking on a fracture feel like?
You likely feel a dull ache where the fracture is located. The pain intensifies when you're on your feet and lessens or goes away when you're resting. Over half of stress fractures are in the lower leg/ankle. If the fracture has gone untreated for a while, you feel significant pain when you bear any weight on the foot.
How long does a broken thumb base take to heal?
Recovery times Most of the healing happens between 3 to 6 weeks after your thumb fracture. It's normal to have aches and discomfort beyond this. This usually happens when you try activities you haven't done for a while. It's also normal for the area to be more sensitive for a while after the injury.
How is a Bennett fracture treated?
Treatment / Management [8] Surgical treatment of Bennett fractures is varied but generally consists of either closed reduction with percutaneous pinning or open reduction with either pins or interfragmentary screws. All methods of fixation have been shown to be effective in case reviews and series.
Is Bennett's fracture painful?
Symptoms will be similar to other wrist and hand fractures: Immediate and severe pain over the thumb side of the wrist. There will be rapid swelling and bruising may develop. The patient will find it very difficult to move the wrist and thumb.
What is the fastest way to heal a broken metacarpal?
Treatment optionsapplying ice to the hand.using a splint to hold it stable while it heals.not using your hand for a period of time.keeping your hand above heart level.taking prescription or over-the-counter pain medication, depending on the amount of pain.cleaning and treating any wounds on the skin of the injured hand.More items...
What type of fracture is Bennett?
Based upon the radiographic appearance, Gredda classified Bennett fractures into three types, with type 1 being a fracture with a single ulnar fragment and subluxation of the metacarpal base, type 2 an impaction fracture without subluxation of the first metacarpal, and type 3 an injury with a small ulnar avulsion fragment in association with metacarpal dislocation. [5]
How to treat Bennett fractures?
[6][7]Historical reports have shown good outcomes with this treatment, although more recent studies have shown poor outcomes when treating these fractures with casting alone.[8] Surgical treatment of Bennett fractures is varied but generally consists of either closed reduction with percutaneous pinning or open reduction with either pins or interfragmentary screws. All methods of fixation have been shown to be effective in case reviews and series. Treating with closed reduction with intermetacarpal fixation from the first to the second metacarpal and/or to the trapezium is usually effective in reducing the first metacarpal shaft subluxation. If it is decided to treat this fracture with open reduction, it is most commonly performed through a Wagner incision.[4] The decision to treat these fractures with either open reduction or closed reduction is still a matter of debate.
What fracture pattern is the first metacarpal?
The fracture pattern is distinct. The base of the first metacarpal is fractured with intraarticular extension due to the palmar ulnar fragment of the first metacarpal held in place by its ligamentous attachment to the trapezium (known as the anterior oblique ligament) during the axial loading with the rest of the metacarpal moving in the opposite direction and the main fracture line occurring along this point of weakness.[4] Due to this fracture, the first metacarpal shaft subluxes dorsally, proximally, and radially due to the pull of the abductor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis brevis, and the adductor pollicus brevis, which remain attached to the fracture fragment.
What is the most common fracture of the thumb?
The Bennett fracture is the most common fracture involving the base of the thumb. This fracture refers to an intraarticular fracture that separates the palmar ulnar aspect of the first metacarpal base from the remaining first metacarpal. The injury is typically caused by axial loading on a partially flexed metacarpal and may be associated ...
Which fracture is a comminuted fracture at the base of the first metacarpal with a maintained vol?
Rolando fracture which is a comminuted fracture at the base of the first metacarpal with a maintained volar carpal ligament, preventing displacement of the volar fragment.
What is the surgical treatment for fractures?
The surgical treatment is varied for these fractures. It may consist of closed reduction with percutaneous pinning or open reduction with either pins or inter-fragment pinning. If there is a good alignment of the fracture fragments at postsurgical fixation, clinical outcomes are generally good.
What percentage of thumb fractures are tubular?
Total fractures that involve the thumb have been found to occur most commonly in children and the elderly. In children between ages of infant to 16 years, 22% of all tubular bone fractures involved the first ray; whereas in patients older than 65 years, 20% of hand fractures occurred in the thumb.
How to tell if you have Bennett's fracture?
Bruising and numbness are also common. A break and dislocation can be diagnosed after a doctor examines your hand with an X-ray. Your doctor can also use a computed tomography (CT) scan for a more detailed read on the fracture.
What is the procedure for a fractured bone?
The diagnosis will determine severity of the injury and the type of treatment needed. If a fracture didn’t cause too severe of a displacement between the joints, a closed reduction may be recommended by your doctor. The procedure doesn’t require surgery and involves bones being reset back into place from the outside. For a more severe break to heal, an open reduction may be needed, which requires surgery to realign the bones using pins and screws.
Why do boxers break their thumbs?
Athletes, such as boxers, football or rugby players, and martial artists, are more prone to Bennett’s fracture due to how often they encounter direct contact to a bent thumb. While such sports often cause the break, falls and accidents can also lead to a Bennet’s fracture.
What is Bennett fracture?
A Bennett fracture is a fracture of the base of the thumb resulting from forced abduction of the first metacarpal. It is defined as an intra-articular two-part fracture of the base of the first metacarpal bone. On this page:
What is the term for a fracture of the 1st metacarpal?
When an intra-articular fracture of the 1 st metacarpal is comminuted, producing at least three parts, it is referred to as a Rolando fracture which has a worse prognosis.
Can a fracture cause pain?
Untreated or malreduced fractures can lead to post-traumatic osteoarthritis, which can cause significant pain and functional decline.
What is Bennett fracture?
A Bennett Fracture is an oblique, intra-articular fracture at the volar-ulnar base of the thumb metacarpal. In simpler words, a fracture-subluxation of the first carpometacarpal joint (CMCJ).
What is the treatment for Bennett fracture?
Surgical treatment is varied for the treatment of Bennett fractures but has typically included closed reduction with percutaneous pinning or open reduction with either pins or interfragmentary fixation. Oblique traction pinning and external fixation have also been described. All methods of fixation have been shown to be effective in case reviews and series
What is a fragment of a metacarpal base?
The fragment is of variable size, is pyramidal in shape, and consists of the volar-ulnar aspect of the metacarpal base. Variations do exist and this is described in the table classification by Gedda3
What is Bennett reduction?
The reduction of a Bennett Fracture has been described in various different ways. The “screwhome-torque” reduction technique, described by Edmunds , is generally accepted as a reasonable technique 4. This involves palmar abduction of the thumb and pronation of the metacarpal base. Thumb extension (hitchhiker position) has been shown to cause fracture displacement and should be avoided 4.
What ligament is used to hold a fractured fragment in its anatomical position?
The anterior oblique (beak) ligament acts as a stationary force on the volar-dorsal fragment. This ligament runs from the fractured fragment to the trapezium and holds the fragment in its anatomical position 1.
Which direction does the metacarpal subluxe?
As a result of the fracture, the metacarpal shaft subluxes in a dorsal, proximal, and radial direction due to the pulling force of the abductor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis brevis, and the adductor pollicis longus 2. The flexor tendon and pulley system has a limited role in this injury.
Who created the Bennett fragment?
A Bennett Fracture is best understood by this “ One, Two, Three ” Mnemonic, created by ThePlasticsFella.
What is Bennett fracture?
Definition/Description. A Bennett fracture is a fracture of the base of the thumb resulting from forced abduction of the first metacarpal. It is defined as an intra-articular two-part fracture of the base of the first metacarpal bone. Despite a relatively simple appearance on radiographs, Bennett fractures are considered unstable.
What is the most common mechanism of injury for a Bennett fracture?
The most common mechanism of injury is an axial force (compression) applied to the thumb whilst in flexion.
What is the fracture of the first metacarpal?
The base of the first metacarpal is fractured with an intraarticular extension due to the palmar ulnar fragment of the first metacarpal held in place by its ligamentous attachment to the trapezium (anterior oblique ligament) during the axial loading with the rest of the metacarpal moving in the opposite direction and the main fracture line occurring along with this point of weakness.
What injuries can be found in the first metacarpal?
Other common injuries involving the first metacarpal include Rolando fractures, extra-articular fractures and gamekeepers thumb. The first differentiation clue can be found during the inspection/palpation of the location of the injury.
Which metacarpal subluxes dorsally, proximally, and radially?
Due to this fracture, the first metacarpal shaft subluxes dorsally, proximally, and radially due to the pull of the abductor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis brevis, and the adductor pollicus brevis, which remain attached to the fracture fragment.
How to treat a fractured hand?
Generally, hand fractures are treated by immobilization with a cast or splint regardless of whether surgical or conservative treatment was required. Physical therapists and / or occupational therapists are usually heavily involved in creating and adapting these in consultation with the treating team or surgeon.
How long does a thumb spica cast last?
Non-operative treatment in a thumb spica cast for 3-4 weeks can be considered in stable, non-displaced fractures.
What causes a Bennett fracture?
The Bennett fracture is an oblique intraarticular metacarpal fracture dislocation, caused by an axial force directed against the partially flexed metacarpal. This type of compression along the metacarpal bone is often sustained when a person punches a hard object, such as the skull or tibia of an opponent, or a wall. It can also occur as a result of a fall onto the thumb. This is a common injury sustained from bike falls, as the thumb is generally extended while around the handle bars. It is also a common injury in car crashes, especially into fixed objects, from the driver holding the steering wheel during impact. The hand moves forward, while the steering wheel rim hyperextends the thumb. Some authors have recently made an assertion against popular belief that the APL tendon is not a deforming force on the Bennett fracture.
Who is the Bennett fracture named after?
The Bennett fracture is named after Edward Hallaran Bennett, Professor of Surgery (1837–1907) at Trinity College of the University of Dublin, who described it in 1882.
How to tell if you have Bennett fracture?
Symptoms of Bennett fracture are instability of the CMC joint of the thumb, accompanied by pain and weakness of the pinch grasp. Characteristic signs include pain, swelling, and ecchymosis around the base of the thumb and thenar eminence, and especially over the CMC joint of the thumb. Physical examination demonstrates instability of the CMC joint of the thumb. The patient will often manifest a weakened ability to grasp objects or perform such tasks as tying shoes and tearing a piece of paper. Other complaints include intense pain experienced upon catching the thumb on an object, such as when reaching into a pants pocket.
Why do Bennett fractures require intervention?
Because of the aforementioned biomechanical features, Bennett fractures nearly always require some form of intervention to ensure healing in the correct anatomical position and restoration of proper function of the thumb CMC joint.
What happens if you don't treat Bennett fracture?
With this in mind, failure to properly recognize and treat the Bennett fracture will not only result in an unstable, painful, arthritic CMC joint with diminished range of motion: it will also result in a hand with greatly diminished overall function.
Which bone possesses the majority of the articular surface of the first CMC joint?
The distal fragment of the first metacarpal bone possesses the majority of the articular surface of the first CMC joint. Unlike the proximal fracture fragment, strong ligaments and muscle tendons of the hand tend to pull this fragment out of its correct anatomical position. Specifically:
Where is the proximal metacarpal fragment attached?
In the case of the Bennett fracture, the proximal metacarpal fragment remains attached to the anterior oblique ligament, which in turn is attached to the tubercle of the trapezium bone of the CMC joint. This ligamentous attachment ensures that the proximal fragment remains in its correct anatomical position.