SUMMARY:
- All free morphemes are words.
- All free morphemes are roots.
- A bound morpheme is an affix.
Full Answer
Which of the following best describes a bound morpheme?
Bound morphemes have no linguistic meaning unless they are connected to a root or base word, or in some cases, another bound morpheme. Prefixes and suffixes are two types of bound morphemes. Depending on how they modify a root word, bound morphemes can be grouped into two categories: inflectional morphemes and derivational morphemes.
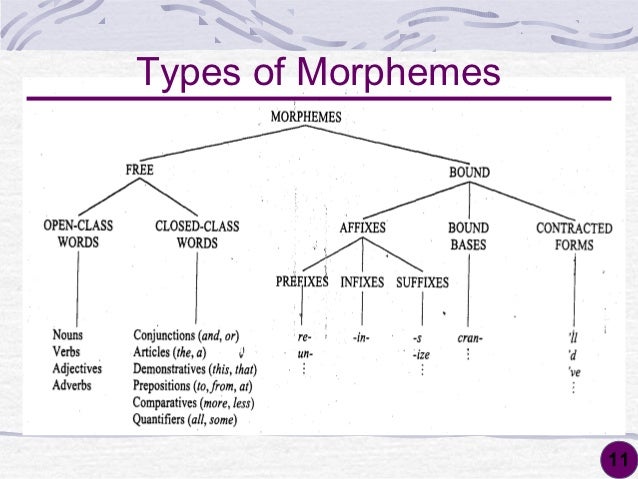
What are the 3 types of morphemes?
What are the 3 types of morphemes?
- free vs. bound.
- root vs. affixation.
- lexical vs. grammatical.
What is the antonym of bound?
Synonyms for BOUND: boundary, cap, ceiling, confines, end, extent, limit, limitation; Antonyms for BOUND: faltering, hesitant, indecisive, irresolute, undetermined ...
What is the plural of bound?
The plural form of bound is bounds. Find more words! Another word for Opposite of Meaning of Rhymes with Sentences with Find word forms Translate from English Translate to English Words With Friends Scrabble Crossword / Codeword Words starting with Words ending with Words containing exactly Words containing letters Pronounce Find conjugations ...

What is bound morpheme and examples?
There are two types of morphemes-free morphemes and bound morphemes. "Free morphemes" can stand alone with a specific meaning, for example, eat, date, weak. "Bound morphemes" cannot stand alone with meaning. Morphemes are comprised of two separate classes called (a) bases (or roots) and (b) affixes.
Which is a bound morpheme?
A bound morpheme is a word element that cannot stand alone as a word, including both prefixes and suffixes. Free morphemes, by contrast, can stand alone as a word and cannot be broken down further into other word elements.
What is an example of a bound?
The definition of bound is destined to happen or tied or secured physically or emotionally. An example of bound is an accident occurring if someone continuously plays dangerously with sharp knives. An example of bound is hands tied together with rope. A leap; a jump.
What are the 3 types of morphemes?
There are three ways of classifying morphemes:free vs. bound.root vs. affixation.lexical vs. grammatical.
What is an example of a morpheme?
In English grammar and morphology, a morpheme is a meaningful linguistic unit consisting of a word such as dog, or a word element, such as the -s at the end of dogs, that can't be divided into smaller meaningful parts. Morphemes are the smallest units of meaning in a language.
What are the types of bound morphemes?
Bound grammatical morphemes can be further divided into two types: inflectional morphemes (e.g., -s, -est, -ing) and derivational morphemes (e.g., - ful, -like, -ly, un-, dis-).
What is the function of bound morpheme?
Bound Morphemes are used to change the function of some words and to identify the function of some others.
How do you find morphemes in a word?
We can identify a morpheme by three criteria: It is a word or part of a word that has meaning. It cannot be divided into smaller meaningful parts without violation of its meaning or without meaningless remainders. It recurs in differing word environments with a relatively stable meaning.
Is able a bound morpheme?
In the word unable, we find one bound morpheme (un-) and one free morpheme (able).
What are the 4 types of morphemes?
Bound, free, inflectional and derivational are types of morphemes.
What are the 5 morphemes?
Morphemes include;prefixes such as un, re, dis.suffixes such as s/es, ed, er, ing.base words such as help, form.roots such as rupt, port, ject.
What are characteristics of bound morpheme?
A bound morpheme is that morpheme that cannot stand or occur as an independent word. It has to be attached to a free morpheme or word to have a clear meaning. Examples of bound morphemes are –ment, -en, -ing, -ed, -ness, –ful, mis-, -anti, -less, etc. in the following free morphemes or words.
What are free and bound morphemes give examples?
Free morphemes are considered to be base words in linguistics. Base words that can stand alone (such as “book”) are known as free bases, while bound bases (including Latin roots like “ject”) are not individual words in English. Most free morphemes can be modified by affixes to form complex words.
What is a bound root?
Definition: A bound root is a root which cannot occur as a separate word apart from any other morpheme.
Is able a bound morpheme?
In the word unable, we find one bound morpheme (un-) and one free morpheme (able).
Is Ness a bound morpheme?
Derivational bound morphemes For example, in the word happiness, the addition of the bound morpheme -ness to the root happy changes the word from an adjective (happy) to a noun (happiness). In the word unkind, un- functions as a derivational morpheme since it inverts the meaning of the root morpheme (word) kind.
What is a derivational morpheme?
A morpheme is derivational when it changes the semantic meaning of a word. Most derivational morphemes have roots in Greek or Latin. Unlike inflectional morphemes, derivational morphemes can change a word’s part of speech.
How many inflectional morphemes are there?
This type of morpheme alters the grammatical function of a word, whether it be the verb tense, number, mood, or another language inflection. The eight inflectional morphemes are organized by which part of speech they modify:
What is bound morpheme?
Bound and Free Morpheme Examples. Morphemes are the smallest units in a language that have meaning. They can be classified as free morphemes, which can stand alone as words, or bound morphemes, which must be combined with another morpheme to form a complete word. Bound morphemes typically appear as affixes in the English language.
What is the first step in mastering a language?
Understanding the morphology of a language is the first step in mastering it. Learn more about how prefixes and suffixes can modify base words, or utilize the practice worksheet on morpheme identification provided here.
What is function word?
Function words serve as a grammatical connection between content words. They are not typically combined with affixes that change their meaning.
What are the two types of free morphemes?
There are two kinds of free morphemes based on what they do in a sentence: content words and function words.
What are some examples of content words?
Their parts of speech include nouns, verbs, and adjectives. Here are some examples of content words from everyday speech. Nouns: girl, hat, house, fire. Verbs: walk, sleep, say, eat. Adjectives: quick, nice, fun, big. These words are the most important parts of a sentence. The meaning of content words might change when combined with other ...
What is bound morpheme?
In morphology, a bound morpheme is a morpheme that only appears as part of a larger word; a free or unbound morpheme is one that can stand alone. A bound morpheme is also known as a bound form, and similarly a free morpheme is a free form. Affixes are always bound in English, although languages such as Arabic have forms which sometimes affix ...
What is an affix in English?
English language affixes are almost exclusively prefixes or suffixes. E.g., pre- in "prefix" and -ment in "shipment". Affixes may be inflectional, indicating how a certain word relates to other words in a larger phrase, or derivational, changing either the part of speech or the actual meaning of a word.
What is a cranberry morpheme?
Cranberry morphemes are a special form of bound morpheme that does not have an independent meaning or grammatical function but serves only to distinguish one word from another, like in cranberry, in which the free morpheme berry is preceded by the bound morpheme cran -, which does not have an independent meaning.
What is bound morpheme?
Bound morphemes are the counterparts of free morphemes. In simple, a morpheme is the smallest unit in language to carry meaning. This includes things like prefixes, suffixes, -s to mark plurals, and in other languages can include tense markers within a word.
What does an affix mean?
Affixes may be inflectional, indicating how a certain word relates to other words in a larger phrase, or derivational, changing either the part of speech or the actual meaning of a word : -ing, -ed, -s
What is the meaning of vowels in Semitic?
Semitic languages have what is called “root-and-pattern” or “templatic” morphology, in which certain consonants encode the lexical meaning, while vowels indicate inflectional information. For example, the consonants /ktb/ in Arabic indicate all things to do with books — reading, writing, books, etc.. A selection of examples from K-T-B - Wikipedia:
Is "clitic" an affix?
A final example would be clitics. Like how “le” shortens to “l’” before vowel-initial words in French (e.g. “L’apine agile”). This particular case does not really feel like an affix because the clitic is referential; it is not exactly an inflectional morpheme, and not really an inflectional one either. But I suppose if you were willing to call clitics affixes, you could maintain that all bound morphemes are affixes.
Why is it important to have good English writing skills?
First off, the fact that you want to improve is terrific! English writing skills are vitally important if you’re thinking of going on to further education in an English-speaking c(Continue reading)
Is "unkempt" a bound morpheme?
Bound morphemes exist in English for a couple of historical reasons. In words like “unkempt,” the situation is that at one time in the past, people used to use “kempt” as a word (i.e., it was a free morpheme). However, over time, this changed and we no longer use this morpheme as an independent word. Another example of this type of bound morpheme is “uncouth.”
What is bound morpheme?
BOUND MORPHEME: "A bound morpheme is part of a larger, longer word without which it lacks meaning ."
What is a morpheme that cannot stand alone?
n. in linguistics, refers to a morpheme that cannot stand alone but rather needs to be attached to a root word in order to have meaning. The most common examples include ed, er, and ing. For example, miss becomes missed. Compare free morpheme.
