A carotid bruit is an abnormal sound that can be heard when a stethoscope is placed on either side of the neck, on top of the carotid arteries, which carry blood from the heart to the brain.
What is a bruit in cardiology?
An audible swishing sound or murmur heard by auscultation over an artery, which indicates increased turbulence often due to partial obstruction by atherosclerosis. When heard over the carotid arteries, bruits predict future cerebrovascular accidents. Segen's Medical Dictionary. © 2012 Farlex, Inc. All rights reserved.
Is carotid bruit caused by narrowing of the artery?
Luminal narrowing of the carotid artery, however, is not the only cause of carotid bruit. Auscultatory sounds from cardiac valvular murmurs that radiate to the neck, cervical venous hums, and intracranial arteriovenous malformations can produce vascular sounds similar to the carotid bruit.
Is a bruit over the heart a bad thing?
A murmur is abnormal noises made by heart valves. So a bruit over the heart would be a... bad thing, since other than the AV fistula, it's not a sound you want to hear in a big vessel. Either something's really blocked the vessel, or there's a pseudoaneurysm going on.
What is a bruit in auscultation?
An audible swishing sound or murmur heard by auscultation over an artery, which indicates increased turbulence often due to partial obstruction by atherosclerosis. When heard over the carotid arteries, bruits predict future cerebrovascular accidents.

What causes cardiac bruits?
Carotid bruits generally result from turbulent, non-laminar flow through a stenotic lesion, which causes arterial wall vibrations distal to the stenosis. The vibrations are transmitted to the body surface, where they can be detected with a stethoscope.
What does it mean if you have a bruit?
A bruit is the sound of blood flowing through a narrowed portion of an artery. The sound means that the blood flow may be partially blocked; artery blockage is most often due to atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries).
What is a bruit in cardiology?
Definition. A bruit is an audible vascular sound associated with turbulent blood flow. Although usually heard with the stethoscope, such sounds may occasionally also be palpated as a thrill.
What does a bruit in the carotid artery mean?
A carotid bruit is a vascular sound usually heard with a stethoscope over the carotid artery because of turbulent, non-laminar blood flow through a stenotic area. A carotid bruit may point to an underlying arterial occlusive pathology that can lead to stroke.
What's the most common cause of a carotid bruit?
Atherosclerosis is the most common cause of a carotid bruit. Atherosclerosis is a medical term that refers to the buildup of plaque (a fatty substance) in arteries throughout your body. This plaque narrows the lumen (opening) of your arteries, limiting blood flow.
Can a carotid bruit go away?
Sometimes the bruit goes away on its own, but in cases when it doesn't, medication can help keep the blood from clotting. If the carotid artery is more than 50 percent blocked, surgery to remove the fatty buildup – called an endarterectomy – might be necessary.
How do you examine for a bruit?
If bruits are present, you'll typically hear them over the aorta, renal arteries, iliac arteries, and femoral arteries. The bell of the stethoscope is best for picking up bruits. The diaphragm is more attuned to relatively high-pitched sounds; the bell is more sensitive to low-pitched sounds like bruits.
How do you check for bruits?
When assessing for carotid bruits, ask the patient to hold their breath for no more than 10 seconds while auscultating to better distinguish bruits from sounds transmitted from the trachea. Other areas to assess for bruits includes the abdominal aorta, as well as the renal and iliac arteries.
Where is bruit normal?
Like any murmur generated outside the four heart chambers, abdominal bruits may extend beyond the confines of the first and second heart sounds from systole into diastole (i.e., they may be “continuous”; see Chapter 39). Most bruits are detected in the epigastrium or upper abdominal quadrants.
What are the warning signs of a blocked carotid artery?
Carotid Artery Blockage SymptomsBlurred vision or vision loss.Confusion.Memory loss.Numbness or weakness in part of your body or one side of your body.Problems with thinking, reasoning, memory and speech.
How can I naturally unblock my carotid artery?
Eat a heart-healthy dietAdd more good fats to your diet. Good fats are also called unsaturated fats. ... Cut sources of saturated fat, such as fatty meat and dairy. Choose lean cuts of meat, and try eating more plant-based meals.Eliminate artificial sources of trans fats. ... Increase your fiber intake. ... Cut back on sugar.
Does aspirin reduce plaque in arteries?
Now, a team led by a University of Florida Health researcher has found that aspirin may provide little or no benefit for certain patients who have plaque buildup in their arteries. Aspirin is effective in treating strokes and heart attacks by reducing blood clots.
Is a bruit a normal finding?
Patients without hypertension should not have auscultation for asymptomatic renal artery bruits because bruits frequently are a normal finding. The search for renal artery stenosis should be confined to certain patient populations (see below).
What does abdominal bruit indicate?
An abdominal bruit is a swishing, or washing machine like sound heard when the diaphragm of stethoscope is placed over the spleen, renal arteries, or abdominal aorta. It is often indicative of partial occlusion of a vessel, as can be observed in renal artery stenosis or atherosclerosis of the abdominal vasculature.
Where is bruit normal?
Like any murmur generated outside the four heart chambers, abdominal bruits may extend beyond the confines of the first and second heart sounds from systole into diastole (i.e., they may be “continuous”; see Chapter 39). Most bruits are detected in the epigastrium or upper abdominal quadrants.
What's the difference between a bruit and a murmur?
When normal laminar blood flow within the heart is disrupted, an audible sound is created by turbulent blood flow. Outside of the heart, audible turbulence is referred to as a bruit, whereas inside the heart it is called a murmur.
What is a bruit in a stethoscope?
Bruit: A bruit is a turbulent flow sound heard with the stethoscope. Turbulent flow happens across a valve in your heart. Either a valve does not close tightly during systolic ejection of blood. Or a valve does not open completely during ejection of blood. During systole the aortic and pulmonic valves should open wide and the mitral and tricuspid valves should close, to prevent "backflow ".
What is cardiac output?
Cardiac output: In strict physiologic terms, cardiac output is determined by something called stroke volume and heart rate. Heart rate is self-explanatory. Stroke volume is the amount of blood that the heart pumps out with each beat. This in turn is dependent on blood pressure, total blood volume, and how strong the heart contracts.
Is a cardiac murmur normal?
Misunderstanding: A cardiac murmur is a noise that can be detected when the examiner listens with his/her ears - usually through a stethoscope. It's caused by turbulence of blood flow through a valve or a chamber. When a murmur is detected outside the heart, it's called a "bruit". Thus, there is no such thing as a "cardiac bruit". Some bruits are quite normal - for instance, they're often found in pregnancy.
What is a Carotid Bruit?: The Bottom Line?
A carotid bruit requires further investigation – usually an ultrasound study. In some cases, it can indicate a higher risk of stroke or heart disease, but in young people it may be a normal finding.
What Happens if Your Doctor Hears a Carotid Artery Bruit Sound During an Exam?
One test that’s used is an ultrasound study of the carotid arteries in the neck. This is a non-invasive, painless procedure that uses sound waves to look for obstruction or narrowing in the arteries.
What is the procedure to narrow the carotid arteries?
If an ultrasound shows obstruction or narrowing in one or both of the carotid arteries, doctors sometimes recommend carotid angioplasty or a surgery called carotid endarterectomy to reduce the risk of stroke. Whether or not these procedures are recommended will depend on how narrow the carotid arteries are and whether or not the narrowing is causing symptoms. Some people with narrowing of the carotid arteries will have stroke-like symptoms that come and go – and these people need treatment because their risk for stroke will be higher.
Can a carotid artery be a bruit?
If an ultrasound test shows no obstruction or narrowing of the arteries, a carotid artery bruit may be called innocent, since it doesn’t increase the risk for stroke. Innocent carotid bruits are more common in children and young people who have a faster heart rate and greater flow of blood through the carotid arteries. Innocent carotid bruits require no treatment.
Is carotid artery bruit a sign of heart disease?
Recent studies show that a carotid artery bruit on physical exam may be a marker for an increased risk of heart disease. In fact, an analysis of a variety of studies showed that carotid artery bruits are associated with a higher risk for heart attack. This makes sense. If the carotid arteries are narrowed with plaque, there’s a good chance that other vessels such as the coronary arteries that carry blood to the heart are too.
Why is carotid bruit important?
Carotid bruits can be a significant clue to an underlying carotid artery disease. Clear lines of communication between the patient and the treatment team are important in expediting referrals and subsequent additional testing to exclude carotid artery disease and promptly institute measures to mitigate the chance of stroke.
Why do we hear carotid bruit?
A carotid bruit is a vascular sound usually heard with a stethoscope over the carotid artery because of turbulent, non-laminar blood flow through a stenotic area. A carotid bruit may point to an underlying arterial occlusive pathology that can lead to stroke. Stroke is a significant cause of morbidity, mortality, and loss of physical mobility.
What is the sound of auscultation?
The auscultated sound is usually the result of turbulent, non-laminar blood flow through a stenotic area. The turbulent flow creates vibrations in the arterial wall that then transmits to the body surface, where stethoscopic auscultation is possible.
What causes bruit in a patient with a carotid artery dissection?
Disruption of the blood vessels can cause bruit and have presented in patients having a carotid artery dissection. [10]
How many children have carotid bruit?
A carotid bruit can also present in 20% of healthy children less than 15 years old . Nearly 22% of patients diagnosed with cervical fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) are found to have carotid bruits, although patients are seldom found to be symptomatic. [14] Pathophysiology.
What causes carotid bruit?
A case of bovine-type aortic arch and compression of the kissing carotid arteries by a retrosternal goiter is also a rare cause of a carotid bruit. [7] . Vascular occlusion from an extrinsic compression such as carotid body tumors and carotid paraganglioma have also been reported to cause carotid bruit.
When is a bruit audible?
When the diameter reduces to 70%-80%, a bruit can is audible during systole and early diastole. As the occlusion becomes very severe, blood flow turbulence becomes insufficient to cause vibratory sounds, and a bruit may disappear. [1]
What is bruit in the neck?
Bruits and Hums of the Head and Neck - Clinical Methods - NCBI Bookshelf. A bruit is an audible vascular sound associated with turbulent blood flow. Although usually heard with the stethoscope, such sounds may occasionally also be palpated as a thrill. In the head and neck, these auscultatory sounds may originate in the heart ...
Why is bruit important?
Head and neck bruits loom especially important today because physicians encounter arterial occlusive disease more frequently as a greater proportion of our population lives longer. A bruit is an audible vascular sound associated with turbulent blood flow. Although usually heard with the stethoscope, such sounds may occasionally also be palpated as ...
Why is it important to trace proximally the audibility of an arterial sound?
Because a bruit may be auscultated directly over a stenosis, or distally in the direction of the blood jet producing the vibrations, it is important to trace proximally the audibility of an arterial sound to determine the exact anatomic site of the flow disturbance.
What is compression of arterial side branches?
In the second category (side branch factors), compression of arterial side branches should augment a bruit in the main artery and diminish a side branch bruit, whereas augmentation of flow through a side branch would have the opposite effect. This concept is especially applicable for evaluation of carotid artery bruits.
What is supraclavicular bruit?
Supraclavicular bruitsduring systole are a frequent finding in normal children and in adults with subclavian or vertebral artery stenosis. Supraclavicular auscultation is usually initiated to evaluate vertebral artery occlusive symptoms, arm claudication, or "subclavian steal" in the adult with atherosclerosis.
What is the lumen diameter of a soft systolic bruit?
A soft early systolic bruit is noted with a lumen diameter of 50%. As the obstruction increases to 60%, the bruit becomes high pitched, more intense, and holosystolic. At 70 to 80% diameter reduction, a pressure gradient may remain even during diastole, and the bruit is auscultated in both systole and early diastole.
Can arterial bruit be heard?
An arterial bruit usually implies stenosis at or proximal to the site of auscultation. Very severe obstruction, however, may not manifest a bruit; conversely, bruits may be heard over unoccluded normal arteries in certain high-flow circumstances. Because a bruit may be auscultated directly over a stenosis, or distally in the direction of the blood jet producing the vibrations, it is important to trace proximally the audibility of an arterial sound to determine the exact anatomic site of the flow disturbance.
What is a shunt in the heart?
Cardiac shunts. Cardiac shunts occur when there's an abnormal blood flow between the heart chambers or blood vessels , which may lead to a heart murmur.
What is the sound of a heart murmur?
Heart murmurs are sounds — such as whooshing or swishing — made by turbulent blood in or near your heart. Your doctor can hear these sounds with a stethoscope. A normal heartbeat makes two sounds like "lubb-dupp" (sometimes described as "lub-DUP") when your heart valves are closing.
Why do older people have abnormal heart murmurs?
In older children and adults, causes of abnormal heart murmurs include infections and conditions that damage the structures of the heart. For example:
Why do children murmur?
In children, abnormal murmurs are usually caused by structural problems of the heart (congenital heart defects). Common congenital defects that cause heart murmurs include: Holes in the heart. Known as septal defects, holes in the heart may or may not be serious, depending on the size of the hole and its location. Cardiac shunts.
How do you know if you have a heart murmur?
An abnormal heart murmur may cause the following signs and symptoms, depending on the cause of the murmur: Skin that appears blue, especially on your fingertips and lips. Swelling or sudden weight gain. Shortness of breath.
Can a heart murmur go away?
While there's not much you can do to prevent a heart murmur, it is reassuring to know that heart murmurs are not a disease and are often harmless. For children, many murmurs go away on their own as children grow. For adults, murmurs may disappear as the underlying condition causing them improves.
Is a heart murmur a sign of heart disease?
An innocent heart murmur is not a sign of heart disease and doesn't need treatment. Abnormal heart murmurs require follow-up testing to determine the cause. Treatment is directed at the cause of your abnormal heart murmur.
What is bruit in medical terms?
bruit. A sound heard on auscultation of the heart, lungs, large arteries or veins, or any large cavity (e.g. the orbit). The auscultation is carried out with a stethoscope. Example: An occlusive disease of the carotid artery caused by atherosclerosis leads to a reduction in blood flow through the carotid arteries ...
What is the audible sound of a carotid artery?
Cardiology An audible swishing sound or murmur heard over an arterial 'thrill' caused by atherosclerosis; when auscultated over the carotid arteries, bruits predict future CVAs; it is unclear whether surgical correction improves the ultimate outcomes, as the ischemic event often occurs at a distance from the identified 'danger zone'; artery or vascular channel; indicates ↑ turbulence often caused by a partial obstruction. See Carotid endarterectomy.
What is an intermittent sound?
A harsh or musical intermittent auscultatory sound, especially an abnormal one.
What is the sound of the blood current in the placenta called?
placental bruita soft, blowing auscultatory sound supposed to be produced by the blood current in the placenta. Called also placental souffle.
What orbit disappeared on carotid compression?
Physical examination was unremarkable except for a bruitin the left orbit which disappeared on carotid compression.
What does "murmur" mean?
An abnormal swishing, blowing, or murmuring sound.
What is the difference between a murmur and a bruit?
A bruit is generally a sound made by a non-cardiac vessel, while a murmur is made by abnormal flow through a cardiac valve (either accelerated by a narrowing, or backflowing through an incompetent valve). Hope that helps, tell me if it was too basic. Specializes in ICU, telemetry, LTAC. Has 5 years experience.
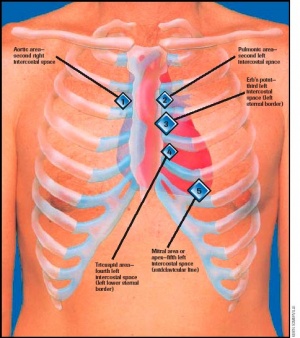
Where can you hear a bruit?
A bruit is not usually heard over the part of the chest where you hear heart sounds. It can be heard over the carotids, femoral arteries, A-V fistula sites , etc. A bruit sounds like a washing machine to me. (Ok, a really small washing machine...) A murmur is abnormal noises made by heart valves. So a bruit over the heart would be a... bad thing, since other than the AV fistula, it's not a sound you want to hear in a big vessel. Either something's really blocked the vessel, or there's a pseudoaneurysm going on. Both of which could happen to the aorta near the heart, but golly. I think if I heard that I'd have several other people in there listening just to make sure.
What is a murmur in a heart?
A murmur is abnormal noises made by heart valves. So a bruit over the heart would be a... bad thing, since other than the AV fistula, it's not a sound you want to hear in a big vessel. Either something's really blocked the vessel, or there's a pseudoaneurysm going on.
Does an aortic aneurysm cause a loud noise?
Again, as to your initial question, if it is of cardiac origin it's a murmur, no matter how it sounds. An aortic aneurysm doesn't usually cause a loud bruit, as there is generally aortic widening at the weak site, rather than narrowing which would cause the rushing sound caused by acceleration of the blood. 0 Likes.
Is murmur loud?
Sorry. The loudness depends on the severity of the underlying pathological condition. That is like asking "how long is a piece of string?" - there is no answer to that. I have definitely heard murmurs which were "whooshing", loud noises and not "clicks".
