How do you treat leukopenia?
Leukopenia treatment depends on the underlying cause of the condition. Treatment options can include: Intravenous antibiotics if needed, if a severe infection is found (Examples include cephalosporins, anti-pseudomonal penicillins, carbapenems, aminoglycosides, aztreonam and fluoroquinolone.)
How can I treat leukopenia?
Treating leukopenia
- Medications. Medications can be used to stimulate your body to make more blood cells. ...
- Stopping treatments that cause leukopenia. Sometimes you may need to stop a treatment like chemotherapy to give your body time to make more blood cells.
- Growth factors. ...
- Diet. ...
- At home. ...
What medications cause leukopenia?
Medications that can cause leukopenia include: bupropion (Wellbutrin) clozapine (Clozaril) cyclosporine (Sandimmune) interferons. lamotrigine (Lamictal) minocycline (Minocin) mycophenolate mofetil (CellCept) penicillin.
Is possible for clonazepam to provoke leukopenia?
Leukopenia is found among people who take Clonazepam, especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month. The phase IV clinical study is created by eHealthMe based on reports of 100,381 people who have side effects when taking Clonazepam from the FDA, and is updated regularly.
What is leukopenia and how is it treated?
Leukopenia is when the levels of WBCs in your blood are lower than average. People with leukopenia are at an increased risk for infections. In fact, you may not know that you have leukopenia until you develop symptoms of an infection like fever or chills.
What is the most common cause of leukopenia?
A low white blood cell count usually is caused by: Viral infections that temporarily disrupt the work of bone marrow. Certain disorders present at birth (congenital) that involve diminished bone marrow function. Cancer or other diseases that damage bone marrow.
Can leukopenia be normal?
Mild or chronic reductions in white blood cells can be benign and in the absence of alarming symptoms may not require further evaluation. However, new or severe leukopenia, especially neutropenia, especially when accompanied by any of the signs or symptoms described below, should prompt a thorough investigation.
How can I increase my leukopenia?
That being said, there are ways to reduce your risk for some health conditions that can trigger leukopenia and to support your immune system while you recover.Immune-Boosting Diet. ... Good Hygiene To Prevent Infections. ... Supplements. ... Other Lifestyle Habits to Boost Immunity and Manage Symptoms.
What kind of disease is leukopenia?
Leukopenia is a condition where the body doesn't have enough disease-fighting leukocytes in the blood. It is associated with a low white blood cell count. White blood cells are produced by the bone marrow.
What drugs cause leukopenia?
Among the drugs that can cause leukopenia are antithyroid drugs, chemotherapy agents, antimetabolites, phenothiazines, antihypertensives, antihistamines, monoclonal antibody drugs, antivirals, anticonvulsants, antipsychotics, anti-inflammatories, antibiotics, and alkylating agents.
When does leukopenia occur?
A 2019 article notes that leukopenia typically occurs due to a low neutrophil count. When a person has low neutrophil levels, healthcare professionals refer to it as neutropenia. When leukopenia involves low lymphocyte levels, it is called lymphocytopenia.
What is mild leucopenia?
A low white blood cell count (leukopenia) is a decrease in disease-fighting cells (leukocytes) in your blood. Leukopenia is almost always related to a decrease in a certain type of white blood cell (neutrophil). The definition of low white blood cell count varies from one medical practice to another.
What is a dangerously low WBC?
A blood test that shows a WBC count of less than 4,000 per microliter (some labs say less than 4,500) could mean your body may not be able to fight infection the way it should.
What foods help leukopenia?
Some sources of quality protein are fish, eggs, poultry, beef, milk, Greek yogurt and beans. If your diet is poor, or you're having trouble eating, you can take a multivitamin or supplement with vitamin B12 and folate. The body uses vitamin B12 and folate to make WBCs.
What foods to avoid if you have low white blood cells?
Avoid raw milk, any yogurt or cheeses made with raw milk, and unpasteurized juice. Be sure to wash all fresh fruits and vegetables well. You may want to switch from fresh fruits and vegetables to cooked, canned, or frozen fruits and vegetables during treatment.
What vitamins increase white blood cells?
Vitamin B6 is responsible for producing white blood cells and T cells, which regulate immune responses. Vitamin B6 also helps the body make the protein interleukin-2 to direct white blood cell activity.
What does leukopenia indicate?
Definition. By Mayo Clinic Staff. A low white blood cell count (leukopenia) is a decrease in disease-fighting cells (leukocytes) in your blood. Leukopenia is almost always related to a decrease in a certain type of white blood cell (neutrophil).
What vitamin deficiency causes low white blood cells?
Some vitamins and minerals like vitamin B12 and folate play a crucial role in WBC formation. Low levels of vitamin B6, copper, and zinc may also play a role in low WBC production. A blood test can identify whether these nutrients are low, as you should not take supplements of these nutrients if your levels are normal.
Is leukopenia a leukemia?
Cancer: Leukemia cells can force out the cells in the bone marrow that make normal blood cells. This can lead to leukopenia.
What cancers cause low WBC?
Low white blood cell count. Some cancer treatments, mainly chemotherapy, may lower your body's white blood cells. Cancers that affect the blood and bone marrow can also lower the count. These types of cancers include leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma.
What are some examples of leukopenia?
Blood cell and bone marrow conditions: These can lead to leukopenia. Examples include aplastic anemia, overactive spleen, and myelodysplastic syndromes. Cancer: Leukemia and other cancers may damage the bone marrow and lead to leukopenia. Infectious diseases: Examples include HIV, AIDS, and tuberculosis.
Which disease is more likely to cause leukopenia?
Infectious diseases: Examples include HIV, AIDS, and tuberculosis. According to a 2015 study, women with tuberculosis are more likely to develop leukopenia than men.
What causes leukopenia in the bone marrow?
Causes. There are several medical conditions that cause leukopenia by interfering with the production of white blood cells in the bone marrow. Other conditions cause leukopenia by destroying white blood cells rather than affecting their production. Leukopenia may also be the result of some treatments and medications.
What is the difference between leukopenia and neutrophils?
However, they refer to slightly different conditions. Leukopenia is an umbrella term that refers to a reduction in any of the white blood cell types. Neutropenia is a type of leukopenia but refers specifically to a decrease in neutrophils, the most common type of white blood cell. A person’s neutrophil count is an important indicator ...
Why are leukocytes important?
Leukocytes are a vital part of the immune system. People who have leukopenia have fewer white blood cells than they should. This makes them more likely to get infections. This article explores the effect leukopenia has on the body, what causes it, and the treatment options available.
What is the condition where a person has a reduced number of white blood cells?
Leukopenia is a condition where a person has a reduced number of white blood cells. This increases their risk of infections. A person’s blood is made up of many different types of blood cells. White blood cells, also known as leukocytes, help to fight off infection. Leukocytes are a vital part of the immune system.
Why do doctors check white blood cells?
A doctor will regularly check a person’s white blood cell count if they have a condition known to cause leukopenia. Getting regular blood tests helps leukopenia to be identified early and treated before it leads to complications. Last medically reviewed on December 13, 2017. Lymphoma.
What is leukopenia in medicine?
Diagnosis. Treatment. Leukopenia is the medical term that is used to describe a low white blood cell (leukocyte) count. Depending on the severity, leukopenia may increase the risk of infections, sometimes to a serious degree. There are many possible causes, including medications, infections, autoimmune conditions, cancer, vitamin deficiencies, ...
What causes leukopenia?
Protein-calorie malnutrition is a common cause of leukopenia resulting from inadequate production of leukocytes.
What causes leukopenia in developed countries?
In developed countries, drug induced leukopenia is most common, and can be caused by different mechanisms depending on whether the drug injures bone marrow or results in autoimmunity that causes the breakdown of the cells. Worldwide, malnutrition (leading to decreased production) is most common.
Why does leukopenia occur?
With sepsis, an overwhelming body-wide bacterial infection, leukopenia may occur as available white blood cells are "used up" fighting the infection.
What is benign neutropenia?
Benign ethnic neutropenia (also called physiologic leukopenia or constitutional neutropenia) is an inherited condition in which a person has a low white blood cell count. These lower white blood cell counts are a very common cause of apparent neutropenia in people of African, Middle Eastern, or West Indian heritage. The hallmark of benign ethnic neutropenia is that even though the white blood cell count is below the normal range, these people do not have an increased risk of infection. 1
Why is it important to have a low white blood cell count?
An isolated low level of some types of white blood cells may also be important in predicting the presence of or severity of a disease. Neutropenia: A low level of neutrophils is often the most concerning of the leukopenia due to the risk of infection.
How to tell if you have leukopenia?
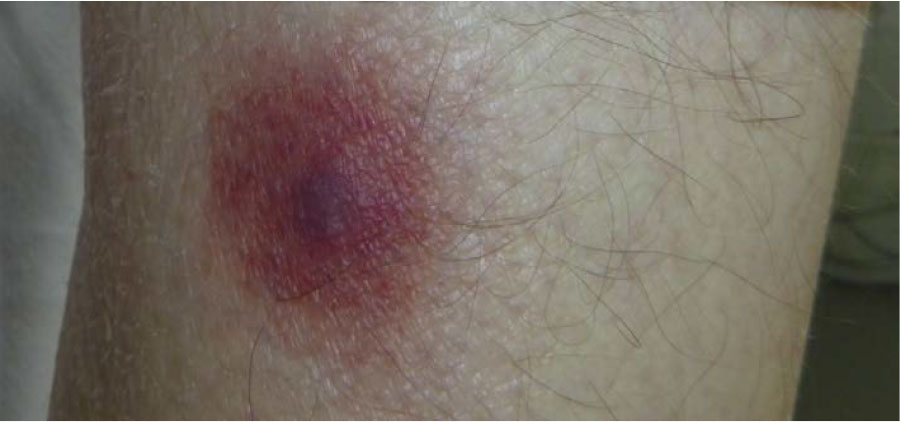
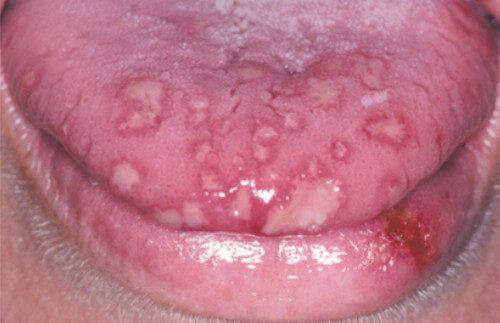
Warning signs for potential leukopenia include frequent infections, infections that won't resolve, a general feeling of being ill, and inflammation or ulcers in or around the mouth. Symptoms of infection may include: Fever, chills, and/or night sweats. Headache or stiff neck. Sore throat.
What is leukopenia?
White blood cells (WBCs) are an important part of the immune system, which is why they are called as "fighter cells". There are five different types of white blood cells (WBCs) in our body. They are neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes. Each type of WBC has a specific role in fighting infections.
What happens when you have leukopenia?
However, most of these parasites are taken care of by our immune system. When you have leukopenia, your body becomes more vulnerable to a number of infections.
Why do people with cancer have low WBC?
1) Cancer. People with cancer tend to have a low WBC count because of their cancer treatment. When chemotherapy drugs are given, the WBC count can significantly go down. Moreover, when there is bone marrow cancer, only a few neutrophils are produced, leading to leukopenia.
What is the most common form of leukopenia?
Neutropenia is the most common form of leukopenia. Both of these terms are interchangeably used. Neutropenia refers to a form of leukopenia, wherein there is a significant decrease in the count of neutrophils. Neutrophils are the primary defenders of the body’s immune system.
What drugs can cause leukopenia?
Drugs such as antihistamines or anti-rejection medications are meant to decrease the immune response and can have similar effects causing leukopenia.
What causes low RBC count?
Such conditions are attributed to an impaired bone marrow function. A low RBC count can cause fatigue, dizziness, pale skin, leg cramps, breathlessness, poor concentration, and a lack of sleep leading to insomnia.
Why is there a false positive for leukopenia?
This false positive is known as a "pseudoleukopenia". happens because white blood cells suddenly migrate to the site of infection.
What is leukopenia in a patient?
What is Leukopenia? Leukopenia is a pathological condition in which there is a decrease in white blood cell count. Talking in figures, in patients with Leukopenia the WBC count falls below 4,000 which is significantly low. There can be numerous causes for this to happen like viral infections or cancer in which bone marrow is involved.
How is Leukopenia Diagnosed?
Blood test is the mainstay for diagnosing Leukopenia as a blood draw will clearly show low levels of white blood. Apart from that the physician will take a history of the patient about whether the patient has a past history of undergoing any chemotherapy treatments or whether the patient has been exposed to any forms of radiation.
What are the Causes of Leukopenia?
The main cause for Leukopenia has been noted to be excessive use of neutrophils by the body result ing in decreased amount of neutrophils or the inability of the body to produce enough neutrophils resulting in neutropenia and then Leukop enia. Some of the supposed causes of Leukopenia are:
What are the symptoms of anemia in a patient with leukopenia?
The patient will have symptoms of anemia like severe lethargy and weakness as the level of hemoglobin falls in Leukopenia
What test is used to diagnose leukopenia?
The physician will also order a platelet count, urinalysis, sedimentation rate, and chemistry panel to confirmatively diagnose Leukopenia. Sometimes, ANA, serum protein electrophoresis and B12, and folate levels will be checked to look for any deficiencies and confirm the diagnosis of Leukopenia. Some other tests that can be done to diagnose Leukopenia and the cause of it are:
What is the sign of low white blood cells?
Fever which is an indicator of an infectious process going on in the body which is a sign of low white blood cells or Leukopenia
What causes low white blood cell count?
Hodgkin’s lymphoma is also one of the causes that can result in low white blood cell count or Leukopenia
What Is Leukopenia?
Leukopenia (also called leukocytopenia) describes low white blood cell count, which can be caused by various diseases such as iron-deficiency anemia, an overactive spleen or cancers that damage bone marrow.
What causes leukopenia?
Causes of leukopenia include various diseases such as: anemia, viruses and infections, autoimmune diseases, an overactive spleen or cancers that damage bone marrow like lymphoma and leukemia.
How long does leukopenia last?
Leukopenia can either develop acutely, meaning over several weeks or less, or be chronic and occur for many months or even years. Acute leukopenia is considered to be more serious and requires prompt evaluation in order to check for conditions like drug-induced leukopenia, infections or acute leukemia.
What is the blood count for leukopenia?
Doctors diagnose leukopenia based on whether a patient’s white blood cell count is low on a blood test known as the complete blood count. What qualifies as “low white blood cell count?” Normally adults have a leukocyte count that ranges from approximately 4,000 to 10,000 cells/mm 3. ( 7) There is some variability in the exact cut-off as to what’s considered leukopenia, but most medical practitioners consider anything less than 3,000 to 4,000 white blood cells per microliter of blood (or cells/mm 3) in adults to be considered abnormally low. ( 8)
What is the most common form of leukopenia?
Neutropenia is a reduction in the number of neutrophils. This is the most common form of leukopenia, which is almost always due to neutropenia or lymphopenia. Severe congenital neutropenia syndrome typically begins in infancy. Adults can also develop neutropenia for a variety of reasons.
What can you do to defend yourself against potential health problems if you’re experiencing leukopenia?
What can you do to defend yourself against potential health problems if you’re experiencing leukopenia? Your doctor will decide if you need treatment with antibiotics, steroids, vitamins, fluids, etc. depending on the underlying cause of your condition. But you can also help strengthen your immune system by eating a nutrient-dense diet and practicing good hygiene.
What is agranulocytosis leukopenia?
Agranulocytosis describes severe and dangerous leukopenia, usually the neutrophil type.
What to eat if you have leukopenia?
If the leukopenia is caused by vitamin deficiency, then be sure to eat plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables. Also, you can take vitamin supplements, from the B complex and folate, copper and zinc
What is the medical term for the decrease in white blood cells?
Leukopenia is a medical condition in which the number of white cells in the blood decreases, the risk for infection being increased. Also known as leukocytopenia, this medical condition presents several sub-types, depending on the type of white blood cells that are affected. One of the most encountered sub-types is neutropenia, a medical condition in which the number of neutrophils (a sub-type of white blood cells) are decreased. The neutrophil count is a good indicator for the risk of infection, as these are among the most numerous white blood cells.
What is the best medicine to increase white blood count?
Corticosteroids – these are recommended in order to increase the white blood count in the blood stream
Which condition has the lowest white blood cells?
HIV/AIDS – this is a medical condition in which the immune system is at its lowest point, with really low numbers of white blood cells
Can leukopenia be caused by medication?
If the leukopenia is caused by certain medication that you are taking, such as diure tics, make sure that you reduce the dose or stop taking the medication altogether. Talk to your doctor about the alternatives you might have to this treatment, so that your white blood cell count is not affected
Can antibiotics cause white blood cells to decrease?
Prolonged treatments with antibiotics or diuretics – these can harm the immune system, causing a decrease of the white blood cells
